

Articles
Understanding Your Home’s Circuits
Modified: January 8, 2024
Gain a comprehensive understanding of your home's circuits with our informative articles. Learn about electrical wiring, safety measures, troubleshooting, and more.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to understanding the inner workings of your home, one essential aspect to grasp is the electrical circuits. These circuits are the intricate networks that power the various electrical devices and appliances in your home. Whether it’s the lights that illuminate your rooms, the appliances that make daily tasks easier, or the outlets that charge your devices, circuits play a crucial role in delivering electricity safely and efficiently.
In this article, we will delve into the world of home circuits, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of how they work, the different types of circuits you might find in your home, and essential tips for troubleshooting issues or making upgrades. By the end, you’ll feel confident in navigating your home’s electrical system and ensuring the safe operation of your devices.
Before we dive into the details, it’s important to note that working with electrical circuits can be hazardous if not done properly. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with any electrical tasks, it’s always recommended to consult a licensed electrician for assistance.
Now, let’s explore the basics of home circuits and take a closer look at what powers your home!
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding Your Home’s Circuits
Gain confidence in navigating your home’s electrical system by understanding the basics of circuits, identifying and labeling them, and troubleshooting common issues. Prioritize safety and consult a professional for upgrades. - Safety First When Dealing with Circuits
Always prioritize safety when working with electrical circuits. Turn off power, use protective gear, avoid overloading circuits, and seek professional assistance if unsure. Keep children and pets away from the work area for a safe environment.
The Basics of Home Circuits
Before we get into the specific types and components of home circuits, it’s important to understand the fundamental concepts. At its core, a circuit is a path that allows electricity to flow from a power source to the devices and appliances in your home. It is essentially a closed loop that enables the continuous flow of electrical current.
Every circuit consists of three essential elements:
- Power source: The power source is where the electrical energy originates. In most residential homes, the power source is the main electrical grid, supplied by the utility company. The electricity enters your home through the main service panel or breaker box.
- Wiring: Wiring serves as the conduit for the electrical current. It consists of insulated copper or aluminum wires that connect the devices, outlets, and fixtures in your home to the power source.
- Load: The load refers to the devices, appliances, and fixtures that consume electrical energy. This can include lights, outlets, fans, refrigerators, stoves, and more. Each load has a specific electrical requirement, measured in volts and amps, which determines the size and capacity of the circuit needed to power it.
Now that we understand the basic elements, let’s explore the different types of circuits you might encounter in your home.
Types of Circuits in Your Home
Your home may have several types of circuits, each designed for specific purposes and powering different areas or devices. Understanding these circuit types will help you identify and troubleshoot electrical issues effectively. Here are some common circuit types you might find in your home:
- Lighting Circuits: Lighting circuits are dedicated to powering the lights in your home. These circuits typically have lower voltage and power requirements compared to other circuits. They are designed to handle the load of multiple light fixtures and switches in different rooms.
- Receptacle Circuits: Receptacle circuits, also known as outlets circuits, provide power to the electrical outlets throughout your home. These circuits supply electricity to devices like televisions, computers, kitchen appliances, and other plug-in devices. They are usually wired with heavier gauge wires to handle higher power demands.
- Appliance Circuits: Appliance circuits are dedicated to high-power consuming appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, dryers, dishwashers, and HVAC systems. These circuits have larger amperage capacity and are designed to handle the heavy electrical load of these appliances.
- Dedicated Circuits: Dedicated circuits are individual circuits that serve a specific appliance or device. These circuits ensure that the appliance has its own dedicated power supply without sharing it with other devices. Common examples of appliances that require dedicated circuits include electric stoves, ovens, water heaters, and garage door openers.
- GFCI Circuits: GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) circuits are designed to provide an added layer of protection against electrical shocks. These circuits incorporate special outlets that have built-in sensors to detect any imbalances in electrical current. If a fault is detected, the GFCI quickly shuts off power to prevent electrical shock.
