Home>Home Security and Surveillance>What Happens If You Eat Pepper Spray


Home Security and Surveillance
What Happens If You Eat Pepper Spray
Modified: March 6, 2024
Discover the consequences of ingesting pepper spray and learn how to stay safe with home security and surveillance measures. Protect yourself with expert advice!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive article on what happens if you eat pepper spray. Pepper spray is a widely used self-defense tool that can incapacitate an attacker by causing temporary blindness, intense pain, and difficulty breathing. While it is highly effective for personal safety, it is essential to understand the potential risks and consequences associated with ingesting pepper spray.
In this article, we will delve into the details of pepper spray, how it affects the body, potential health risks, immediate effects of ingestion, treatment options, and long-term implications. By gaining a thorough understanding of what happens if you eat pepper spray, you can make informed decisions regarding its safe use and take appropriate actions if accidental ingestion occurs.
Please note that the information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. If you have ingested pepper spray or are experiencing any adverse effects, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Key Takeaways:
- Accidental ingestion of pepper spray can cause intense burning, nausea, and respiratory distress. Seek immediate medical attention and avoid inducing vomiting to minimize discomfort and potential health risks.
- Handle pepper spray with care to prevent accidental ingestion. Rinse the mouth, consume dairy products, and seek medical assistance if ingestion occurs. Prioritize safety and responsible use.
Read more: What Happens If You Inhale Pepper Spray
What is pepper spray?
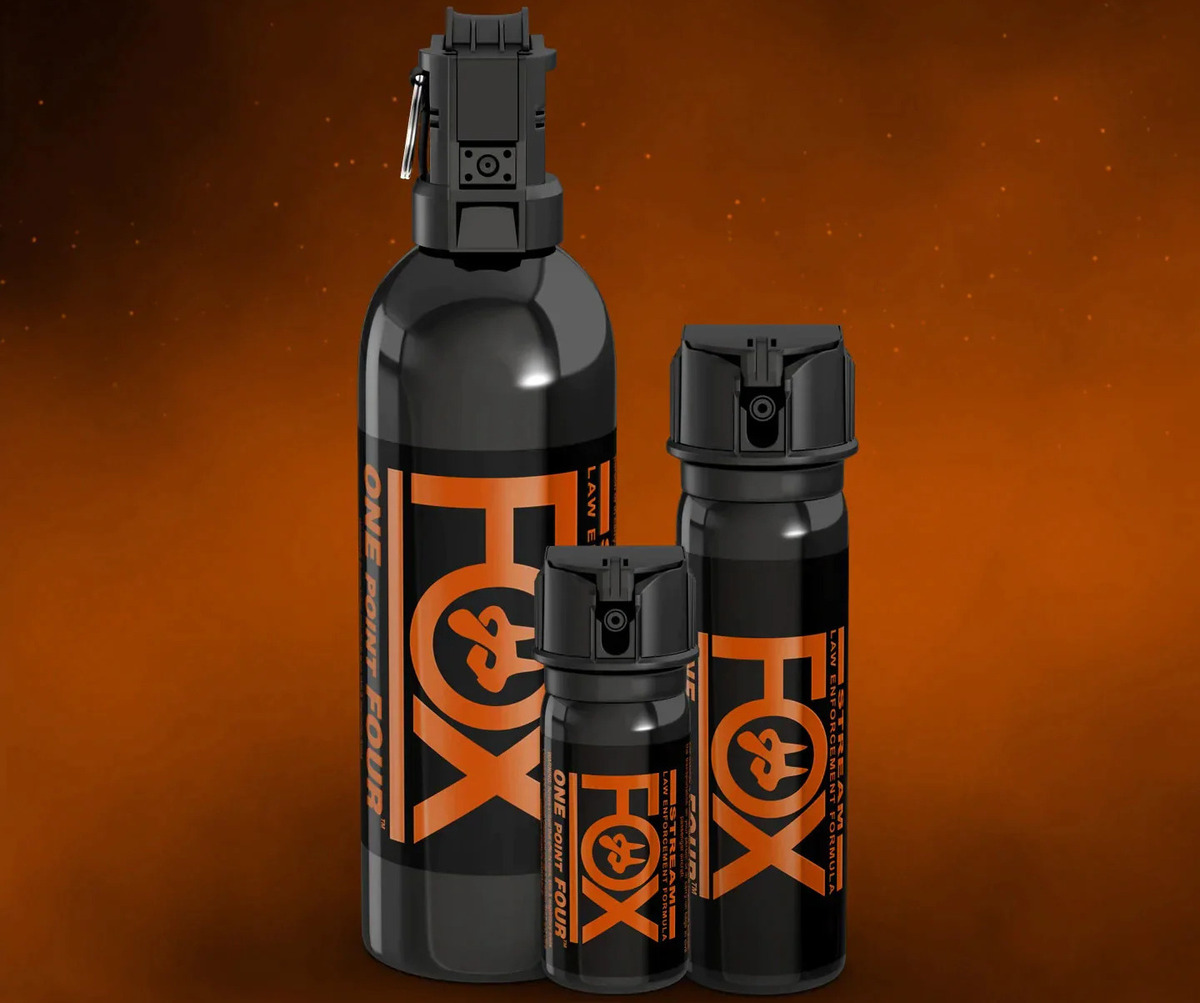
Pepper spray, also known as OC spray (oleoresin capsicum), is a non-lethal self-defense tool commonly used by individuals to protect themselves from potential attackers. It consists of a chemical compound derived from hot peppers, specifically capsaicin, which is the active ingredient responsible for its powerful effects.
Pepper spray is typically sold in small, handheld canisters that can easily be carried in a purse, pocket, or on a keychain. When sprayed, it releases a fine mist or stream, depending on the type of dispenser, which comes into contact with the eyes, nose, and mouth of the attacker.
The severity of the effects depends on the concentration of capsaicin in the pepper spray, with higher concentrations resulting in stronger reactions. It is designed to incapacitate the attacker temporarily, allowing the victim to escape from the situation and seek help.
Pepper spray is readily available to the general public for self-defense purposes, but it is important to note that laws and regulations surrounding its purchase and use may vary depending on your jurisdiction. It is always advisable to familiarize yourself with local laws and guidelines before obtaining or using pepper spray.
