Home>Home Appliances>Kitchen Appliances>What Is The Difference Between A Dehydrator And A Freeze Dryer

Kitchen Appliances
What Is The Difference Between A Dehydrator And A Freeze Dryer
Modified: January 19, 2024
Discover the distinctions between a dehydrator and a freeze dryer for kitchen appliances. Learn which one suits your needs best.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of food preservation, where the age-old art of keeping food fresh meets cutting-edge technology. In this article, we will explore the fascinating realm of kitchen appliances, specifically focusing on the difference between a dehydrator and a freeze dryer. These appliances play a crucial role in extending the shelf life of various food items, allowing us to enjoy the flavors and nutrients of fruits, vegetables, meats, and more long after their harvest or purchase.
Understanding the mechanics and distinctions between these two devices is essential for anyone interested in food preservation, whether for personal use, culinary endeavors, or commercial purposes. By delving into the inner workings of dehydrators and freeze dryers, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the science behind food preservation and the unique benefits each method offers.
So, join us on this enlightening journey as we unravel the mysteries of dehydration and freeze drying, uncovering the practical applications and advantages of these innovative appliances. By the end of this exploration, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how these technologies differ and how they can be utilized to elevate your culinary experiences and ensure food longevity.
Key Takeaways:
- Dehydrators use heat to dry food, great for making healthy snacks and preserving seasonal produce. They’re affordable and easy to use, perfect for home cooks and health-conscious individuals.
- Freeze dryers use sublimation to preserve food, retaining original textures and flavors. Ideal for emergency supplies, gourmet cooking, and scientific research due to their long shelf life and lightweight nature.
Purpose of Food Preservation
Food preservation has been a fundamental practice throughout human history, driven by the need to store food for extended periods without sacrificing its nutritional value or succumbing to spoilage. The primary purpose of food preservation is to prevent the growth of microorganisms, such as bacteria, yeast, and mold, which can lead to food spoilage and pose health risks.
Another key objective of food preservation is to retain the sensory qualities of food, including taste, texture, and aroma. By preserving these attributes, we can enjoy a diverse range of foods regardless of seasonal availability, geographic location, or perishability. Additionally, food preservation helps reduce food waste by extending the shelf life of perishable items, contributing to sustainable consumption and resource management.
Preserving food also serves as a means of food security, especially in regions where access to fresh produce may be limited due to environmental factors or logistical challenges. By employing various preservation methods, communities can stockpile food supplies to withstand periods of scarcity or unforeseen circumstances, ensuring a consistent food source for sustenance.
Furthermore, food preservation plays a vital role in culinary arts and food production, enabling the creation of unique flavors, ingredients, and culinary masterpieces. Chefs and food enthusiasts alike leverage preservation techniques to craft artisanal products, experiment with flavor profiles, and elevate the gastronomic experience.
Overall, the purpose of food preservation encompasses safeguarding food quality, enhancing culinary creativity, minimizing waste, and promoting food security. Dehydrators and freeze dryers are instrumental in achieving these goals, offering distinct methods of preserving food with their own set of advantages and applications.