These are just a few examples of the circuit types you may find in your home. It’s important to familiarize yourself with the different circuits and their functions, as it can help you troubleshoot problems, make upgrades, or even plan home improvements.
Next, let’s explore the key component that ties all these circuits together: the circuit breaker panel.
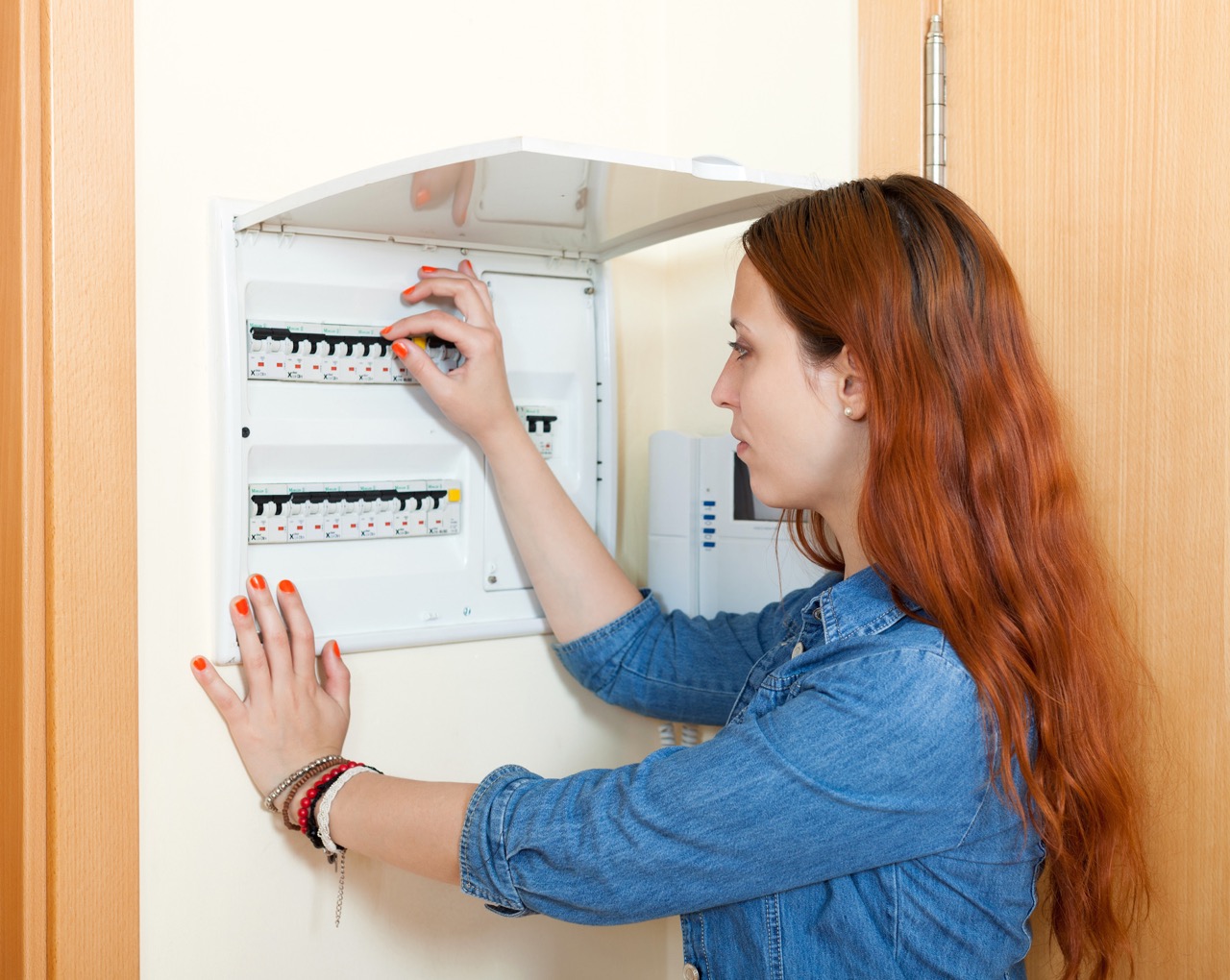
Understanding the Circuit Breaker Panel
The circuit breaker panel, also known as the breaker box or distribution board, is a vital component of your home’s electrical system. It acts as the control center for all the circuits in your home, providing protection against electrical overloads and short circuits.
