Home>Articles>Why Is A Compact Fluorescent Light Bulb More Efficient Than An Incandescent Bulb?


Articles
Why Is A Compact Fluorescent Light Bulb More Efficient Than An Incandescent Bulb?
Modified: January 19, 2024
Discover why compact fluorescent light bulbs are more efficient than incandescent bulbs in this informative article. Learn about the benefits and savings of choosing energy-efficient lighting options.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to energy-efficient lighting, there are two main contenders: compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) and incandescent bulbs. In recent years, CFLs have gained popularity due to their higher energy conversion efficiency compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. But why is this the case? What makes a compact fluorescent light bulb more efficient than an incandescent bulb?
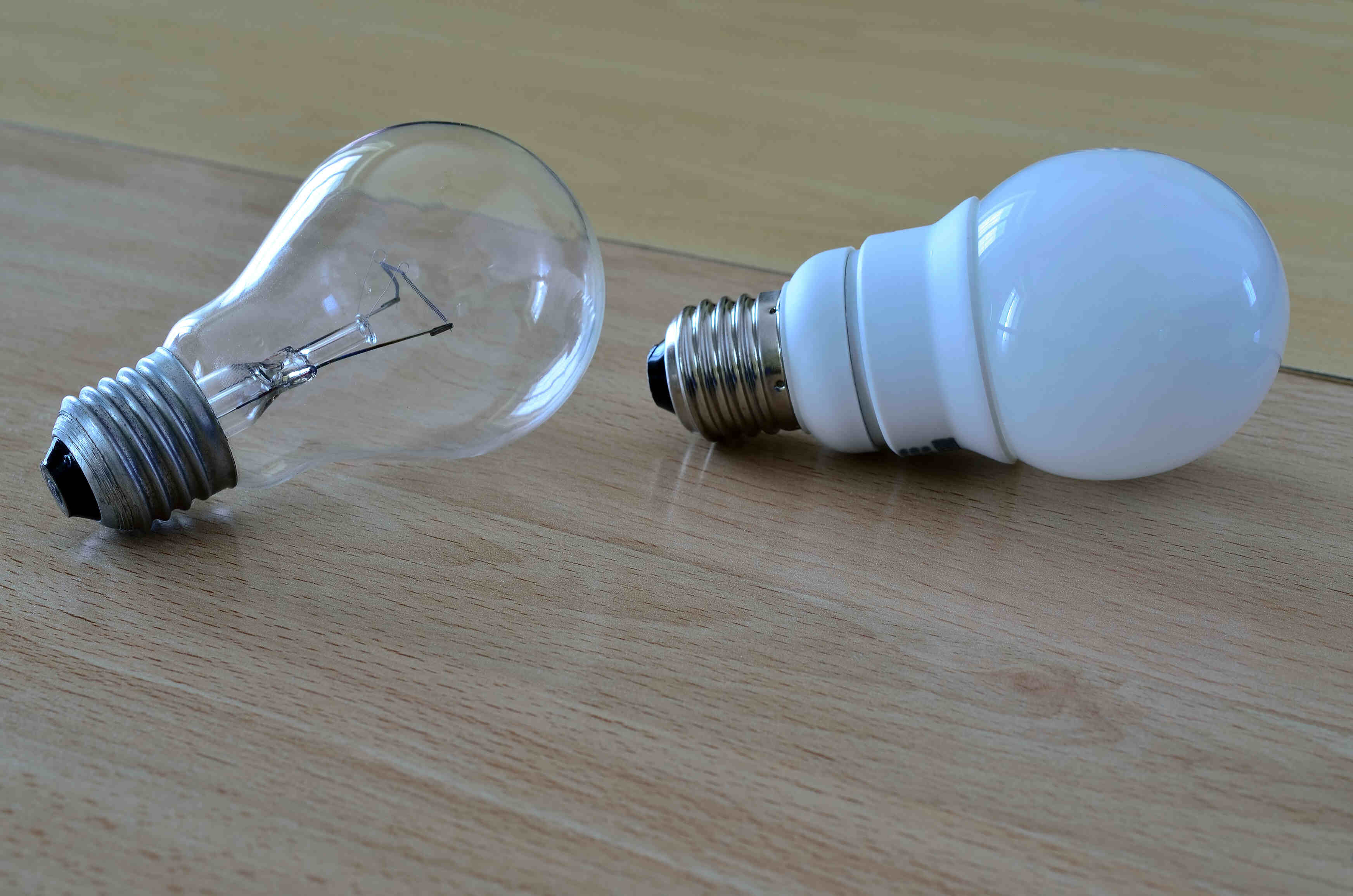
To understand the difference in efficiency between these two types of bulbs, it is important to delve into their working principles. Both CFLs and incandescent bulbs rely on the conversion of electrical energy into light, but they do so in very different ways. An incandescent bulb produces light by heating a tungsten filament until it glows, while a compact fluorescent light bulb uses a combination of electric current and mercury vapor to generate light.