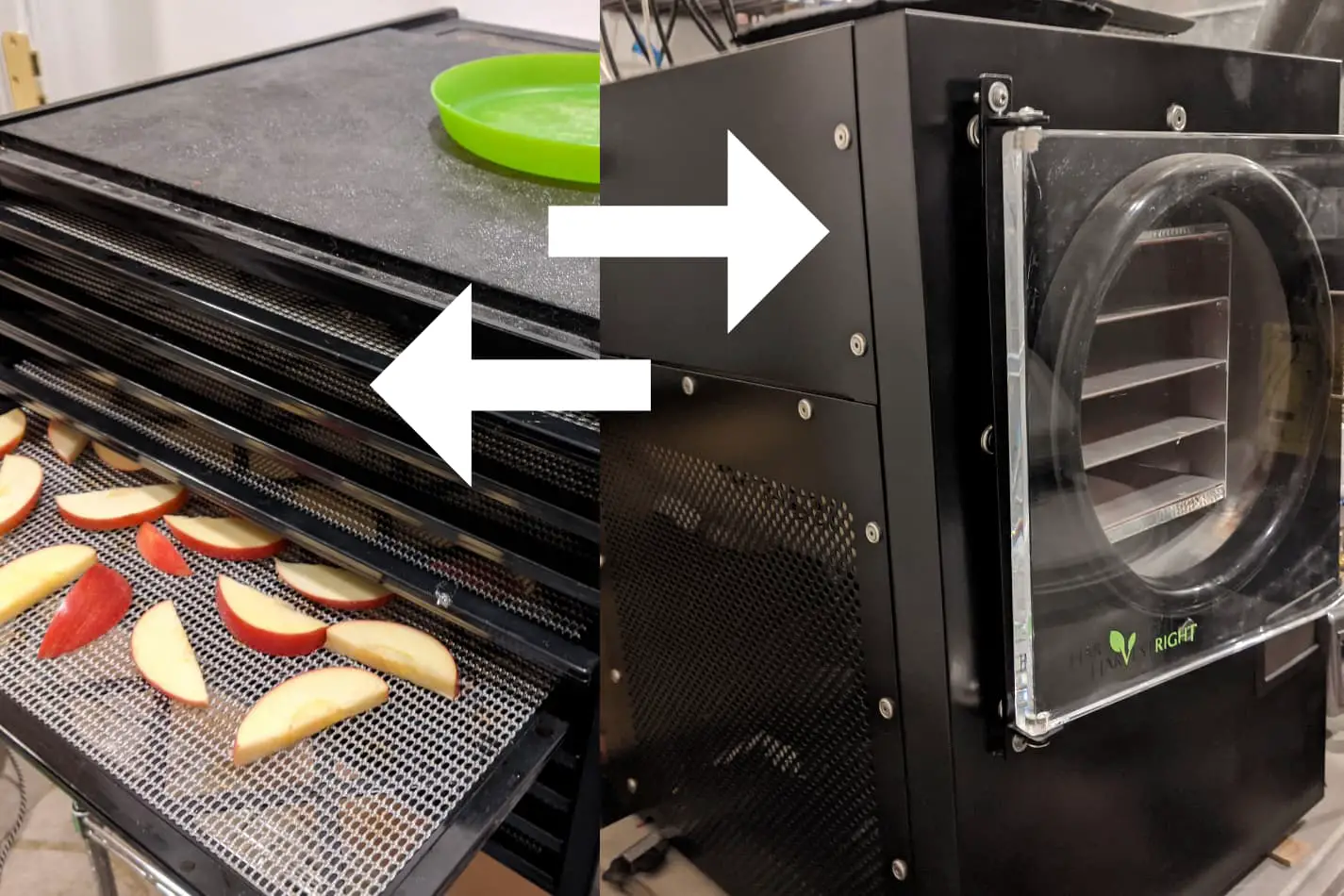
Dehydrator: How It Works
A dehydrator is a versatile kitchen appliance designed to remove moisture from various foods, thereby preserving them for long-term storage. The process of dehydration involves circulating warm air over the food, gradually reducing its moisture content without cooking it. This gentle and controlled dehydration process helps retain the nutritional integrity and flavor of the food while inhibiting the growth of spoilage-causing microorganisms.
Dehydrators typically consist of a series of trays or shelves, allowing for ample space to arrange fruits, vegetables, meats, herbs, and even prepared snacks like jerky or fruit leather. The appliance houses a heating element and a fan, which work in tandem to facilitate the dehydration process. As the heating element warms the air inside the dehydrator, the fan distributes the heated air evenly across the trays, ensuring consistent drying throughout the entire batch of food.
One of the key principles behind dehydration is the concept of moisture evaporation. As the warm air circulates around the food, it absorbs the moisture present in the food items, carrying it away and effectively drying the food. This controlled removal of moisture inhibits the proliferation of bacteria and molds, thereby extending the shelf life of the dehydrated products.
Dehydrators offer a convenient and efficient means of preserving seasonal produce, allowing individuals to enjoy the flavors of ripe fruits and vegetables year-round. Additionally, the dehydration process intensifies the natural sweetness and flavors of many fruits, making them ideal for snacking, baking, or incorporating into various culinary creations.
