

Articles
How Cold Does An Attic Get In Winter
Modified: January 4, 2024
Discover how cold an attic can get during the winter months. Read our informative articles to find out more.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of attics and their temperatures during the winter season. Attics, being the highest point in a house, are subject to various factors that can cause them to get cold during the winter months. In this article, we will delve into the factors that contribute to attic temperature, discuss the importance of insulation, explore the common causes of cold attics in winter, and assess the impact of cold attics on energy efficiency. We will also highlight the potential risks associated with cold attics and provide valuable tips for preventing them.
There is a common misconception that attics are naturally warm in the winter due to the heat rising from the lower levels of the house. However, this is not always the case. Attic temperatures can vary significantly depending on various factors, including insulation, ventilation, and external climatic conditions.
Understanding the factors that affect attic temperatures is crucial for homeowners who want to ensure a comfortable and energy-efficient living environment. By taking the necessary steps to prevent a cold attic, you can not only save money on heating bills but also protect your home and promote overall indoor comfort.
So, let’s dive into the key factors that contribute to attic temperature during the winter season and explore ways to keep your attic warm and cozy.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper insulation, ventilation, and addressing air leaks are crucial for preventing a cold attic in winter. By taking proactive measures, you can create a warm, energy-efficient, and comfortable living environment while reducing heating costs.
- Cold attics can lead to increased energy consumption, potential mold growth, and risks such as freezing pipes and ice dam formation. By addressing insulation, ventilation, and maintenance, you can mitigate these risks and ensure a safe and cozy home during the winter season.
Read more: How Cold Does A Crawl Space Get
Factors contributing to attic temperature in winter
Several factors play a significant role in determining the temperature of an attic during the winter months. Understanding these factors can help you identify why your attic may be colder than desired and take the necessary steps to address the issue. Let’s explore the key factors:
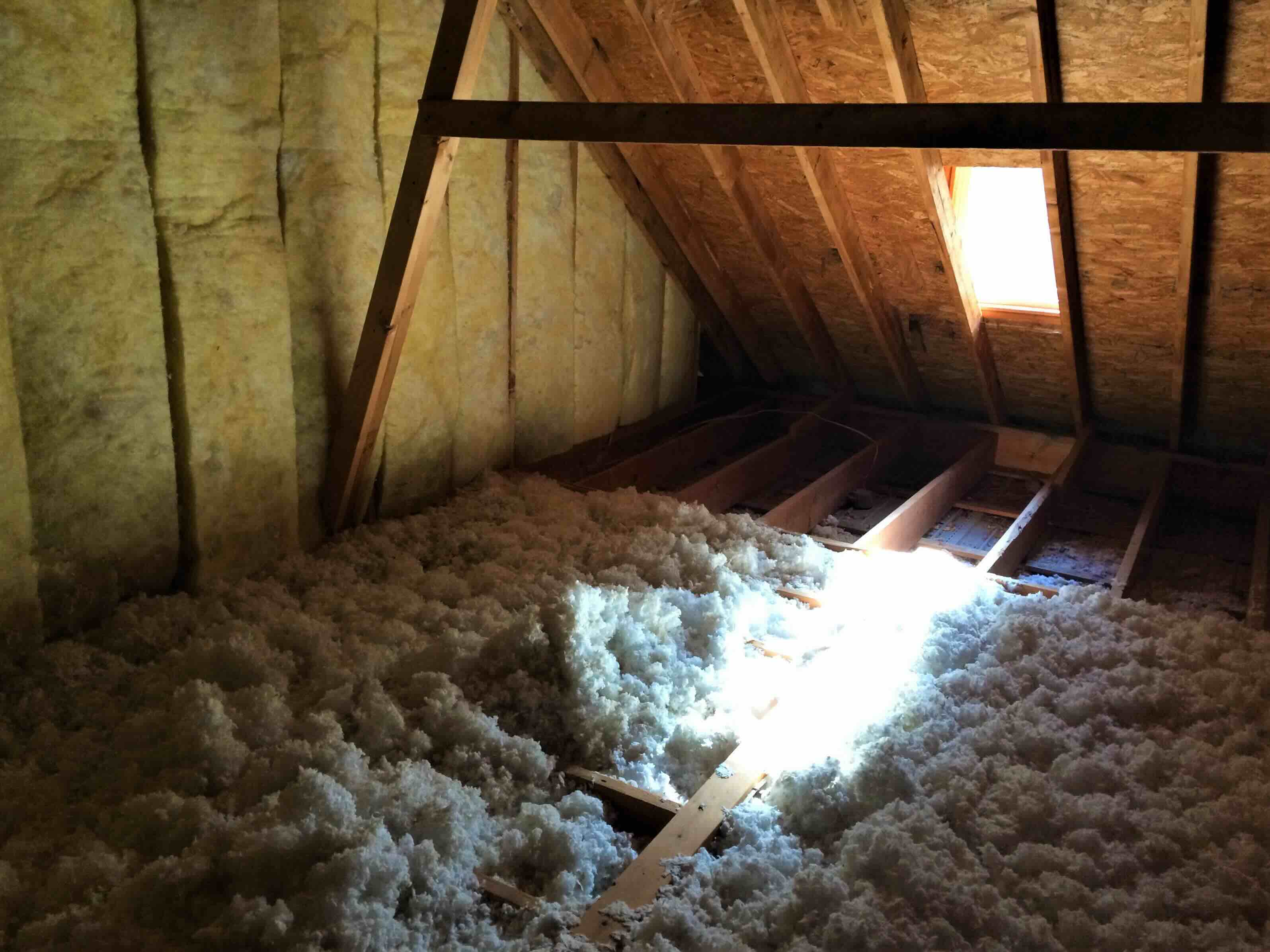
- Insulation: The level and quality of insulation in your attic are critical in regulating its temperature. Insulation acts as a barrier, preventing heat transfer between the interior space and the attic. Insufficient insulation or gaps in the insulation can lead to heat loss, resulting in a colder attic.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining a comfortable attic temperature. It allows for the exchange of air and prevents excessive moisture buildup, which can lead to condensation and mold growth. Insufficient ventilation can cause the attic to become cold and damp during the winter.
- Exterior conditions: External weather conditions, such as temperature, wind, and snow, can have a direct impact on attic temperature. Cold outdoor temperatures can penetrate the attic through roofing materials and cause the interior space to become colder.
- Roof color: The color of your roof can also influence attic temperature. Dark-colored roofs absorb more heat from the sun, which can result in warmer attic temperatures. On the other hand, light-colored roofs reflect more heat and help keep the attic cooler.
