Home>Furniture & Design>Interior Design Trends>What Happens When You Eat Glass

Interior Design Trends
What Happens When You Eat Glass
Modified: February 18, 2024
Discover the impact of consuming glass and explore the latest interior design trends to elevate your living space. Uncover the potential dangers and stay updated on the latest decor styles.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
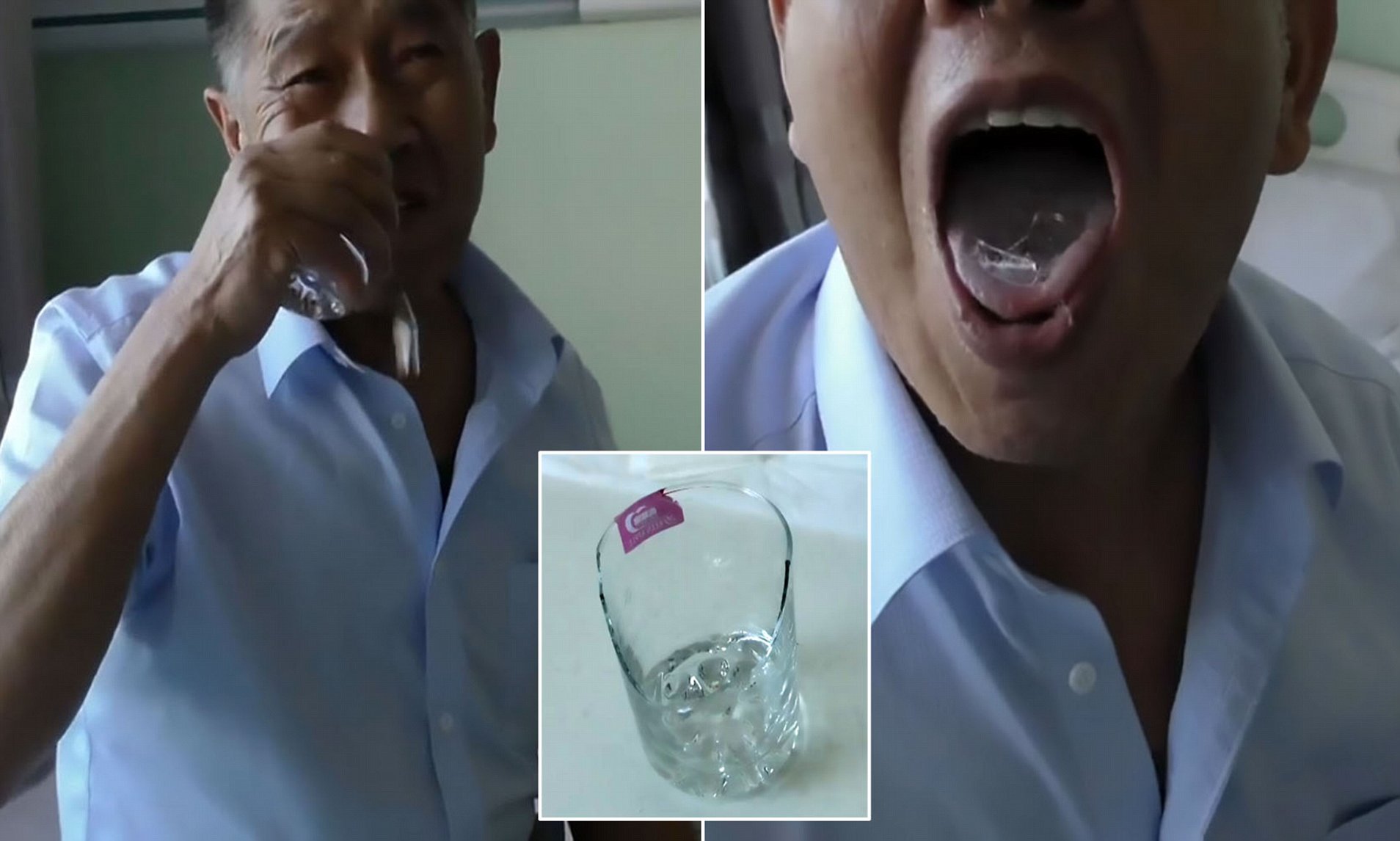
Imagine sitting down to enjoy a meal, only to discover that a piece of glass has found its way into your food. The mere thought of ingesting glass is enough to send shivers down anyone's spine. While it may seem like a rare and unlikely occurrence, accidents involving glass in food or drink can happen, posing serious risks to one's health.
