

Articles
How Cold Does A Deep Freezer Get
Modified: May 6, 2024
Discover how cold a deep freezer can get in this informative article. Learn about the freezing temperatures and their impact on food storage.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Deep freezers are essential appliances for storing a wide range of perishable items at ultra-low temperatures. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to preserve food or a laboratory technician storing sensitive samples, understanding how cold a deep freezer can get is crucial.
In this article, we will explore the temperature capabilities of deep freezers and the factors that influence their cooling capacity. Additionally, we will provide tips on maintaining optimal freezer temperature and maximizing efficiency.
So, let’s delve into the fascinating world of deep freezers and discover just how cold they can get.
Key Takeaways:
- Deep freezers can reach temperatures as low as -10°C to -40°C (-14°F to -40°F) or even lower, making them ideal for long-term preservation of food, vaccines, drugs, and biological samples.
- Factors such as insulation, sealing, and compressor power influence a deep freezer’s ability to achieve and maintain ultra-low temperatures, while proper maintenance and organization are key to maximizing efficiency and preserving items.
Understanding Deep Freezers
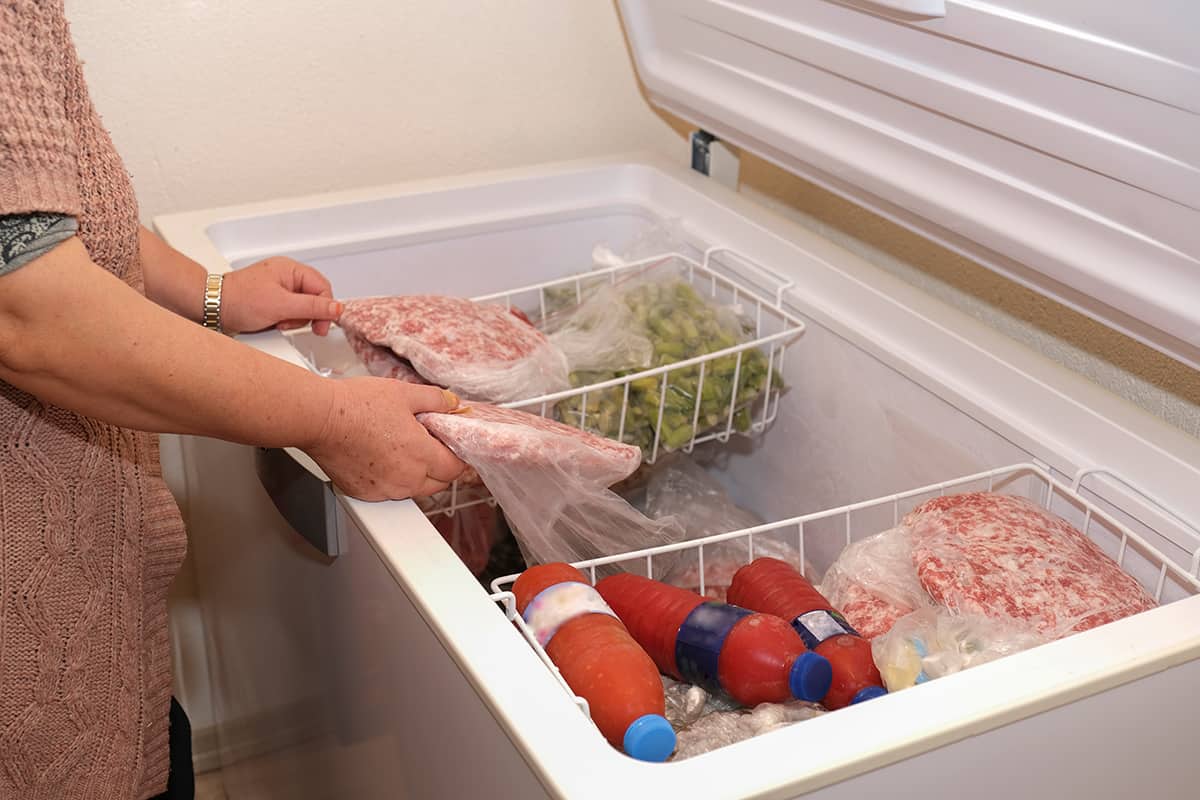
Deep freezers, also known as chest freezers or ultra-low temperature freezers, are specialized appliances designed to maintain temperatures well below freezing point. Unlike regular refrigerators, deep freezers provide a significantly lower temperature range, typically between -10°C to -40°C (-14°F to -40°F) or even lower.