- Location and orientation: The geographical location of your home and the orientation of the attic can affect its winter temperature. Attics in colder climates or those exposed to strong winds may experience lower temperatures than attics in milder regions.
By considering these factors, you can gain insights into why your attic may be cold during the winter. Effectively addressing these factors will help you create a warmer and more comfortable living environment while potentially reducing your energy consumption.
Insulation and its role in keeping attics warm
Insulation is a crucial component when it comes to maintaining a warm and comfortable attic during the winter season. It acts as a barrier against heat transfer, preventing the escape of warm air from the lower levels of your home to the attic. Let’s explore the role insulation plays in keeping attics warm and how it can contribute to energy savings.
1. Retaining heat: The primary purpose of attic insulation is to retain heat within the living spaces of your home. Adequate insulation helps to create a thermal barrier that minimizes heat transfer, ensuring that the warm air generated by your heating system stays inside your living areas instead of escaping to the attic. This can significantly improve indoor comfort and reduce the need for excessive heating.
2. Preventing heat loss: Insufficient or poorly installed insulation can lead to heat loss through conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs when heat moves through solid materials such as walls and ceilings. Convection happens when warm air rises and escapes through gaps or cracks in the insulation. Radiation involves the movement of heat as infrared energy. Properly installed insulation with the right R-value helps prevent these heat loss mechanisms and keeps the attic warmer.
3. Energy efficiency: Good insulation not only keeps your attic warm but also contributes to energy efficiency. With a well-insulated attic, you can reduce your reliance on artificial heating sources, such as furnaces or heaters, resulting in lower energy consumption and decreased utility bills. Insulation acts as an effective barrier against temperature fluctuations, helping to maintain a consistent and comfortable indoor climate.
4. Moisture control: Insulation also plays a crucial role in moisture control within the attic. Without proper insulation, warm, moist air from the living areas can penetrate into the attic and condense on cold surfaces, leading to moisture buildup and potential mold growth. Insulation creates a barrier that helps prevent this moisture infiltration and maintains a drier and healthier attic environment.
Proper insulation is essential for keeping your attic warm, promoting energy efficiency, and preventing moisture-related issues. It is recommended to consult an insulation professional to assess the insulation needs of your attic and ensure adequate insulation levels based on your geographic location and climate. By investing in quality insulation, you can create a comfortable and energy-efficient atmosphere while protecting your home from temperature fluctuations and potential damage.
Common causes for cold attics in winter
A cold attic during the winter can be frustrating, leading to discomfort, higher heating bills, and potential damage to your home. Understanding the common causes for cold attics can help you identify the underlying issues and take appropriate steps to address them. Let’s explore some of the most common causes:
- Inadequate insulation: Insufficient or poorly installed insulation is one of the primary causes of a cold attic. If your attic lacks the proper amount and type of insulation, heat from the lower levels of your home will escape to the attic, leaving it colder than desired.
