

Articles
How To Fix Fertilizer Burn
Modified: January 19, 2024
Learn how to fix fertilizer burn and prevent it from damaging your plants with our informative articles on effective organic gardening techniques.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on fixing fertilizer burn. If you’re a gardener or a plant enthusiast, you’ve likely encountered fertilizer burn at some point. It can be frustrating to see your plants suffer from the very thing that was supposed to help them grow and thrive. But fear not, because in this article, we will explain what fertilizer burn is, how to recognize its signs and symptoms, and most importantly, how to fix it.
Fertilizer burn occurs when an excessive amount of fertilizer is applied to plants, causing damage to the roots, leaves, and overall health of the plant. While fertilizers are essential for providing nutrients to plants, applying too much or using the wrong type can have detrimental effects. However, with the right knowledge and techniques, you can easily remedy the situation and help your plants recover.
In the following sections, we will dive deeper into the signs and symptoms of fertilizer burn, explore the causes behind it, and provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to fix it. We will also share some helpful tips on preventing fertilizer burn in the first place, so you can ensure the healthy growth and vitality of your plants.
So, whether you’re dealing with fertilizer burn currently or simply want to be prepared for any future mishaps, let’s get started on our journey to fixing and preventing fertilizer burn. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and tools to nurture your plants and keep them thriving.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper watering, diluting the soil, and applying organic amendments like activated charcoal or compost are crucial steps in fixing fertilizer burn. Monitoring and adjusting the watering routine is essential for the plant’s recovery.
- Prevention tips such as using balanced fertilizers, conducting soil tests, and avoiding fertilizing stressed plants can help prevent fertilizer burn. Following these tips ensures the optimal health and growth of your plants.
Read more: What To Do If Fertilizer Burns Grass
What is Fertilizer Burn?
Fertilizer burn is a condition that occurs when plants suffer damage from an excess amount of fertilizer. It typically affects the leaves, roots, and overall health of the plant, inhibiting its growth and vitality. While fertilizers are essential for providing plants with the necessary nutrients to thrive, overapplication or improper use can result in fertilizer burn.
When fertilizer is applied to the soil, it releases nutrients that are taken up by the plant’s roots. However, if too much fertilizer is applied, the concentration of nutrients becomes too high for the plant to handle. This excess concentration can cause an imbalance of nutrients, leading to a condition known as fertilizer burn.
The primary cause of fertilizer burn is the high salt content present in most fertilizers. Fertilizers contain salts such as ammonium nitrate, potassium nitrate, and urea, among others, which are necessary for providing nutrients to plants. However, if these salts are applied in excessive amounts, they can dehydrate the plant, disrupt its biochemical processes, and ultimately lead to damage.
Fertilizer burn can occur in various types of plants, including vegetable crops, lawns, flowers, and even houseplants. It is important to note that different plants have different tolerance levels to fertilizers, so what may be an appropriate amount for one plant could be excessive for another.
Identifying fertilizer burn is crucial in order to take appropriate action and minimize further damage. The signs and symptoms of fertilizer burn can manifest in different ways, depending on the severity of the burn and the type of plant. In the next section, we will explore the common signs and symptoms of fertilizer burn to help you identify and address the issue effectively.
