

Articles
How Many Watts Does A 60-Watt LED Bulb Use
Modified: January 8, 2024
Discover the energy efficiency of LED bulbs and find out how many watts a 60 watt LED bulb actually uses. Explore more informative articles on energy-saving lighting options.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
LED bulbs have revolutionized the lighting industry with their energy efficiency and long lifespan. With traditional incandescent bulbs gradually phasing out, LED bulbs have become the go-to choice for both residential and commercial lighting solutions. But when it comes to understanding the power consumption of LED bulbs, there seems to be some confusion, especially regarding the wattage rating.
In this article, we will delve into the world of LED bulbs and shed light on the myth surrounding their wattage. We will specifically focus on the power consumption of a 60 watt LED bulb, as it is a popular choice for many households. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of how many watts a 60 watt LED bulb actually uses and the factors that can influence its power consumption.
Key Takeaways:
- LED bulbs, including 60 watt ones, use significantly less power than their wattage suggests. Understanding the relationship between wattage, brightness, and actual power consumption is crucial for making informed and energy-efficient lighting choices.
- Factors such as brightness level, usage duration, lighting setup, quality and design, and environmental conditions can influence the power consumption of LED bulbs. By considering these factors, you can optimize energy efficiency and minimize wastage.
Read more: How Many Amps Does A 60-Watt LED Bulb Use
Understanding LED Bulbs
LED, which stands for Light Emitting Diode, is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, which rely on a filament that emits light when heated, LED bulbs operate through a different mechanism. Through a process called electroluminescence, LED bulbs convert electricity directly into light, making them highly efficient and long-lasting.
LED bulbs are composed of multiple LED chips grouped together, which emit light in a specific color when activated. These LED chips are housed in a casing that is designed to disperse the light evenly and protect the delicate electronics.
LED bulbs offer several advantages over traditional bulbs. Firstly, they have a significantly longer lifespan. While incandescent bulbs typically last for around 1,000 hours, LED bulbs can last up to 50,000 hours or more, depending on the quality and usage.
In addition to their longevity, LED bulbs are highly energy efficient. They consume much less power compared to incandescent bulbs while producing the same or even greater amount of light. This is where the confusion arises, as people are used to equating wattage with brightness.
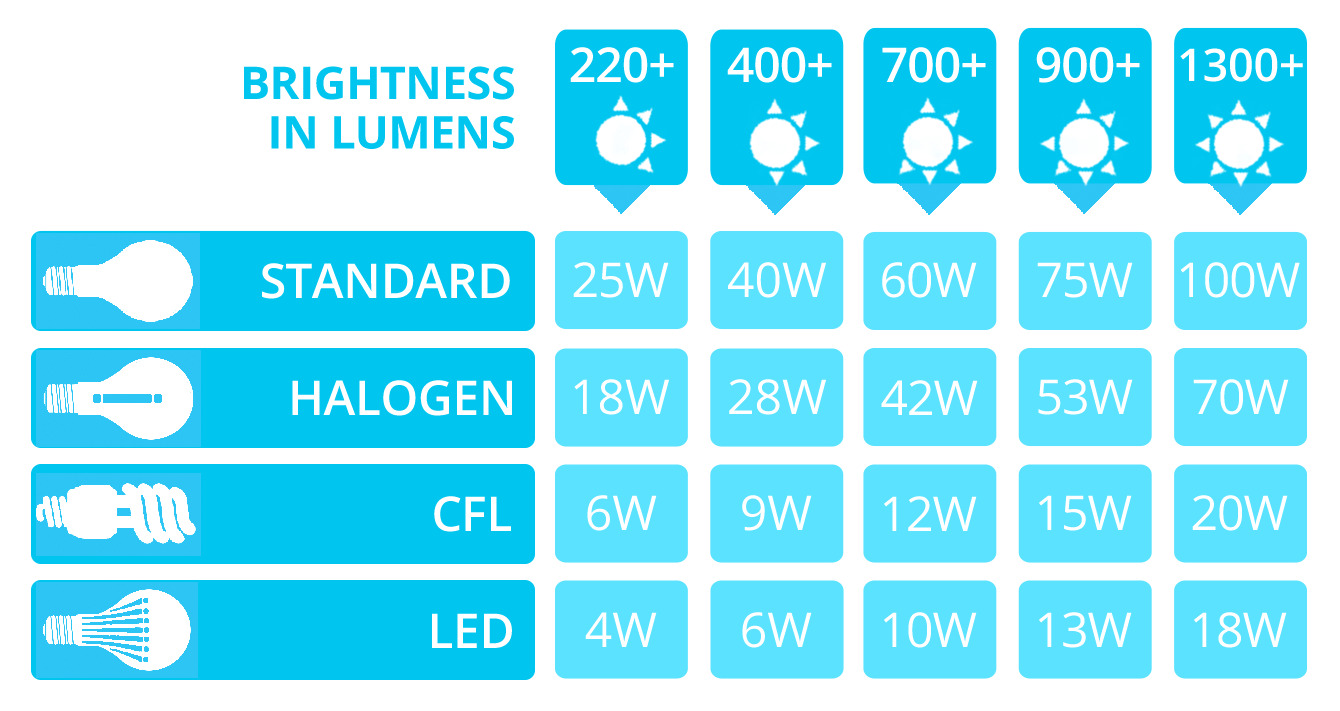
However, when it comes to LED bulbs, the wattage rating does not directly correlate to the brightness. In fact, the wattage rating is a measure of the power consumed by the bulb and not the amount of light it produces. To measure the brightness of an LED bulb, we need to look at its lumen output rather than its wattage.