Moreover, dehydrators are popular among health-conscious individuals seeking to create their own nutritious snacks, such as kale chips, dried fruits, and vegetable crisps, without the additives and preservatives often found in store-bought equivalents. The simplicity and versatility of dehydrators make them a valuable addition to any kitchen, empowering individuals to embrace food preservation and culinary exploration.
Freeze Dryer: How It Works
A freeze dryer, also known as a lyophilizer, is a sophisticated appliance that employs advanced technology to remove moisture from food products. Unlike traditional dehydrators, which use heat to evaporate moisture, freeze dryers operate under a unique principle known as sublimation. Sublimation is the process of converting a substance directly from a solid to a gas without passing through the intermediate liquid state.
The freeze-drying process begins by placing the food items in a freezing chamber within the appliance. The temperature is then lowered significantly, causing the water content in the food to freeze. Once frozen, the freeze dryer creates a vacuum environment, effectively reducing the surrounding air pressure. This low-pressure environment allows for the sublimation of the frozen water within the food, transforming it from ice directly into vapor without undergoing the liquid phase.
As the frozen water sublimates, it is captured by the freeze dryer’s condenser, which converts the vapor back into a solid state, effectively removing it from the food. This process results in the preservation of the food’s cellular structure, texture, and nutritional content, as the gentle sublimation process minimizes damage to the food’s delicate components.
One of the remarkable advantages of freeze drying is its ability to preserve the original shape, color, and flavor of the food, offering a high-quality end product that closely resembles its fresh counterpart. Additionally, freeze-dried foods boast an exceptionally long shelf life, making them ideal for emergency food supplies, backpacking provisions, and space missions due to their lightweight and durable nature.
Freeze dryers are widely utilized in commercial food production, pharmaceuticals, and scientific research, where the preservation of delicate substances and biological materials is paramount. In the realm of culinary arts, freeze-dried ingredients are prized for their convenience and versatility, as they can be rehydrated quickly and used in a variety of recipes, from soups and stews to desserts and garnishes.
While freeze dryers are more complex and expensive than dehydrators, their ability to retain the original qualities of food and produce shelf-stable, lightweight products has positioned them as a valuable asset in various industries and culinary pursuits.
Key Differences
While both dehydrators and freeze dryers serve the purpose of preserving food, they employ distinct methods and offer unique benefits. Understanding the key differences between these appliances is essential for determining the most suitable preservation method for specific foods and desired outcomes.
Dehydration vs. Sublimation:
One of the fundamental distinctions between dehydrators and freeze dryers lies in the mechanisms they utilize to remove moisture from food. Dehydrators rely on the application of heat to evaporate water from the food items, while freeze dryers harness the process of sublimation, which involves freezing the moisture and then converting it directly into vapor without transitioning through the liquid phase.
Texture and Nutrient Retention:
Freeze drying excels in preserving the original texture, color, and nutritional content of food, as the sublimation process is gentle and minimizes structural damage. In contrast, dehydrated foods may undergo textural changes and some nutrient loss due to the application of heat during the dehydration process.
Shelf Life and Rehydration:
Freeze-dried foods typically have a longer shelf life compared to dehydrated foods, as the sublimation process effectively eliminates moisture, inhibiting the growth of spoilage-causing microorganisms. Additionally, freeze-dried products rehydrate more rapidly and retain their original form when exposed to moisture, making them convenient for quick meal preparation and on-the-go consumption.
Complexity and Cost:
Dehydrators are generally more affordable and straightforward to use, making them accessible to a wide range of consumers seeking to preserve fruits, vegetables, and meats. On the other hand, freeze dryers are more complex and expensive, often found in commercial settings, scientific laboratories, and specialized culinary environments due to their advanced technology and precise control over the preservation process.
Applications and Culinary Versatility:
Both dehydrators and freeze dryers offer diverse applications in the culinary world, but their unique attributes cater to different needs. Dehydrators are well-suited for creating snacks, spices, and ingredients for cooking and baking, while freeze dryers excel in producing lightweight, shelf-stable ingredients for backpacking, emergency supplies, and gourmet culinary creations.
By recognizing these key differences, individuals can make informed decisions regarding the most suitable method for preserving specific foods based on factors such as texture retention, shelf life requirements, and intended culinary applications.