How does pepper spray affect the body?
When pepper spray comes into contact with the body, particularly the eyes, nose, and mouth, it triggers a response that can be quite intense. The active ingredient in pepper spray, capsaicin, binds to the pain receptors in these areas, leading to a series of physiological reactions.
Upon exposure, the capsaicin causes an immediate burning sensation, intense pain, and inflammation of the mucous membranes. This reaction is accompanied by involuntary closure of the eyes and difficulty in breathing due to the irritation of the respiratory system.
Pepper spray can also cause temporary blindness by irritating the eyes and causing excessive tearing. This effect can last anywhere from several minutes to several hours, depending on the concentration of capsaicin and the individual’s sensitivity to the chemical.
In addition to the immediate effects, pepper spray can also trigger other bodily reactions. It can induce coughing, gagging, and difficulty swallowing, further exacerbating the discomfort and distress experienced by the individual exposed to it.
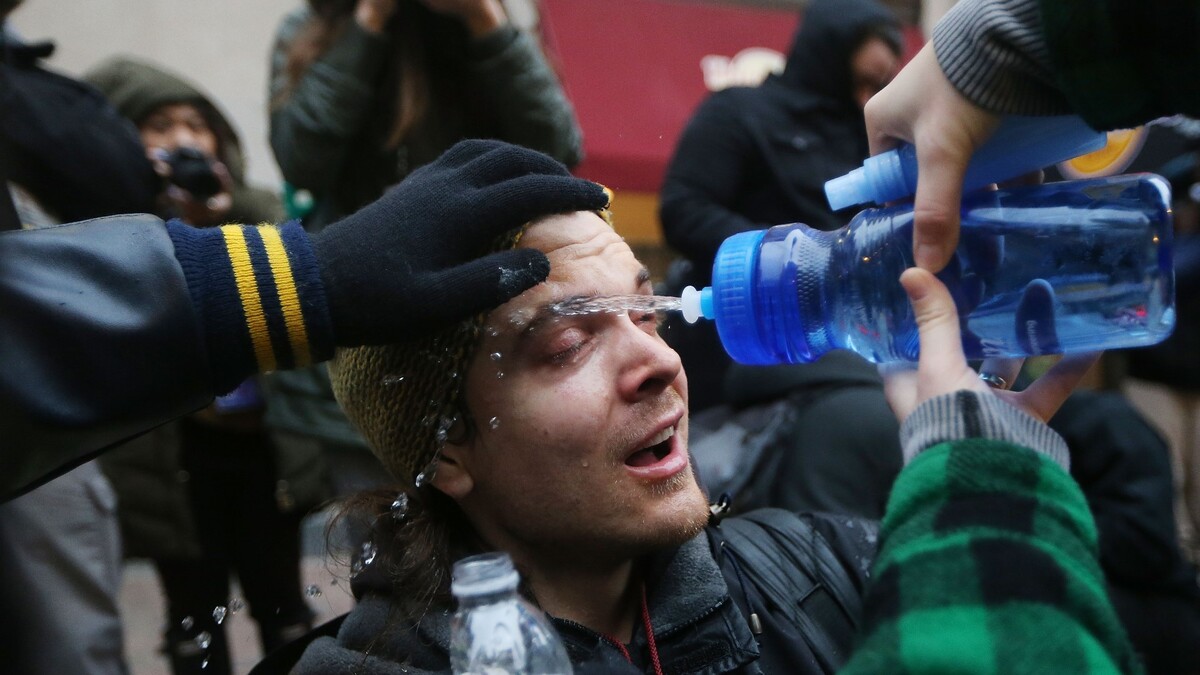
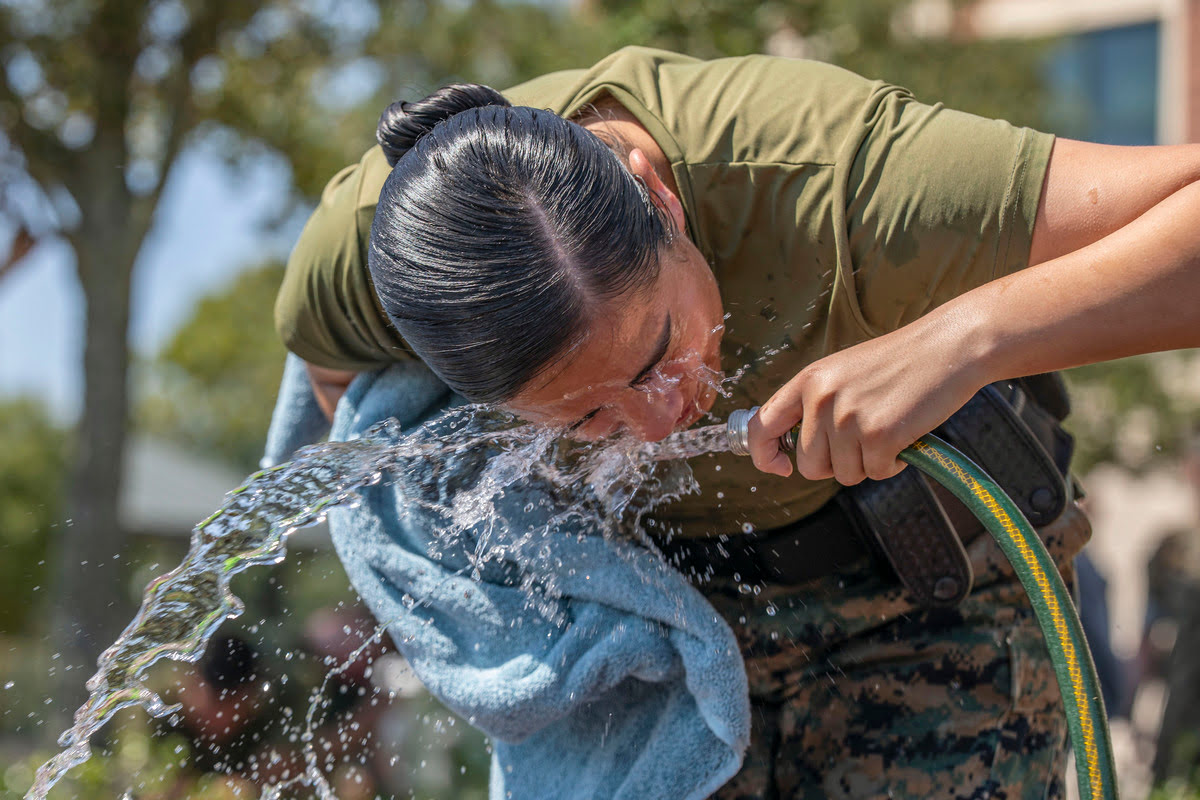
It is important to note that the effects of pepper spray are temporary and typically subside over time. After exposure, it is crucial to flush the affected areas with water to help alleviate the burning sensation and assist in the recovery process. Seeking medical attention is advised if the symptoms persist or worsen.