This difference in the underlying technology is a key factor in understanding why CFLs are more efficient than incandescent bulbs. The process of heating a filament in an incandescent bulb consumes a significant amount of energy, resulting in a large proportion of energy being lost as heat rather than light. In contrast, a compact fluorescent light bulb can produce the same amount of light with significantly less energy expenditure.
Energy conversion efficiency is a crucial metric to compare the performance of different light bulbs. It measures how effectively a light bulb converts electrical energy into visible light. The higher the efficiency, the less energy is wasted as heat and the more light is produced per unit of energy consumed. In this regard, CFLs have a clear advantage over incandescent bulbs.
There are several factors that contribute to the higher efficiency of compact fluorescent light bulbs. Firstly, the use of mercury vapor in CFLs allows for more efficient light production compared to the heating process in incandescent bulbs. When electricity passes through the vapor-filled tube of a CFL, it excites the mercury atoms, causing them to emit ultraviolet light. This light, in turn, reacts with the phosphor coating inside the tube, producing visible light.
Additionally, CFLs are designed to emit light in a more focused and directional manner, minimizing wastage. They also have a longer lifespan, lasting up to ten times longer than incandescent bulbs. This extended lifespan not only reduces the frequency of bulb replacements but also contributes to the overall energy efficiency of CFLs.
The environmental implications of choosing compact fluorescent light bulbs over incandescent bulbs are another significant factor to consider. CFLs require less energy to operate, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced dependence on fossil fuel resources. Furthermore, the longer lifespan of CFLs means fewer bulbs end up in landfills, reducing the overall environmental impact.
Looking toward the future, advancements in energy-efficient lighting technology continue to drive innovation. LED (light-emitting diode) bulbs are emerging as an even more efficient alternative to CFLs. LED bulbs are highly energy-efficient, have an even longer lifespan, and do not contain mercury. As these technologies evolve, it is essential to stay informed and make conscious choices that contribute to a more sustainable future.
Key Takeaways:
- Compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) outperform incandescent bulbs in energy efficiency due to their use of fluorescent technology, focused light emission, longer lifespan, and lower heat generation. Making the switch to CFLs can significantly reduce energy consumption and promote sustainability.
- Choosing CFLs over incandescent bulbs has substantial environmental benefits, including lower energy consumption, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, conservation of fossil fuels, decreased pollution, and reduced waste generation. Embracing energy-efficient lighting technology, such as LEDs and smart solutions, will further drive sustainability in the future.
Read more: What Is A Fluorescent Light Bulb
The Working Principles of Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs and Incandescent Bulbs
To understand why compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) are more efficient than incandescent bulbs, it is important to delve into their working principles.
Incandescent bulbs, which have been used for over a century, rely on a simple but energy-intensive process. Inside an incandescent bulb, an electric current passes through a filament made of tungsten, a highly resistant metal. The electrical resistance of the tungsten filament causes it to heat up, reaching temperatures of around 2,700 degrees Celsius (4,900 degrees Fahrenheit). This intense heat causes the filament to emit visible light, producing the desired illumination.
However, this heating process consumes a significant amount of energy, leading to a fundamental limitation in the efficiency of incandescent bulbs. The majority of the energy, approximately 90%, is lost as heat rather than being converted into visible light. This inefficiency makes incandescent bulbs highly energy-wasteful and contributes to their short lifespan.
On the other hand, compact fluorescent light bulbs operate on a completely different principle. Inside a CFL, an electric current passes through a tube filled with a small amount of mercury vapor and a phosphor coating. The mercury vapor, when excited by the electric current, emits ultraviolet (UV) light. This high-frequency UV light interacts with the phosphor coating on the walls of the tube, causing it to fluoresce and emit visible light.
