

Articles
How Much Manure For Garden
Modified: August 28, 2024
Find out how much manure you need for your gardening needs. Get expert tips on using manure in your garden for optimal growth and results.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to gardening, one crucial aspect that often gets overlooked is the importance of replenishing nutrients in the soil. While chemical fertilizers can do the job, they often come with harmful side effects for both your plants and the environment. This is where the use of manure in the garden comes into play.
Manure is a natural and sustainable source of nutrients that can help improve soil fertility, enhance plant growth, and promote overall garden health. Its organic composition provides a wide range of essential minerals, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as trace elements necessary for robust plant development.
Not only does manure nourish your plants, but it also enhances soil structure, increases moisture retention, promotes beneficial microbial activity, and reduces the risk of soil erosion. Additionally, using manure in your garden fosters sustainable agriculture practices by recycling organic waste and minimizing the reliance on synthetic chemicals.
However, determining the right amount of manure to use in your garden can be a bit challenging. It depends on several factors, including the size of your garden, the types of plants you’re growing, and the nutrient content of the manure. In this article, we will explore the benefits of using manure in the garden, factors to consider when calculating manure amount, methods for determining the application rate, and precautions to take while handling manure.
By understanding how to utilize manure effectively in your garden, you can provide your plants with the nourishment they need to thrive, leading to a bountiful and vibrant garden.
Key Takeaways:
- Manure is a natural and sustainable source of nutrients that can improve soil fertility, enhance plant growth, and promote overall garden health. Understanding the factors involved in calculating the right amount of manure is crucial for maximizing its benefits.
- Proper application techniques, precautions, and avoiding common mistakes are essential for safe and effective use of manure in the garden. By following these guidelines, gardeners can ensure optimal garden health and minimize potential risks.
Read more: How To Store Rabbit Manure
Benefits of Using Manure in the Garden
Using manure in the garden offers numerous benefits that contribute to the overall health and productivity of your plants. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
1. Nutrient-rich soil: Manure is an excellent source of organic matter and essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are vital for plant growth and development, helping to produce lush foliage, vibrant blooms, and healthy fruits or vegetables.
2. Improved soil structure: The organic matter in manure helps improve soil structure by enhancing its ability to retain moisture and promote better drainage. This creates an optimal growing environment for plants, allowing their roots to access water, oxygen, and nutrients more efficiently.
3. Enhanced microbial activity: Manure contains beneficial microorganisms that promote the growth of a diverse microbial community in the soil. These microorganisms aid in breaking down organic matter, releasing nutrients, suppressing harmful pathogens, and improving overall soil health.
4. Reduced soil erosion: Manure helps to prevent soil erosion by improving soil structure, increasing water infiltration, and binding soil particles together. By minimizing soil erosion, you can protect your garden from nutrient loss and maintain a stable and healthy growing environment.
5. Environmentally friendly: Using manure as a natural fertilizer reduces the reliance on synthetic chemicals, minimizing the risk of water contamination and environmental pollution. Manure is readily available, renewable, and a sustainable alternative for nourishing your plants while reducing your ecological footprint.
6. Promotes biodiversity: Incorporating manure into your garden ecosystem encourages biodiversity by supporting a wide array of beneficial insects, earthworms, and soil organisms. This enhances the overall resilience and ecological balance of your garden, reducing the need for pest control measures.
7. Cost-effective: Manure is often an affordable or even free source of nutrients, especially if you have access to livestock farms or local composting facilities. It can be a cost-effective way to enrich your soil and improve the health and productivity of your garden without breaking the bank.
By using manure in your garden, you can harness these benefits to create a thriving and sustainable ecosystem where your plants can flourish. However, it’s important to understand how to calculate and apply the appropriate amount of manure for optimal results, which we will explore in the next sections.
Factors to Consider When Calculating Manure Amount
Calculating the right amount of manure to use in your garden is essential to ensure that your plants receive adequate nutrients without overloading the soil. Several factors should be taken into consideration when determining the appropriate manure amount:
1. Garden size: The size of your garden plays a significant role in estimating the quantity of manure needed. Larger gardens will generally require more manure to cover a greater surface area and provide enough nutrients for all the plants.