- Insulation gaps and voids: Even if you have insulation in your attic, gaps, voids, or compression in the insulation can compromise its effectiveness. These openings create pathways for heat to escape, resulting in a cold attic. Ensuring a uniform and complete insulation layer is crucial for maintaining a warm attic.
- Inadequate ventilation: Poor or insufficient attic ventilation can contribute to a cold attic. Without proper airflow, moisture can accumulate, leading to condensation and dampness, which can make the attic feel colder. Additionally, ventilation helps regulate temperature by allowing warm air to escape and cold air to enter, creating a balanced attic environment.
- Leaks and drafts: Leaky roofs, gaps around vents or chimneys, and poorly sealed windows can allow cold air to enter the attic, causing it to become cold. Identifying and sealing these leaks is essential for maintaining a warm attic and preventing energy loss.
- Insufficient attic floor insulation: Insulating the attic floor is as important as insulating the walls and roof. If the attic floor is not adequately insulated, heat from the lower levels of your home can escape through the floor, leaving the attic cold. Adding insulation to the attic floor can help prevent this heat loss.
- Unsealed attic access points: Attic access points, such as hatches or doors, are often overlooked sources of heat loss. If these access points are not properly sealed and insulated, cold air can enter the attic, contributing to its coldness. Sealing and insulating the attic access points can help maintain a warmer attic.
By addressing these common causes, you can significantly improve the temperature and comfort of your attic during the winter months. It is recommended to consult a professional to assess your attic and determine the most appropriate solutions based on your specific circumstances.
Make sure your attic is properly insulated to prevent it from getting too cold in the winter. This will help protect your home from heat loss and potential damage from freezing temperatures.
Impact of cold attics on energy efficiency
A cold attic during the winter can have a significant impact on the energy efficiency of your home. Understanding how a cold attic affects energy consumption can help you make informed decisions to improve energy efficiency and reduce heating costs. Let’s explore the key impacts:
- Increased heating load: A cold attic acts as a heat sink, absorbing warmth from the lower levels of your home. This means your heating system needs to work harder and consume more energy to compensate for the heat lost to the attic. As a result, your heating bills can increase significantly when your attic is cold.
- Inconsistent indoor temperature: A cold attic can lead to temperature imbalances within your home. Cold air from the attic can infiltrate the living spaces, resulting in chilly rooms and uncomfortable indoor conditions. To compensate for this, you might be tempted to crank up the thermostat, further increasing energy consumption.
- Drafts and heat loss: Cold air from the attic can find its way into your home through gaps, cracks, and poorly insulated areas. These drafts can make your home feel colder, prompting you to use more heating to maintain a comfortable temperature. This not only drives up energy usage but also indicates that your energy efficiency is compromised.
- Reduced insulation effectiveness: Cold attics can impact the overall effectiveness of insulation in your home. When the attic is cold, it can draw warmth from the interior spaces, making insulation less effective in preventing heat loss. This can lead to further energy waste and a decrease in the overall thermal performance of your home.
- Potential moisture and condensation issues: A cold attic can contribute to moisture-related problems, such as condensation and mold growth. Moisture from the living areas can rise to the attic and condense on cold surfaces, leading to dampness and potential mold issues. These problems not only compromise indoor air quality but also require additional energy to manage and resolve.
Addressing the cold attic issue and improving energy efficiency can have a range of benefits, including lower heating costs, improved indoor comfort, and reduced environmental impact. By properly insulating and sealing your attic, you can create a more energy-efficient home, enhance thermal comfort, and minimize heat loss, resulting in long-term energy savings and a greener footprint.
Read more: How Cold Does A Deep Freezer Get
Risks of cold attics in winter
Cold attics during the winter season pose several risks that can impact both the comfort of your home and the overall condition of the building. It is important to be aware of these risks to take appropriate measures to address them. Let’s explore some of the potential risks associated with cold attics:
- Freezing pipes: Cold attics can lead to freezing temperatures, especially if there is inadequate insulation or ventilation. When pipes are exposed to freezing temperatures, the water inside them can freeze, leading to pipe bursts and subsequent water damage to your home.
- Ice dam formation: An improperly insulated and ventilated attic can contribute to the formation of ice dams on the roof edges. Ice dams occur when snow melts on the warmer parts of the roof and refreezes along the colder eaves. This can result in water backup, leading to roof leaks and potential structural damage.
- Increased energy costs: Cold attics can cause heat loss from the living spaces of your home, resulting in higher energy consumption and increased heating costs. This can strain your budget and lead to financial discomfort, especially during the winter months when heating needs are highest.