These freezers are commonly used in various settings such as homes, medical facilities, research laboratories, and commercial establishments. They are primarily used for long-term storage of perishable items, including food, vaccines, drugs, biological samples, and laboratory reagents.
Deep freezers are specifically designed to have a larger storage capacity and to maintain consistent sub-zero temperatures. Their construction typically involves thick insulation and airtight seals to prevent heat penetration and maintain a stable internal environment.
It’s important to note that deep freezers come in different sizes, ranging from small countertop models to larger chest freezers. The size and capacity of the freezer will determine the amount and variety of items it can store.
Now that we have a basic understanding of deep freezers, let’s explore the factors that affect their temperature capabilities.
Factors Affecting the Temperature
Several factors influence the temperature capabilities of deep freezers. Understanding these factors is essential for setting the desired temperature and ensuring optimal performance. Let’s take a closer look at the key factors:
- Insulation: The insulation quality of a deep freezer plays a crucial role in maintaining a consistent temperature. High-quality insulation helps minimize heat transfer from the external environment, keeping the internal temperature low. Thick insulation materials like polyurethane foam are commonly used in deep freezer construction.
- Sealing: Airtight seals around the lid or doors of the deep freezer are vital for preventing warm air from entering the unit. Any gaps or leaks in the seals can compromise temperature stability and increase energy consumption. It’s important to regularly check and replace worn-out seals to maintain an effective seal.
- Location: The placement of a deep freezer can impact its temperature. It is recommended to position the freezer away from heat sources such as ovens, direct sunlight, or heating vents to prevent temperature fluctuations. Ideally, the freezer should be placed in a cool, well-ventilated area for optimal performance.
- External Temperature: The ambient temperature of the room or environment where the deep freezer is located can affect its ability to reach and maintain low temperatures. If the room temperature is consistently high, the freezer may have to work harder to achieve lower temperatures. It is advisable to maintain a cooler environment to support the freezer’s performance.
- Frequency of Opening: Opening the deep freezer frequently and leaving the lid or door open for extended periods can lead to temperature fluctuations and affect the freezer’s ability to maintain ultra-low temperatures. Minimizing the frequency and duration of door opening is crucial for temperature stability.
- Load Capacity: The amount and type of items stored in the freezer can impact its temperature. Overloading the freezer excessively can hamper airflow and limit the cooling capacity. It’s important to allow space for air circulation to ensure efficient cooling performance.
Now that we have explored the factors that affect the temperature capabilities of deep freezers, let’s dive into the cooling mechanism behind these appliances.
Cooling Mechanism of Deep Freezers
The cooling mechanism of deep freezers is based on the principles of refrigeration. These appliances utilize a combination of components and processes to create and maintain the low temperatures required for long-term storage. Let’s explore the key elements of the cooling mechanism:
- Compressor: The compressor is the heart of the cooling system. It circulates a refrigerant, typically a gas like Freon or R-134a, through a series of coils to transfer heat out of the freezer. The compressor compresses the refrigerant, raising its temperature and pressure.
- Condenser: The hot, high-pressure refrigerant flows into the condenser, a set of coils located either inside or outside the freezer. As the refrigerant passes through the condenser, it releases heat to the surrounding environment and undergoes a phase change, transforming into a high-pressure liquid.
- Expansion Valve: After leaving the condenser, the high-pressure liquid refrigerant enters the expansion valve. The expansion valve restricts the flow of the refrigerant, causing a drop in pressure. This sudden pressure drop results in the refrigerant evaporating and transitioning back into a low-pressure gas.
- Evaporator: The low-pressure refrigerant gas enters the evaporator, located inside the deep freezer. As the refrigerant passes through the evaporator coils, it absorbs heat from the interior of the freezer, causing the temperature to drop. This process cools down the items stored in the freezer.
- Fan: A fan is often used to enhance the airflow inside the freezer. It helps distribute the cooled air evenly, ensuring consistent temperatures throughout the storage space. The fan also aids in removing any excess moisture, reducing the risk of frost buildup.
