

Articles
What Is An Incandescent Bulb
Modified: August 25, 2024
Discover the benefits and drawbacks of incandescent bulbs in our informative articles. Find out why they are being phased out and explore more energy-efficient alternatives.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
The incandescent bulb has long been a staple in households and commercial spaces, providing illumination for over a century. However, with advancements in technology and growing concerns about energy efficiency, the popularity of incandescent bulbs has started to fade.
In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of incandescent bulbs, from their basic definition to how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, and their impact on energy consumption and the environment. We will also discuss alternative lighting options that have gained prominence as more sustainable choices for lighting our spaces.
So, let’s dive in and shed some light on the world of incandescent bulbs!
Key Takeaways:
- Incandescent bulbs, while traditional, are energy-inefficient and have a significant environmental impact. Transitioning to LED or CFL bulbs can reduce energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable future.
- The drawbacks of incandescent bulbs, such as low energy efficiency and short lifespan, highlight the need for more sustainable lighting alternatives. Embracing LED technology and smart lighting systems can lead to significant energy savings and environmental benefits.
Read more: Who Invented The Incandescent Bulb
Definition of Incandescent Bulb
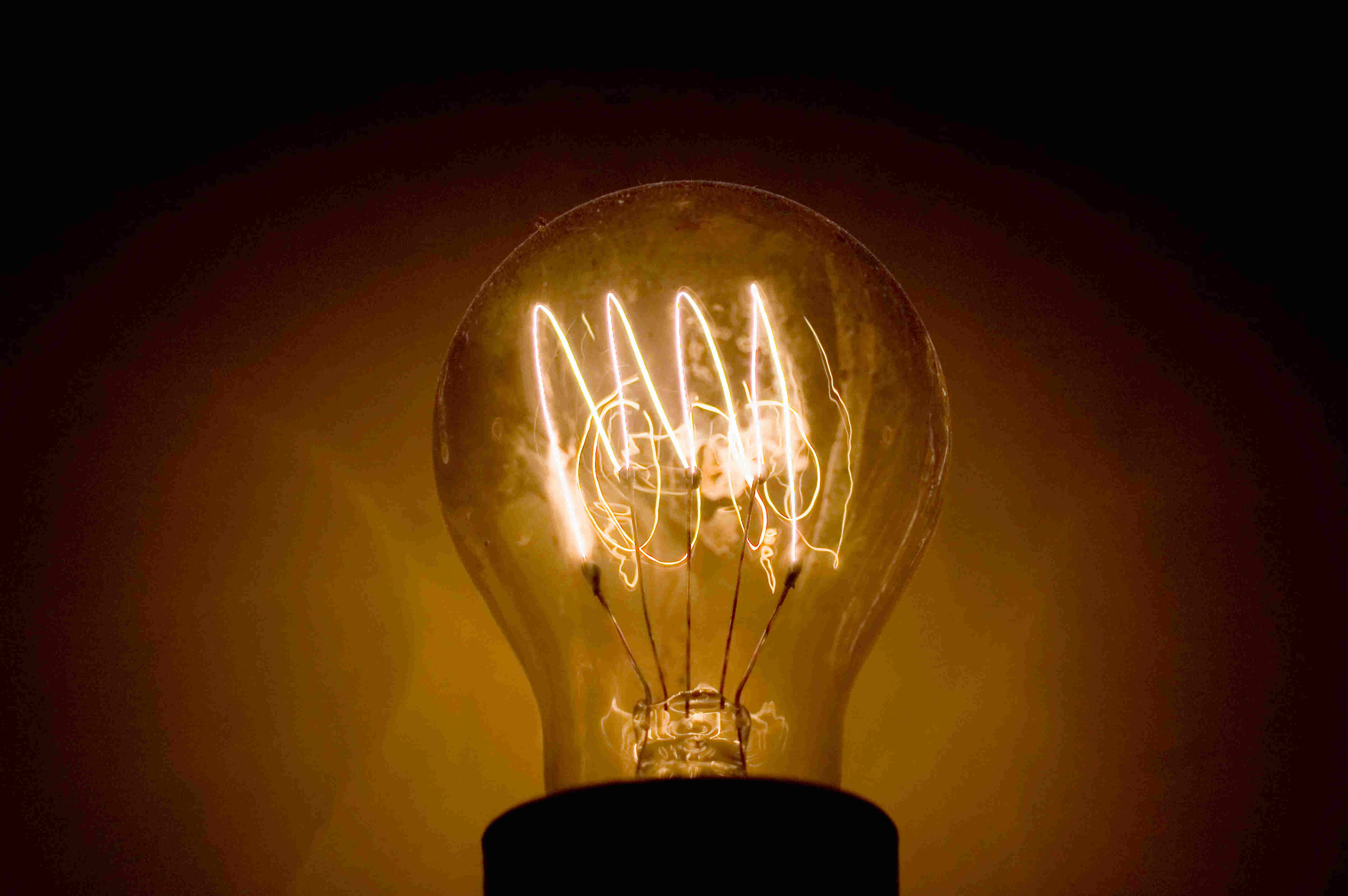
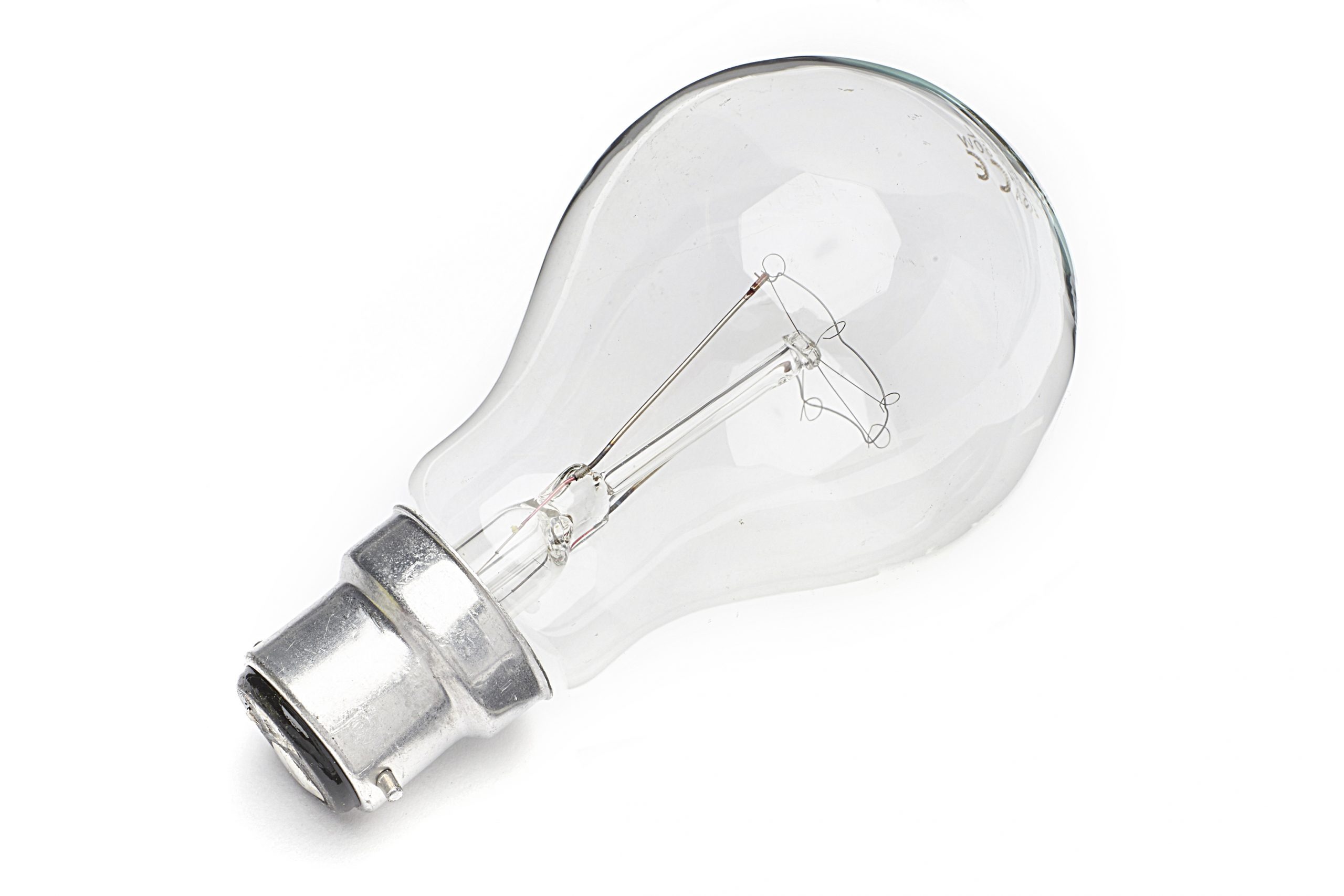
An incandescent bulb is a type of light bulb that produces light by heating a filament wire until it glows. It is one of the oldest and most traditional forms of artificial lighting, commonly used in residential and commercial spaces.
