

Articles
How Many Watts In A Light Bulb
Modified: February 22, 2024
Discover the answer to "how many watts in a light bulb" and more with our informative articles. Stay informed and make smart lighting choices today.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Light bulbs are an integral part of our everyday lives, allowing us to illuminate our homes, workspaces, and public spaces. With advancements in technology, light bulbs have evolved significantly over the years, offering various options in terms of brightness, energy efficiency, and longevity. One important aspect to consider when choosing a light bulb is the wattage, which determines the amount of power consumed and the brightness level it produces.
In this article, we will explore the concept of wattage in light bulbs and delve into the different types of bulbs available in the market. We will also discuss the energy efficiency and brightness factors that come into play when determining the appropriate wattage for your specific needs.
So, how many watts are in a light bulb? Let’s find out!
Key Takeaways:
- Wattage alone is not a reliable indicator of brightness for modern light bulbs. Consider lumen output and energy efficiency when choosing the right bulb for your space.
- LED bulbs offer exceptional energy efficiency, longevity, and versatility, making them the preferred choice for environmentally friendly and cost-effective lighting solutions.
Wattage Defined
Wattage, in the context of light bulbs, refers to the amount of power consumed by the bulb to produce light. It is a measure of the bulb’s energy consumption and is typically indicated on the packaging or on the bulb itself.
Wattage is named after James Watt, the Scottish inventor who pioneered improvements to the steam engine during the 18th century. It is a unit of power and is defined as the rate at which work is done or energy is consumed.
In the case of light bulbs, wattage determines the brightness of the bulb. Generally, the higher the wattage, the brighter the light produced. However, it is essential to note that the relationship between wattage and brightness has changed with the introduction of more energy-efficient lighting technologies.
In the past, traditional incandescent bulbs were commonly used, and the wattage directly corresponded to the brightness levels. For example, a 60-watt incandescent bulb would produce a certain amount of brightness. However, with the advent of newer lighting technologies, such as LED and CFL bulbs, the same brightness level can be achieved with significantly lower wattages.
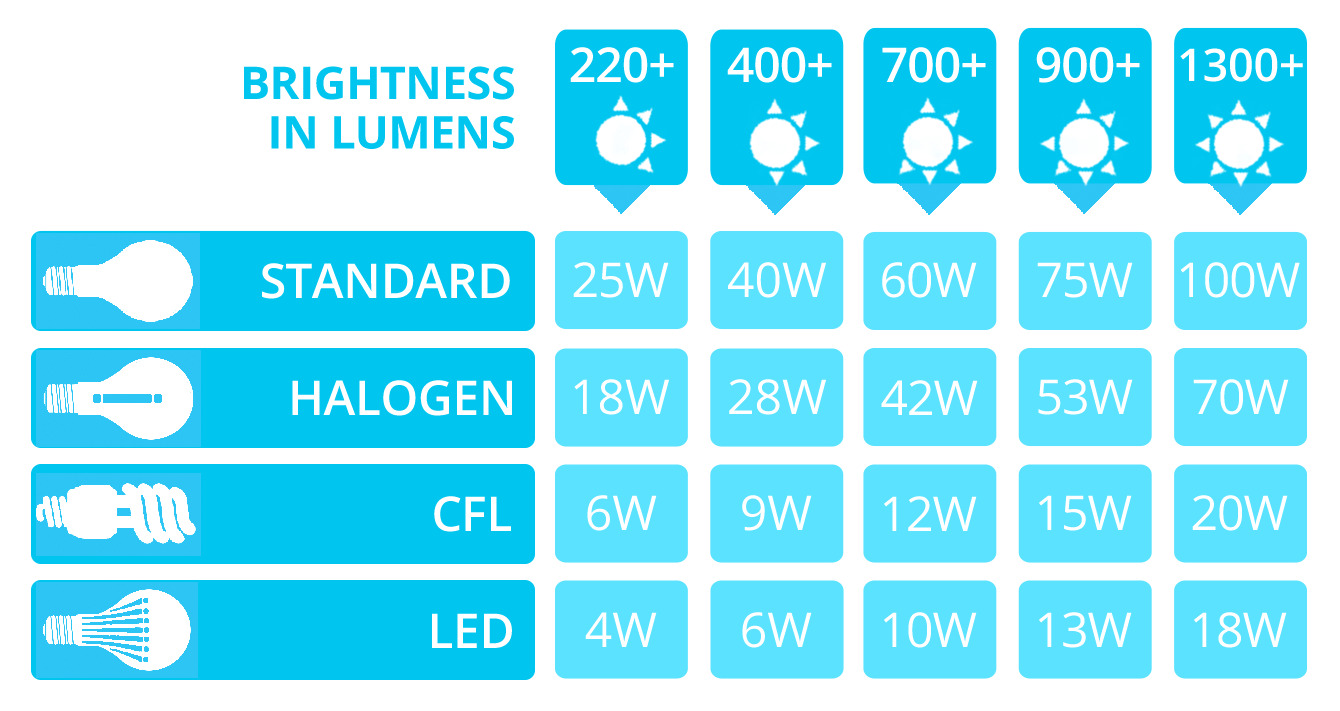
To accurately compare the brightness of different types of light bulbs, it is important to look beyond wattage and consider the lumen output. Lumens measure the actual amount of light emitted by a bulb, providing a more accurate representation of brightness.