Overall, the primary objective of pepper spray is to incapacitate an attacker temporarily, allowing the victim to escape from a dangerous situation. However, it is essential to recognize that its use can have significant physiological effects and should be employed responsibly and within legal boundaries.
Potential health risks of ingesting pepper spray
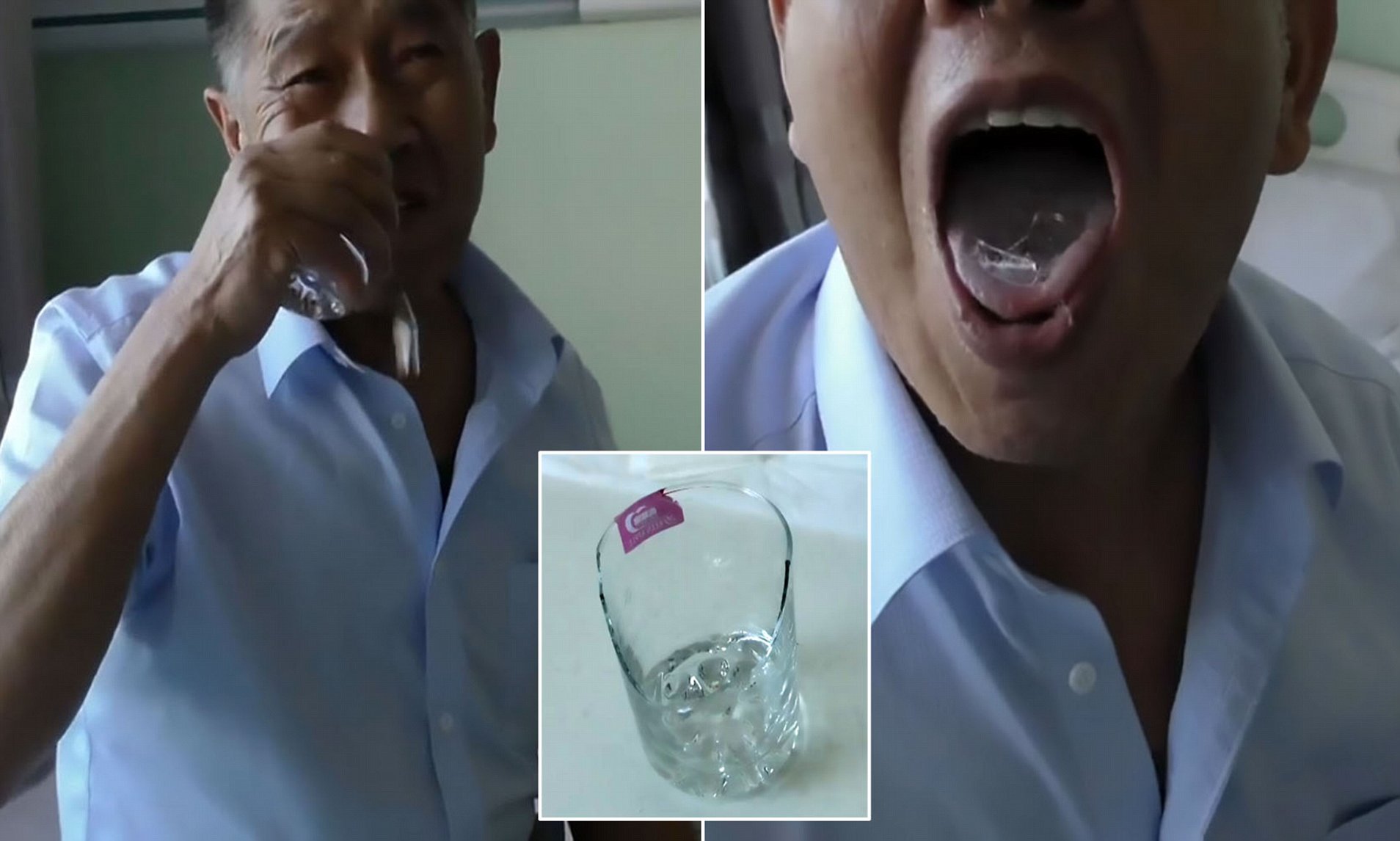
While pepper spray is primarily designed for external use, accidental ingestion can occur in certain situations. Ingesting pepper spray can pose potential health risks and may result in adverse effects on the body. It is essential to be aware of these risks and understand the appropriate course of action.