In this article, we will delve into the potential dangers and health risks associated with ingesting glass, as well as the body's reaction to this foreign substance. Understanding the implications of such an event is crucial for raising awareness and promoting caution in food preparation and consumption.
The ingestion of glass, whether in the form of small shards or tiny fragments, can lead to a range of health complications. It is essential to explore the implications of this scenario, shedding light on the potential harm it can cause to the human body. Let's embark on this insightful journey to gain a deeper understanding of what happens when one ingests glass and the measures that can be taken to address this alarming situation.
Key Takeaways:
- Eating glass can cause serious harm to the body, including cuts, inflammation, and the risk of poisoning. It’s important to be cautious and seek medical help if this happens.
- If you accidentally ingest glass, seek immediate medical attention. Treatment may involve surgery, medication, and specialized care to address the potential health risks and ensure your well-being.
Read more: What Happens When You Eat Pomegranate Seeds
The Dangers of Ingesting Glass
The dangers of ingesting glass cannot be overstated, as this scenario presents a significant threat to one's health and well-being. When glass is accidentally consumed, whether through contaminated food or drink, it can lead to a range of serious complications. The sharp and abrasive nature of glass makes it particularly hazardous when it comes into contact with the delicate tissues of the digestive system.
Upon ingestion, glass can cause immediate damage to the mouth, throat, esophagus, and stomach. The sharp edges of glass fragments can lacerate and puncture these internal organs, leading to bleeding, pain, and potential infection. Furthermore, the abrasive nature of glass can cause irritation and inflammation, exacerbating the damage and posing a risk of perforation within the digestive tract.
In addition to the physical harm caused by the sharp edges of glass, the potential for chemical contamination is also a significant concern. Glass may contain various substances, such as lead or other toxic compounds, which can leach into the body upon ingestion. This can result in poisoning and long-term health issues, further compounding the dangers associated with ingesting glass.
Moreover, the presence of glass in the digestive system can obstruct the normal passage of food and waste, leading to blockages and potential complications such as bowel perforation or intestinal damage. These obstructions can be life-threatening and may necessitate emergency medical intervention to address the immediate risks posed by ingested glass.
Overall, the dangers of ingesting glass extend beyond the initial physical harm, encompassing the potential for chemical toxicity and obstructive complications within the digestive system. It is crucial to recognize the severity of these dangers and take proactive measures to prevent the accidental ingestion of glass in food and beverages.
In the subsequent sections, we will explore how the body reacts to ingested glass, the potential health risks associated with this scenario, and the available treatments to address such alarming incidents. Understanding the implications of ingesting glass is essential for promoting awareness and ensuring the safety of food consumption.
How the Body Reacts to Ingested Glass
When glass is ingested, the body initiates a series of responses to address the presence of this foreign and potentially harmful substance. The initial reaction occurs as the sharp edges of the glass come into contact with the delicate tissues of the mouth, throat, and esophagus. These tissues, which are not designed to withstand the abrasive nature of glass, may sustain lacerations and punctures upon contact, leading to immediate pain, bleeding, and inflammation.
As the glass fragments travel through the digestive system, they can cause further damage to the stomach and intestinal lining. The abrasive nature of glass exacerbates the injury, potentially resulting in tissue irritation, inflammation, and the risk of perforation within the digestive tract. This can lead to severe complications, including internal bleeding and the potential for infection as the body attempts to respond to the presence of foreign objects.
Moreover, the body may react to ingested glass by triggering an inflammatory response to address the damage caused by the sharp edges of the glass fragments. Inflammation is the body's natural defense mechanism, aimed at protecting and repairing injured tissues. However, in the case of ingested glass, the inflammatory response may contribute to further complications, such as swelling and obstruction within the digestive system.