Here are the key components and functions of a typical circuit breaker panel:
- Main Service Panel: The main service panel is the primary panel where the electrical power from the utility company enters your home. It houses the main circuit breaker, which controls the entire electrical supply to your home.
- Branch Circuit Breakers: The branch circuit breakers are individual switches or levers located within the circuit breaker panel. Each breaker corresponds to a specific circuit in your home and can be turned ON or OFF to control the power supply to that circuit.
- Labels: A well-organized breaker panel will have labels that identify each circuit and its corresponding area or appliance. These labels make it easier to locate and troubleshoot specific circuits when needed.
- Amperage Ratings: Each branch circuit breaker has an amperage rating, which indicates the maximum amount of current that the circuit can safely handle. It’s crucial to ensure that the circuit’s amperage rating matches the electrical load it serves. Exceeding the rated amperage can result in overheating, tripped breakers, or even electrical fires.
- Neutral and Ground Bars: The neutral bar is where the white neutral wires from the circuits are connected, while the ground bar is where the grounding wires are attached. These bars provide the necessary grounding and help prevent electrical shocks or electrical surge issues.
When a circuit experiences an overload or short circuit, the corresponding breaker will trip, interrupting the electrical flow and shutting off power to the circuit. This protects your electrical system from damage and reduces the risk of electrical fires. To restore power, simply locate the tripped breaker in the panel and flip it back to the ON position.
Understanding the circuit breaker panel and its components is essential for maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system in your home. It allows you to easily control power to individual circuits, protect against electrical issues, and perform routine maintenance when needed.
Now that we have a good grasp of the circuit breaker panel, let’s move on to the importance of identifying and labeling circuits.
Identifying and Labeling Circuits
Properly identifying and labeling circuits in your home is crucial for several reasons. It helps you locate specific circuits, troubleshoot electrical issues, and ensure the safety of your electrical system. Whether you’re a new homeowner or have been in your home for years, taking the time to label your circuits will save you time, effort, and potential headaches in the future.
Here are some steps to effectively identify and label your circuits:
- Mapping Out Your Circuits: Begin by creating a plan or diagram of your home, including all the rooms and areas where electrical devices and fixtures are present. This will serve as a guide for mapping out your circuits and labeling them accordingly.
- Using a Circuit Finder Tool: A circuit finder tool, also known as a circuit tracer, is a handy device that helps you locate and identify specific circuits in your electrical panel. By plugging the transmitter into an outlet and using the receiver to scan the breakers in the panel, you can easily determine which breaker controls which circuit.
- Testing and Labeling: Once you have identified a circuit, test it by turning it off and on while someone else checks which lights or outlets are affected. After verifying the devices or areas powered by the circuit, label the breaker accordingly using a label maker or adhesive labels.
- Creating a Legend: Alongside the circuit map or diagram, create a legend that lists the corresponding labels for each breaker in the panel. This legend will serve as a reference in case you need to troubleshoot or perform any electrical work in the future.
- Including Additional Details: In addition to labeling the circuits, consider adding additional information such as the amperage rating, purpose, or any specific safety precautions related to a particular circuit. This extra information can be invaluable for future reference.
By taking the time to identify and label your circuits, you’ll have a clear understanding of how your electrical system is organized. This knowledge allows you to quickly locate and troubleshoot any electrical issues, make upgrades or changes to your circuits, or even plan for future renovations.
