Home>Gardening & Outdoor>Landscaping Ideas>How To Treat Grass Tetany


Landscaping Ideas
How To Treat Grass Tetany
Modified: February 18, 2024
Learn effective landscaping ideas to prevent and treat grass tetany. Discover expert tips for maintaining healthy grass and preventing nutrient deficiencies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
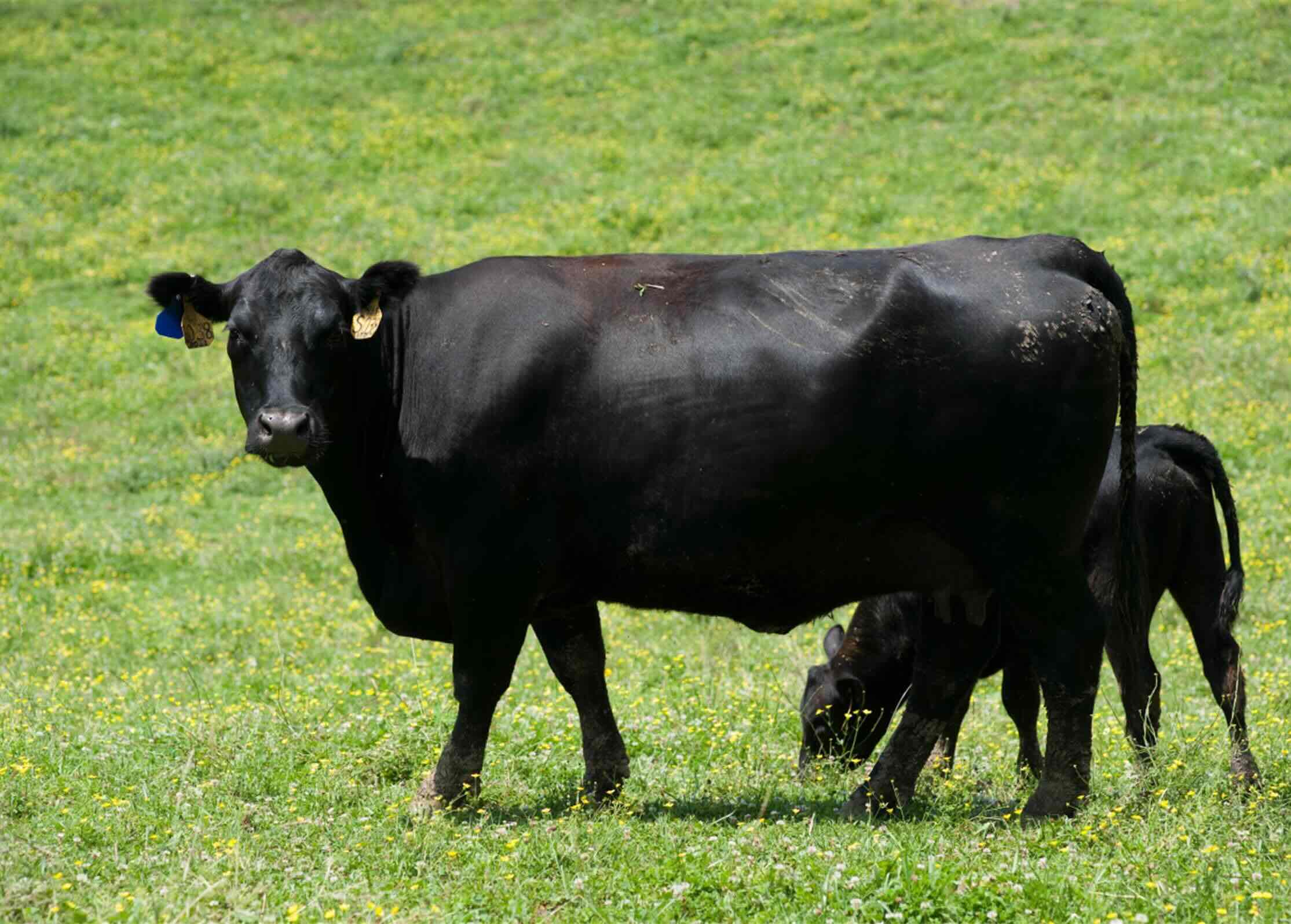
Grass tetany, also known as grass staggers or hypomagnesemia, is a serious and potentially fatal metabolic disorder that affects grazing livestock, particularly cattle. This condition arises when there is a deficiency of magnesium in the animal's bloodstream, leading to a range of distressing symptoms. As a livestock owner or caretaker, it is crucial to understand the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of grass tetany to safeguard the well-being of your animals.
