

Articles
When Were Mirrors Created
Modified: October 27, 2024
Discover the history of mirrors and when they were first created. Explore fascinating articles on the evolution of mirrors throughout time.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
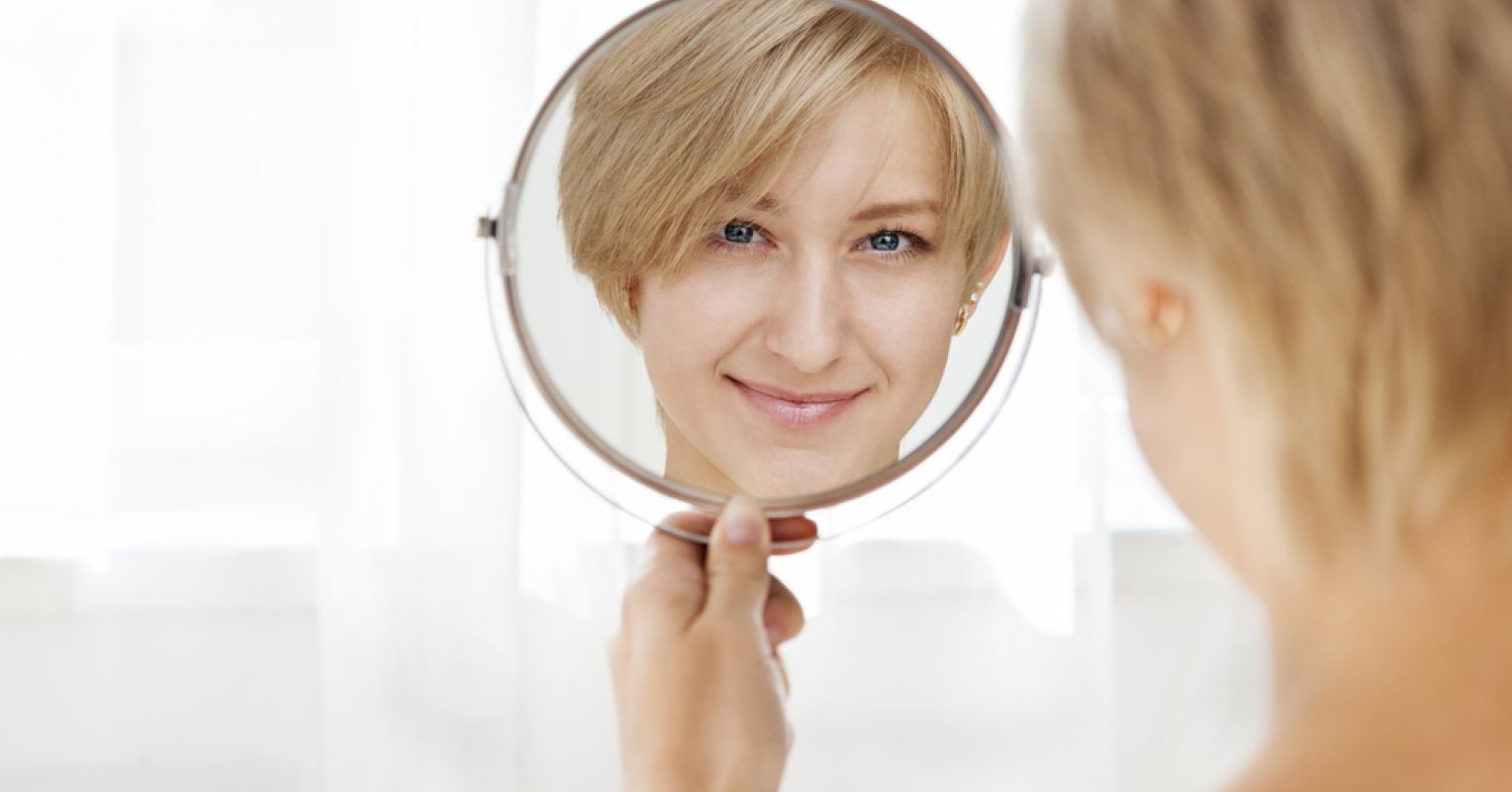
Mirrors play a significant role in our daily lives, allowing us to admire our reflections, apply makeup, and check our appearance before stepping out into the world. But have you ever wondered when mirrors were first created? The invention of mirrors dates back thousands of years, and their evolution has been influenced by various civilizations and technological advancements.