The basic structure of an incandescent bulb consists of a glass envelope enclosing a tungsten filament, supported by a base that connects to the electrical supply. When electricity passes through the filament, it generates heat, causing the filament to emit visible light.
Incandescent bulbs are known for their warm, yellowish light that closely resembles natural sunlight. They are available in various shapes and sizes to suit different lighting needs, ranging from standard household bulbs to specialized bulbs for decorative purposes.
Historically, incandescent bulbs have been the go-to choice for lighting due to their affordability and wide availability. However, with the advent of more energy-efficient lighting options, the use of incandescent bulbs has begun to decline.
How Incandescent Bulbs Work
Understanding how incandescent bulbs work requires delving into the physics of how the filament produces light. The filament, usually made of tungsten, is tightly coiled to maximize its surface area and minimize its length within the bulb. This design allows for efficient heating and light emission.
When an electric current passes through the filament, it encounters resistance, causing the filament to heat up. As the temperature of the filament rises, it begins to emit thermal radiation, including infrared (IR) radiation, which is not visible to the human eye. However, as the temperature continues to rise, the filament reaches a point where it emits visible light in addition to IR radiation.
The wavelengths of the emitted visible light depend on the temperature of the filament. At lower temperatures, the light emitted has longer wavelengths, appearing more reddish in color. As the temperature increases, the light shifts towards shorter wavelengths, resulting in a whiter and then bluer light.
Incandescent bulbs are not highly efficient in converting electrical energy into light. In fact, the majority of the energy is converted into heat rather than visible light. This inefficiency is due to the basic principle of incandescent lighting, where heat is required to produce light.
As a result, incandescent bulbs tend to get hot during operation. This heat emission can pose safety concerns, especially when used in enclosed fixtures or in close proximity to flammable materials.
It’s important to note that the amount of light emitted by an incandescent bulb diminishes over time as the filament gradually wears out. The average lifespan of an incandescent bulb is typically much shorter compared to newer lighting technologies, such as LEDs.
Advantages of Incandescent Bulbs
While incandescent bulbs have faced criticism for their energy inefficiency, they still possess certain advantages that make them a popular choice for specific lighting needs. Let’s take a closer look at some of the advantages of incandescent bulbs:
- Instant Illumination: One of the key advantages of incandescent bulbs is their ability to provide instant illumination. Unlike some other lighting technologies that require warm-up time, incandescent bulbs light up immediately when turned on, providing immediate brightness to the space.
- Color Rendering: Incandescent bulbs have exceptional color rendering capabilities, meaning they can accurately reproduce colors in a more natural and vibrant way. This makes them popular for applications where color quality is important, such as photography studios or areas where precise color perception is necessary.
- Dimming Capability: Incandescent bulbs are easily dimmable, allowing users to adjust the brightness according to their preference and needs. This flexibility in lighting control is particularly useful in creating ambiance or setting the mood in certain spaces.