Grass tetany typically occurs in early spring when animals are grazing on lush, rapidly growing forage. During this period, the magnesium levels in the forage can plummet, creating an imbalance in the animals' diets. This imbalance, coupled with other factors such as low potassium and high nitrogen levels, can contribute to the onset of grass tetany.
As a livestock owner, it is essential to be proactive in recognizing the risk factors associated with grass tetany. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of this condition, you can take preemptive measures to protect your animals from its debilitating effects. This includes implementing effective management practices and nutritional strategies to mitigate the likelihood of grass tetany occurring within your herd.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of grass tetany, exploring its symptoms, preventative measures, and treatment options. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you will be better prepared to identify and address grass tetany, ultimately ensuring the health and vitality of your livestock.
Key Takeaways:
- Grass tetany, a serious condition in grazing livestock, is caused by magnesium deficiency. Proactive measures like balanced nutrition and weather monitoring can prevent it, ensuring the health of animals.
- Recognizing symptoms like muscle tremors and providing oral magnesium supplements are crucial for treating grass tetany. Collaborating with veterinarians and adjusting forage can aid in the recovery of affected animals.
Read more: What Causes Grass Tetany
Understanding Grass Tetany
Grass tetany, also referred to as grass staggers or hypomagnesemia, is a metabolic disorder that commonly affects grazing livestock, particularly cattle. This condition arises due to a deficiency of magnesium in the animal's bloodstream, leading to a range of distressing symptoms. Magnesium plays a crucial role in various physiological functions within the animal's body, including nerve and muscle function. When magnesium levels become critically low, it can result in severe health implications for the affected animals.
The onset of grass tetany is often associated with the consumption of lush, rapidly growing forage, typically during the early spring months. During this period, the magnesium levels in the forage can plummet, creating an imbalance in the animals' diets. Additionally, other factors such as low potassium and high nitrogen levels in the forage can exacerbate the risk of grass tetany. These conditions collectively contribute to the increased susceptibility of grazing livestock to this metabolic disorder.
Furthermore, certain environmental and management factors can also influence the likelihood of grass tetany occurring. For instance, adverse weather conditions, such as cold and wet weather, can impede the animal's ability to absorb magnesium from the forage, further exacerbating the risk of deficiency. Additionally, factors such as poor soil fertility, imbalanced mineral supplementation, and inadequate grazing management practices can contribute to the prevalence of grass tetany within a herd.
It is important to recognize that grass tetany can have detrimental effects on the overall health and productivity of the affected animals. The manifestation of this condition can lead to a range of symptoms, including muscle tremors, incoordination, staggering gait, and in severe cases, convulsions and death. Therefore, understanding the underlying causes and risk factors associated with grass tetany is paramount for livestock owners and caretakers to effectively safeguard the well-being of their animals.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of grass tetany, including its triggers and predisposing factors, livestock owners can implement proactive measures to mitigate the risk of this metabolic disorder within their herds. This includes adopting sound nutritional management practices, ensuring adequate magnesium supplementation, and implementing grazing strategies that minimize the likelihood of magnesium deficiency in the animals' diets.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the symptoms, prevention, and treatment of grass tetany, providing valuable insights to empower livestock owners in effectively managing and mitigating the impact of this condition on their herds.
Symptoms of Grass Tetany
The symptoms of grass tetany can manifest rapidly and have a profound impact on the affected animals. It is crucial for livestock owners and caretakers to be vigilant in recognizing these symptoms to facilitate prompt intervention and treatment. The following are common symptoms associated with grass tetany:
-
Muscle Tremors: Affected animals may exhibit involuntary muscle tremors, particularly in the hindquarters and neck region. These tremors are indicative of the neurological disturbances resulting from magnesium deficiency.
-
Incoordination: Animals suffering from grass tetany may display signs of incoordination and an unsteady gait. This lack of coordination can be observed in their movements, reflecting the neurological effects of the condition.
-
Staggering Gait: A notable symptom of grass tetany is the presence of a staggering gait in affected animals. This is characterized by an unsteady and swaying motion as they attempt to move, indicating compromised neuromuscular function.