2. Soil type and fertility: The fertility level of your soil affects how much additional nutrients it requires. If you have nutrient-depleted soil, you may need to apply a larger amount of manure to replenish the necessary nutrients. Conversely, if your soil is already rich in nutrients, you may need to use less manure.
3. Plant types and nutritional needs: Different plants have varying nutrient requirements. Some crops, such as leafy greens, require higher nitrogen levels, while others, like tomatoes, benefit from increased phosphorus and potassium. Consider the nutritional needs of the specific plants you are growing to determine the appropriate manure application rate.
4. Manure type and nutrient content: Different types of manure have varying nutrient compositions. For example, chicken manure tends to be higher in nitrogen, while cow manure has a more balanced nutrient profile. Understanding the nutrient content of the manure you are using will help you calculate the right amount to provide adequate nourishment.
5. Manure maturity: Fresh or raw manure is higher in nitrogen and can potentially burn plants if applied directly. Aged or composted manure is more stable and releases nutrients gradually, making it a safer option. Consider the maturity of the manure when determining the application rate to avoid any negative effects on your plants.
6. Environmental conditions: Environmental factors, such as temperature and rainfall, can impact the nutrient availability in the soil. In regions with high rainfall or frequent irrigation, nutrients may leach out more quickly, requiring more frequent manure applications. Conversely, in arid regions with minimal rainfall, less frequent applications may be needed.
Considering these factors will help you calculate the optimal amount of manure to use in your garden, providing your plants with the nutrients they need while avoiding nutrient imbalances or potential harm. In the next section, we will explore different methods for calculating the manure quantity based on the garden area.
Calculating the Manure Quantity Based on Garden Area
Calculating the amount of manure needed based on the size of your garden is a straightforward approach to ensure proper nutrient distribution. By following these steps, you can determine the appropriate manure quantity:
1. Measure the garden area: Start by measuring the length and width of your garden in feet or meters. Multiply these dimensions together to get the total area of your garden in square feet or square meters.