In summary, wattage is a measure of the power consumed by a light bulb, and it is commonly used to indicate the brightness level of traditional incandescent bulbs. However, with the introduction of more energy-efficient lighting options, wattage alone is not a reliable indicator of brightness. To make an informed choice, it is crucial to consider the lumen output in addition to the wattage when selecting a light bulb.
Types of Light Bulbs
When it comes to light bulbs, there are several types available on the market, each with its own set of characteristics and advantages. Let’s take a closer look at the most common types:
- Incandescent Bulbs: Incandescent bulbs have been around for over a century and are the traditional type of light bulb that most people are familiar with. They operate by passing an electric current through a filament, which then emits light and heat. Incandescent bulbs are known for their warm glow and are available in various shapes and sizes. However, they are not very energy-efficient, as they convert only a small percentage of electricity into light, with the rest being wasted as heat.
- Halogen Bulbs: Halogen bulbs are a variation of incandescent bulbs but incorporate a halogen gas fill and a quartz envelope. These bulbs produce a bright and crisp light that closely resembles natural sunlight. They are more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs and have a longer lifespan. Halogen bulbs are often used in task lighting and are available in different shapes and sizes for various applications.
- Compact Fluorescent Bulbs (CFLs): CFL bulbs are energy-saving alternatives to incandescent bulbs. They work by passing an electric current through a gas-filled tube that contains mercury vapor. When the mercury vapor is stimulated, it emits ultraviolet light, which then interacts with a phosphor coating inside the tube to produce visible light. CFL bulbs use significantly less energy than incandescent bulbs and have a longer lifespan. However, they do contain a small amount of mercury, requiring special disposal procedures.
- LED Bulbs: LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulbs have gained immense popularity in recent years due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and versatility. They operate by passing an electric current through a semiconductor material, which emits light when energized. LED bulbs are highly energy-efficient, converting a large percentage of electricity into light and generating minimal heat. They are available in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and color temperatures to suit various lighting needs. LED bulbs are considered the most environmentally friendly option and are rapidly replacing other types of bulbs in homes and businesses.
It’s important to consider your specific lighting requirements and preferences when choosing a light bulb. Take into account factors such as brightness, color temperature, energy efficiency, and lifespan to determine the best type of bulb for your needs.
Incandescent Bulbs
Incandescent bulbs have long been the go-to choice for residential and commercial lighting. They have a familiar warm glow that many people find comforting and reminiscent of traditional lighting. However, with advancements in lighting technology, incandescent bulbs have become less popular due to their low energy efficiency and shorter lifespan.
Incandescent bulbs operate by passing an electric current through a thin tungsten filament that is housed inside a glass bulb filled with inert gas, typically nitrogen or argon. As the electric current flows through the filament, it heats up to a high temperature, causing it to emit visible light.
One of the unique characteristics of incandescent bulbs is their ability to produce a wide spectrum of light, including warm tones that are pleasing to the human eye. This is one reason why incandescent bulbs are often preferred for ambient lighting applications, such as living rooms and bedrooms.
However, incandescent bulbs are not very energy efficient compared to other lighting options. They convert only about 10% of the electrical energy into light, with the remaining 90% being wasted as heat. This inefficiency is one of the main reasons why governments and environmental organizations have been pushing for more energy-efficient alternatives.