- Affordability: Incandescent bulbs are typically more affordable than other lighting options, making them accessible to a wide range of consumers. Their low upfront cost often makes them an attractive choice for those on a tight budget or for large-scale lighting installations.
- Compatibility: Incandescent bulbs are compatible with traditional lighting fixtures and do not require any additional equipment or modifications. This makes them easy to replace and install, particularly in older buildings or existing infrastructure where retrofitting may be challenging.
Despite these advantages, it’s important to weigh them against the disadvantages and consider more sustainable lighting alternatives for long-term energy savings and environmental benefits.
Disadvantages of Incandescent Bulbs
While incandescent bulbs have been widely used for many years, they come with several significant drawbacks that have contributed to their decline in popularity. Let’s explore some of the disadvantages of incandescent bulbs:
- Low Energy Efficiency: Incandescent bulbs are notorious for their low energy efficiency. A significant portion of the energy consumed by these bulbs is converted into heat rather than light, resulting in wasted energy and higher electricity bills. Compared to more modern lighting options, such as LEDs or CFLs, incandescent bulbs consume much more energy for the same level of brightness.
- Short Lifespan: Incandescent bulbs have a relatively short lifespan compared to other lighting technologies. On average, they last for only about 1,000 to 2,000 hours, which means frequent replacements are necessary. This not only increases maintenance costs but also generates more waste from discarded bulbs.
- Heat Emission: Due to their design, incandescent bulbs emit a significant amount of heat during operation. This can be a concern in enclosed fixtures or small spaces, as it can cause discomfort and potentially increase the risk of fire. Additionally, the heat emitted from incandescent bulbs can contribute to higher cooling costs in warm climates.
- Environmental Impact: The energy inefficiency of incandescent bulbs translates into a greater environmental impact. The higher electricity consumption contributes to increased greenhouse gas emissions, further contributing to climate change. Additionally, the disposal of incandescent bulbs poses a potential hazard, as they contain trace amounts of mercury, a toxic substance.
- Lack of Options: Incandescent bulbs have limited options in terms of color temperature and customization. They generally produce a warm, yellowish light that may not be suitable for all applications or personal preferences. Other lighting technologies, such as LEDs, offer a wider range of color options and customization features.
Given these disadvantages, it is advisable to consider alternative lighting options that provide better energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and reduced environmental impact for a more sustainable and cost-effective lighting solution.
When handling incandescent bulbs, be sure to turn off the power and allow the bulb to cool before attempting to replace it. This will help prevent burns and electrical shock.
Read also: 11 Best Incandescent Bulb for 2025
Energy Efficiency Concerns
Energy efficiency is a critical factor to consider when evaluating lighting options, and incandescent bulbs fall short in this aspect. Here are some energy efficiency concerns associated with incandescent bulbs:
- High Energy Consumption: Incandescent bulbs are known for their high energy consumption. Only about 10% of the energy they consume is converted into visible light, while the remaining 90% is wasted as heat. This inefficiency results in unnecessary and excessive energy usage.
- Inefficient Spectrum Distribution: Incandescent bulbs emit light in a wide spectrum, including a significant portion in the infrared range, which is not visible to the human eye. This means that a substantial amount of energy is used to produce light that is not perceptible or useful to us, resulting in a waste of energy resources.
