Home>Furniture & Design>Bedroom Furniture>What Is Memory Foam Made From


Bedroom Furniture
What Is Memory Foam Made From
Modified: January 14, 2024
Discover what memory foam is made from and how it can enhance your bedroom furniture. Learn about the materials and design of this popular bedding option.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
**
Introduction
**
Welcome to the world of memory foam! If you've ever nestled into a cozy memory foam mattress or lounged on a supportive memory foam pillow, you've experienced the comfort and luxury this material offers. But have you ever wondered what memory foam is made from? In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating world of memory foam, exploring its history, composition, manufacturing process, and environmental impact. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of this innovative material and its place in the realm of bedroom furniture and design. So, let's embark on a journey to uncover the secrets of memory foam and gain insight into the intricate details that make it such a sought-after component of modern comfort.
**
Key Takeaways:
- Memory foam, developed by NASA, offers exceptional comfort and support in bedroom furniture. Its composition, including polyols and diisocyanates, creates a luxurious and eco-friendly option for restful sleep.
- Understanding memory foam’s environmental impact and sustainable alternatives empowers consumers to make eco-friendly choices in bedroom furniture. Plant-based memory foam and responsible disposal practices minimize its ecological footprint.
Read more: What Is A Memory Foam Pillow
History of Memory Foam
**
The history of memory foam is as intriguing as the material itself. Developed in the 1960s by NASA scientists, memory foam, originally known as “temper foam,” was designed to improve seat cushioning and crash protection for airline pilots and passengers. This innovative material was created to enhance impact resistance and overall comfort during long hours of sitting, making it a crucial component in the realm of aeronautics.
However, memory foam gained widespread recognition and popularity when it was introduced to the public domain in the 1980s. Its unique ability to conform to body contours and distribute weight evenly made it a game-changer in the mattress and pillow industry. This led to the production of memory foam mattresses and pillows, revolutionizing the way people experience comfort during sleep and relaxation.
Over the years, memory foam has evolved to meet the diverse needs of consumers, with advancements in technology and manufacturing processes leading to the creation of various types of memory foam, including traditional, gel-infused, and plant-based formulations. This evolution has further solidified memory foam’s status as a staple in modern bedroom furniture and design, offering unparalleled support and comfort for individuals seeking a restful and rejuvenating sleep experience.
As memory foam continues to make its mark in the world of comfort and ergonomics, its rich history serves as a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of enhancing everyday experiences through innovative materials and design.
**
Composition of Memory Foam
**
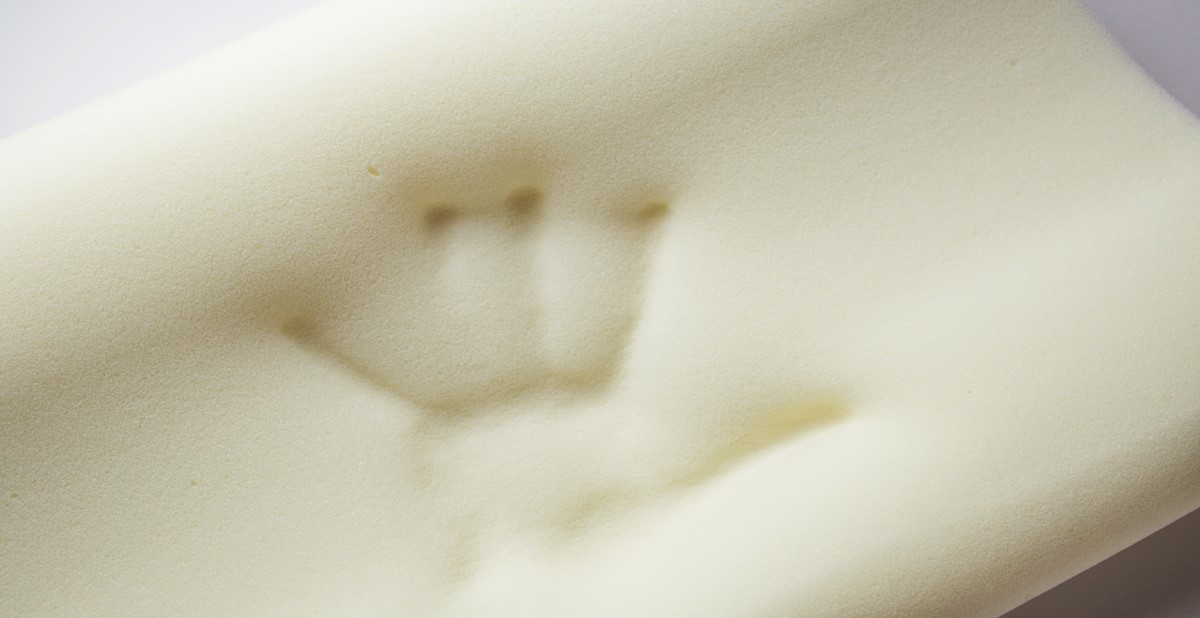
Memory foam, also known as viscoelastic foam, is renowned for its exceptional cushioning and contouring properties. Understanding its composition unveils the science behind its remarkable performance. At its core, memory foam is a polyurethane-based material blended with additional compounds that give it its distinctive characteristics.