-
Agitation and Restlessness: Animals experiencing grass tetany may exhibit signs of agitation and restlessness, often pacing or displaying signs of discomfort. This behavior can be attributed to the neurological and physiological distress caused by the condition.
-
Head Pressing: In severe cases, affected animals may engage in head pressing against objects or structures within their environment. This abnormal behavior is indicative of neurological dysfunction and can signal the urgency of intervention.
-
Hyperexcitability: Grass tetany can lead to heightened excitability in affected animals, causing them to display increased sensitivity to stimuli and heightened reactivity.
-
Convulsions: In advanced stages of grass tetany, animals may experience convulsions, characterized by uncontrollable muscle contractions and seizures. This represents a critical stage of the condition and necessitates immediate veterinary attention.
It is imperative for livestock owners to closely monitor their animals for these symptoms, especially during periods of heightened risk, such as early spring when grazing on lush, rapidly growing forage. Early recognition of these signs can facilitate timely intervention and treatment, potentially mitigating the severity of the condition and improving the prognosis for the affected animals. Additionally, proactive measures to prevent grass tetany, such as ensuring adequate magnesium supplementation and implementing balanced nutritional management, can significantly reduce the likelihood of these distressing symptoms manifesting in grazing livestock.
Prevention of Grass Tetany
Preventing grass tetany in grazing livestock is paramount for ensuring their health and well-being. Implementing proactive measures to mitigate the risk of magnesium deficiency and minimize the occurrence of this metabolic disorder is essential for livestock owners and caretakers. The following strategies can significantly contribute to the prevention of grass tetany:
-
Forage Management: Adopting sound forage management practices is crucial in preventing grass tetany. This includes avoiding overgrazing of pastures, particularly during periods of rapid forage growth. Overgrazing can deplete the magnesium content in the forage, increasing the risk of deficiency in grazing animals. Rotational grazing and strategic pasture management can help maintain optimal forage quality and minimize the likelihood of magnesium depletion.
-
Mineral Supplementation: Providing adequate mineral supplementation, particularly magnesium, is vital for preventing grass tetany. Offering free-choice mineral supplements specifically formulated to address magnesium deficiency can help ensure that grazing animals receive the necessary dietary magnesium to meet their physiological requirements. Additionally, incorporating mineral supplements into the animals' feed or water sources can facilitate consistent intake, reducing the risk of deficiency.
-
Balanced Nutrition: Ensuring a balanced and nutritionally adequate diet for grazing livestock is essential for preventing grass tetany. This includes formulating diets that encompass the appropriate ratio of magnesium to other minerals, such as calcium and potassium. Balancing the overall mineral composition of the animals' diet can help mitigate the risk of magnesium imbalance and deficiency, thereby reducing the likelihood of grass tetany.
-
Soil Testing and Fertilization: Conducting regular soil testing to assess the mineral composition of grazing pastures is instrumental in preventing grass tetany. Understanding the magnesium levels in the soil can guide targeted fertilization practices to optimize forage quality and mineral content. Applying magnesium-rich fertilizers or lime to deficient soils can enhance the magnesium availability in the forage, contributing to the prevention of grass tetany.
-
Weather Monitoring: Monitoring weather conditions, particularly during periods of heightened risk, such as early spring, is crucial for preventing grass tetany. Cold and wet weather can impede magnesium absorption in grazing animals, increasing their susceptibility to deficiency. Implementing protective measures, such as providing shelter or supplemental feed during adverse weather, can help mitigate the impact of environmental factors on magnesium intake and utilization.
By diligently implementing these preventative strategies, livestock owners can effectively minimize the risk of grass tetany in grazing animals, promoting their overall health and productivity. Proactive management practices, coupled with a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing magnesium availability and utilization, are instrumental in safeguarding animals from the debilitating effects of this metabolic disorder.
Treatment of Grass Tetany
Effective treatment of grass tetany is essential for mitigating the detrimental effects of this metabolic disorder on affected livestock. When confronted with cases of grass tetany, prompt intervention and targeted therapeutic measures are crucial in addressing the underlying magnesium deficiency and alleviating the distressing symptoms exhibited by the animals.