Through this continuous cycle of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation, the cooling mechanism of deep freezers effectively removes heat from the storage compartment, resulting in the maintenance of low temperatures required for long-term preservation.
Now that we have a better understanding of the cooling mechanism, let’s explore the temperature range that deep freezers can achieve.
Temperature Range of Deep Freezers
Deep freezers are designed to provide a significantly lower temperature range compared to regular refrigerators. The specific temperature range can vary depending on the model, but most deep freezers can achieve temperatures as low as -10°C to -40°C (-14°F to -40°F) or even lower.
The temperature range of a deep freezer is governed by various factors, including the cooling system, insulation, and technological advancements. Ultra-low temperature freezers, often used in scientific and medical applications, can reach temperatures as low as -86°C (-123°F) or even colder, enabling the storage of highly sensitive materials and samples.
It’s worth noting that the temperature inside a deep freezer may vary slightly throughout the storage space. The temperature near the cooling elements, such as the evaporator, may be slightly colder than in other areas. However, most modern deep freezers are designed to provide uniform cooling and maintain a consistent temperature range throughout the storage chamber.
The ability to reach and maintain such low temperatures is essential for preserving food, extending shelf life, and storing temperature-sensitive items like vaccines, drugs, and biological samples. The extreme cold temperatures in deep freezers not only inhibit the growth of bacteria and microorganisms but also slow down biochemical reactions that lead to spoilage.
Now that we understand the temperature range deep freezers can achieve, let’s dive deeper into the factors that determine just how cold a deep freezer can get.
The temperature of a deep freezer typically ranges from -20°C to -30°C (-4°F to -22°F), which is much colder than a standard refrigerator. Always check the specific temperature range of your deep freezer to ensure proper food storage.
Factors That Determine How Cold a Deep Freezer Can Get
The ability of a deep freezer to reach and maintain low temperatures is influenced by several key factors. Understanding these factors can help users optimize the performance of their deep freezers. Let’s explore the factors that determine how cold a deep freezer can get:
- Cooling System: The design and efficiency of the cooling system play a significant role in the temperature capabilities of a deep freezer. Advanced cooling systems, such as cascade refrigeration or dual-compressor systems, are more effective in achieving and maintaining extremely low temperatures.
- Insulation Quality: The insulation used in a deep freezer is crucial for temperature retention. High-quality, thick insulation materials like polyurethane foam or vacuum-sealed panels help prevent heat transfer from the external environment and keep the internal temperature consistently low.
- Compressor Power: The power and efficiency of the compressor can impact how cold a deep freezer can get. A more powerful compressor allows for quicker cooling and can handle larger temperature differentials, resulting in the ability to reach and maintain lower temperatures.
- Climate Class: Deep freezers are classified according to their maximum ambient temperature capabilities. The climate class indicates the range of temperatures in which the freezer can effectively operate. Freezers with a lower climate class rating, such as N or SN, are designed to operate at higher ambient temperatures, while those with higher ratings, such as ST or T, can operate at lower ambient temperatures.
- Cooling Agent: The type and quality of the refrigerant used in the cooling system can affect the temperature capabilities of the deep freezer. Different refrigerants have varying heat transfer properties, which can impact the maximum low temperatures that can be achieved.
- Control Systems: The control systems and temperature regulation mechanisms of the deep freezer also play a role in determining how cold it can get. Advanced digital controls and sensors help maintain precise temperature settings, ensuring optimal cooling performance.
It’s important to note that while these factors significantly influence the temperature capabilities of deep freezers, the specific temperature range may vary depending on the model and manufacturer. It’s always recommended to consult the product manual or specifications for accurate information regarding the temperature capabilities of a specific deep freezer.
Now that we have explored the factors that determine how cold a deep freezer can get, let’s move on to discussing the common temperature settings for deep freezers.
Common Temperature Settings for Deep Freezers
When it comes to setting the temperature of a deep freezer, there are general guidelines that users can follow to ensure optimal preservation and storage conditions. While the specific temperature settings may vary based on individual needs and the type of items being stored, here are some common temperature ranges for deep freezers:
- -18°C (0°F): This is a typical temperature setting for deep freezers used in households. It is suitable for general food storage, freezing items like meat, vegetables, and leftovers. At this temperature, most bacteria and microorganisms are unable to survive, effectively preserving the quality and extending the shelf life of food.