The primary components of memory foam include polyols, diisocyanates, and various additives. Polyols, derived from petroleum-based chemicals or plant-based sources, serve as the building blocks of the foam. These polyols undergo a chemical reaction with diisocyanates, forming a viscoelastic polymer. This process creates the signature viscoelastic properties of memory foam, allowing it to respond to body heat and pressure, conforming to the body’s shape while providing exceptional support.
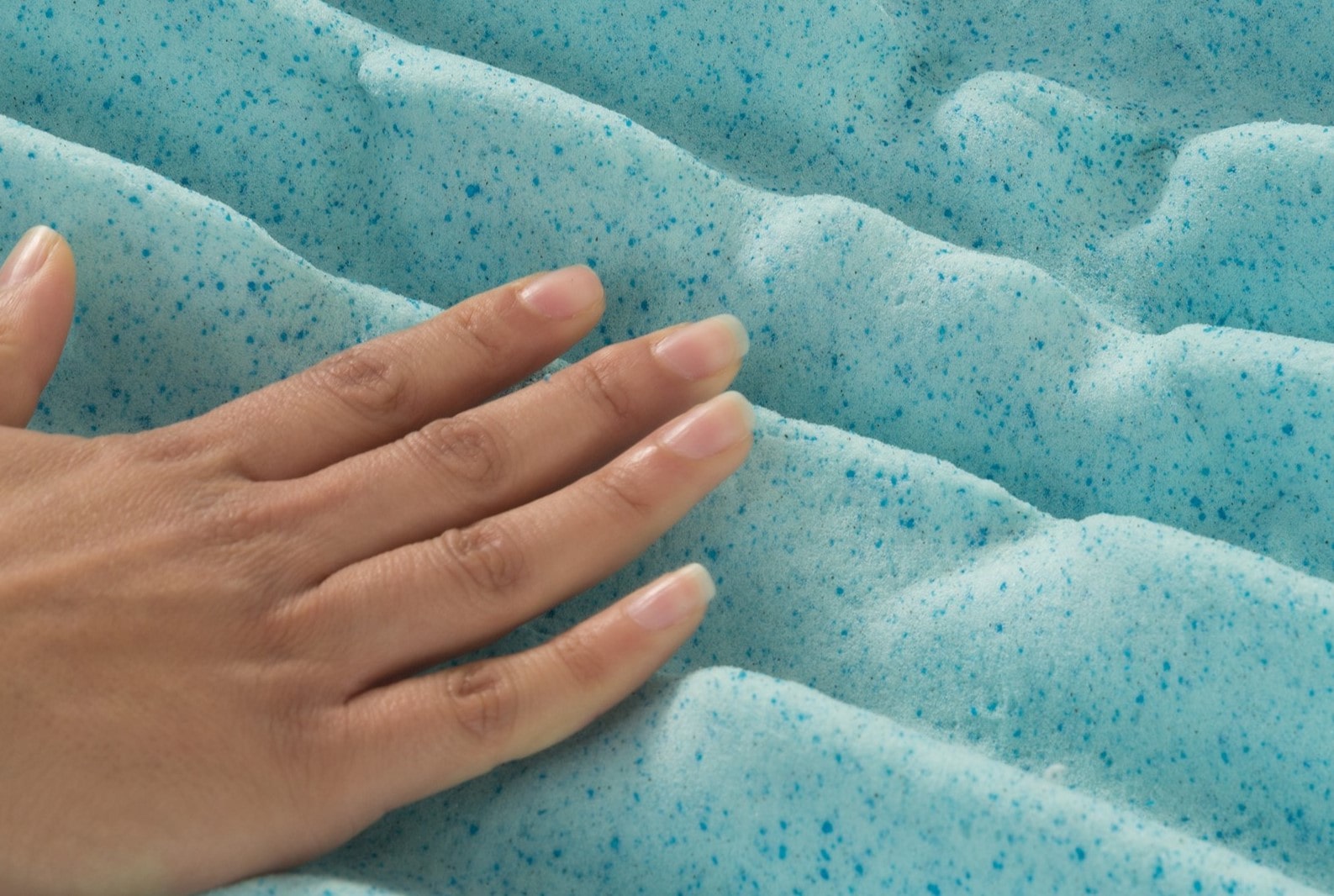
Furthermore, memory foam often contains additional ingredients such as blowing agents, catalysts, and flame retardants. Blowing agents contribute to the foam’s cellular structure, resulting in its characteristic open-cell or closed-cell configuration. This structure impacts the foam’s breathability, density, and overall feel. Catalysts play a vital role in controlling the foam’s expansion and curing process during manufacturing, ensuring uniform density and consistency. Flame retardants are incorporated to enhance the foam’s resistance to combustion, meeting safety standards and regulations.