One of the primary concerns associated with ingesting pepper spray is the irritation and inflammation it can cause in the digestive system. The capsaicin in pepper spray can lead to intense burning sensations in the mouth, throat, and stomach, accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Furthermore, ingesting pepper spray can potentially exacerbate respiratory issues, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Due to the irritant properties of capsaicin, it can trigger or worsen breathing difficulties and respiratory distress.
Additionally, ingesting high concentrations of capsaicin can lead to gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea and abdominal cramping. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and may persist for some time after ingestion.
It is important to note that the severity of the health risks may vary depending on factors such as the concentration of capsaicin in the pepper spray and the individual’s underlying health conditions. Therefore, each case of pepper spray ingestion should be evaluated independently, and appropriate medical attention should be sought.
If you or someone you know accidentally ingests pepper spray, it is advisable to seek immediate medical assistance. A healthcare professional will be able to assess the situation, provide appropriate treatment, and monitor for any potential complications.
Remember, prevention is key to avoiding the potential health risks of ingesting pepper spray. Always handle pepper spray with care, store it securely, and keep it out of reach of children or anyone who may mistake it for a condiment or beverage.
By being mindful and responsible in the use and storage of pepper spray, you can minimize the chances of accidental ingestion and mitigate the associated health risks.
If you accidentally ingest pepper spray, rinse your mouth with milk or a milk-based product like yogurt to help ease the burning sensation. Do not induce vomiting. Seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
Immediate effects of ingesting pepper spray
Accidental ingestion of pepper spray can lead to immediate and distressing effects on the body. The active ingredient, capsaicin, can cause a range of symptoms that can be quite intense and uncomfortable.
One of the primary immediate effects of ingesting pepper spray is the intense burning sensation in the mouth, throat, and digestive system. This burning sensation can be excruciating and may lead to difficulty swallowing, excessive salivation, and gagging.
In addition to the burning sensation, nausea and vomiting are also common immediate effects of pepper spray ingestion. The powerful irritant properties of capsaicin can trigger the body’s natural defense mechanisms, resulting in an urge to vomit.
Respiratory symptoms may also arise from ingesting pepper spray. Coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath can occur due to the irritation of the respiratory tract. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions may experience more severe symptoms.
Other immediate effects include swelling of the lips, tongue, and throat, as well as excessive tearing and redness of the eyes. These symptoms are a result of the inflammatory response triggered by capsaicin.
The severity and duration of the immediate effects may vary depending on factors such as the concentration of capsaicin, the amount ingested, and the individual’s sensitivity. It is important to note that these effects are usually temporary and should subside with time.
If you or someone you know accidentally ingests pepper spray, it is crucial to remain calm and take immediate action. Rinse the mouth and any affected areas with cold water to help alleviate the burning sensation. Do not induce vomiting unless instructed to do so by a healthcare professional.
It is highly recommended to seek medical attention after ingesting pepper spray, even if the symptoms appear to be mild. A healthcare professional will be able to assess the situation, provide appropriate guidance, and monitor for any potential complications.
Remember, the immediate effects of ingesting pepper spray can be distressing, but with prompt and appropriate care, recovery is generally swift, and long-term complications are rare.
Read more: What Happens If You Pepper Spray A Raccoon
Treatment for ingesting pepper spray
If you or someone you know accidentally ingests pepper spray, it is crucial to take immediate action and seek appropriate treatment. Various steps can be taken to alleviate the discomfort and minimize the potential health risks associated with pepper spray ingestion.