Signs and Symptoms of Fertilizer Burn
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of fertilizer burn is essential for addressing the issue promptly and minimizing damage to your plants. The symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the burn and the type of plant affected. Here are some common signs to look out for:
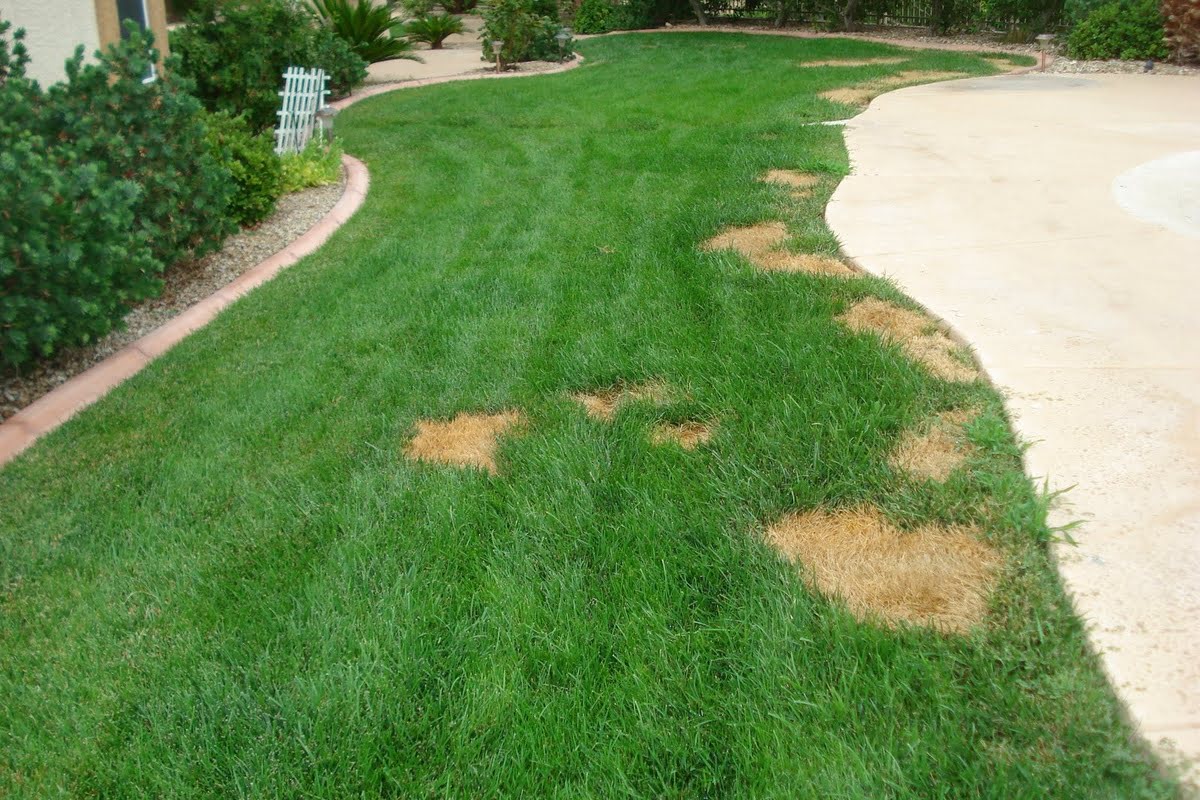
- Leaf Discoloration: One of the most noticeable signs of fertilizer burn is the discoloration of leaves. The affected leaves may turn yellow, brown, or even develop burnt patches. In some cases, the edges of the leaves may appear scorched.
- Wilting: Fertilizer burn can cause plants to experience wilting, even when the soil is adequately moist. This wilting is a result of the excessive salts in the soil, hindering the plant’s ability to take up water and nutrients effectively.
- Stunted Growth: If your plants are not growing as expected, it could be a sign of fertilizer burn. Excessive salts in the soil can inhibit root development and nutrient absorption, leading to stunted growth and a lack of vigor.
- Leaf Curling: Another common symptom of fertilizer burn is the curling or distortion of leaves. The leaf edges may curl upwards or downwards, giving them a distorted appearance. This curling is a response to the salts and dehydration caused by the excessive fertilizer.
- Tip Burn: Tip burn refers to the browning or drying out of the tips of leaves. It commonly occurs in leafy plants such as lettuce or spinach. The excessive salts in the soil disrupt the plant’s water balance, causing the edges of the leaves to dry out and turn brown.
- Plant Death: In severe cases of fertilizer burn, the plant may eventually die. Continued exposure to high levels of salts and nutrient imbalances can cause irreversible damage to the plant’s root system and overall health.
It is important to monitor your plants regularly and look for any signs of distress. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is crucial to take action promptly to save your plants and help them recover. In the next section, we will explore the common causes of fertilizer burn to better understand how to prevent it in the future.
Causes of Fertilizer Burn
Understanding the causes of fertilizer burn is crucial for preventing it from occurring in the first place. By knowing what contributes to this condition, you can make informed decisions when it comes to fertilizing your plants. Here are some common causes of fertilizer burn:
- Overapplication: Applying too much fertilizer is the most common cause of fertilizer burn. Many gardeners mistakenly believe that more fertilizer equates to better plant growth. However, excessive amounts of fertilizer can lead to a buildup of salts in the soil, overwhelming the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients effectively.
- Improperly balanced fertilizer: Using a fertilizer that is not properly balanced for your specific plants can also result in fertilizer burn. Different plants have different nutrient requirements, and using a fertilizer with an incorrect nutrient ratio can lead to imbalances that harm the plants.
- Inadequate watering: Fertilizer burn can be exacerbated by inadequate watering practices. When plants are not watered properly, the salts in the fertilizer become more concentrated in the soil. This concentration of salts can cause dehydration and damage to the plant’s root system.
