Home>Ideas and Tips>Understanding Home Ventilation: Improving Indoor Air Quality


Ideas and Tips
Understanding Home Ventilation: Improving Indoor Air Quality
Published: September 26, 2024
Learn how proper home ventilation can enhance indoor air quality, reduce health risks, and improve comfort with our comprehensive guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Indoor air quality is a critical aspect of maintaining a healthy and comfortable living environment. Poor indoor air quality can lead to a variety of health issues, ranging from mild irritation to severe respiratory diseases. One of the most effective ways to improve indoor air quality is through proper ventilation. In this article, we will delve into the importance of home ventilation, explore different types of ventilation systems, and provide practical tips on how to enhance indoor air quality.
The Importance of Ventilation
Ventilation is essential for maintaining good indoor air quality. It involves the exchange of indoor air with outdoor air, which helps to dilute and remove airborne pollutants. Without adequate ventilation, indoor air can become stagnant and polluted, leading to a buildup of harmful gases and particles.
Health Risks Associated with Poor Ventilation
Poor ventilation can lead to several health risks, including:
- Build-up of Airborne Pollution: Ventilation helps control the levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and other pollutants that can cause respiratory problems and other health issues.
- High Humidity Levels: Inadequate ventilation can result in high humidity levels, which can foster mold growth and damage building materials.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Poor ventilation can increase the risk of infection from airborne pathogens.
Benefits of Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Indoor Air Quality: By bringing in fresh outdoor air and removing stale indoor air, ventilation systems significantly improve the quality of indoor air.
- Reduced Moisture: Ventilation helps control indoor humidity levels, preventing mold growth and damage to building materials.
- Improved Health: Enhanced ventilation rates have been shown to positively impact respiratory health and overall well-being.
- Energy Efficiency: Proper ventilation can improve energy efficiency by reducing the need for air conditioning and heating systems.
Types of Ventilation Systems
There are several types of ventilation systems that can be used to improve indoor air quality. Each type has its own advantages and is suited for different applications.
Natural Ventilation
Natural ventilation involves opening windows and doors to allow fresh air to enter and stale air to escape. This method is simple and cost-effective but relies on weather conditions.
Advantages:
- Low Cost: Natural ventilation is free and requires no additional equipment.
- Flexibility: It can be used in any type of building.
Disadvantages:
- Weather Dependence: Natural ventilation is effective only when windows and doors can be opened.
- Limited Control: It does not provide consistent air exchange rates.
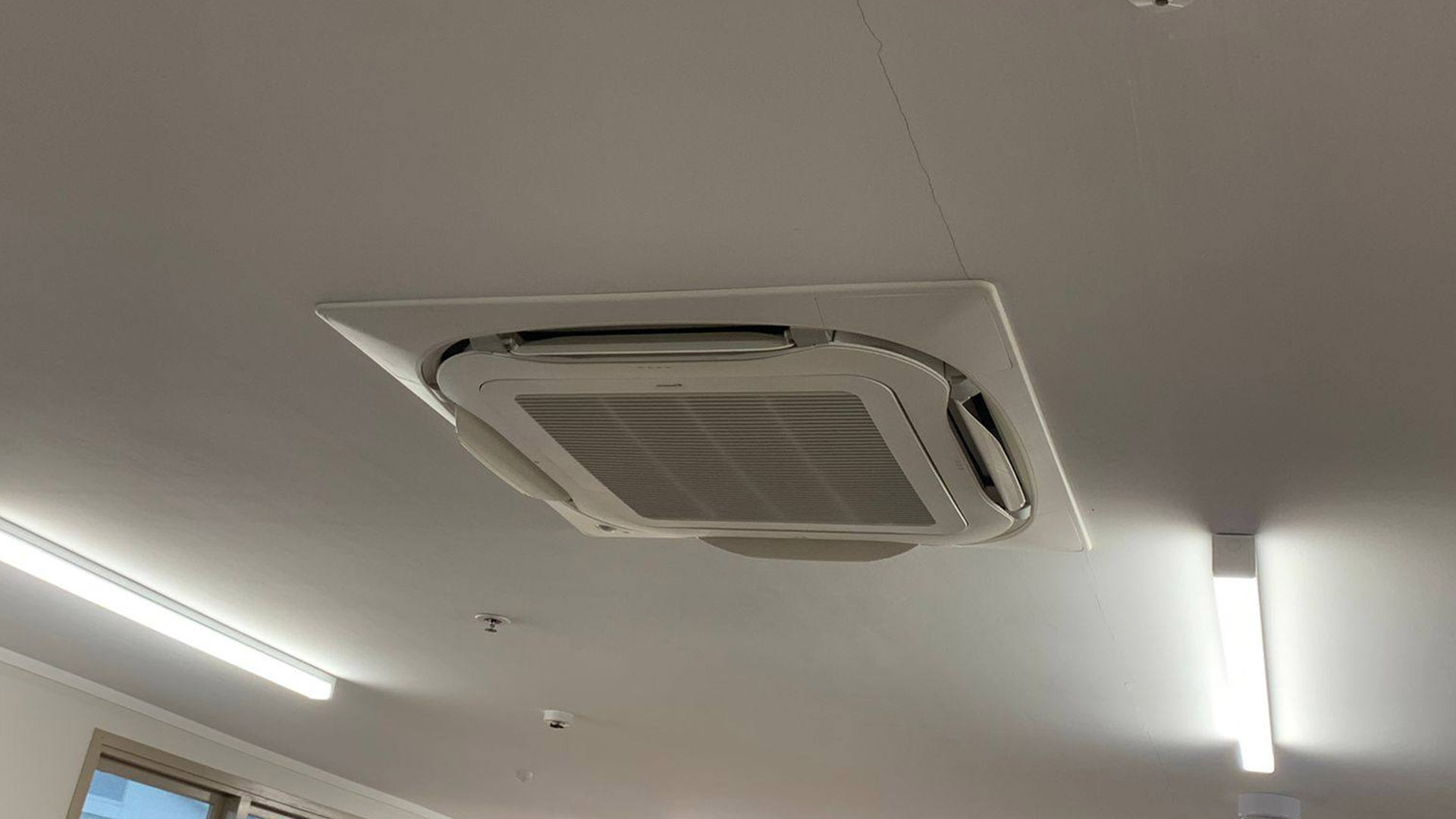
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation systems use fans and ducts to circulate and exchange air. These systems are more efficient than natural ventilation but require installation and maintenance.