The concept of reflection has always fascinated humans. From early times, people must have observed their reflections in calm bodies of water or shiny surfaces such as polished stones or obsidian. However, these reflections were transient and not easily accessible.
As civilizations progressed, so did the technology used to create reflective surfaces. Let’s explore the fascinating journey of mirror development and discover when the polished stones and calm waters transformed into the sleek and clear glass mirrors we know today.
Key Takeaways:
- The journey of mirrors from natural reflections to the sophisticated glass mirrors we have today reflects human curiosity, innovation, and the desire to see ourselves with greater clarity and insight.
- Mirrors have evolved from humble objects to cultural artifacts, artistic elements, and technological marvels, embodying our desires for self-reflection, self-improvement, and visual beauty.
Read more: When Were Glass Mirrors Invented
Origins of Reflection
The origins of reflection can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where people first observed their reflections in natural surfaces. The earliest form of reflection was likely seen in bodies of water, such as lakes, ponds, or even shallow pools.
It is believed that our ancestors noticed their own reflections when they leaned over to drink water or washed their faces in these water sources. These transient reflections must have intrigued them, leading to the exploration of other reflective surfaces.
Natural materials like polished stones, obsidian, and even highly reflective metals like copper or bronze were likely used to create rudimentary mirrors in those early times. By smoothing and polishing these materials, our ancestors could catch glimpses of their own images and study their appearances more closely.
The fascination with reflection spread across different ancient civilizations, each adding their unique touch to the development of mirrors. For example, the Chinese used polished bronze mirrors adorned with intricate designs, while the Ancient Egyptians crafted mirrors from polished copper.
These early reflective surfaces served both practical and decorative purposes. They allowed individuals to present themselves in a more polished manner, especially during important events and rituals. Additionally, the reflective surfaces were incorporated into artwork and jewelry, showcasing the valued reflection as a symbol of beauty and power.
This experimentation with reflective surfaces laid the foundation for the future development of mirrors. The quest for a clearer, more durable, and easily accessible reflection continued, ultimately leading to revolutionary breakthroughs in mirror technology.
Early Reflective Surfaces
As civilizations advanced, so did the techniques and materials used to create reflective surfaces. In addition to polished stones and obsidian, ancient civilizations discovered other materials that offered better reflection quality.
One such material was polished metal, particularly bronze and copper. The Ancient Greeks and Romans were pioneers in using metal for mirror production. They would meticulously shape and polish these metals to achieve a smooth and reflective surface. These early metal mirrors were usually small in size and handheld, making them portable and convenient for personal grooming.
However, metal mirrors had their limitations. They were prone to tarnishing and required regular polishing to maintain their reflective quality. Additionally, they were relatively expensive to produce and resulted in a somewhat distorted reflection due to the unevenly shaped surfaces.
Despite these limitations, metal mirrors continued to be widely used throughout antiquity. They were associated with wealth and power and often used as status symbols by the elite. These mirrors were also incorporated into religious rituals and were considered sacred objects in some cultures.
Another material that gained prominence as a reflective surface was polished stone, specifically obsidian. Obsidian, a naturally occurring volcanic glass, was highly prized by many ancient civilizations for its reflective properties. It was often shaped into handheld mirrors with one side polished to act as a reflective surface.
Obsidian mirrors became particularly popular in Mesoamerican cultures such as the Mayans and Aztecs. These mirrors played a significant role in various religious and ritualistic practices. They were believed to possess mystical powers and were used by priests and shamans for divination and communicating with the spiritual realm.
While metal and stone mirrors provided valuable insights into early mirror technology, they were limited in terms of clarity and convenience. The search for a more refined and practical reflective surface continued, ultimately leading to the invention of glass mirrors.
Ancient Mirror Technology
The development of mirror technology took a significant leap forward with the invention of glass mirrors. The ancient Romans are credited for pioneering the use of glass as a reflective surface. This breakthrough allowed for clearer and more accurate reflections, setting the stage for modern mirror production.
The Roman glass mirrors were created using a technique known as “silvering.” This process involved coating the back surface of a glass sheet with a reflective layer of molten metal. Initially, this reflective layer was made using a tin-mercury amalgam, which provided a reflective surface but was toxic and prone to decay.