- Reduced indoor comfort: A cold attic can affect the overall thermal performance of your home, leading to discomfort and temperature imbalances. Cold air seeping into the living areas can create chilly rooms and drafts, compromising your indoor comfort and well-being.
- Potential mold growth: Cold attics can contribute to moisture buildup and condensation, which creates an ideal environment for mold growth. Mold not only damages the structure of your home but can also cause respiratory issues and allergies. The presence of mold can also lead to costly remediation and negatively impact indoor air quality.
- Compromised insulation: A cold attic can impact the effectiveness of insulation in your home. When the attic is cold, it can draw heat from the interior spaces, making insulation less efficient in preventing heat loss. This compromises the energy efficiency of your home and can lead to increased energy consumption.
It is crucial to address these risks by properly insulating, ventilating, and sealing your attic. Focus on adequate insulation levels, proper ventilation, and addressing any issues that may contribute to heat loss or moisture buildup. By doing so, you can mitigate these risks, protect your home, and create a safer, more comfortable living environment.
Tips for preventing a cold attic in winter
Preventing a cold attic during the winter season is key to maintaining a warm, comfortable, and energy-efficient home. By taking proactive measures, you can minimize heat loss, improve insulation effectiveness, and create a cozy living environment. Here are some valuable tips to prevent a cold attic:
- Insulate properly: Ensure that your attic has adequate insulation with the recommended R-value for your climate. Pay attention to insulating not just the walls and roof but also the attic floor to prevent heat loss from the lower levels of your home.
- Seal air leaks: Identify and seal any gaps, cracks, or openings that allow air to flow between your home and the attic. Use weatherstripping and caulk to seal around windows, doors, vents, and other potential air leakage points.
- Improve attic ventilation: Proper attic ventilation is essential for maintaining a balanced and comfortable temperature. Ensure that your attic has both intake and exhaust vents to allow for airflow and prevent moisture buildup. Consult a professional to determine the right ventilation system for your attic.
- Seal attic access points: Attic access points, such as hatches and doors, can be sources of heat loss. Use weatherstripping and insulation to seal these access points and prevent cold air from entering the attic.
- Check roof insulation: Inspect the insulation in your roof and ensure that it is in good condition and properly installed. Consider adding additional insulation if needed, especially if the existing insulation is old or inadequate.
- Consider radiant barriers: Install radiant barriers, such as reflective foil insulation, to reduce heat transfer and enhance insulation effectiveness. These barriers can help prevent heat loss and maintain a warmer attic.
- Clear attic vents: Regularly check and clear any debris or obstructions from attic vents to ensure proper airflow. Blocked vents can impede ventilation and contribute to a colder attic.
- Inspect for roof leaks: Regularly inspect your roof for leaks and address any issues promptly. Water infiltration can lead to moisture buildup, compromising insulation and contributing to a cold attic.
- Maintain consistent indoor temperatures: Keep your home at a consistent temperature, even in unused areas. This helps minimize temperature fluctuations and prevents the attic from experiencing extreme coldness.
- Consider professional consultation: If you’re unsure about how to address specific issues or optimize your attic’s insulation and ventilation, consult with a professional insulation contractor or energy auditor. They can assess your attic and provide recommendations tailored to your home’s needs.
By following these tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of a cold attic, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the overall comfort of your home during the winter months.
Conclusion
Having a warm and comfortable attic during the winter is essential for maintaining a cozy living environment and maximizing energy efficiency. In this article, we explored the factors that contribute to attic temperature, the role of insulation in keeping attics warm, common causes for cold attics, the impact of cold attics on energy efficiency, the risks associated with cold attics, and valuable tips for preventing a cold attic.
Insufficient insulation, inadequate ventilation, exterior conditions, and insulation gaps are common culprits behind cold attics. The consequences of a cold attic include increased heating costs, temperature imbalances, potential mold growth, and compromised insulation effectiveness. By properly insulating, ventilating, and sealing your attic, you can mitigate these risks and improve the overall comfort and energy efficiency of your home.
Remember to ensure adequate insulation levels, seal air leaks, improve attic ventilation, and address any issues that may contribute to heat loss or moisture buildup. Regular maintenance, such as clearing attic vents and checking for roof leaks, is also crucial for preventing a cold attic.
Consulting professionals, such as insulation contractors or energy auditors, can provide expert guidance tailored to your specific needs. They can help assess your attic and recommend the most effective solutions to prevent a cold attic and optimize energy efficiency.
By implementing these measures, you can enjoy a warm and cozy home, lower your energy consumption, and reduce heating costs. Don’t let a cold attic dampen your winter experience – take charge and create a comfortable living space for you and your loved ones.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Cold Does An Attic Get In Winter
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Cold Does An Attic Get In Winter”