- Using the wrong type of fertilizer: Different plants have different nutrient needs, and using the wrong type of fertilizer can cause imbalances and fertilizer burn. It is essential to select a fertilizer that is suitable for the specific needs of your plants.
- Applying fertilizer to stressed plants: Plants that are already stressed due to factors such as drought, disease, or insect infestation are more vulnerable to fertilizer burn. It is important to address any existing plant stress before applying fertilizer to avoid further damage.
- Applying fertilizer at the wrong time: Timing is crucial when it comes to fertilizing. Applying fertilizer during periods of extreme heat or drought can increase the risk of fertilizer burn. It is best to fertilize plants when they are actively growing and can readily absorb nutrients.
By understanding these causes, you can take proactive measures to prevent fertilizer burn and ensure the well-being of your plants. In the next section, we will outline a step-by-step guide on how to fix fertilizer burn if you have already encountered this issue.
How to Fix Fertilizer Burn
If you’ve encountered fertilizer burn and noticed the symptoms in your plants, don’t worry. There are steps you can take to fix the issue and help your plants recover. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to fix fertilizer burn:
- Step 1: Stop Applying Fertilizer: The first and most important step is to immediately stop applying any more fertilizer. Continuing to fertilize the affected plants will only worsen the burn and hinder the recovery process.
- Step 2: Water the Affected Area: Thoroughly water the affected area to help flush out the excess salts from the soil. Proper watering will dilute the concentration of salts and reduce stress on the plant’s roots.
- Step 3: Dilute the Soil: If the fertilizer burn is severe and concentrated in a specific area, consider diluting the soil further by applying additional water. This will help in leaching out the excessive salts from the root zone.
- Step 4: Apply Activated Charcoal or Compost: Activated charcoal or compost can help absorb the excess salts and improve the soil’s quality. Applying a layer of activated charcoal or adding compost around the affected plants can aid in the recovery process by replenishing the nutrients and improving the soil structure.
- Step 5: Monitor and Adjust Watering Routine: After treating the fertilizer burn, closely monitor the plants and adjust the watering routine as needed. Ensure that the plants receive adequate moisture but avoid overwatering, as this can lead to other issues.
- Step 6: Reapply Fertilizer Properly: Once the plants have fully recovered, you can slowly reintroduce fertilizer. However, it is crucial to follow the recommended dosage and application instructions specified for the particular type of plant you are fertilizing.
Remember, patience is key during the recovery process. It may take some time for the plants to bounce back and regain their vitality. Providing proper care, including regular watering and monitoring, will help them recover more effectively.
Now that you know how to fix fertilizer burn, let’s move on to the next section, where we will discuss some preventative tips to help you avoid fertilizer burn in the future.
Read more: What Part Of Fertilizer Burns Lawns
Step 1: Stop Applying Fertilizer
When you notice signs of fertilizer burn in your plants, the first and most crucial step is to immediately stop applying any more fertilizer. Continuing to fertilize the affected plants will only exacerbate the burn and hinder the recovery process.
Fertilizer burn occurs when there is an excessive buildup of salts and nutrients in the soil, causing damage to the roots and overall health of the plant. By ceasing the application of fertilizer, you prevent further accumulation of these salts and give your plants a chance to recuperate.
It is essential to remember that plants require a balanced amount of nutrients for healthy growth. Overfertilizing disrupts this balance and leads to nutrient imbalances, dehydration, and stress on the plant. By stopping the application of fertilizer, you allow the plant to regain its equilibrium and recover from the burn.
If you have been using a continuous-release fertilizer, it is advisable to remove any pellets or granules from the soil surface or top-dress layer. This will reduce the release of more nutrients and salts into the soil, giving the plant a chance to recover.
Additionally, take note of the frequency of fertilizer application. In some cases, frequent or consecutive applications of fertilizers can overload the plant with nutrients and contribute to fertilizer burn. By halting the application of fertilizer, you give the plant a chance to recover and reassess its nutritional needs.
In summary, stopping the application of fertilizer is the first and crucial step in fixing fertilizer burn. By doing so, you halt the buildup of excessive salts and nutrients, allowing the plant to recover and regain its health. In the following steps, we will explore further measures to help your plants recover from fertilizer burn.
Step 2: Water the Affected Area
Once you have stopped applying fertilizer, the next step in fixing fertilizer burn is to water the affected area. Adequate watering is crucial in helping flush out the excess salts and promote the recovery of your plants.
When plants experience fertilizer burn, the high concentration of salts in the soil can cause dehydration and hinder the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients effectively. By providing a thorough watering, you help dilute the salts and reduce stress on the plant’s roots.
