

Articles
How Hot Does Fireplace Get
Modified: May 6, 2024
Discover articles on how hot fireplaces can get and keep your home cozy and warm during the winter months. Learn about fireplace safety and maintenance tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
A fireplace is not just a source of warmth and comfort; it is also a focal point of any living space, creating an inviting atmosphere and adding charm to a home. As beautiful as a fireplace may be, it is important to understand the temperature it can reach to ensure safety and proper usage.
Fireplaces come in various types, including traditional wood-burning fireplaces, gas fireplaces, and electric fireplaces. Each type operates differently and produces different amounts of heat. Understanding the temperature range of a fireplace is essential for both safety and optimizing its functionality.
In this article, we will explore how hot fireplaces can get, the factors that affect fireplace heat, safety concerns and precautions, and measures to control fireplace temperature.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding fireplace temperature is crucial for safety and comfort. Wood-burning fireplaces can reach high temperatures, while gas and electric fireplaces offer more controlled heat output. Safety precautions and proper maintenance are essential for all types of fireplaces.
- Controlling fireplace temperature is achievable through measures such as adjusting airflow, using fireplace grates, and choosing the right fuel. Heat-resistant materials, fireplace fans, and programmable thermostats also play a role in tailoring the heat to your desired level of comfort.
Read more: How Hot Does A Gas Fireplace Get
Understanding Fireplace Temperature
Fireplace temperature refers to the level of heat that a fireplace can generate during operation. The temperature can vary depending on factors such as the type of fuel, the size and design of the fireplace, and the ventilation system. The temperature reached by a fireplace can have implications for safety, energy efficiency, and comfort.
Wood-burning fireplaces, for example, can reach higher temperatures compared to gas or electric fireplaces. The combustion of wood produces intense heat that can radiate throughout the room. Gas fireplaces, on the other hand, tend to have more controlled and consistent heat output. Electric fireplaces typically have adjustable temperature settings, allowing users to customize the level of heat they want.
The temperature of a fireplace also depends on the size and design of the firebox and chimney. Larger fireboxes tend to generate more heat, as they can accommodate larger fires. A well-designed chimney can effectively draw smoke out of the house and maintain proper airflow, which can impact the temperature. A poorly designed or clogged chimney may result in lower temperatures and inadequate ventilation, leading to smoke buildup and potential safety hazards.
It is important to note that fireplace temperature can be unevenly distributed throughout a room. The area closer to the fireplace will naturally experience higher temperatures, while areas further away may feel less warmer. This variation in temperature must be considered when positioning furniture and ensuring proper insulation to maximize heat efficiency.
Factors Affecting Fireplace Heat
Several factors can influence the amount of heat generated by a fireplace, including the type of fuel, the ventilation system, and the condition of the fireplace itself. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing fireplace heat output and ensuring safe operation.
Type of Fuel: The type of fuel used in a fireplace significantly impacts the heat produced. Wood-burning fireplaces can generate intense heat, with temperatures reaching over 1000 degrees Fahrenheit. Gas fireplaces offer more controlled heat output, as the temperature can be regulated through the gas flow. Electric fireplaces have adjustable temperature settings, allowing users to customize the level of heat they desire.
Ventilation System: The ventilation system plays a key role in maintaining fireplace heat. A properly designed and functioning chimney or vent allows for adequate airflow, facilitating efficient combustion and heat distribution. On the other hand, a poorly designed or clogged chimney can restrict airflow, leading to lower heat output and potential safety hazards.
Fireplace Design and Size: The design and size of the fireplace also impact its heat generation. A larger firebox has the capacity to accommodate larger fires, resulting in higher heat output. Similarly, a well-insulated fireplace can retain more heat, ensuring better efficiency.
Fireplace Maintenance: The condition of the fireplace itself affects its heat output. Regular maintenance, including cleaning the firebox and chimney, ensures proper airflow and efficient combustion. A clean and well-maintained fireplace will produce more heat compared to one with accumulated debris or obstructions.
Fuel Efficiency: The efficiency of fuel combustion is another factor that affects fireplace heat. Properly seasoned wood, for example, burns more efficiently, resulting in increased heat output. Using quality gas or electric fireplace inserts can also improve fuel efficiency and optimize heat production.
By considering these factors and taking appropriate measures, homeowners can maximize the heat output of their fireplaces while ensuring safety and energy efficiency. Regular maintenance, proper fuel choice, and attention to ventilation will help create a warm and inviting ambiance in the home.