The key advantage of this process is that it requires significantly less energy compared to the heating mechanism in incandescent bulbs. As a result, CFLs can produce as much as four times more light per unit of electrical energy consumed, translating into a higher energy conversion efficiency.
Moreover, CFLs are designed with a spiral or helical shape to maximize the surface area of the phosphor coating and improve light output. The compact design also contributes to the efficient use of space and allows for better heat dissipation.
It is important to note that, due to the presence of mercury in CFLs, proper disposal is crucial to avoid environmental contamination. Many countries have established recycling programs to safely handle used CFLs and recover the mercury for reuse.
In summary, while incandescent bulbs rely on heating a tungsten filament to produce light, compact fluorescent light bulbs utilize the combination of mercury vapor and phosphor coating to generate light through fluorescent technology. This significant difference in working principles contributes to the superior energy conversion efficiency of CFLs over incandescent bulbs, making CFLs the more efficient lighting option.
Energy Conversion Efficiency Comparison between Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs and Incandescent Bulbs
When it comes to energy conversion efficiency, compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) outperform traditional incandescent bulbs by a significant margin. This efficiency comparison is a key factor in the growing popularity of CFLs as a more sustainable lighting option.
Energy conversion efficiency measures how effectively a light source converts electrical energy into visible light, with higher efficiency indicating less energy wasted as heat and more light produced for each unit of electricity consumed.
Incandescent bulbs have low energy conversion efficiency due to their fundamental working principle. As electrical current flows through the tungsten filament inside an incandescent bulb, it heats up, eventually reaching temperatures as high as 2,700 degrees Celsius (4,900 degrees Fahrenheit). The intense heat causes the filament to emit light, but a significant portion of the electrical energy is wasted in the form of heat rather than converted into visible light. As a result, incandescent bulbs have an energy conversion efficiency of only about 10%.
On the other hand, compact fluorescent light bulbs operate on a different mechanism that enables them to convert electrical energy into light at much higher efficiency levels. In a CFL, the electric current passes through a tube containing a small amount of mercury vapor and a phosphor coating. The mercury vapor, when excited by the electric current, emits ultraviolet (UV) light. The phosphor coating on the tube’s walls then absorbs the UV light and re-emits it as visible light.
This fluorescent technology allows CFLs to achieve energy conversion efficiency levels of around 25%-30%. In other words, CFLs can convert up to 30% of the electrical energy they consume into visible light, leaving minimal energy wastage as heat. Compared to incandescent bulbs, CFLs can produce up to four times more light per unit of electrical energy consumed, resulting in significantly reduced electricity usage.
It’s important to note that energy conversion efficiency can vary slightly between different CFL models and manufacturers. However, even the least efficient CFLs still far surpass the energy efficiency of incandescent bulbs.
This stark contrast in energy conversion efficiency has significant implications on energy consumption and environmental impact. By adopting CFLs in place of incandescent bulbs, households and businesses can achieve substantial energy savings and reduce their carbon footprints. The increased efficiency also means lower electricity bills and reduced dependence on fossil fuel resources.
While CFLs have proven to be a more energy-efficient lighting option, it’s worth mentioning that advancements in LED (light-emitting diode) technology have taken efficiency to even greater heights. LEDs have energy conversion efficiency levels surpassing 50%, making them the most energy-efficient lighting option available today.
In summary, compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) have a significantly higher energy conversion efficiency compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. CFLs can convert electrical energy into light at a rate of around 25%-30%, while incandescent bulbs operate at an efficiency level of only about 10%. This efficiency difference translates into lower electricity consumption, reduced utility bills, and decreased environmental impact, making CFLs a more sustainable lighting choice.
A compact fluorescent light bulb is more efficient than an incandescent bulb because it produces less heat and more light, using less energy to achieve the same brightness.
Factors Contributing to the Higher Efficiency of Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs
The higher efficiency of compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) compared to traditional incandescent bulbs can be attributed to several key factors. These factors contribute to the reduced energy consumption and increased light output of CFLs, making them a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective lighting choice. Let’s explore these factors in more detail:
- Fluorescent Technology: The underlying technology used in CFLs is the key driver of their higher efficiency. Unlike incandescent bulbs that rely on heating a filament to produce light, CFLs use fluorescent technology. This technology requires less electrical energy since it primarily involves the excitation of mercury vapor, which in turn emits ultraviolet light. The ultraviolet light then interacts with the phosphor coating on the tube, producing visible light. This process results in significantly reduced energy wastage as heat, allowing CFLs to convert more electrical energy into light.