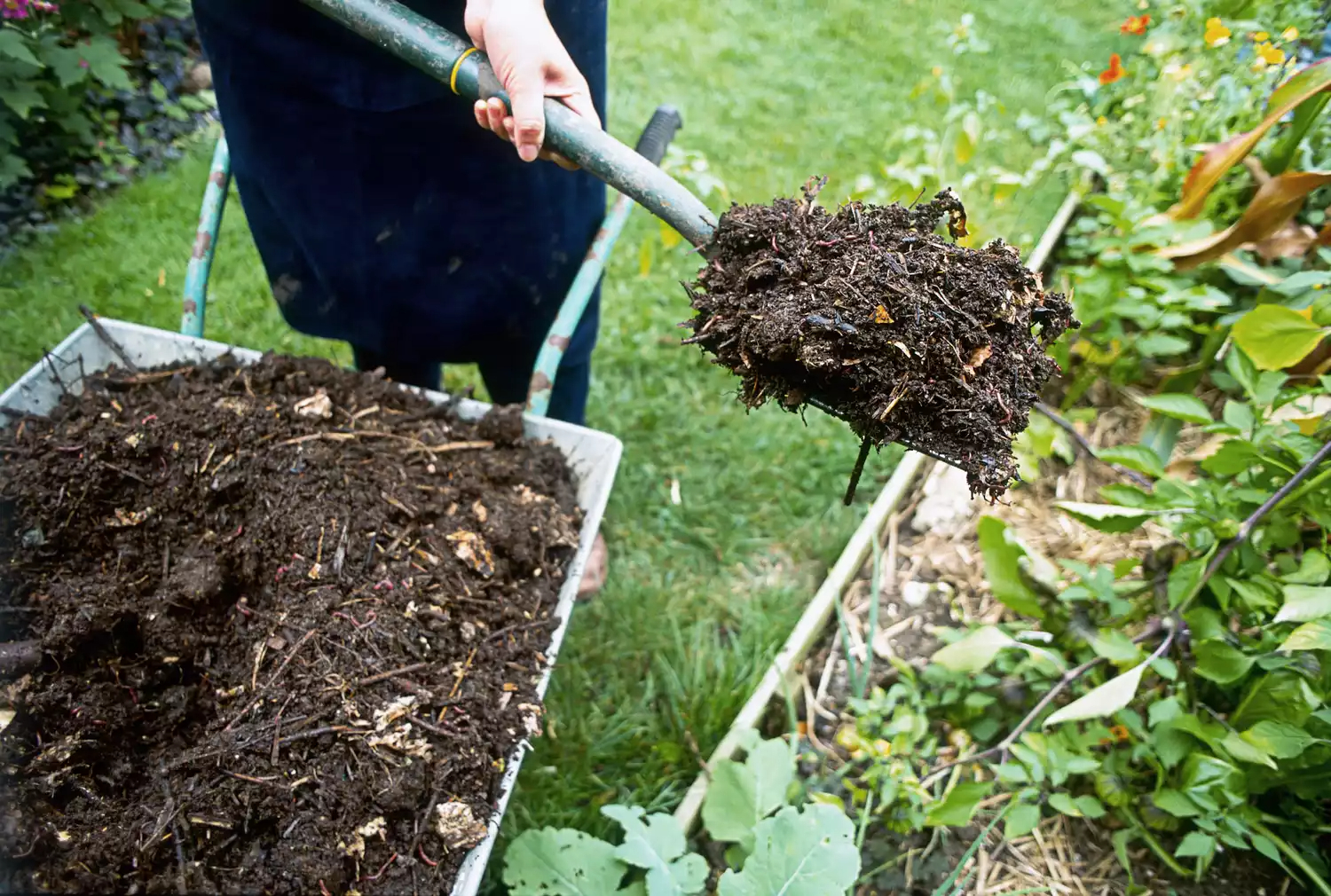
2. Determine the application rate: The application rate refers to the desired amount of manure to apply per square foot or square meter of garden area. This rate can vary depending on the crop, soil type, and nutrient requirements. A general guideline is to apply approximately 1-2 pounds (0.45-0.9 kg) of manure per square foot or 20-40 pounds (9-18 kg) per 100 square feet (9 square meters) of garden area.
3. Calculate the manure quantity: Multiply the total garden area by the desired application rate to determine the amount of manure needed. For example, if your garden is 200 square feet and you want to apply 1 pound of manure per square foot, you will need 200 pounds (90 kg) of manure.
4. Adjust for nutrient content: Consider the nutrient content of the manure you are using. If the manure has a high nutrient content, you may need to adjust the quantity accordingly. For example, if the manure has double the nitrogen content than what is typically recommended, you can reduce the quantity by half.
5. Divide application into multiple sessions: It is often beneficial to divide the total manure quantity into multiple applications throughout the growing season. This allows for a gradual release of nutrients and prevents overloading the soil at once. Consider splitting the total amount into two or three applications, with the first application during soil preparation and subsequent ones during the growing season.
Remember, these calculations are general guidelines, and the specific needs of your garden may vary. Monitoring plant growth, conducting soil tests, and observing the overall health of your plants can help you determine if adjustments are needed in subsequent seasons.
In the next section, we will discuss how to determine the appropriate manure application rate based on the specific plants you are growing.
Determining the Manure Application Rate for Different Plants
Each plant has unique nutrient requirements, and determining the appropriate manure application rate can help ensure optimal growth and productivity. Here are some guidelines to help you determine the right amount of manure to apply for different types of plants:
1. Leafy greens (lettuce, spinach, kale): Leafy greens generally require higher nitrogen levels for healthy foliage development. Apply approximately 1-2 pounds (0.45-0.9 kg) of well-aged manure per 10 square feet (1 square meter) of garden area. Alternatively, you can use a nitrogen-rich manure, such as chicken or rabbit manure, at a slightly lower quantity.