Now that we’ve covered the importance of identifying and labeling circuits, let’s move on to troubleshooting common circuit issues that you may encounter in your home.
Label your circuit breakers with the corresponding areas of your home to easily identify which breaker controls each area. This will make it easier to troubleshoot and perform maintenance on your home’s electrical system.
Troubleshooting Circuit Issues
Although electrical circuits are designed to operate smoothly, issues can arise from time to time. Understanding how to troubleshoot common circuit problems will save you time and money, allowing you to quickly resolve issues and restore power. Here are some common circuit issues and their possible solutions:
- Tripped Circuit Breaker: If a circuit suddenly loses power, the first thing to check is the circuit breaker panel. A tripped breaker can be easily identified by a switch in the middle or OFF position. Simply flip the tripped breaker back to the ON position. However, if the breaker keeps tripping repeatedly, it could indicate an underlying issue, such as an overloaded circuit or a short circuit. In such cases, it’s best to consult a licensed electrician.
- Power Outage in a Specific Area: If electricity is working fine in most parts of your home, but a specific area is experiencing a power outage, it could be due to a localized circuit issue. Check the affected area’s circuit breaker and ensure it’s in the ON position. If the breaker is ON and the problem persists, the issue might lie with the wiring or connections in that area. Seek professional assistance to diagnose and repair the problem.
- Intermittent Power Loss: If a circuit sporadically loses power or devices connected to it work intermittently, it could be indicative of a loose connection. Start by checking the outlet or device connections. If you find a loose wire, safely tighten it. If the problem persists, it might be necessary to call an electrician to assess and fix any underlying wiring issues.
- Dim or Flickering Lights: If you notice your lights dimming or flickering, it could indicate an overloaded circuit or an issue with the electrical service to your home. Check if any appliances or devices are causing excessive power consumption. Consider redistributing the load or consulting an electrician to upgrade the electrical service if necessary.
- Outlets Not Working: If an outlet is not providing power, first check if the circuit breaker for that outlet is on. If the breaker is on and the outlet is still not working, it may be a faulty outlet or a wiring issue. Use caution when working with outlets and consider contacting a professional electrician for assistance.
Remember, safety should always be a top priority when troubleshooting circuit issues. If you’re unsure of how to proceed or encounter any potentially dangerous situations, it’s best to contact a qualified electrician for assistance.
Now that we’ve covered some common circuit troubleshooting scenarios, let’s move on to discussing upgrading and adding circuits to meet your electrical needs.
Upgrading and Adding Circuits
As our reliance on electrical devices and appliances continues to grow, you may find yourself needing to upgrade or add circuits in your home to meet the increasing demand. Whether you’re renovating your home, adding new appliances, or simply looking to improve your electrical system, it’s essential to understand the process of upgrading and adding circuits. Here are some key points to consider:
- Evaluate Your Electrical Needs: Start by assessing your current electrical needs and future requirements. Determine the specific circuits that need upgrading or adding based on the devices or appliances you plan to use. Consider the power requirements, voltage, and amperage needed for each circuit.
- Consult a Professional: For major electrical upgrades or additions, it’s advisable to consult a licensed electrician. They can assess your electrical system, determine the feasibility of the upgrades, and ensure compliance with local electrical codes and regulations.
- Calculate Load and Capacity: Upgrading or adding circuits requires careful consideration of load and capacity. Ensure that the new or upgraded circuits can safely handle the increased electrical load without overloading the system. This may involve upgrading the circuit breaker panel or installing subpanels to accommodate the additional circuits.
- Plan the Wiring Route: Determine the optimal wiring route for the new or upgraded circuits. Consider the accessibility, safety, and aesthetics when planning the wiring path. It’s crucial to follow proper wiring guidelines, such as avoiding proximity to water pipes or other potential hazards.