Another drawback of incandescent bulbs is their relatively short lifespan. On average, they last for about 1,000 to 2,000 hours, which is significantly shorter compared to other bulb types. This means that incandescent bulbs need to be replaced more frequently, resulting in higher maintenance costs and environmental impact.
In recent years, many countries have phased out or limited the use of incandescent bulbs in an effort to reduce energy consumption. These regulations have led to a shift towards more energy-efficient lighting options, such as LED and CFL bulbs, which significantly outperform incandescent bulbs in terms of energy efficiency and lifespan.
Despite their disadvantages, incandescent bulbs still have some applications. They are often favored for uses where dimmability and color rendering are critical, such as in certain art galleries or restaurants. However, for general household and commercial lighting, it is recommended to consider more energy-efficient alternatives.
Halogen Bulbs
Halogen bulbs are a type of incandescent bulb that offer improved efficiency and a higher quality of light compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. They are widely used in a variety of lighting applications, ranging from residential to commercial settings.
Halogen bulbs operate on the same principle as incandescent bulbs, passing an electric current through a filament to produce light. However, what sets halogen bulbs apart is the addition of halogen gas, typically bromine or iodine, inside the bulb. This halogen gas creates a chemical reaction with the tungsten filament, preventing the filament from degrading as quickly and extending the lifespan of the bulb.
One of the key advantages of halogen bulbs is their ability to produce a bright and crisp light that closely resembles natural daylight. The color temperature of halogen bulbs typically falls within the range of 3000K to 3500K, creating a warm and inviting atmosphere. This makes them ideal for task lighting, where accurate color representation is important, such as in art galleries or kitchens.
In addition to their superior light quality, halogen bulbs are also more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs. They typically consume about 15-30% less energy and can produce the same amount of brightness. This energy efficiency translates to cost savings on electricity bills over time.
Halogen bulbs also have a longer lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, typically lasting around 2,000 to 4,000 hours. This extended lifespan reduces the frequency of bulb replacements and lowers maintenance costs.
It is worth noting that halogen bulbs operate at higher temperatures due to the halogen gas inside the bulb. This means that they should be handled with caution and not touched with bare hands, as the oils from your skin can cause hot spots and decrease their longevity. It is recommended to use a cloth or gloves when replacing halogen bulbs to avoid any potential damage.
Overall, halogen bulbs are a versatile lighting option that provides bright, high-quality light and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. They are commonly used in residential and commercial spaces where accurate color representation is important. However, it is important to weigh the energy efficiency and lifespan benefits against the potential safety considerations when considering the use of halogen bulbs.
When choosing a light bulb, consider the lumens instead of watts. Lumens measure the brightness of the bulb, while watts measure the energy it uses. Look for the lumens that match your needs for the right brightness.
Read more: How Many Watt Light Bulb For Living Room
Compact Fluorescent Bulbs (CFLs)
Compact Fluorescent Bulbs (CFLs) are a popular and energy-efficient alternative to traditional incandescent bulbs. They offer significant energy savings and have a longer lifespan, making them an environmentally-friendly choice for lighting.
CFLs work differently compared to incandescent bulbs. Inside a CFL, an electric current is applied to a tube that contains a small amount of mercury vapor. The mercury vapor emits ultraviolet (UV) light when ionized by the electric current. The UV light then strikes a phosphor coating on the inside of the tube, causing it to fluoresce and emit visible light.
One of the primary advantages of CFL bulbs is their energy efficiency. They use approximately 75% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, while providing the same amount of brightness. This energy savings not only reduces electricity costs but also contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
CFLs also have a significantly longer lifespan compared to incandescent bulbs, typically lasting up to 10,000 hours or more. This extended lifespan helps to reduce the frequency of bulb replacements, which is not only convenient but also environmentally beneficial by reducing waste.
When it comes to light quality, CFLs have improved over the years. In the past, some people found the light emitted by CFLs to be harsh or stark. However, modern CFLs are available in various color temperatures, ranging from warm white to cool white, allowing users to choose the desired ambiance for their space. Additionally, CFLs now have better color rendering capabilities, meaning they can accurately represent colors without distortions or dullness.
It’s important to note that CFL bulbs contain a small amount of mercury, averaging about 4 milligrams per bulb. While this amount is relatively small, proper disposal practices should be followed to minimize environmental impact. Many municipalities have recycling programs in place to ensure safe disposal and recycling of CFL bulbs.