2. Root crops (carrots, beets, radishes): Root crops benefit from a well-balanced nutrient profile. Apply approximately 1-2 pounds (0.45-0.9 kg) of composted manure per 10 square feet (1 square meter) of garden area before planting to provide adequate nutrients throughout the growing season.
3. Fruiting plants (tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers): Fruiting plants have higher potassium and phosphorus requirements to promote flower production and fruit development. Apply approximately 1-2 pounds (0.45-0.9 kg) of composted manure per 10 square feet (1 square meter) of garden area, supplementing with additional potassium-rich amendments if necessary.
4. Herbs (basil, rosemary, parsley): Herbs generally have lower nutrient requirements compared to other plants. Apply approximately 0.5-1 pound (0.23-0.45 kg) of well-aged manure per 10 square feet (1 square meter) of garden area or incorporate a smaller quantity into the planting hole for individual plants.
5. Perennials (blueberries, strawberries, fruit trees): Perennial plants require a steady supply of nutrients over an extended period. Apply approximately 2-3 pounds (0.9-1.4 kg) of composted manure per 10 square feet (1 square meter) of garden area before planting or spread around the base of the plants as a topdressing.
6. Annual flowers and ornamental plants: For annual flowers and ornamental plants, apply approximately 1-2 pounds (0.45-0.9 kg) of composted manure per 10 square feet (1 square meter) of garden area during soil preparation or topdress with a smaller quantity around the base of the plants.
Keep in mind that these are general recommendations, and it is essential to monitor the growth and health of your plants. Conducting a soil test can provide more specific information about nutrient deficiencies or excesses, allowing you to fine-tune the manure application rate accordingly.
In the next section, let’s explore the different types of manure available and their nutrient content to help you make more informed choices for your garden.
For most garden plants, a general guideline is to apply 1-2 inches of composted manure to the soil before planting. This will provide essential nutrients and improve soil structure.
Understanding Different Types of Manure and Their Nutrient Content
When it comes to choosing the right type of manure for your garden, understanding their nutrient content is essential. Different animals produce manure with varying nutrient profiles. Here are some common types of manure and their nutrient content:
1. Cow Manure: Cow manure is a well-balanced fertilizer with a moderate nutrient content. It typically contains a good amount of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making it suitable for general garden use. However, the exact nutrient composition can vary depending on the cow’s diet and the manure’s level of maturity.
2. Chicken Manure: Chicken manure is high in nitrogen, making it especially beneficial for leafy green vegetables and plants that require a nitrogen boost. However, fresh chicken manure can contain high levels of ammonia and may burn plants if not composted or aged properly.
3. Horse Manure: Horse manure is rich in organic matter and contains a moderate level of nutrients. It is commonly used as a soil amendment to improve soil structure and fertility. However, horse manure can have a lower nitrogen content compared to other types of manure.
4. Sheep and Goat Manure: Sheep and goat manure are similar to cow manure and provide a balanced mix of nutrients. They are often well-composted and have a milder odor compared to other types of manure.
5. Pig Manure: Pig manure is relatively high in nitrogen and phosphorus and can be used as a nutrient-rich fertilizer. However, it may contain higher levels of pathogens compared to other types of manure. It is important to compost pig manure properly to reduce the risk of spreading diseases.
6. Rabbit Manure: Rabbit manure is one of the most concentrated and nutrient-rich manures available. It has high levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making it an excellent choice for promoting overall plant growth. Additionally, rabbit manure is typically well-aged and safe to use without the need for extensive composting.
7. Composted Manure: Composted manure, regardless of the animal source, has gone through a decomposition process, making it less odorous, weed-free, and safer to use. Composting allows the manure to break down, resulting in a more stable and nutrient-rich end product.
It is important to note that the nutrient content of manure can be influenced by several factors, including the animal’s diet, the manure’s age and composition, and the composting process. Conducting a soil test can provide more specific information about your garden’s nutrient needs and help you determine the appropriate manure type and quantity to use.