Furthermore, the potential for chemical contamination from the glass itself adds another layer of complexity to the body's reaction. If the glass contains toxic substances, such as lead or other harmful compounds, the body may be exposed to chemical toxicity upon ingestion. This can lead to poisoning and long-term health issues, as the body attempts to process and eliminate these toxic substances.
In response to the presence of ingested glass, the body may also attempt to expel the foreign objects through vomiting or diarrhea. These mechanisms are the body's natural defense mechanisms to rid itself of harmful substances. However, in the case of glass ingestion, these responses may not effectively eliminate all the glass fragments, potentially leading to ongoing complications within the digestive system.
Overall, the body's reaction to ingested glass involves a complex interplay of physical, inflammatory, and potential toxic responses. Understanding these reactions is crucial for recognizing the severity of ingesting glass and the potential health risks it poses. In the following section, we will delve into the potential health risks associated with ingesting glass and the available treatments to address this alarming scenario.
Do not eat glass as it can cause serious harm to your digestive system, including cuts, bleeding, and potential internal damage. If you accidentally ingest glass, seek medical help immediately.
Potential Health Risks
The ingestion of glass poses a myriad of potential health risks, encompassing both immediate and long-term implications for the individual's well-being. The sharp and abrasive nature of glass fragments can lead to a range of complications within the digestive system, as well as the potential for chemical toxicity from the glass itself. Understanding these health risks is essential for recognizing the severity of ingesting glass and the implications it holds for one's health.
One of the immediate health risks associated with ingesting glass is the potential for internal lacerations and punctures within the mouth, throat, esophagus, and stomach. The sharp edges of glass fragments can cause immediate damage upon contact with these delicate tissues, leading to bleeding, pain, and the risk of infection. Moreover, the abrasive nature of glass can exacerbate the injury, causing tissue irritation, inflammation, and the potential for perforation within the digestive tract.
In addition to the physical harm caused by ingested glass, the potential for chemical contamination from the glass itself presents a significant health risk. Glass may contain various substances, such as lead or other toxic compounds, which can leach into the body upon ingestion. This can result in poisoning and long-term health issues, as the body attempts to process and eliminate these toxic substances. The implications of chemical toxicity from ingested glass extend beyond the immediate damage, posing risks for systemic health issues and long-term complications.
Furthermore, the presence of glass fragments within the digestive system can lead to obstructive complications, potentially causing blockages and obstructions in the normal passage of food and waste. These obstructions can result in severe complications, including bowel perforation, intestinal damage, and the potential for life-threatening emergencies. The obstructive nature of ingested glass poses a significant health risk, necessitating prompt medical intervention to address the potential complications within the digestive system.
Moreover, the inflammatory response triggered by the body in reaction to ingested glass presents another health risk. Inflammation is the body's natural defense mechanism to protect and repair injured tissues. However, in the case of ingested glass, the inflammatory response may contribute to further complications, such as swelling and obstruction within the digestive system. This can exacerbate the damage caused by the glass fragments, leading to ongoing health risks and potential long-term implications for the individual's well-being.
Overall, the potential health risks associated with ingesting glass are multifaceted, encompassing immediate physical harm, the potential for chemical toxicity, obstructive complications, and inflammatory responses. Recognizing these health risks is crucial for understanding the severity of ingesting glass and the implications it holds for one's health. In the subsequent section, we will explore the available treatments to address ingested glass and the measures that can be taken to mitigate the potential health risks associated with this alarming scenario.
Treatment for Ingested Glass
The treatment for ingested glass is a critical aspect of addressing this alarming scenario and mitigating the potential health risks it poses. Upon the accidental ingestion of glass, prompt and appropriate medical intervention is essential to assess the extent of the damage, address potential complications, and ensure the individual's well-being.