Overall, CFL bulbs are a popular and energy-efficient lighting option. Their long lifespan, energy savings, and improved light quality make them a viable choice for residential and commercial lighting applications. By transitioning from traditional incandescent bulbs to CFLs, you can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
LED Bulbs
LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulbs have revolutionized the lighting industry in recent years, offering unparalleled energy efficiency, longevity, and versatility. LED bulbs have quickly become the preferred choice for both residential and commercial lighting applications.
LED bulbs work by passing an electric current through a semiconductor material, typically made of a combination of gallium, arsenic, and phosphorus. When the electrons in the semiconductor material are energized, they release photons of light, resulting in illumination.
One of the key advantages of LED bulbs is their exceptional energy efficiency. They convert a large percentage of electricity into light, wasting minimal energy as heat. In fact, LED bulbs are up to 80% more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs, and they can last up to 25 times longer.
The longevity of LED bulbs is a significant benefit. With an average lifespan of around 25,000 to 50,000 hours, or even more in some cases, LED bulbs far outlast other lighting options. This extended lifespan means fewer bulb replacements, reducing maintenance costs and minimizing environmental impact.
LED bulbs also offer excellent light quality. They produce a bright and consistent light output with high color rendering capabilities, accurately representing colors without any distortions. LED bulbs are available in a range of color temperatures, allowing users to create different lighting moods and atmospheres in their spaces.
Furthermore, LED bulbs are highly versatile. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs to suit different applications, from general lighting to specialty lighting. LED technology allows for dimmable options, compatibility with smart home systems, and the ability to produce different hues and effects.
While LED bulbs initially had a higher price point compared to other lighting options, the cost has significantly decreased over the years, making them more accessible to consumers. The long-term energy savings, reduced maintenance costs, and environmental benefits make LED bulbs a wise investment in the long run.
LED technology has also made significant advancements in terms of sustainability. LED bulbs are free from toxic materials, making them safe for both users and the environment. Additionally, LED bulbs produce minimal waste and can be recycled, further reducing their environmental impact.
Overall, LED bulbs are the future of lighting. Their energy efficiency, longevity, versatility, and superior light quality make them a compelling choice for any lighting application. By switching to LED bulbs, you can not only save energy and money but also contribute to a greener and more sustainable world.
Energy Efficiency and Light Bulb Brightness
When it comes to choosing the right light bulb, energy efficiency and brightness are two crucial factors to consider. Understanding the relationship between these factors will help you make an informed decision while balancing your lighting needs and energy consumption.
Energy efficiency in light bulbs refers to the amount of energy consumed to produce a certain level of brightness. Traditional incandescent bulbs are known for their low energy efficiency, converting a significant portion of electricity into heat rather than light. On the other hand, modern lighting technologies, such as CFLs and LEDs, offer much higher energy efficiency.
Brightness, measured in lumens, is a crucial factor to consider when selecting a light bulb. It determines the strength and intensity of the light emitted by the bulb. The higher the lumens, the brighter the light produced.
It is important to note that wattage alone is not a reliable indicator of brightness, especially with the introduction of more energy-efficient lighting options. In the past, higher wattage typically meant brighter light. However, with CFLs and LEDs, you can achieve the same brightness level using significantly lower wattages.
To accurately compare the brightness of different types of light bulbs, look for the lumen output information on the packaging. This information will give you a better understanding of the actual amount of light emitted by the bulb, allowing you to make a more informed decision.
For example, a traditional 60-watt incandescent bulb typically produces around 800 lumens of brightness. To achieve the same level of brightness with a CFL or an LED bulb, you may only need a 10-15 watt bulb, resulting in significant energy savings.
Beyond energy efficiency and brightness, another factor to consider is the color temperature of the bulb. Color temperature is measured in Kelvin (K) and determines the “warmth” or “coolness” of the light. Lower Kelvin values, around 2700K to 3000K, produce warm and cozy light similar to incandescent bulbs, while higher Kelvin values, around 4000K to 6500K, produce cooler and crisper light.
When choosing a bulb, consider the specific lighting needs for the room or space. For areas where you want a relaxing and cozy atmosphere, such as living rooms or bedrooms, opt for lower color temperatures. On the other hand, higher color temperatures are suitable for task lighting in areas like kitchens or offices, where clarity and brightness are important.