As time went on, the amalgam was replaced with silver, a more durable and less hazardous material. This advancement in mirror technology made glass mirrors more accessible and popular among the Roman elite. Large wall-mounted mirrors, known as “specula,” adorned the palaces and villas of the wealthy, allowing them to admire their reflections in grand style.
However, the production of glass mirrors was still a laborious and expensive process, limiting their availability to only the wealthiest members of society. It wasn’t until the Middle Ages that the art of glassmaking and mirror production spread beyond the Roman Empire, making mirrors more accessible to a wider range of people.
During the Middle Ages, the techniques for creating glass mirrors evolved. The silvering process was refined, and the reflective layer was often backed with a protective coating to prevent tarnishing and damage. This protective layer consisted of materials such as wax, varnish, or even a layer of mercury or gold leaf.
Mirrors during this period were often small and portable, designed to be handheld or placed on a table or stand. They were crafted with elaborate and ornate frames, showcasing the craftsmanship of the time. Mirrors became an essential part of noble households, reflecting the opulence and grandeur of the Renaissance era.
The development of glass mirrors revolutionized the way people observed themselves. The clarity of the reflection in these mirrors allowed for closer attention to detail and enhanced self-perception. The demand for mirrors grew, leading to further advancements in mirror production techniques.
Next, we’ll explore the role of mirrors during the Renaissance and the modern development of mirrors.
The Invention of Glass Mirrors
The invention of glass mirrors marked a significant milestone in mirror technology. Prior to the development of glass mirrors, reflective surfaces were limited to metals and polished stones. However, the introduction of glass as a reflective material revolutionized the mirror industry.
While the Romans are credited with pioneering glass mirrors, it was during the Islamic Golden Age that significant advancements were made in glassmaking and mirror production. Islamic scholars and artisans in the Middle East developed new techniques and refined the process of creating glass mirrors.
One of the key innovations was the use of molten glass and molten metal to create the reflective surface. Instead of coating the back of a glass sheet, the metal was mixed with the molten glass, resulting in a smoother and more uniform reflective surface.
During the 11th century, the city of Venice became a prominent center for glassmaking and mirror production. The Venetian glassmakers, known as the Murano glassmakers, perfected the art of making high-quality glass mirrors. They were able to produce mirrors with greater clarity and accuracy, thanks to their expertise in glassmaking and the availability of high-quality materials.
The invention and popularity of glass mirrors gradually spread throughout Europe, and by the 16th century, glass mirrors became more accessible to the general population. The production process became more streamlined, and advances in glass technology allowed for the creation of larger mirrors.
One of the key advancements in glass mirror production during this time was the introduction of a metallic backing. Instead of mixing the metal with the molten glass, a thin layer of metal, usually silver or aluminum, was applied to the back of the glass. This method provided a highly reflective surface while maintaining the desired clarity and durability.
With the availability of glass mirrors, people could now obtain clearer and more accurate reflections of themselves. This had a profound impact on society, influencing self-perception, fashion, and personal grooming. Mirrors became an essential fixture in homes, palaces, and public spaces, reflecting the growing importance of self-image and vanity.
Today, glass mirrors are ubiquitous and come in various shapes, sizes, and designs. The advancements in mirror technology continue, with the introduction of features such as anti-reflective coatings, LED lighting, and smart mirrors with integrated technology.
The invention of glass mirrors was a pivotal moment in our history, enabling us to see ourselves more clearly and examine the finer details of our appearance. From humble beginnings of natural reflections to the sophisticated glass mirrors we have today, these reflective surfaces have become an integral part of our lives.
The earliest known manufactured mirrors date back to around 6000 BC in modern-day Turkey. These were made from polished obsidian, a naturally occurring volcanic glass.
Read more: When Were Rugs Invented
Mirrors in the Medieval Period
The medieval period saw continued advancements in mirror technology and the increasing prevalence of mirrors as both functional and decorative objects. During this time, mirrors played a significant role in the lives of individuals, households, and the ruling elite.
In the early medieval period, mirrors were still primarily made of polished metal or polished stone. These mirrors were often small and portable, allowing individuals to carry them for personal grooming and self-reflection. The reflective surface was usually made of bronze or copper, which provided a reasonably clear reflection but with some distortion.