- Obtain Permits and Inspections: Depending on the scope of the electrical work, you may need to obtain the necessary permits from your local authority. Ensure that all work is done to code and schedule inspections as required. This ensures the safety and compliance of your electrical system.
- Hire a Qualified Electrician: While some minor electrical tasks can be DIY, it’s recommended to hire a qualified electrician for complex upgrades or additions. They have the expertise, knowledge, and tools to complete the work safely and effectively.
Remember, electrical work can be dangerous if not done correctly. If you’re unsure about any aspect of upgrading or adding circuits, it’s always best to seek professional assistance to ensure the safety and reliability of your electrical system.
Now that we’ve explored upgrading and adding circuits, let’s move on to discussing essential safety tips when dealing with circuits in your home.
Safety Tips for Dealing with Circuits
Working with electrical circuits can be potentially dangerous if proper safety precautions are not followed. Whether you’re performing routine maintenance, troubleshooting issues, or upgrading circuits in your home, it’s crucial to prioritize your safety. Here are some essential safety tips to keep in mind:
- Turn Off Power: Always turn off the power to the circuit you’re working on before doing any electrical work. Locate the corresponding circuit breaker in the panel and switch it to the OFF position. Use a voltage tester to double-check that the power is indeed off.
- Use Protective Gear: When working with circuits, wear appropriate protective gear such as safety goggles, insulated gloves, and non-conductive footwear. This reduces the risk of electrical shock and injury.
- Avoid Water Contact: Water and electricity don’t mix. Avoid working on circuits with wet hands or in damp conditions. Ensure that the work area is dry, and consider using a non-conductive mat or standing on a dry surface.
- Handle Tools Properly: Use insulated tools with rubber or non-conductive handles when working on electrical circuits. Insulated tools reduce the risk of electric shock and help prevent accidental short circuits.
- Avoid Overloading Circuits: Do not overload circuits by plugging in too many devices or appliances. Spread out the electrical load across multiple circuits to prevent overheating, tripped breakers, and electrical fires.
- Label and Test Circuits: Ensure that each circuit is properly labeled in the breaker panel, making it easy to identify and work on specific circuits. Test outlets and switches for proper grounding and polarity using a reliable tester.
- Don’t DIY if Unsure: If you’re uncertain about any electrical task or lack the necessary knowledge and experience, it’s best to hire a licensed electrician. They have the expertise to handle complex electrical work safely and effectively.
- Keep Children and Pets Away: When working on electrical circuits, keep children and pets away from the work area. Educate family members on the importance of electrical safety and discourage them from tampering with electrical outlets and devices.
Remember, safety should always be your top priority when dealing with electrical circuits. By following these safety tips and using common sense, you can minimize the risks and hazards associated with working on circuits, ensuring a safe environment for yourself and your home.
Now that we’ve covered safety tips for dealing with circuits, let’s summarize the key points we’ve discussed in this article.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You now have a comprehensive understanding of your home’s circuits. From the basics of how circuits work to the different types you may encounter, you are equipped with the knowledge to navigate and troubleshoot electrical issues in your home.
We covered the importance of understanding your circuit breaker panel and how to identify and label circuits for easy reference. By following the safety tips provided, you can ensure that working with circuits is done safely and efficiently.
Whether you’re upgrading circuits to meet increased power demands or adding new circuits for specific appliances, it’s essential to consult a qualified electrician to ensure compliance with safety standards and local regulations.
Remember, safety should always be a top priority. If you ever feel unsure or uncomfortable with any electrical task, it’s best to seek professional assistance rather than risking injury or damage to your home.
By understanding your home’s circuits and implementing the tips and knowledge shared in this article, you can have peace of mind knowing that your electrical system is functioning optimally and safely.
Now, go forth and confidently navigate your home’s circuits with the expertise you have gained!
Frequently Asked Questions about Understanding Your Home's Circuits
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Understanding Your Home’s Circuits”