The Temperature Range of Typical Fireplaces
The temperature range of a typical fireplace can vary depending on the type of fuel and the design of the fireplace. Wood-burning fireplaces tend to produce the highest temperatures, while gas and electric fireplaces offer more controlled and adjustable heat output.
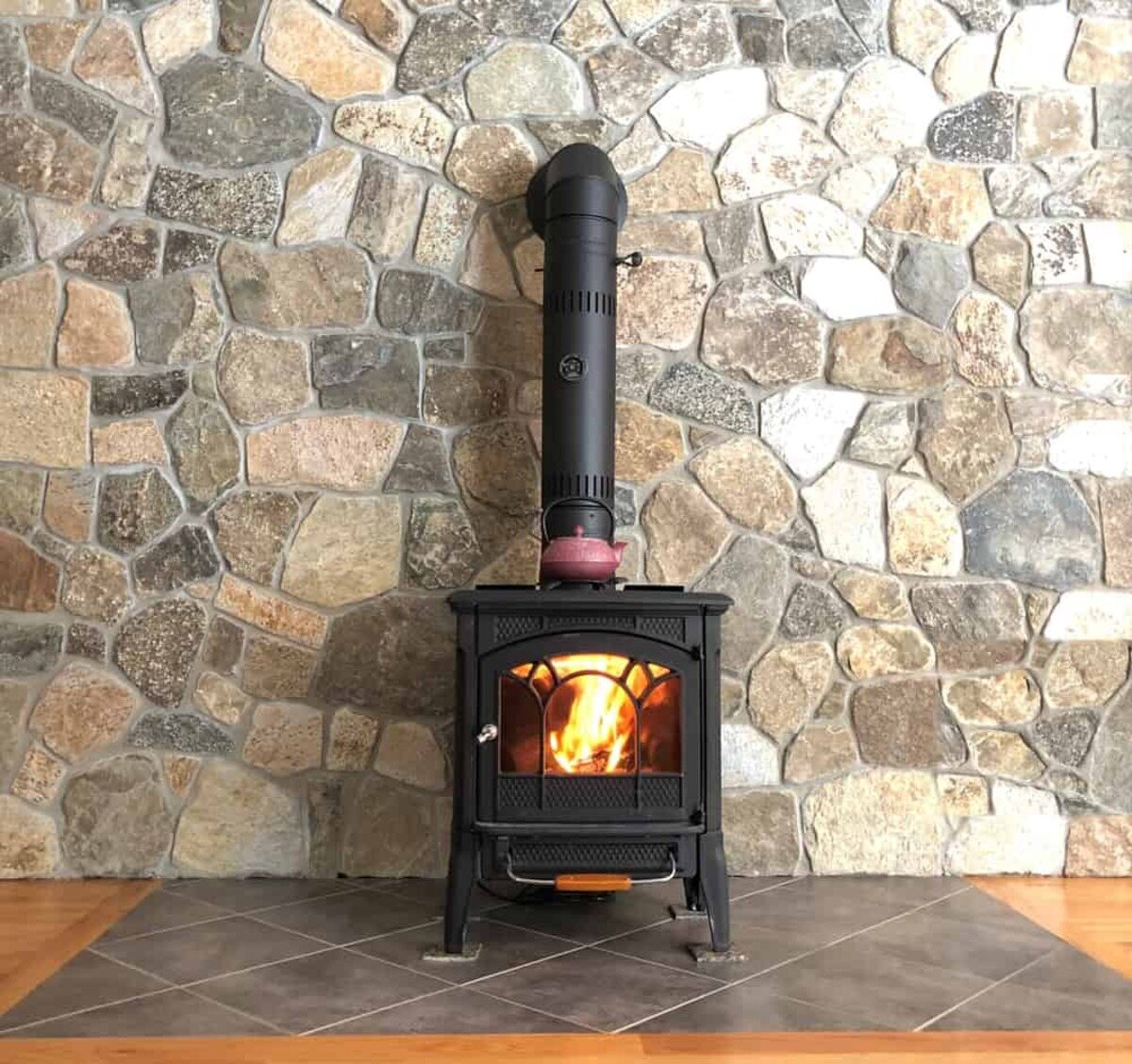
Wood-Burning Fireplaces: Wood-burning fireplaces can reach temperatures of 1000 to 1200 degrees Fahrenheit (538 to 649 degrees Celsius) during operation. The high temperatures are a result of the combustion of wood logs, which releases intense heat. It is essential to exercise caution and follow safety guidelines when operating a wood-burning fireplace due to the potential for sparks, embers, and direct contact with hot surfaces.