Mirrors during the medieval period were not only practical objects but also symbols of wealth and status. They were often adorned with intricate designs, engraved patterns, and gemstone embellishments. The frames surrounding the mirrors became works of art themselves, showcasing the craftsmanship of the time.
The demand for mirrors grew among the medieval nobility, who used these reflective surfaces to display their wealth and sophistication. Mirrors became prominent fixtures in noble households and palaces, placed in prominent locations such as dressing rooms and reception halls.
With the rise of trade and commerce during the medieval period, mirrors became more accessible to the general population. The production techniques for mirrors improved, and artisans experimented with different materials to achieve clearer reflections.
One notable advancement in mirror production during this time was the use of polished metal plates with a thin layer of mercury applied to the surface. This mercury backing provided a highly reflective and clear image, surpassing the quality of earlier mirrors. However, mercury was toxic, and its use in mirror production posed health risks to the artisans involved.
As the medieval period progressed, glass mirrors with silver or gold backing became more prevalent. Glass mirrors offered improved clarity and consistency in reflection. These mirrors were often larger in size and mounted on walls or placed on stands. They became essential items in the chambers of noblewomen, allowing them to admire and perfect their appearances.
The presence of mirrors in medieval society extended beyond personal grooming. Mirrors held symbolic and religious meanings as well. In Christian religious artwork, mirrors were often depicted as symbols of vanity and temptation. Reflective surfaces were associated with the feminine, representing the duality of physical beauty and inward reflection.
The medieval period laid the groundwork for the continued development and refinement of mirror technology. The desire for clearer reflections and more refined mirror designs pushed artisans and craftsmen to innovate and experiment, paving the way for the artistic and technological advancements that awaited in the Renaissance period.
Mirrors in the Renaissance
The Renaissance period brought about a renewed focus on art, culture, and scientific progress. Mirrors played a prominent role during this time, both as functional objects and as symbols of status and sophistication. The advancements in mirror production and design during the Renaissance significantly shaped the way mirrors were perceived and used.
One of the most significant advancements in mirror technology during the Renaissance was the improvement of glass quality. Glassmakers refined their techniques, producing higher quality and clearer glass sheets that could be used for mirrors. This improvement in glass quality led to mirrors with fewer imperfections and a more accurate reflection.
Mirror frames during the Renaissance became works of art themselves. Craftsmen excelled in creating intricately carved and embellished frames, adding decorative elements such as motifs, symbols, and ornate details. These frames elevated the status of mirrors, turning them into focal points in lavish chambers and palaces.
The use of mirrors in the Renaissance expanded beyond personal grooming and self-reflection. They became integral in artistic and scientific endeavors. Artists, such as Jan van Eyck and Diego Velázquez, incorporated mirrors into their paintings to explore the concept of perspective and capture intricate details. Mirrors were used to create mesmerizing self-portraits and reflect the surrounding environment.
In addition to their artistic significance, mirrors played a crucial role in the scientific advancements of the Renaissance. Scholars and scientists, such as Leonardo da Vinci and Galileo Galilei, used mirrors to study optics and the behavior of light. They devised experiments and optical instruments that utilized mirrors to reflect and manipulate light, advancing our understanding of optics and paving the way for future discoveries.
The prominence of mirrors during the Renaissance extended beyond the elite and noble classes. With advancements in mirror production and increased trade, mirrors became more accessible to the emerging middle class. They were seen as symbols of refinement and prosperity, displayed in the homes of merchants, scholars, and skilled artisans.
The growing popularity of mirrors during the Renaissance also influenced personal grooming and fashion. Mirrors aided individuals in perfecting their appearance, allowing them to scrutinize their clothing, hairstyles, and facial features. The desire for self-improvement and physical beauty became intertwined with the use of mirrors.
Renaissance mirrors were often placed strategically within rooms to maximize natural light and create a sense of spaciousness. Mirrors became focal points, reflecting light and drawing attention to the opulence and grandeur of the surroundings. They were positioned in entryways, hallways, and chambers to create an illusion of depth and enhance the overall aesthetic of the space.
The Renaissance period marked a significant turning point in mirror history. The combination of technological advancements, artistic creativity, and scientific inquiry led to the production of mirrors that were not only functional but also exquisite works of art. Mirrors became a reflection of the cultural and intellectual achievements of the time, forever leaving their mark on history and our perception of beauty.