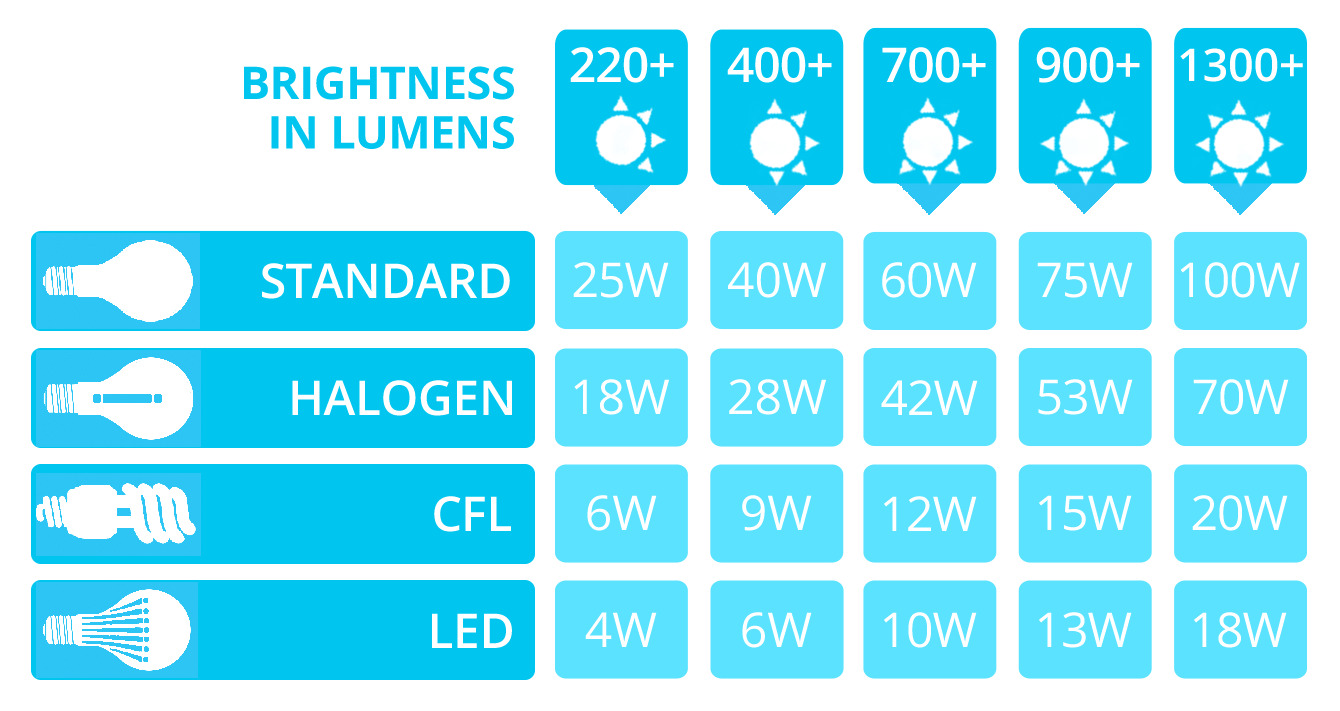
- Comparatively Low Lumens per Watt: The measure of efficiency for light sources is lumens per watt (lm/W), which indicates how much visible light is produced for each unit of electrical power consumed. Incandescent bulbs have a relatively low lm/W compared to newer lighting technologies, such as LEDs, which can be up to 80% more energy-efficient.
- Impact on Electricity Bills: Due to their high energy consumption, using incandescent bulbs can lead to higher electricity bills. This is particularly noticeable in households or commercial spaces with a large number of light fixtures, where the cumulative energy usage can significantly impact overall energy costs.
- Carbon Footprint: The excessive energy consumption of incandescent bulbs contributes to a larger carbon footprint. The higher energy demands result in increased greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change and environmental degradation.
Considering the energy efficiency concerns associated with incandescent bulbs, it is important to explore alternative lighting options that offer higher efficiency and reduced energy consumption, such as LEDs or compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs).
Environmental Impact of Incandescent Bulbs
The environmental impact of incandescent bulbs extends beyond their energy inefficiency. Let’s explore some of the key environmental concerns associated with these bulbs:
- Carbon Emissions: The high energy consumption of incandescent bulbs translates into significant carbon emissions. The electricity generation required to power these bulbs often relies on fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases contribute to climate change and its associated negative impacts, such as rising temperatures and more frequent extreme weather events.
- Resource Depletion: Incandescent bulbs require the use of various materials, including tungsten for the filament and glass for the bulb envelope. The extraction and production of these materials can have significant environmental consequences, including habitat destruction, ecosystem disruption, and pollution. The finite nature of these resources also raises concerns about long-term sustainability.