Gas Fireplaces: Gas fireplaces generally have a more controlled temperature range compared to wood-burning fireplaces. The heat output of gas fireplaces can be regulated to suit personal preferences through knobs or remote control. The temperature can range from 80 to 90 degrees Fahrenheit (27 to 32 degrees Celsius) for a gentle heat ambiance, up to 500 to 600 degrees Fahrenheit (260 to 316 degrees Celsius) for higher heat output. Gas fireplaces provide a safer and more convenient option, as they eliminate the need for handling wood and cleaning up ashes.
Electric Fireplaces: Electric fireplaces offer the most flexibility in terms of temperature control. They typically feature adjustable heat settings, allowing users to customize the level of heat they desire. Electric fireplaces can generate temperatures ranging from 65 to 95 degrees Fahrenheit (18 to 35 degrees Celsius) for a cozy ambiance, up to 400 to 500 degrees Fahrenheit (204 to 260 degrees Celsius) for a warmer environment. Electric fireplaces are known for their energy efficiency and ease of use, as they do not require venting or fuel storage.
It is important to note that the temperature mentioned above represents the heat generated by the fireplace itself. The actual temperature experienced in the room will depend on factors such as insulation, room size, and proximity to the fireplace. Additionally, it is crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines and safety precautions when operating any type of fireplace to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of all occupants.
By understanding the temperature range of different types of fireplaces, homeowners can select the most suitable option for their needs and enjoy a cozy and comfortable living space.
Always use a fireplace screen to protect from sparks and keep flammable items at a safe distance. The temperature of a fireplace can reach up to 1100°F, so caution is crucial.
Safety Concerns and Precautions
While fireplaces provide warmth and ambiance, it is important to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and protect both property and individuals. Here are some safety concerns and precautions to keep in mind when using a fireplace:
- Fireplace Screen: Always use a fireplace screen or glass door to prevent sparks, embers, and logs from escaping the firebox. This will help protect against accidental fires and burns.
- Clearance Area: Maintain a safe clearance area around the fireplace. Keep combustible materials such as furniture, curtains, and rugs at a safe distance to prevent them from catching fire. Check the manufacturer’s guidelines for the recommended clearance distances.
- Carbon Monoxide Detector: Install a carbon monoxide detector near the fireplace and throughout the house. Carbon monoxide is a colorless and odorless gas that can be produced during the combustion process. Detecting its presence is crucial for the safety of the occupants.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation by having a chimney or vent installed and regularly inspected. Proper ventilation removes harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide, from inside the house. It also aids in maintaining a healthy indoor air quality.
- Fireplace Maintenance: Regularly clean the firebox, chimney, and vents to remove any buildup of soot, creosote, or debris. Schedule professional inspections and cleanings to ensure the fireplace is in optimal condition and functioning efficiently.
- Use Dry and Seasoned Wood: If using a wood-burning fireplace, only burn dry and seasoned wood. Wet or unseasoned wood can produce excessive smoke, increase the risk of creosote buildup, and affect the efficiency of the fireplace.
- Supervision: Never leave a fire unattended, especially when there are children or pets present. Extinguish the fire completely before leaving the room or going to sleep.
- Fire Extinguisher and Smoke Alarms: Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and ensure smoke alarms are installed in the house. Regularly check the smoke alarms to ensure they are in working order.
- Educate Children: Teach children about the dangers of fire and the importance of maintaining a safe distance from the fireplace. Establish clear rules and guidelines to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Professional Maintenance: Consult with a professional or certified technician to inspect and maintain the fireplace regularly. They will ensure that the fireplace and chimney are in proper working condition and identify any potential safety concerns.
By following these safety precautions, homeowners can enjoy the warmth and beauty of their fireplace while minimizing the risk of accidents or property damage. Safety should always be a top priority when using any type of fireplace.
Read more: How Hot Does A Chimney Get
Measures to Control Fireplace Temperature
Controlling the temperature of a fireplace is crucial for maintaining comfort, ensuring energy efficiency, and preventing overheating. Here are some measures you can take to control the temperature of your fireplace:
- Adjust the Airflow: Most fireplaces have a damper or air control mechanism that allows you to adjust the airflow. Opening the damper fully increases the air supply and boosts the flames, resulting in higher temperatures. Closing the damper partially restricts the airflow and reduces heat output.