- -20°C to -30°C (-4°F to -22°F): This range is commonly used in medical and pharmaceutical settings. It is ideal for storing vaccines, medications, and laboratory samples, as it maintains the required temperature for stable storage and preservation.
- -40°C (-40°F) and below: Deep freezers with the capability to reach these extreme low temperatures are often found in scientific and research laboratories. They are used for storing highly sensitive samples, such as cell cultures and biological specimens, which require long-term preservation at ultra-low temperatures to maintain integrity.
Ultimately, the temperature setting of a deep freezer should be based on the specific requirements of the items being stored. It is crucial to consult manufacturer guidelines, product manuals, or industry standards for recommended temperature ranges related to specific items, such as vaccines or biological samples.
Keep in mind that it is essential to regularly monitor the temperature inside the deep freezer using an external thermometer or the built-in temperature display, adjusting as needed to maintain the desired temperature range. Additionally, it’s important to avoid frequent temperature fluctuations by minimizing door openings and ensuring a properly sealed freezer lid or door.
Now that we understand the common temperature settings for deep freezers, let’s explore some tips for maintaining the optimal freezer temperature.
Maintaining Optimal Freezer Temperature
To ensure the longevity of stored items and maximize the efficiency of your deep freezer, it’s important to maintain an optimal temperature. Here are some tips to help you achieve and maintain the ideal temperature:
- Set the correct temperature: Start by setting the deep freezer to the recommended temperature range based on the type of items being stored. Refer to the product manual or guidelines provided by the manufacturer for the appropriate temperature setting.
- Monitor the temperature regularly: Use an external thermometer or the built-in temperature display to monitor the temperature inside the freezer regularly. This will help you identify any temperature fluctuations and take necessary corrective measures promptly.
- Avoid frequent door openings: Every time you open the freezer door, warm air enters, causing a temporary rise in temperature. Minimize the frequency and duration of door openings to prevent temperature fluctuations. Organizing and labeling items can help you locate what you need more efficiently, reducing the time the door is open.
- Ensure proper sealing: Check the gaskets or seals around the freezer door to ensure they are clean, intact, and properly sealing. Any gaps or leaks can allow warm air to enter and compromise temperature stability. Clean the seals regularly to remove any debris or buildup that could impact their effectiveness.
- Avoid overloading: Do not overload the freezer beyond its recommended capacity. Excessive items obstruct airflow and make it more challenging for the freezer to maintain optimal temperatures. Allow space between items for proper air circulation, promoting better cooling efficiency.
- Organize items strategically: Arrange the items in a way that allows for efficient airflow and easy access. By organizing items properly, you can minimize the time spent searching for specific items and reduce the need for extended door openings.
- Keep the freezer clean: Regularly clean the interior of the deep freezer to remove any spills, ice buildup, or frost. Excess frost can insulate and reduce the efficiency of cooling. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for defrosting and cleaning the freezer to maintain optimal performance.
- Address temperature fluctuations promptly: If you notice any significant temperature fluctuations or if the freezer is unable to maintain the desired temperature, investigate the cause immediately. Check for any issues such as a malfunctioning compressor, damaged seals, or power supply problems. Timely troubleshooting and maintenance can prevent further temperature instability.
By implementing these tips, you can ensure that your deep freezer maintains the optimal temperature for the long-term storage and preservation of various items.
Now that we have discussed maintaining the optimal freezer temperature, let’s explore some additional tips for maximizing freezer efficiency.
Tips for Maximizing Freezer Efficiency
In addition to maintaining the optimal temperature, there are several other steps you can take to maximize the efficiency of your deep freezer. By following these tips, you can enhance the performance of the freezer and potentially reduce energy consumption:
- Keep the freezer stocked: A well-stocked freezer helps maintain lower temperatures because the frozen items act as thermal mass, helping to regulate the temperature. If your freezer is not fully stocked, consider using containers filled with water, which can help maintain a consistent temperature even with less food inside.
- Avoid unnecessary opening: Minimize the frequency of opening the freezer and avoid prolonged door openings. Each time the freezer is opened, warm air enters, and cold air escapes, causing temperature fluctuations. Plan ahead and remove all the items you need at once, reducing the need for frequent openings.