- Waste Generation: Incandescent bulbs have a relatively short lifespan and need to be replaced frequently. This generates a significant amount of waste, as discarded bulbs end up in landfills. Moreover, incandescent bulbs contain trace amounts of mercury, a toxic substance. While the mercury content is relatively low compared to other types of bulbs, proper disposal is still essential to prevent environmental contamination.
- Ecosystem Impact: The environmental impact of incandescent bulbs extends beyond their manufacturing and disposal. Light pollution, caused by excessive and misdirected artificial lighting, can disrupt natural ecosystems and wildlife behavior. This can have far-reaching consequences for various species, including their feeding patterns, mating habits, and migration routes.
- Sustainable Alternatives: To mitigate the environmental impact of incandescent bulbs, it is crucial to explore more sustainable lighting alternatives. LED bulbs, for example, are highly energy-efficient, have a longer lifespan, and contain fewer hazardous materials. By transitioning to these alternatives, we can significantly reduce carbon emissions, waste generation, and overall environmental footprint.
Considering the environmental impact of incandescent bulbs, it is important to prioritize energy-efficient and eco-friendly lighting options that not only save energy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also minimize resource depletion and waste generation.
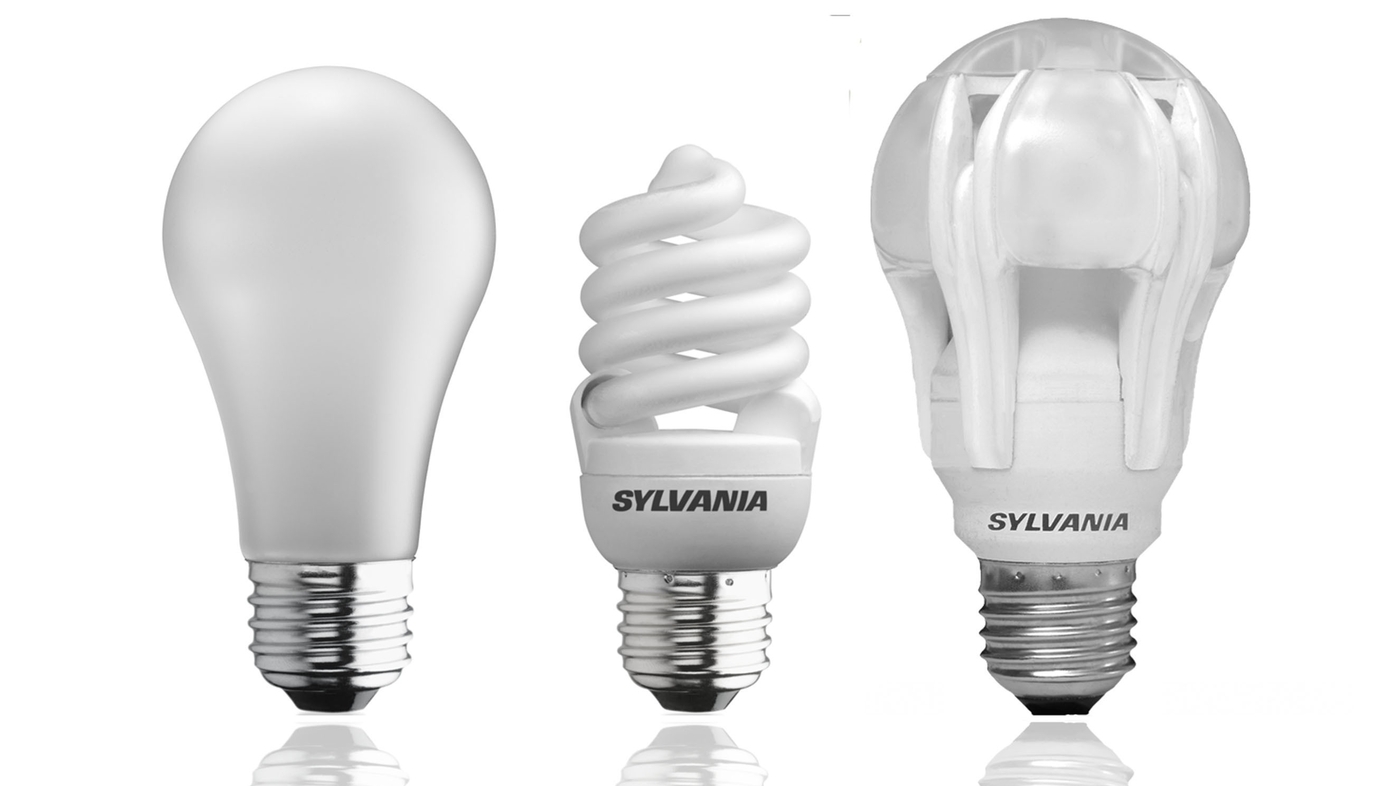
Alternatives to Incandescent Bulbs
As the drawbacks of incandescent bulbs become more apparent, it is important to consider alternative lighting options that offer higher energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and reduced environmental impact. Here are some popular alternatives to incandescent bulbs:
- LED Bulbs: LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulbs have gained significant popularity in recent years. They are highly energy-efficient, consuming significantly less electricity compared to incandescent bulbs while providing similar or better levels of brightness. LED bulbs also have a longer lifespan, making them a cost-effective and sustainable option for lighting.