- Use a Fireplace Grate: A fireplace grate enhances airflow by lifting the fire off the floor of the firebox. This enables more oxygen to circulate around the fire, allowing it to burn hotter and produce more heat. Grates with adjustable settings can help control the temperature more effectively.
- Choose the Right Fuel: The type of fuel you use can impact the temperature of your fireplace. If you want to lower the temperature, switch to smaller logs or use wood that has a lower heat output. Conversely, if you want to increase the temperature, use larger logs or hardwoods that burn hotter and longer.
- Consider Fireplace Inserts: Fireplace inserts, such as a gas or electric insert, offer more precise control over temperature. These inserts typically come with adjustable settings that allow you to increase or decrease the heat output as desired.
- Install a Heat Reclaimer: A heat reclaimer or a heat exchanger can help to maximize the heat output of your fireplace. It captures excess heat that would otherwise be lost through the chimney and recirculates it back into the room, increasing the overall efficiency of the fireplace.
- Position Heat-Resistant Materials: By placing heat-resistant materials such as ceramic tiles or heat shields around the fireplace, you can help absorb and distribute the heat more evenly. This can prevent hotspots near the fireplace and ensure a comfortable temperature throughout the room.
- Use a Fireplace Fan: A fireplace fan, also known as a blower or circulator, helps to distribute the heat generated by the fireplace more effectively. These fans blow the hot air away from the fireplace and into the room, improving heat circulation and increasing the overall temperature.
- Install a Programmable Thermostat: If you have a gas or electric fireplace, installing a programmable thermostat can allow you to control the temperature more precisely. You can set the desired temperature and let the thermostat automatically adjust the heat output to maintain the desired level.
- Monitor Room Temperature: Keep an eye on the room temperature while the fireplace is in use. Use a thermometer or a smart thermostat to ensure the room doesn’t overheat. If the temperature becomes too high, open windows or doors to allow excess heat to escape.
Remember to follow manufacturer instructions and consult with professionals when installing or making modifications to your fireplace. By employing these measures, you can effectively control the temperature of your fireplace according to your comfort and needs.
Conclusion
A fireplace can be a wonderful addition to any home, providing warmth, ambiance, and a cozy atmosphere. Understanding the temperature range and factors that affect fireplace heat is crucial for both safety and maximizing its functionality. Whether you have a wood-burning, gas, or electric fireplace, taking the necessary precautions and implementing measures to control the temperature will ensure a comfortable and enjoyable experience.
Wood-burning fireplaces can reach high temperatures, providing intense heat but requiring careful handling and maintenance. Gas fireplaces offer more controlled heat output, allowing for convenient temperature adjustment. Electric fireplaces provide flexibility with adjustable heat settings and easy operation.
Safety should always be a top priority when using a fireplace. Installing fireplace screens, maintaining proper ventilation, and following maintenance guidelines will help prevent accidents and protect your home and loved ones. Additionally, practicing fire safety measures, such as never leaving a fire unattended and keeping clearance areas free of combustible materials, is essential.
If you want to control the temperature of your fireplace, adjusting the airflow, using fireplace grates, choosing the right fuel, considering fireplace inserts, and utilizing heat reclaimers are effective measures to consider. Heat-resistant materials, fireplace fans, programmable thermostats, and monitoring room temperature can also help tailor the fireplace heat to your desired level of comfort.
Remember to consult professionals, follow manufacturer instructions, and conduct regular inspections and maintenance to ensure the safe and efficient operation of your fireplace. By understanding and implementing these measures, you can enjoy the warmth and beauty of your fireplace while keeping safety at the forefront.
A well-cared-for fireplace will not only provide comfort but also serve as a centerpiece, creating lasting memories for you, your family, and friends for many years to come.
Now that you've learned about the heat levels a fireplace can reach, you might be wondering about its safety and design. Ensuring your fireplace is up to snuff not only keeps your home safe but also enhances its charm. If you're curious about whether your hearth is hazard-free, our guide on assessing fireplace safety is a must-read. For those looking to refresh their living space, our collection of stylish fireplace design ideas offers inspiration that can transform any room. Don't miss out on these exciting reads to make the most of your fireplace at home!
Frequently Asked Questions about How Hot Does Fireplace Get
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Hot Does Fireplace Get”