- Focused Light Emission: CFLs are designed to emit light in a more directed and focused manner. The shape and configuration of the CFLs, such as the commonly seen spiral or helical shape, help to maximize the light output by ensuring that the emitted light is directed where it is needed. This focused light emission minimizes light scattering and wastage, resulting in better illumination and improved overall efficiency.
- Longer Lifespan: CFLs have a significantly longer lifespan compared to incandescent bulbs. While incandescent bulbs typically last for around 1,000 hours, CFLs can last up to 10,000 hours or more. This extended lifespan means fewer bulb replacements, resulting in reduced energy consumption, less waste generation, and overall cost savings. The longer lifespan of CFLs also contributes to their higher efficiency since less energy is expended in manufacturing and transporting replacement bulbs.
- Lower Heat Generation: Incandescent bulbs generate a significant amount of heat during operation due to the heating of the filament. This heat generation not only wastes energy but also increases the risk of fire hazards and discomfort in enclosed spaces. In contrast, CFLs produce much less heat since most of the energy consumed is converted into light rather than heat. This lower heat generation contributes to the increased efficiency of CFLs and makes them safer and more comfortable to use.
- Improved Technology and Design: As technology has advanced, CFLs have undergone continuous improvements in both efficiency and performance. Manufacturers have focused their efforts on developing more efficient ballasts and phosphor coatings that enhance the overall efficiency of CFLs. Additionally, the design of CFLs has become more compact and streamlined, allowing for better heat dissipation and improved light distribution. These advancements in technology and design have further contributed to the higher efficiency of CFLs.
By considering these factors, it becomes evident why compact fluorescent light bulbs are more efficient than incandescent bulbs. The combination of fluorescent technology, focused light emission, longer lifespan, lower heat generation, and ongoing technological advancements all play key roles in making CFLs a more energy-efficient lighting choice. By using CFLs, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their energy consumption, lower utility costs, and promote environmental sustainability.
Environmental Implications of Choosing Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs over Incandescent Bulbs
Choosing compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) over traditional incandescent bulbs has several significant environmental implications. By opting for these energy-efficient alternatives, individuals can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving natural resources, and minimizing environmental impacts. Let’s explore these implications in more detail:
- Lower Energy Consumption: One of the primary environmental benefits of CFLs is their reduced energy consumption. CFLs can produce the same amount of light as incandescent bulbs while using significantly less electricity. This lower energy demand translates into reduced fossil fuel combustion and, consequently, lower greenhouse gas emissions. By adopting CFLs, individuals can help mitigate climate change and its associated environmental impacts.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), are major contributors to global warming and climate change. Incandescent bulbs are highly inefficient, with most of the electrical energy they consume being wasted as heat rather than converted into light. The increased efficiency of CFLs significantly reduces the amount of electricity needed to achieve the desired lighting level. By using CFLs, individuals can help reduce their carbon footprint by lowering their household or business emissions.
- Conservation of Fossil Fuels: The decreased energy consumption associated with CFLs also contributes to the conservation of fossil fuel resources. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are finite resources that have significant environmental impacts associated with their extraction and combustion. By using CFLs and reducing overall energy demand, there will be less dependence on these limited resources, helping to conserve them for present and future generations.
- Reduced Air and Water Pollution: Electricity generation from fossil fuels can result in various forms of pollution, including air pollution from the emissions of particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. Additionally, the extraction and processing of fossil fuels can lead to water pollution through chemical leaks and spills. By reducing energy consumption, CFLs help to decrease the overall pollution associated with electricity generation and contribute to cleaner air and water quality.
- Decreased Waste Generation: CFLs have a significantly longer lifespan compared to incandescent bulbs, often lasting up to ten times longer. This extended lifespan means fewer bulbs are discarded and end up in landfills, reducing waste generation. Furthermore, many CFLs are recyclable, and proper recycling programs are available in many regions. Recycling CFLs allows for the recovery and reuse of valuable materials, such as mercury and glass, further reducing their environmental impact.