Modern Mirror Development
From the Renaissance to the present day, mirrors have continued to evolve and adapt to the changing needs and advancements in technology. The modern era has witnessed significant developments in mirror production, materials, and functionality.
One of the notable advancements in modern mirror development is the use of silver or aluminum coatings on glass surfaces. This technique, known as silvering, involves applying a thin layer of metal to the back of the glass. The metal coating enhances the reflectivity and clarity of the mirror, creating a more accurate and distortion-free reflection.
Advancements in glass manufacturing have also contributed to the production of high-quality mirrors. Float glass, a technique introduced in the mid-20th century, involves pouring molten glass onto a bed of molten metal, resulting in a perfectly flat and uniform glass surface. This process revolutionized mirror production, allowing for the creation of larger, clearer, and more durable mirrors.
Modern mirrors come in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and designs to suit various aesthetic preferences and functional needs. Wall-mounted mirrors, floor mirrors, vanity mirrors, and even portable handheld mirrors have become staple pieces in households, offices, and public spaces.
Technological advancements have led to the development of innovative mirror features. Anti-reflective coatings are applied to the front surface of mirrors, reducing glare and improving the clarity of the reflection. LED lighting integrated into mirrors has become popular, providing enhanced visibility and adding a stylish touch to bathroom and vanity mirrors.
Smart mirrors have emerged as a product of the digital age. These mirrors are equipped with built-in screens and connectivity, allowing users to access information, check the weather, and even control other smart devices through voice commands or touch controls. Smart mirrors have found applications in homes, gyms, and retail settings.
While functionality and technology have advanced, mirrors continue to serve a fundamental purpose in our daily lives. They enable self-reflection, aid in personal grooming, and contribute to our sense of self-esteem and confidence. Mirrors have also retained their decorative value, adding depth, light, and a touch of elegance to interior spaces.
The future of mirror development holds exciting possibilities. Researchers are exploring new materials and technologies, such as nano-coatings and electrochromic films, to create mirrors that can adapt and change their reflectivity or transform into dynamic displays.
The evolution of mirrors over centuries highlights the innate human desire for self-reflection, improvement, and visual beauty. As technology continues to advance, mirrors will continue to play an essential role in our lives, reflecting not only our physical appearances but also our ever-changing aspirations and aspirations.
Conclusion
The invention and evolution of mirrors have had a profound impact on human civilization. From the early observations of reflections in natural surfaces to the polished stones, metals, and ultimately the glass mirrors we have today, this humble object has transformed the way we see ourselves and the world around us.
Throughout history, mirrors have served practical, aesthetic, and symbolic purposes. They have been coveted as status symbols, used in art and science, and become essential items in our daily routines. The development of mirror technology has been driven by the quest for clearer, more accurate reflections, and advances in materials and manufacturing processes have made mirrors more accessible to people from all walks of life.
The medieval period saw the refinement of metal and polished stone mirrors, while the Renaissance introduced intricate frame designs and the integration of mirrors into art and science. The invention of glass mirrors during the Islamic Golden Age and their subsequent advancements during the Roman and Venetian times paved the way for the modern mirrors we have today.
In the modern era, mirrors continue to adapt to our changing needs and technological advancements. With features like silver or aluminum coatings, anti-reflective treatments, LED lighting, and smart functionalities, mirrors have become more versatile and personalized. They not only serve practical purposes but also enhance the visual appeal and functionality of our living spaces.
Ultimately, mirrors are more than just objects reflecting our appearances. They embody our desires for self-reflection, self-improvement, and visual beauty. Mirrors have become a reflection of our culture, our aspirations, and our ever-evolving understanding of ourselves.
As we move forward, it is exciting to imagine the future of mirror technology. With ongoing research into new materials, coatings, and interactive capabilities, we can expect mirrors to continue to evolve and transform our experiences. The journey of mirrors is a testament to human curiosity, innovation, and the desire to see ourselves with greater clarity and insight.
In conclusion, mirrors have come a long way from their humble beginnings. They have transcended their functional purpose to become cultural artifacts, artistic elements, and technological marvels. As we gaze into the reflection they provide, we are reminded of our shared humanity and the never-ending quest to better understand and appreciate ourselves.
Frequently Asked Questions about When Were Mirrors Created
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “When Were Mirrors Created”