- CFL Bulbs: CFL (Compact Fluorescent Lamp) bulbs are another common alternative to incandescent bulbs. They use less energy and last longer than traditional incandescent bulbs. However, they contain a small amount of mercury, and proper recycling is necessary to prevent environmental contamination.
- Halogen Bulbs: Halogen bulbs are similar to incandescent bulbs in terms of the technology used. However, they are more energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan. Halogen bulbs produce a bright, white light and are often used for spotlighting or directional lighting.
- Smart Lighting Systems: Smart lighting systems, such as those using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity, offer advanced lighting control and energy management features. These systems allow users to customize lighting settings, schedule automatic on/off times, and adjust brightness levels remotely. The combination of smart bulbs and intelligent lighting controls can significantly reduce energy consumption and increase convenience.
- Natural Light: Maximizing the use of natural light through windows, skylights, or light tubes can help reduce the reliance on artificial lighting altogether. It not only saves energy but also provides numerous health benefits, such as improved mood and increased productivity.
When considering alternatives to incandescent bulbs, it is important to look for energy-efficient options that align with your lighting needs and preferences. It’s worth noting that while these alternatives may have a higher upfront cost, the long-term energy savings and environmental benefits outweigh the initial investment.
By transitioning to these alternative lighting options, we can contribute to reducing energy consumption, lowering carbon emissions, and promoting a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
The era of incandescent bulbs, once a staple in lighting, is gradually fading away as more energy-efficient and sustainable alternatives take center stage. While incandescent bulbs have served us well for over a century, their low energy efficiency, short lifespan, and environmental impact have brought attention to the need for more efficient lighting solutions.
LED bulbs have emerged as one of the most popular alternatives to incandescent bulbs. They offer significant energy savings, have a longer lifespan, and provide a range of customization options. CFL bulbs and halogen bulbs also offer improved energy efficiency and longer lifespans compared to incandescent bulbs.
Energy efficiency and environmental considerations play a crucial role in our lighting choices. The excessive energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with incandescent bulbs contribute to climate change and resource depletion. Additionally, the waste generated from frequently replacing incandescent bulbs and the trace amounts of mercury they contain pose environmental risks.
By adopting energy-efficient lighting alternatives, we not only reduce our energy consumption and electricity bills but also contribute to mitigating climate change and minimizing our environmental footprint. Smart lighting systems, natural light utilization, and proper light management techniques can also enhance our overall lighting experience while reducing energy consumption.
As consumers, it is essential to be mindful of our lighting choices and prioritize sustainable lighting options that offer better energy efficiency, longer lifespans, and reduced environmental impact. Upgrading to LED or CFL bulbs, utilizing natural light whenever possible, and incorporating smart lighting systems can significantly contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.
Let’s embrace the advancements in lighting technology and make conscious choices to illuminate our lives while preserving the planet for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is An Incandescent Bulb
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is An Incandescent Bulb”