It is important to note that CFLs do contain a small amount of mercury, which requires proper handling and disposal. Mercury is a toxic substance that can be harmful to human health and the environment if not managed correctly. However, the environmental benefits of using CFLs outweigh the potential risks associated with their mercury content. It is crucial to follow local guidelines and recycling programs to ensure safe disposal and minimize any potential environmental impacts.
In summary, choosing compact fluorescent light bulbs over incandescent bulbs has substantial environmental implications. The lower energy consumption, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, conservation of fossil fuel resources, decreased pollution, and reduced waste generation make CFLs a more eco-friendly lighting choice. By making the switch to CFLs, individuals can make a positive impact on the environment and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The Future of Energy-efficient Lighting Technology
The rapid advancements in lighting technology are driving the future of energy efficiency, with a focus on developing lighting solutions that offer even greater efficacy, longevity, and sustainability. As we move forward, several emerging technologies and trends hold promise for further improving energy-efficient lighting. Let’s explore the future of energy-efficient lighting technology:
- LED (Light-Emitting Diode) Lighting: LED lighting has already revolutionized the lighting industry with its exceptional energy efficiency and longevity. LEDs are highly efficient at converting electrical energy into light, far surpassing both incandescent and compact fluorescent bulbs. Additionally, LEDs have a remarkably longer lifespan, some lasting up to 50,000 hours or more. This extended lifespan and reduced energy consumption make LEDs the leading energy-efficient lighting technology. The ongoing research and development in LED technology continue to enhance its efficiency, affordability, and versatility.
- Smart Lighting Solutions: The integration of LED lighting with smart technologies opens up new possibilities for energy-efficient lighting control and management. Smart lighting systems enable users to customize and automate lighting settings, adjusting brightness levels, scheduling lighting cycles, and even incorporating motion sensors and natural light sensors. These smart solutions optimize energy usage, providing the right amount of light when and where it is needed and reducing unnecessary energy consumption. The future will likely see further advancements in smart lighting, making it more accessible and seamlessly integrated into our daily lives.
- Human-Centric Lighting: Human-centric lighting focuses on enhancing well-being and productivity by mimicking natural light patterns. By adjusting the color temperature and intensity of artificial light according to the time of day, human circadian rhythms can be better regulated. This technology aims to improve sleep quality, mood, and overall health. Human-centric lighting holds great potential in various settings, including homes, offices, healthcare facilities, and schools, offering energy-efficient lighting that positively impacts our well-being.
- Wireless Power Transfer: Wireless power transfer technology, such as using radiofrequency or magnetic induction, has the potential to revolutionize how we power and control lighting systems. With wireless power transfer, energy-efficient lighting can be achieved without the need for wired connections or traditional power outlets. This technology allows for greater flexibility in lighting placement and control, making it easier to incorporate energy-efficient lighting solutions into various architectural designs and spaces.
- Light Harvesting: Light harvesting technologies involve the capture and utilization of natural light to supplement or offset artificial lighting. Methods such as daylight harvesting, which adjusts artificial lighting levels based on the presence and intensity of natural light, are already in use. However, future advancements may enable more efficient light harvesting systems that maximize the use of natural light, reducing reliance on electricity during daylight hours and further enhancing energy efficiency.
- Circular Economy and Sustainable Materials: With increasing environmental awareness, the future of energy-efficient lighting also lies in adopting sustainable practices and materials. Manufacturers are focusing on closing the loop and implementing circular economy principles, including the use of recyclable and eco-friendly materials, reducing waste generation, and promoting product longevity and repairability. These efforts ensure that energy-efficient lighting solutions are not only efficient during use but also sustainable throughout their lifecycle.
The future of energy-efficient lighting technology is promising, with continuous innovation and research driving advancements in efficiency, control, and sustainability. LED lighting will continue to dominate the market, becoming even more affordable and versatile. Smart lighting solutions will offer greater customization and energy optimization. Human-centric lighting will prioritize human well-being. Meanwhile, wireless power transfer, light harvesting, and sustainable practices will shape the future of lighting design and implementation.
As consumers, businesses, and policymakers embrace the importance of energy efficiency, we can expect a brighter and more sustainable future, where lighting technology plays a significant role in creating greener and healthier spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions about Why Is A Compact Fluorescent Light Bulb More Efficient Than An Incandescent Bulb?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Why Is A Compact Fluorescent Light Bulb More Efficient Than An Incandescent Bulb?”