- Label and organize items: Properly labeling and organizing items in the freezer can help you find what you need quickly and efficiently. This minimizes the time spent searching, reducing the duration of door openings and temperature fluctuations.
- Group similar items together: Arrange similar items together in the freezer. This helps maintain temperature consistency within specific sections or compartments. Grouping similar items also makes it easier to access them without needing to search through the entire freezer.
- Allow for proper airflow: Ensure that the airflow within the freezer is not obstructed. Proper positioning of items allows for better circulation of cold air, optimizing cooling efficiency. Avoid blocking the vents or air pathways with tightly packed items.
- Regularly defrost and clean: Frost buildup can decrease the efficiency of the freezer’s cooling power. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for regular defrosting and cleaning. Removing frost and ice buildup ensures proper airflow and temperature maintenance.
- Check and maintain seals: Inspect the gaskets or seals around the freezer door regularly. Damaged or aging seals can result in leaks, leading to temperature fluctuations and energy wastage. Clean the seals regularly and replace them if necessary to ensure a tight seal.
- Position the freezer correctly: Place the deep freezer in a cool, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Ambient temperatures affect the efficiency of the freezer’s cooling capabilities. Extreme temperatures can put additional strain on the cooling system and increase energy consumption.
- Consider energy-saving features: If you are in the market for a new deep freezer, consider models with energy-saving features, such as high-efficiency compressors or improved insulation. Energy-efficient freezers can save money on operating costs in the long run while maintaining optimal temperature.
- Regular maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance inspections to ensure that the deep freezer is functioning properly. This includes lubricating the compressor, cleaning coils, and checking electrical connections. Regular maintenance can help identify and address any issues that may affect the efficiency of the freezer.
By implementing these tips, you can maximize the efficiency of your deep freezer, ensuring optimal performance and energy savings.
Now that we have covered tips for maximizing freezer efficiency, let’s conclude our exploration of deep freezers.
Conclusion
Deep freezers are essential appliances for storing perishable items at ultra-low temperatures. Understanding the temperature capabilities and factors that influence deep freezers is crucial for optimal performance and preservation. By following the tips and considerations discussed in this article, you can ensure that your deep freezer operates efficiently and maintains the desired temperature range.
We learned that deep freezers have a temperature range typically between -10°C to -40°C (-14°F to -40°F) or even lower, allowing for the long-term preservation of various items. Factors such as insulation, sealing, location, external temperature, and frequency of door openings can influence a deep freezer’s ability to reach and maintain low temperatures.
The cooling mechanism of deep freezers involves a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, evaporator, and fan, working together to remove heat from the interior, thus achieving and maintaining cold temperatures. The precise temperature settings for a deep freezer depend on the items being stored, with common temperature ranges falling between -18°C to -40°C (-0°F to -40°F).
Maintaining the optimal freezer temperature involves setting the correct temperature, monitoring regularly, avoiding frequent door openings, ensuring proper sealing, avoiding overloading, organizing items strategically, and keeping the freezer clean. Additionally, maximizing freezer efficiency can be achieved through practices such as stocking the freezer, minimizing unnecessary opening, labeling and organizing items, allowing for proper airflow, regular defrosting and cleaning, checking and maintaining seals, positioning the freezer correctly, considering energy-saving features, and scheduling regular maintenance.
By following these guidelines and taking proper care of your deep freezer, you can ensure that it performs optimally, extends the shelf life of stored items, and maximizes energy efficiency.
So, whether you are storing food for your family or preserving highly sensitive laboratory samples, understanding how cold a deep freezer can get and how to maintain optimal temperature is essential. Embrace the technology and functionality of deep freezers to keep your items in pristine condition for as long as possible.
Remember, each deep freezer may have specific instructions and features, so always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for accurate information related to your model. Enjoy the benefits of a well-maintained deep freezer, and experience the convenience and peace of mind it brings.
Now that you've got the scoop on how deep freezers can chill, why not delve into the latest options for keeping your goods frosty? Our article on the best cold storage solutions for the upcoming year offers a rundown on the most efficient units that promise to keep your perishables perfectly preserved. Whether you're upgrading your current setup or setting up a new space, this guide is indispensable. Don't miss out on ensuring your storage needs are met with the utmost efficacy.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Cold Does A Deep Freezer Get
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Cold Does A Deep Freezer Get”