Types of Mechanical Ventilation:
-
Spot Ventilation:
- Spot ventilation involves installing fans in specific areas like bathrooms and kitchens. These fans remove humidity and carbon monoxide directly from the source.
- Example: Bathroom fans should be run for about 45 minutes after a shower to remove moisture and prevent mold growth.
-
Dilution Ventilation:
- Dilution ventilation addresses low-level contamination throughout the home by exchanging indoor air with outdoor air.
- Example: Using exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms helps dilute pollutants and maintain a healthy environment.
-
Centralized Ventilation:
- Centralized systems involve a central unit that distributes air throughout the house using ducts.
- Example: HVAC systems can be equipped with filters to remove particulates and allergens from the air.
-
Personalized Ventilation:
- Personalized systems deliver clean air directly to an individual’s breathing space, creating a personal “clean air zone.”
- Example: Real-time sensors in indoor environments enable targeted mitigation measures by monitoring air quality and adjusting ventilation rates accordingly.
Practical Tips for Improving Indoor Air Quality
Improving indoor air quality through ventilation involves both short-term and long-term strategies. Here are some practical tips:
Short-Term Strategies
-
Open Windows and Doors:
- Opening windows and doors for 15 minutes each day can significantly improve ventilation.
- However, it is important to avoid opening windows on days with poor outdoor air quality or when living close to busy highways, ports, airports, or factories with high emissions.
-
Use Exhaust Fans:
- Install exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens to remove moisture and gases from these areas.
- Run fans while bathing and for 30-45 minutes afterward to ensure thorough drying.
-
Fit Kitchen with Exhaust Fan:
- Use an exhaust fan in the kitchen to remove fumes, airborne particles, and moisture from cooking activities.
-
Ceiling Fans:
- Use ceiling fans to improve air flow in the home, preferably with windows open to enhance natural ventilation.
-
Portable Window Fans:
- If you are painting or using hobby supplies that release chemicals indoors, add extra ventilation by opening windows and using portable window fans to pull the air out of the room.
Long-Term Strategies
-
Install Centralized Ventilation System:
- Consider installing a centralized ventilation system that can provide consistent air exchange rates throughout the house.
- Ensure that the system is properly sized to meet the specific needs of your home.
-
Use High-Quality Filters:
- Use filters with a MERV 6-8 rating for HVAC systems to effectively filter particulates and allergens from incoming air.
- Higher MERV levels trap smaller particles but may be more appropriate for homes with high concentrations of mold spores or other allergens.
-
Seal Ducts Properly:
- Ensure that ducts are sealed properly, especially on the return side (the side drawing air into the duct).
- Proper duct sealing is crucial for maintaining efficient air distribution and preventing contamination.
-
Monitor Indoor Air Quality:
- Use real-time sensors to monitor indoor air quality and adjust ventilation rates accordingly.
- This approach allows for targeted mitigation measures based on real-time data.
-
Regular Maintenance:
- Regularly inspect and maintain ventilation systems to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Clean filters regularly and replace them as needed to maintain optimal performance.
Building a New Home? Consider Indoor Air Quality
When building a new home, it is crucial to consider indoor air quality from the outset. Here are some key actions to take:
-
Express Concerns to Architect or Builder:
- Express your concerns about indoor air quality to your architect or builder and enlist their cooperation in taking measures to provide good indoor air quality.
-
Choose Low-Emitting Materials:
- Choose building materials and furnishings that are low-emitting to minimize indoor air pollution.
- For example, use exterior-grade pressed wood products made with phenol-formaldehyde resin in floors, cabinetry, and wall surfaces instead of solid wood products.
-
Install Radon-Resistant Construction Techniques:
- Use radon-resistant construction techniques to prevent radon buildup in your home.
- Obtain a copy of the EPA booklet on radon-resistant construction techniques for more information.
-
Provide Adequate Ventilation:
- Ensure that your home is designed with adequate ventilation in mind.
- The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) recommends a ventilation rate of 0.35 air changes per hour (ach) for new homes.
Conclusion
Improving indoor air quality through proper ventilation is essential for maintaining a healthy living environment. By understanding the different types of ventilation systems available and implementing practical tips for short-term and long-term strategies, homeowners can significantly enhance their indoor air quality. Whether it is through natural ventilation methods or installing centralized mechanical systems, prioritizing home ventilation is crucial for safeguarding health, preventing mold growth, enhancing energy efficiency, and boosting overall comfort.
For more information on improving indoor air quality:
- Visit the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) website for comprehensive guides on indoor air quality.
- Consult resources from organizations like the American Lung Association and the National Center for Healthy Housing (NCHH).
- Refer to industry standards set by ASHRAE for designing and commissioning HVAC systems.
By taking proactive steps towards improving indoor air quality through effective ventilation strategies, you can create a healthier and more comfortable home for yourself and your family.
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.















0 thoughts on “Understanding Home Ventilation: Improving Indoor Air Quality”