One of the primary considerations in treating ingested glass is the evaluation of the affected individual's condition. Medical professionals will conduct a thorough examination to determine the location and potential impact of the ingested glass fragments within the digestive system. Diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays or endoscopic procedures, may be employed to visualize the presence of glass and assess any associated injuries or obstructions.
In cases where the ingested glass fragments have caused internal lacerations, punctures, or perforations, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the damage and prevent further complications. Surgical procedures aimed at removing the glass fragments and addressing any resulting injuries within the digestive tract are crucial for mitigating the immediate health risks associated with ingested glass.
Furthermore, medical treatment for ingested glass may involve the administration of supportive care to manage potential complications such as bleeding, inflammation, or infection. This may include the use of medications to control pain, reduce inflammation, and prevent infection, as well as supportive measures to ensure the individual's comfort and stability during the recovery process.
In cases where chemical toxicity from the ingested glass is a concern, medical treatment may focus on addressing potential poisoning and mitigating the long-term health risks associated with exposure to toxic substances. This may involve the administration of antidotes or supportive therapies to counteract the effects of chemical toxicity and facilitate the elimination of harmful substances from the body.
Moreover, the management of obstructive complications resulting from ingested glass may require specialized medical interventions to address blockages within the digestive system. Procedures such as endoscopy or surgery may be employed to remove obstructing glass fragments and alleviate the potential risks of bowel perforation or intestinal damage.
In addition to medical treatment, psychological support and counseling may be offered to individuals who have experienced the distressing event of ingesting glass. The emotional impact of such an incident can be significant, and providing compassionate care and support is essential for the individual's overall well-being and recovery.
Overall, the treatment for ingested glass involves a comprehensive approach aimed at addressing the immediate and potential long-term health risks associated with this alarming scenario. Prompt medical intervention, surgical procedures, supportive care, and specialized treatments are essential components of managing ingested glass and ensuring the individual's health and well-being.
This comprehensive approach to treatment underscores the severity of ingesting glass and the importance of proactive measures to prevent such incidents. By raising awareness of the potential dangers and emphasizing the significance of prompt medical intervention, we can work towards minimizing the risks associated with ingesting glass and promoting the safety of food consumption.
Read more: What Happens If You Eat An Apple Seed
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ingestion of glass presents significant dangers and potential health risks, encompassing immediate physical harm, the potential for chemical toxicity, obstructive complications, and inflammatory responses within the digestive system. Understanding the implications of ingesting glass is crucial for raising awareness and promoting caution in food preparation and consumption.
The body's reaction to ingested glass involves a complex interplay of physical, inflammatory, and potential toxic responses. The sharp and abrasive nature of glass fragments can cause immediate damage to the delicate tissues of the mouth, throat, esophagus, and stomach, leading to bleeding, pain, and the risk of infection. Moreover, the potential for chemical contamination from the glass itself adds another layer of complexity to the body's reaction, posing risks for systemic health issues and long-term complications.
Recognizing the severity of ingesting glass and the potential health risks it poses is essential for prompt and appropriate medical intervention. The treatment for ingested glass involves a comprehensive approach aimed at addressing the immediate and potential long-term health risks associated with this alarming scenario. Prompt medical intervention, surgical procedures, supportive care, and specialized treatments are essential components of managing ingested glass and ensuring the individual's health and well-being.
By shedding light on the potential dangers and health risks associated with ingesting glass, we can work towards minimizing the risks and promoting the safety of food consumption. It is imperative for individuals, food manufacturers, and food service providers to exercise vigilance and implement stringent quality control measures to prevent the accidental presence of glass in food and beverages. Additionally, fostering awareness and education regarding the potential hazards of ingesting glass is essential for empowering individuals to recognize and address such incidents effectively.
Ultimately, the prevention of glass ingestion requires a collective effort to prioritize food safety and implement rigorous measures to mitigate the risks. By emphasizing the significance of proactive measures and prompt medical intervention, we can strive towards safeguarding the well-being of individuals and ensuring the safety of food consumption in both domestic and commercial settings.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Happens When You Eat Glass
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.















0 thoughts on “What Happens When You Eat Glass”