Applications
The versatile nature of dehydrators and freeze dryers lends itself to a wide array of practical applications, ranging from culinary endeavors to emergency preparedness and beyond. Understanding the distinct uses and benefits of these preservation methods is essential for leveraging their potential in various contexts.
Dehydrator Applications:
-
Creating Nutritious Snacks: Dehydrators are ideal for producing an assortment of healthy snacks, including dried fruits, vegetable chips, and jerky. These homemade snacks offer a nutritious alternative to store-bought options, free from additives and preservatives.
-
Preserving Seasonal Produce: Dehydrators enable individuals to extend the shelf life of seasonal fruits and vegetables, allowing for year-round enjoyment of fresh flavors and nutrients. Dried produce can be incorporated into recipes, trail mixes, and granolas.
-
Culinary Ingredient Preparation: Herbs, spices, and aromatics can be dried using a dehydrator, preserving their flavors for use in cooking and baking. Dried ingredients contribute to the creation of homemade spice blends and infused oils.
-
Long-Term Food Storage: Dehydrated foods can be stored for extended periods, making them valuable additions to emergency food supplies and camping provisions. Their lightweight and durable nature make them convenient for outdoor adventures.
Freeze Dryer Applications:
-
Emergency Food Supplies: Freeze-dried foods have a significantly longer shelf life compared to dehydrated products, making them essential for emergency preparedness kits and long-term food storage. Their lightweight and compact nature facilitate convenient storage and transportation.
-
Culinary Innovation: Chefs and culinary enthusiasts utilize freeze-dried ingredients to elevate their creations, as freeze-drying preserves the original textures and flavors of food. Rehydrated ingredients can be used in gourmet dishes, desserts, and molecular gastronomy.
-
Backpacking and Travel Provisions: The lightweight and shelf-stable nature of freeze-dried foods makes them popular choices for backpackers, hikers, and travelers seeking convenient and nutritious meal options. Requiring only water for rehydration, these foods offer practical sustenance on the go.
-
Scientific and Pharmaceutical Applications: Freeze dryers are indispensable in scientific research, pharmaceutical production, and the preservation of biological materials, including vaccines, enzymes, and laboratory samples. The precise control over the sublimation process ensures the integrity of sensitive substances.
By harnessing the capabilities of dehydrators and freeze dryers, individuals and industries alike can explore a myriad of applications, from culinary creativity and sustainable food practices to emergency preparedness and scientific advancements.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of dehydrators and freeze dryers, we have gained valuable insights into the distinct methods and applications of these food preservation appliances. Both dehydrators and freeze dryers play pivotal roles in extending the shelf life of various food items, offering unique benefits and applications that cater to diverse needs and preferences.
Dehydrators, with their straightforward operation and affordability, are well-suited for preserving seasonal produce, creating nutritious snacks, and preparing culinary ingredients. Their accessibility makes them an indispensable tool for home cooks, health-conscious individuals, and anyone seeking to minimize food waste while enjoying the flavors of fresh produce year-round.
On the other hand, freeze dryers, with their advanced sublimation technology and exceptional preservation capabilities, excel in producing lightweight, shelf-stable foods with prolonged shelf lives. Their applications extend to emergency preparedness, gourmet culinary pursuits, scientific research, and pharmaceutical production, where the retention of original textures and flavors is paramount.
By recognizing the key differences and applications of dehydrators and freeze dryers, individuals can make informed decisions regarding the most suitable method for preserving specific foods based on factors such as texture retention, shelf life requirements, and intended culinary applications. Whether it’s crafting homemade snacks, stocking emergency provisions, or innovating in the culinary arts, these preservation methods empower individuals to embrace sustainable food practices and culinary creativity.
As we continue to appreciate the art and science of food preservation, the utilization of dehydrators and freeze dryers underscores the enduring human quest to savor the bounties of nature, minimize waste, and adapt to changing circumstances. These appliances not only extend the longevity of food but also enrich our culinary experiences, offering a glimpse into the harmonious synergy of tradition and innovation in the realm of food preservation.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Difference Between A Dehydrator And A Freeze Dryer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is The Difference Between A Dehydrator And A Freeze Dryer”