So, when you see a 60 watt LED bulb, it does not mean that it consumes 60 watts of power. Instead, it is an indication of the equivalent brightness of a traditional 60 watt incandescent bulb. LED bulbs typically consume much lower wattage while providing the same or higher lumen output.
The Myth of Watts
One of the common misconceptions surrounding LED bulbs is the belief that the wattage rating indicates the amount of power they consume. This misconception stems from our familiarity with traditional incandescent bulbs, where the wattage directly correlates to the brightness.
However, with LED bulbs, the relationship between wattage and brightness is not straightforward. LED bulbs are designed to produce more light using less power. This means that an LED bulb with a lower wattage can provide the same or even greater brightness compared to a higher wattage incandescent bulb.
For example, a 60 watt incandescent bulb may produce around 800 lumens of light, while a 60 watt LED bulb may produce the same amount of light or even more with significantly less power consumption. This is due to the superior efficiency of LED technology in converting electricity into light.
So, when you see a 60 watt LED bulb, it does not mean that it will consume 60 watts of power. In fact, LED bulbs are known for their energy efficiency and low power consumption. They can consume around 75% less power compared to incandescent bulbs while producing the same amount of brightness.
Therefore, it is important to understand that the wattage rating of an LED bulb does not directly indicate its power consumption. It is a measure of the equivalent brightness of a traditional incandescent bulb. To determine the actual power consumption of an LED bulb, we need to look at the wattage rating as well as other specifications provided by the manufacturer.
By debunking the myth of watts, we can better understand the energy-saving capabilities of LED bulbs and make informed choices when selecting the right lighting solution for our needs.
Understanding the Wattage Rating
When it comes to LED bulbs, the wattage rating is not a direct measure of their power consumption but rather an indication of their equivalent brightness compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. However, understanding the wattage rating can still provide valuable insights into the performance and energy efficiency of LED bulbs.
The wattage rating of an LED bulb is typically mentioned on the packaging or product specifications. It represents the power consumption of the bulb in watts. However, as mentioned earlier, LED bulbs are designed to be highly energy efficient and consume significantly less power compared to incandescent bulbs.
For instance, a 60 watt LED bulb may actually consume only around 9-12 watts of power. This means that it can provide the same brightness as a traditional 60 watt incandescent bulb while using a fraction of the energy. The actual power consumption of an LED bulb is determined by factors such as the number and efficiency of the LED chips, the driver circuitry, and the overall design.
It is important to note that the wattage rating alone is not sufficient to determine the exact power consumption of an LED bulb. To get a clearer understanding, it is advisable to refer to the manufacturer’s specifications or consult expert resources.
In addition to the wattage rating, there are other technical specifications that can provide more insights into an LED bulb’s performance. These include the luminous flux, measured in lumens, which indicates the amount of light emitted by the bulb. The color temperature, measured in Kelvin, determines the perceived warmth or coolness of the light produced by the bulb.
When choosing an LED bulb, it is important to consider the desired brightness, color temperature, and energy efficiency. This can vary depending on the specific application, such as ambient lighting, task lighting, or decorative lighting. LED bulbs offer a wide range of options to suit different preferences and requirements.
By understanding the wattage rating along with other important specifications, consumers can make informed choices and select LED bulbs that not only provide the desired brightness but also deliver significant energy savings in the long run.
A 60 watt LED bulb actually uses around 10-15 watts of power, making it much more energy efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs.
Actual Power Consumption of a 60 Watt LED Bulb
When it comes to the actual power consumption of a 60 watt LED bulb, it may surprise you to learn that it consumes significantly less power than its traditional incandescent counterpart. While the wattage rating suggests a higher power consumption, LED technology allows for much greater energy efficiency.
On average, a 60 watt LED bulb consumes approximately 9-12 watts of power. This means that it uses only a fraction of the energy compared to a 60 watt incandescent bulb. The substantial reduction in power consumption is a result of the advanced design and efficient use of LED technology.