Moreover, advancements in memory foam technology have led to the development of specialized formulations, including gel-infused memory foam and plant-based memory foam. Gel-infused memory foam incorporates gel microbeads or liquid gel into the foam matrix, enhancing thermal regulation and heat dissipation, making it an ideal choice for individuals seeking a cooler sleep surface. On the other hand, plant-based memory foam replaces a portion of the petroleum-based ingredients with natural plant-derived alternatives, offering a more eco-friendly option without compromising on performance.
By understanding the intricate composition of memory foam, consumers can make informed decisions when selecting products that align with their comfort preferences and sustainability values. The diverse formulations and customizable properties of memory foam cater to a wide range of needs, making it a versatile and adaptable material in the realm of bedroom furniture and design.
**
Chemicals Used in Memory Foam
**
The production of memory foam involves the use of several key chemicals, each playing a crucial role in shaping the material’s performance and characteristics. Understanding these chemicals provides insight into the intricate process of creating memory foam and its diverse applications in the realm of comfort and ergonomics.
One of the primary chemicals used in memory foam is polyols, which are essential components derived from petrochemicals or plant-based sources. These polyols serve as the foundational building blocks for the foam, contributing to its structural integrity and flexibility. The selection of polyols influences the overall sustainability and environmental impact of the memory foam, with plant-based alternatives offering a more eco-friendly option for conscientious consumers.
Diisocyanates, another key chemical in memory foam production, react with polyols to form the polyurethane matrix that gives memory foam its viscoelastic properties. This chemical reaction is pivotal in creating the foam’s ability to contour to body shapes and provide exceptional pressure relief, making it a sought-after material in mattresses, pillows, and seating applications.
Additionally, blowing agents play a significant role in the manufacturing process of memory foam. These agents contribute to the formation of the foam’s cellular structure, impacting its density, breathability, and overall feel. The choice of blowing agents influences the foam’s performance characteristics, allowing manufacturers to tailor the foam’s properties to meet specific comfort and support requirements.
Furthermore, the incorporation of flame retardants is essential to enhance the foam’s resistance to combustion, ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations. These additives contribute to the overall safety and durability of memory foam products, providing consumers with peace of mind regarding the fire-resistant properties of their furniture and bedding items.
As the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials continues to grow, manufacturers are exploring alternative chemicals and formulations to reduce the environmental impact of memory foam. This has led to the development of plant-based memory foam, which replaces a portion of the petroleum-based ingredients with natural plant-derived alternatives, offering a more sustainable and renewable option for consumers seeking environmentally conscious products.
By understanding the chemicals used in memory foam production, consumers can make informed choices when selecting comfort products that align with their preferences for performance, sustainability, and safety. The diverse applications of memory foam in bedroom furniture and design underscore the importance of these chemical components in shaping the modern landscape of comfort and relaxation.
**
Memory foam is made from a material called viscoelastic, which is a type of polyurethane foam. It is known for its ability to contour to the body and provide support, making it popular for mattresses and pillows.
Manufacturing Process of Memory Foam
**
The manufacturing process of memory foam involves a series of intricate steps that transform raw materials into the luxurious and supportive foam known for its exceptional comfort and contouring properties. From chemical blending to foam curing, each stage contributes to the creation of high-quality memory foam products that enhance the sleep and relaxation experience for consumers.
The process begins with the precise blending of polyols, diisocyanates, and other additives in specialized mixing equipment. This blending stage is critical in achieving the desired chemical composition and consistency of the foam. The selection of raw materials and the accuracy of blending directly impact the foam’s performance characteristics, including its density, firmness, and response to body heat and pressure.
Once the chemical mixture is prepared, it undergoes a foaming process where blowing agents are introduced to create the foam’s cellular structure. This step is pivotal in determining the foam’s breathability, supportiveness, and overall feel. The controlled expansion and curing of the foam during this stage contribute to its uniform density and structural integrity, ensuring that the final product meets stringent quality standards.
Following the foaming process, the freshly formed foam undergoes curing and stabilization to set its viscoelastic properties. This stage involves carefully controlled temperature and humidity conditions to facilitate the foam’s transition to its desired firmness and resilience. The curing process is essential in ensuring that the memory foam achieves its characteristic ability to conform to body contours and provide exceptional pressure relief, making it an ideal material for mattresses, pillows, and upholstery.