Now that you have a better understanding of manure and its nutrient content, let’s explore the different techniques for applying manure to your garden for optimal results.
Manure Application Techniques for Optimal Garden Health
Applying manure correctly is crucial to maximize its benefits and ensure the optimal health and productivity of your garden. Here are some techniques you can follow for effective manure application:
1. Composting: Composting manure before application helps reduce any potential pathogens, eliminate weed seeds, and create a stable and nutrient-rich end product. Composting also allows the manure to break down, making it easier for plants to absorb the nutrients. Aim for a composting period of at least 6-9 months to ensure the manure is fully decomposed.
2. Spread evenly: When applying manure, ensure an even distribution throughout the garden area. This helps prevent nutrient imbalances and ensures that all plants receive an adequate supply of nutrients. Use a rake or garden fork to spread the manure evenly, avoiding clumps or piles.
3. Avoid direct contact: Avoid placing manure in direct contact with plant stems or foliage, as it may cause burns or promote the growth of harmful bacteria. Maintain a distance of a few inches from the plant base during application.
4. Timing: Apply manure well in advance of planting to allow it to integrate into the soil. It is recommended to incorporate manure at least two to three weeks before sowing or transplanting. This gives ample time for the nutrients to become available to the plants.
5. Watering: After applying manure, water the garden thoroughly. This helps dissolve the nutrients and enables their absorption by plants’ roots. Adequate moisture also reduces the risk of nitrogen leaching from the manure.
6. Mulching: Consider mulching the garden after applying manure. Mulch helps retain moisture, prevent weed growth, and gradually releases nutrients into the soil. Organic materials like straw, shredded leaves, or wood chips make excellent mulching options.
7. Rotational application: Rather than applying manure to the entire garden at once, consider rotating the application area each season. This helps prevent nutrient buildup in one area and evenly distributes the benefits of manure throughout the garden.
8. Topdressing: As the growing season progresses, you can topdress the plants with a thin layer of well-aged composted manure. This provides a supplemental nutrient boost and helps maintain soil fertility throughout the growing season.
By following these manure application techniques, you can ensure that your garden receives the maximum benefit from this organic fertilizer. Remember to always follow safety guidelines when handling manure, wear protective gloves, and wash hands thoroughly after application.
However, there are certain precautions and guidelines to keep in mind when working with manure in the garden, which we will explore in the next section.
Precautions and Guidelines for Using Manure in the Garden
While manure is an excellent natural fertilizer, it is important to take certain precautions and follow guidelines to ensure safe and effective usage in your garden. Here are some key precautions and guidelines to keep in mind:
1. Source of manure: Ensure that the manure you are using comes from a reliable source. If possible, use manure from animals that have been raised without the use of antibiotics or hormones. Avoid using manure from animals that have been fed with herbicide-treated or genetically modified crops.
2. Composting and aging: Properly compost and age the manure before application to reduce the risk of pathogens and weed seeds. Composting helps break down the manure and stabilizes the nutrients, making it safer and more beneficial for your plants.
3. Handling: When handling manure, wear gloves and protective clothing to prevent direct contact with the skin. This is particularly important because manure can contain harmful bacteria. Wash your hands thoroughly after handling manure.
4. Application timing: Apply manure well in advance of planting to allow it to decompose and integrate into the soil. Avoid applying fresh manure close to the planting time, as it may burn plants or release excessive amounts of nitrogen.
5. Application rate: Apply manure according to the recommended application rate based on your garden size and the specific plants you are growing. Avoid over-application of manure, as excessive nutrients can lead to imbalances, nutrient runoff, and potential harm to your plants.
6. Environmental impact: Be mindful of the potential environmental impact of manure application. Avoid applying manure near water bodies to prevent nutrient runoff, which can contribute to water pollution. Also, consider local regulations regarding manure management and avoid overloading the soil with excess nutrients.
7. Storage and odors: If you have extra manure, store it properly in a well-ventilated area away from living spaces. Manure can produce strong odors, so take measures to minimize the odor and prevent it from causing any nuisance to yourself or your neighbors.