Read more: How To Treat Grass Burn On Skin
Intravenous Magnesium Administration
In severe cases of grass tetany, where animals display pronounced neurological symptoms and signs of magnesium deficiency, intravenous administration of magnesium sulfate is often employed as a primary treatment approach. This method allows for rapid and direct supplementation of magnesium, effectively elevating the depleted magnesium levels in the bloodstream and restoring neurological function. Veterinary professionals are adept at administering intravenous magnesium in a controlled manner, ensuring the safety and efficacy of the treatment.
Oral Magnesium Supplementation
Supplementing affected animals with oral magnesium formulations is a fundamental component of grass tetany treatment. This approach aims to sustainably elevate and maintain magnesium levels in the animals' bodies, addressing the underlying deficiency. Oral magnesium supplements, such as magnesium oxide or magnesium chloride, can be incorporated into the animals' feed or water sources to facilitate consistent intake. Additionally, providing free-choice mineral supplements containing adequate levels of magnesium enables grazing animals to actively regulate their magnesium consumption, supporting their recovery from grass tetany.
Veterinary Monitoring and Support
Close veterinary monitoring and support are integral throughout the treatment process for grass tetany. Veterinary professionals play a pivotal role in assessing the animals' response to treatment, monitoring their neurological status, and adjusting therapeutic interventions as necessary. Furthermore, veterinarians provide valuable guidance on nutritional management, ensuring that the animals receive a balanced diet that meets their magnesium requirements. Collaborating closely with veterinarians facilitates comprehensive care for affected livestock, optimizing their recovery from grass tetany.
Nutritional Management and Forage Adjustment
Incorporating strategic nutritional management practices is essential for the long-term treatment and prevention of grass tetany. Balancing the mineral composition of the animals' diet, particularly the magnesium, calcium, and potassium ratios, is crucial for addressing underlying deficiencies and minimizing the risk of recurrence. Additionally, adjusting the grazing regimen and forage selection to prioritize magnesium-rich forage can contribute to sustained magnesium intake, supporting the animals' recovery and reducing the likelihood of future episodes of grass tetany.
By implementing these targeted treatment strategies and collaborating closely with veterinary professionals, livestock owners can effectively address grass tetany in affected animals, promoting their recovery and well-being. Furthermore, integrating these treatment approaches with proactive preventative measures can significantly reduce the incidence of grass tetany, safeguarding the overall health and productivity of grazing livestock.
Ensure your livestock have access to high-magnesium mineral supplements and avoid grazing them on lush, rapidly growing pastures to prevent grass tetany.
Read more: How To Treat Weeds In Bermuda Grass
Conclusion
In conclusion, grass tetany poses a significant risk to grazing livestock, particularly during periods of rapid forage growth and environmental conditions that contribute to magnesium deficiency. Understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of this metabolic disorder is paramount for livestock owners and caretakers in safeguarding the health and well-being of their animals.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of grass tetany, including its triggers and predisposing factors, livestock owners can proactively implement measures to mitigate the risk of this condition within their herds. Sound nutritional management practices, balanced mineral supplementation, and strategic forage management play pivotal roles in preventing grass tetany and promoting the overall health of grazing livestock.
Recognizing the symptoms of grass tetany and promptly intervening with targeted treatment approaches, such as intravenous magnesium administration and oral supplementation, is essential for addressing magnesium deficiency and alleviating the distressing neurological symptoms exhibited by affected animals. Collaborating closely with veterinary professionals and implementing tailored nutritional management strategies are integral components of the treatment process, supporting the animals' recovery and minimizing the risk of recurrence.
Furthermore, the integration of preventative measures, such as soil testing, weather monitoring, and balanced nutrition, contributes to sustained mitigation of the risk factors associated with grass tetany. By adopting a holistic approach that encompasses both prevention and treatment, livestock owners can effectively safeguard their animals from the debilitating effects of this metabolic disorder.
Ultimately, the proactive management of grass tetany is essential for promoting the overall health, productivity, and welfare of grazing livestock. Through a combination of informed decision-making, vigilant monitoring, and collaborative veterinary care, livestock owners can mitigate the impact of grass tetany and ensure the vitality of their herds. By prioritizing the implementation of preventative and treatment strategies, livestock owners play a pivotal role in safeguarding their animals from the detrimental effects of grass tetany, fostering a thriving and resilient livestock community.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Treat Grass Tetany
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Treat Grass Tetany”