To summarize, energy efficiency and brightness are essential considerations when selecting a light bulb. Be sure to compare lumens rather than wattage to accurately assess the brightness level. Additionally, consider the color temperature to achieve the desired ambiance for your space. By making informed choices, you can strike a balance between energy efficiency, lighting needs, and creating the perfect atmosphere in your home or workplace.
Choosing the Right Wattage for Your Needs
When it comes to choosing the right wattage for your light bulbs, it is important to consider several factors, including the purpose of the lighting, the size of the room, and your personal preferences. Let’s explore some guidelines to help you make an informed decision:
- Determine the purpose of the lighting: Consider the intended use of the space and the desired lighting ambiance. Different activities may require varying levels of brightness. For example, a workspace or kitchen may benefit from brighter lighting, while a bedroom or living room may be better suited for softer, more ambient lighting.
- Consider the size of the room: The size of the room can influence the wattage needed. Larger rooms may require higher wattages to adequately light the space, while smaller rooms may be well-lit with lower wattages. Additionally, take into account the height of the lighting fixtures and whether there are multiple light sources in the room.
- Take into account personal preferences: Your personal preferences regarding the brightness of the light are important. Some individuals prefer a brighter, more intense light, while others may prefer a softer, more subtle glow. Consider what kind of lighting makes you feel comfortable and productive in the space.
- Consider energy efficiency: Energy-efficient lighting options, such as CFLs and LEDs, provide the same or even better brightness with lower wattages compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Choosing bulbs with lower wattages can help reduce energy consumption and lower electricity costs over time.
- Refer to lumen output: When selecting a bulb, also consider the lumen output, which indicates the actual amount of light emitted by the bulb. Instead of relying solely on wattage, look for the desired lumen output to determine the appropriate brightness level for your needs. Remember, lumens provide a more accurate representation of brightness than wattage.
It’s also worth mentioning that experimenting with different wattages and lighting setups can help you find the perfect combination for your space. You can start with a bulb of medium wattage and adjust as needed to achieve the desired lighting effect.
Lastly, don’t hesitate to seek advice from lighting experts or professionals who can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific lighting requirements.
By considering factors such as the purpose of the lighting, room size, personal preferences, energy efficiency, and lumen output, you can choose the right wattage that meets your lighting needs and creates a comfortable and inviting atmosphere in your space.
Read more: How Many Watts Is An LED Bulb
Conclusion
Choosing the right light bulb is essential for creating the perfect lighting atmosphere while minimizing energy consumption. Understanding the concept of wattage and its relationship to brightness is key to making an informed decision.
Traditional incandescent bulbs have been the standard for many years but are being phased out due to their low energy efficiency and shorter lifespan. In their place, more energy-efficient options such as halogen bulbs, compact fluorescent bulbs (CFLs), and LED bulbs have emerged.
Halogen bulbs offer improved energy efficiency and a bright, crisp light that closely resembles natural daylight. However, they still fall short compared to newer technologies in terms of energy savings and lifespan.
CFL bulbs provide significant energy savings and a longer lifespan compared to incandescent bulbs. Although they contain a small amount of mercury and require special disposal, their improved light quality and cost-effectiveness have made them a popular choice.
LED bulbs have revolutionized the lighting industry with their exceptional energy efficiency, long lifespan, versatility, and superior light quality. They are the most environmentally friendly option, and despite their initial higher cost, they offer substantial savings in the long run.
When it comes to selecting the right wattage, factors such as the purpose of the lighting, room size, personal preferences, and energy efficiency should be considered. Looking beyond wattage and focusing on lumen output allows for a more accurate assessment of the desired brightness level.
By choosing energy-efficient bulbs and finding the right balance between brightness and energy consumption, you can create a well-lit and inviting environment while reducing your carbon footprint.
In conclusion, the transition from traditional incandescent bulbs to more energy-efficient options like halogen bulbs, CFLs, and LED bulbs is a smart choice for both your wallet and the environment. Understanding wattage, considering lumen output, and evaluating your specific lighting needs will enable you to find the perfect light bulbs for your space. Embrace the benefits of energy-efficient lighting and take a step towards a brighter and greener future.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Many Watts In A Light Bulb
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Many Watts In A Light Bulb”