1. Rinse the mouth: The first step is to flush the mouth with cold water. Gently swish the water around to help remove any residual pepper spray and alleviate the burning sensation. Avoid swallowing the water, as it may contain traces of capsaicin.
2. Milk or dairy products: Dairy products, such as milk or yogurt, can help to neutralize the effects of capsaicin. Drinking a glass of milk or consuming dairy products can provide temporary relief from the burning sensation and reduce inflammation.
3. Don’t induce vomiting: While the natural response to ingestion may be to induce vomiting, it is not recommended unless instructed to do so by a healthcare professional. Vomiting can potentially worsen the irritation and increase the risk of aspirating the capsaicin into the lungs.
4. Seek medical assistance: It is essential to seek immediate medical attention after ingesting pepper spray. A healthcare professional will be able to assess the situation, provide appropriate guidance, and monitor for any potential complications. They may also administer additional treatments or medications to help alleviate symptoms.
5. Follow medical advice: The healthcare professional may recommend additional measures to aid in recovery, such as anti-inflammatory medications or soothing mouth rinses. It is crucial to follow their advice and complete any prescribed treatments to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of further complications.
It is important to note that prevention is always better than cure. Accidental ingestion of pepper spray can be avoided by handling it with caution, storing it securely, and keeping it out of the reach of children or anyone who may mistake it for a consumable item.
Remember, the information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. If you or someone you know ingests pepper spray, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Long-term effects of ingesting pepper spray
While the immediate effects of ingesting pepper spray are often the primary concern, it is important to consider the potential long-term implications as well. Although accidental ingestion is relatively rare, there have been cases where individuals have experienced prolonged effects following exposure to pepper spray.
One potential long-term effect of ingesting pepper spray is damage to the gastrointestinal system. The intense irritation and inflammation caused by capsaicin can lead to ongoing digestive issues, such as chronic stomach pain, acid reflux, or gastritis. These symptoms may persist and require medical intervention to manage effectively.
In some cases, individuals may experience respiratory complications as a result of pepper spray ingestion. This is particularly true for those with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic bronchitis. The irritant properties of capsaicin can trigger or worsen respiratory symptoms, leading to ongoing breathing difficulties and reduced lung function.
Psychological effects can also arise from the experience of ingesting pepper spray. The traumatic nature of the incident, coupled with the physical discomfort, can contribute to the development of anxiety, panic disorders, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These psychological effects may require therapy or counseling to address effectively.
It is important to note that the severity and duration of the long-term effects may vary from person to person. Factors such as the concentration of capsaicin ingested, individual sensitivity, and overall health contribute to the long-term impact of pepper spray ingestion.
Seeking proper medical care and follow-up is essential for monitoring and managing any potential long-term effects. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help identify and address any lingering issues and provide appropriate treatment options.
As with any traumatic incident, it is crucial to prioritize self-care and seek support from loved ones and mental health professionals. Engaging in stress management techniques, practicing relaxation exercises, and participating in therapy or counseling can aid in the healing process.
While the long-term effects of ingesting pepper spray are not always severe, it is important to take the necessary precautions and seek medical attention to minimize potential complications and ensure a full recovery.
Conclusion
Pepper spray is an effective self-defense tool that can incapacitate an attacker and provide personal safety. However, it is crucial to be aware of the potential risks and consequences associated with ingesting pepper spray.
In this article, we have explored what pepper spray is and how it affects the body. We have discussed the potential health risks of ingesting pepper spray, including immediate effects such as intense burning sensations, nausea, and respiratory distress.
Treatment for pepper spray ingestion involves rinsing the mouth, consuming dairy products, and seeking medical assistance. Long-term effects may include gastrointestinal issues, respiratory complications, and psychological distress, underscoring the importance of proper medical care and support.
It is essential to handle pepper spray with care, store it securely, and keep it out of reach of children or anyone who may mistake it for a consumable item. By taking preventive measures, we can minimize the chances of accidental ingestion and associated risks.
Remember, the information provided in this article serves as a general guide and should not substitute professional medical advice. If you or someone you know ingests pepper spray, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Stay informed, stay safe, and use pepper spray responsibly to enhance personal security while minimizing the risks to your own well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Happens If You Eat Pepper Spray
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.