It is important to water slowly and deeply to ensure that the water reaches the root zone. Use a gentle spray or drip irrigation to avoid excessive runoff that can lead to nutrient loss. Aim to moisten the soil thoroughly, ensuring that the water penetrates deep into the root zone.
Monitor the moisture level of the soil and adjust your watering routine accordingly. The goal is to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Frequent shallow watering should be avoided, as it can promote salt buildup and hinder the recovery process.
Do not be alarmed if you notice some yellowing or browning of leaves during the recovery process. This is a normal response to fertilizer burn and does not necessarily indicate further damage. With proper watering, the affected plants will gradually recover and produce new healthy growth.
In some cases, if the fertilizer burn is severe or concentrated in a specific area, you may consider using a technique called leaching. Leaching involves applying an excessive amount of water to the affected area to flush out the excess salts from the soil. However, be cautious with this approach, as overwatering can lead to other issues such as root rot.
Overall, water the affected area thoroughly and consistently to help dilute the salts, rehydrate the plant, and support its recovery from fertilizer burn. In the next step, we will discuss further measures to help fix and prevent fertilizer burn.
Flush the affected area with water to dilute the excess fertilizer and reduce the risk of further damage. Avoid over-fertilizing in the future to prevent fertilizer burn.
Step 3: Dilute the Soil
Once you have watered the affected area to help flush out the excess salts, the next step in fixing fertilizer burn is to further dilute the soil. This step is particularly important if the fertilizer burn is severe or concentrated in a specific area.
To dilute the soil, you can apply additional water to the affected area or gently irrigate the surrounding soil. The goal is to further leach out the excessive salts and reduce the concentration in the root zone. This process helps create a more balanced and suitable environment for the plant’s recovery.
When watering to dilute the soil, it is important to provide a slow and even application of water to ensure proper penetration. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to waterlogging and other issues. Instead, water the area gradually and allow the water to seep into the ground.
In some cases, you may need to repeat the process of diluting the soil over several watering sessions. This will depend on the severity of the fertilizer burn and the specific needs of your plants. Continuously monitoring the soil moisture and observing the plant’s response will guide you in determining if additional dilution is necessary.
Remember that the goal of diluting the soil is to create a more favorable growing environment for the plant. This step, combined with proper watering practices, helps restore the balance of nutrients and reduces the stress on the plant’s roots. It may take some time for the effects of dilution to be noticeable, so be patient and consistent in your efforts.
In the next step, we will discuss the application of activated charcoal or compost to further aid in the recovery process and promote healthy growth.
Step 4: Apply Activated Charcoal or Compost
As you continue to fix fertilizer burn, applying activated charcoal or compost can be beneficial in aiding the recovery of your plants. These organic amendments help absorb excess salts, improve soil structure, and replenish nutrients necessary for healthy growth.
Activated charcoal is known for its ability to bind to toxins and impurities in the soil. It acts as a natural filter, helping to remove excess salts and chemical residues left behind by the fertilizer. Applying a layer of activated charcoal around the affected plants can help mitigate the negative effects of fertilizer burn and support the plant’s rejuvenation.
Compost, on the other hand, provides a source of organic matter and beneficial microorganisms. It improves soil structure, enhances nutrient availability, and promotes a healthy and balanced ecosystem in the soil. Applying compost as a top dressing or incorporating it into the soil can help replenish nutrients, improve water retention, and enhance overall soil fertility.
When using activated charcoal or compost, ensure proper application techniques. Spread a layer of activated charcoal or a thin layer of compost around the base of the plant, avoiding direct contact with the stems or foliage. This helps prevent potential moisture retention and disease issues.
Remember that activated charcoal and compost are long-term solutions that work gradually. They promote healthy soil conditions and contribute to the plant’s overall recovery, resilience, and long-term growth. It is important to continue monitoring soil moisture, adjusting watering practices, and providing the necessary care to ensure the plant’s successful recovery.
In the next step, we will discuss how to monitor and adjust your watering routine to assist in the revitalization of the affected plants.
Read more: How To Fix A Cigarette Burn In A Carpet
Step 5: Monitor and Adjust Watering Routine
After taking the necessary steps to fix fertilizer burn, it is important to closely monitor and adjust your watering routine to support the recovery of the affected plants. Proper watering is crucial in maintaining a balanced environment for the plants and ensuring their overall health and growth.
Start by regularly checking the moisture level of the soil. Use a moisture meter or simply feel the soil with your fingers to determine if it is adequately moist. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to waterlogged conditions and further stress the plants.