The lower power consumption of LED bulbs is primarily due to their ability to convert a higher proportion of electricity into light. Unlike incandescent bulbs, LED bulbs do not use a filament that heats up and emits light. Instead, they rely on semiconductors to generate light, resulting in less energy waste in the form of heat.
LED bulbs also make use of driver circuitry that helps regulate the flow of electricity to the LED chips. This ensures optimal performance and efficiency, further reducing power consumption.
In addition to the inherent energy-saving features of LED bulbs, advancements in technology have led to the development of more efficient LED chips and better driver circuitry. These advancements allow for even greater energy efficiency in modern LED bulbs.
Another factor that contributes to the lower power consumption of LED bulbs is their durability and longevity. LED bulbs have an average lifespan of 50,000 hours or more, which means they require fewer replacements compared to incandescent bulbs. This not only saves on energy consumption but also reduces the frequency of bulb replacements, resulting in long-term cost savings.
It is important to note that the actual power consumption of a 60 watt LED bulb may vary slightly depending on the specific model, brand, and usage conditions. However, the general trend is that LED bulbs use significantly less power compared to traditional incandescent bulbs.
By opting for a 60 watt LED bulb, you can enjoy the equivalent brightness of a 60 watt incandescent bulb while benefiting from substantial energy savings. This makes LED bulbs not only environmentally friendly but also cost-effective in the long run.
Read more: How Many Lumens In A 60-Watt LED Bulb
Factors Affecting Power Consumption
The power consumption of a 60 watt LED bulb can be influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors can help you optimize the energy efficiency of your lighting and make informed choices when selecting LED bulbs.
- Brightness level: The brightness level you choose for your LED bulb can impact its power consumption. Higher brightness levels generally require more power, while lower brightness levels can result in lower power consumption. Adjusting the brightness level can be done through dimmers or selecting bulbs with adjustable brightness settings.
- Usage duration: The amount of time you keep your LED bulb switched on affects its power consumption. The longer it is in use, the more energy it will consume. To minimize power consumption, consider turning off lights in unoccupied rooms or utilizing timers and motion sensors to automatically control lighting.
- Lighting setup: The arrangement and configuration of your lighting setup can impact power consumption. Using multiple LED bulbs in a large area will require more power than using a single bulb or strategically placing bulbs to maximize coverage and minimize the number needed.
- Quality and design: The quality and design of LED bulbs can also affect their power consumption. Higher-quality bulbs and those with efficient design features, such as optimized heat dissipation or advanced driver circuitry, can result in lower power consumption.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors, such as ambient temperature and humidity, can impact the power consumption of LED bulbs. Some bulbs may be more sensitive to temperature changes, which can affect their efficiency and power usage. It is important to choose bulbs that are suitable for the specific environmental conditions where they will be used.
By considering these factors and making informed decisions, you can optimize the power consumption of your LED bulbs and maximize energy efficiency. Additionally, staying updated with the latest advancements in LED technology can help you select bulbs that offer enhanced energy-saving features.
It is worth noting that while LED bulbs are inherently energy-efficient, their power consumption can still be influenced by external factors. By taking these factors into account and making conscious decisions in your lighting setup and usage, you can minimize energy wastage and contribute to a greener and more sustainable environment.
Conclusion
LED bulbs have undoubtedly transformed the lighting industry with their exceptional energy efficiency and long lifespan. However, understanding the power consumption of LED bulbs, especially when it comes to the wattage rating, can be a source of confusion for many consumers.
It is important to debunk the myth that the wattage rating of an LED bulb directly correlates to its power consumption. LED bulbs are designed to provide the same or even greater brightness compared to traditional incandescent bulbs while consuming significantly less power.
A 60 watt LED bulb, despite its wattage rating, typically consumes only around 9-12 watts of power. This remarkable difference in power consumption is due to the efficient use of LED technology, advanced design, and superior energy-saving features.
When selecting LED bulbs, it is crucial to understand that their wattage rating is an indication of their equivalent brightness and not their power consumption. Additionally, considering other specifications such as lumen output, color temperature, and energy-saving features can help you make informed choices and optimize the energy efficiency of your lighting setup.
Factors such as brightness level, usage duration, lighting setup, quality and design, and environmental conditions can also influence the power consumption of LED bulbs. By being mindful of these factors and making conscious decisions, you can further minimize energy wastage and maximize energy savings.
In conclusion, LED bulbs offer a highly efficient and environmentally friendly lighting solution. Their lower power consumption, longer lifespan, and energy-saving features make them a practical choice for both residential and commercial applications. By understanding the nuances of LED bulb power consumption and making informed decisions, you can enjoy bright, energy-efficient lighting while reducing your environmental impact and saving on electricity costs in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Many Watts Does A 60-Watt LED Bulb Use
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Many Watts Does A 60-Watt LED Bulb Use”