After curing, the memory foam undergoes precision cutting and shaping to create products tailored to specific applications. Whether destined for mattress layers, pillow inserts, or seating components, the foam is meticulously cut to size, ensuring that each piece maintains the desired performance attributes and dimensional accuracy. This stage highlights the versatility of memory foam in accommodating diverse design and comfort requirements.
Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control measures are implemented to assess the foam’s performance characteristics, including its density, firmness, and durability. Rigorous testing and inspection protocols ensure that the memory foam meets the highest standards of comfort, support, and longevity, providing consumers with confidence in the reliability and performance of the finished products.
By understanding the intricacies of the manufacturing process, consumers gain insight into the craftsmanship and technology involved in creating memory foam. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed choices when selecting comfort products, appreciating the artistry and precision that contribute to the luxurious and supportive nature of memory foam in the realm of bedroom furniture and design.
**
Read more: What Is Visco Memory Foam
Environmental Impact of Memory Foam
**
As consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility, understanding the environmental impact of memory foam is essential in making informed choices regarding comfort products. While memory foam offers unparalleled support and comfort, its production and disposal can have implications for the environment, prompting a closer examination of its ecological footprint.
The primary environmental consideration associated with memory foam lies in its manufacturing process, which involves the use of petrochemical-based ingredients and energy-intensive production methods. The extraction and processing of petroleum-based raw materials contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion, highlighting the need for sustainable alternatives and eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Furthermore, the disposal of memory foam products at the end of their lifecycle presents challenges in terms of waste management and environmental impact. Traditional memory foam is not biodegradable, posing concerns about its long-term presence in landfills and its potential contribution to environmental pollution. As a result, the responsible disposal and recycling of memory foam products are crucial in mitigating their environmental footprint.
However, advancements in memory foam technology have led to the development of more sustainable alternatives, such as plant-based memory foam. By incorporating natural, renewable materials in place of petroleum-based substances, plant-based memory foam offers a reduced environmental impact while retaining the comfort and performance attributes that make memory foam desirable.
Additionally, eco-conscious consumers can explore memory foam products that have obtained certifications for environmental standards and sustainability, such as CertiPUR-US® or OEKO-TEX®. These certifications provide assurance that the memory foam has undergone testing for harmful substances and meets stringent criteria for low emissions and environmental impact, aligning with environmentally conscious consumer preferences.
When considering the environmental impact of memory foam, it is essential to recognize the role of responsible consumption and disposal practices. Extending the lifespan of memory foam products through proper care and maintenance can minimize the need for premature replacement, reducing overall waste generation and resource consumption.
Ultimately, the environmental impact of memory foam is a multifaceted consideration that encompasses its production, usage, and end-of-life management. By embracing sustainable alternatives and mindful consumption habits, consumers can enjoy the comfort and support of memory foam while minimizing its ecological footprint, contributing to a more environmentally conscious approach to bedroom furniture and design.
**
Conclusion
**
The journey through the world of memory foam has unveiled the remarkable history, intricate composition, manufacturing process, and environmental impact of this innovative material, shedding light on its significance in the realm of bedroom furniture and design. From its origins in aeronautics to its widespread applications in comfort products, memory foam continues to captivate consumers with its exceptional support and luxurious feel.
The history of memory foam, rooted in NASA’s quest for improved cushioning and crash protection, reflects the spirit of innovation and adaptability that has propelled this material into the spotlight of comfort technology. Its evolution from “temper foam” to the versatile memory foam we know today underscores the relentless pursuit of enhancing everyday experiences through advanced materials and design.
Delving into the composition of memory foam has revealed the intricate blend of polyols, diisocyanates, and additives that give this material its signature viscoelastic properties. The diverse formulations, including gel-infused and plant-based memory foam, offer tailored solutions for consumers seeking personalized comfort and sustainability in their bedroom furnishings.
Moreover, the manufacturing process of memory foam showcases the craftsmanship and technology involved in transforming raw materials into the supportive and contouring foam that enhances sleep and relaxation. From chemical blending to precision cutting, each stage contributes to the creation of high-quality memory foam products that elevate the comfort experience for individuals seeking restful and rejuvenating sleep.
As consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability, the environmental impact of memory foam has come into focus, prompting a closer examination of its ecological footprint. While traditional memory foam presents challenges in terms of manufacturing and end-of-life disposal, sustainable alternatives and responsible consumption practices offer pathways toward minimizing its environmental impact and promoting eco-friendly choices in bedroom furniture and design.
In conclusion, the world of memory foam encompasses a rich tapestry of history, innovation, and environmental considerations, shaping the modern landscape of comfort and ergonomics. By understanding the intricacies of memory foam and embracing sustainable alternatives, consumers can make informed choices that align with their comfort preferences and environmental values, contributing to a more conscious and mindful approach to bedroom furnishings and design.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Memory Foam Made From
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is Memory Foam Made From”