8. Soil testing: Regularly conduct soil tests to assess the nutrient levels in your soil. This will help you determine if additional manure or other amendments are needed and avoid nutrient imbalances.
By following these precautions and guidelines, you can optimize the use of manure in your garden while promoting a safe and healthy environment for both your plants and yourself.
However, there are some common mistakes that gardeners make when using manure, which we will discuss in the next section.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Applying Manure
Using manure in the garden can be highly beneficial, but it’s important to avoid certain common mistakes to ensure optimal results and prevent any potential issues. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when applying manure:
1. Over-application: Applying excessive amounts of manure can result in nutrient imbalances and lead to nutrient runoff, which can harm both your plants and the environment. Follow the recommended application rates specific to your garden size and the type of plants you are growing.
2. Applying fresh or untreated manure: Fresh manure can be high in ammonia and pathogens, which can burn your plants or introduce harmful bacteria. Always compost or age manure properly before application to reduce these risks.
3. Direct contact with plants: Avoid placing manure directly in contact with plant stems or foliage. This can cause burns or create a favorable environment for disease development. Maintain a safe distance from the plant base when applying manure.
4. Applying manure too close to harvest: Applying fresh manure too close to the harvest time can pose a risk of contamination. Allow sufficient time between manure application and harvest to ensure the safety and quality of your produce.
5. Failure to incorporate or cover the manure: Leaving manure exposed on the soil surface can lead to the release of ammonia and the loss of valuable nutrients. Always incorporate the manure into the soil or cover it with a layer of mulch to prevent nutrient loss and odor.
6. Not considering the nutrient content of manure: Different types of manure have different nutrient compositions. It’s important to understand the nutrient content of the manure you are using to avoid over or under-supplying your plants with specific nutrients.
7. Ignoring soil testing: Conducting regular soil tests is essential to assess the nutrient levels in your soil accurately. By knowing the nutrient needs of your soil, you can make informed decisions about the amount and type of manure to apply.
8. Applying manure without proper moisture: Water plays a crucial role in nutrient availability and absorption by plants. Ensure that the soil is adequately moist before and after applying manure to promote the efficient uptake of nutrients.
9. Failing to rotate the application area: Continuous, concentrated manure application in the same area can result in nutrient buildup and potential imbalances. Rotate the application area each season to ensure even nutrient distribution and avoid overloading the soil.
Avoiding these common mistakes will help you optimize the benefits of manure in your garden while ensuring the health and well-being of your plants and the environment.
Now that we have covered these common mistakes, let’s conclude with a brief summary of the key points we have discussed in this article.
Read also: 12 Best Chicken Manure Fertilizer for 2025
Conclusion
Using manure in the garden is a fantastic way to nourish your plants, improve soil fertility, and promote overall garden health. By understanding the benefits of using manure, considering the factors involved in calculating the manure amount, and employing proper application techniques, you can maximize the advantages while avoiding common mistakes.
Benefits of using manure in the garden include providing essential nutrients, improving soil structure, enhancing microbial activity, reducing soil erosion, and promoting a sustainable gardening approach. The type and nutrient content of manure play a crucial role in determining the appropriate application rate for different plant types.
When calculating manure quantity, consider factors such as garden size, soil type, plant nutritional needs, and manure type. It is crucial to apply the manure evenly, compost or age it properly, and avoid direct contact with plants. Taking precautions, such as wearing protective gear, handling manure from reliable sources, and adhering to environmental guidelines, is essential for safe and effective manure use.
Avoid common mistakes, including over-application, using fresh manure, direct contact with plants, and neglecting soil testing. By following proper manure application techniques, you can ensure optimal garden health and maximize the benefits while minimizing any potential risks or pitfalls.
In conclusion, manure is a valuable resource for enhancing your garden’s health and productivity in an environmentally friendly and sustainable way. By incorporating manure into your garden practices, you can create an abundant and thriving garden, filled with beautiful and healthy plants.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Much Manure For Garden
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Much Manure For Garden”