When watering, aim for deep and thorough irrigation, ensuring that the water reaches the plant’s root zone. This encourages the development of a strong and deep root system, allowing the plant to access moisture and nutrients more effectively.
However, it is important to understand that different plants have different water requirements. Consider factors such as plant species, stage of growth, and environmental conditions. Adjust your watering frequency and duration accordingly to meet the specific needs of each plant.
Keep in mind that consistency is key. Avoid allowing the soil to completely dry out, as this can stress the plants. On the other hand, be cautious of overwatering, which can lead to root rot or other issues. Strive to maintain a consistent moisture level that is appropriate for the plants’ needs.
By closely monitoring the plants and adjusting your watering routine as needed, you can provide the optimal conditions for recovery from fertilizer burn. This step, along with the previous ones, will contribute to the plant’s overall revitalization and future health.
In the next step, we will explore how to properly reapply fertilizer after the plants have fully recovered from fertilizer burn.
Step 6: Reapply Fertilizer Properly
Once your plants have fully recovered from fertilizer burn, you can gradually reintroduce fertilizer to support their ongoing growth and development. However, it is important to do so in a careful and proper manner to avoid any potential recurrence of fertilizer burn.
Before reapplying fertilizer, take the time to reassess the nutrient needs of your plants. Consider factors such as the plant species, growth stage, and any specific nutritional requirements. This will ensure that you choose a fertilizer that provides the necessary nutrients in the right proportions.
When selecting a fertilizer, opt for one that is specifically formulated for your plants’ needs. Look for a balanced fertilizer with nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in appropriate ratios. These three macronutrients are essential for plant growth and should be provided in the correct quantities.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions regarding the application rate and frequency, and always err on the side of caution, applying a bit less than the recommended dose to avoid overfertilizing. Remember that it is better to under-fertilize and adjust gradually, rather than risk causing fertilizer burn again.
Consider using slow-release fertilizers or organic fertilizers, as they offer a gentler and more controlled release of nutrients over time. This helps avoid sudden spikes in nutrient concentration and reduces the risk of fertilizer burn.
When applying fertilizer, ensure even distribution around the root zone of the plants, taking care to avoid direct contact with the stems or foliage. Water the area well after application to help dissolve and disperse the fertilizer into the soil.
Continued monitoring is essential even after reapplying fertilizer. Observe the plants for any signs of stress or imbalance, and adjust your fertilization routine accordingly. Keep in mind that the needs of your plants may change over time, so regular reassessment of their nutritional requirements is important.
By reapplying fertilizer properly, you provide the necessary nutrients for your plants’ continued growth while minimizing the risk of fertilizer burn. With proper care and attention, your plants will thrive and remain healthy.
In the next section, we will share some prevention tips to help you avoid fertilizer burn in the future.
Prevention Tips to Avoid Fertilizer Burn
To prevent fertilizer burn and maintain the health of your plants, it is important to follow proper fertilization practices. Here are some prevention tips to help you avoid fertilizer burn in the future:
- Read and follow instructions: Always read and follow the instructions provided on the fertilizer packaging. Pay attention to the recommended application rates, frequency, and specific instructions for your particular plants.
- Use balanced fertilizers: Choose a balanced fertilizer that provides the essential nutrients your plants need in appropriate ratios. Avoid using fertilizers that are excessively high in salt content, which can increase the risk of fertilizer burn.
- Consider slow-release or organic fertilizers: Slow-release or organic fertilizers release nutrients gradually, reducing the risk of fertilizer burn caused by sudden nutrient spikes. These types of fertilizers provide a more controlled and sustained nutrient supply.
- Test your soil: Conduct a soil test to understand the nutrient levels and pH of your soil. This will help you determine the specific nutrient requirements of your plants and avoid over- or under-fertilizing.
- Apply fertilizer evenly: Ensure even distribution of fertilizer around the root zone of your plants. Avoid concentrated application in one area, as this can lead to localized fertilizer burn. Use a spreader or your hands to evenly distribute the fertilizer.
- Water properly: Proper watering is crucial in preventing fertilizer burn. Water your plants deeply and infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between waterings. This helps prevent salt accumulation and promotes healthy root growth.
- Avoid fertilizing stressed plants: Avoid fertilizing plants that are already stressed from factors such as extreme weather, disease, or insect infestation. Address any existing stressors before applying fertilizer to prevent further harm.
- Timing is important: Fertilize your plants at the appropriate time, usually during their active growth stages. Avoid fertilizing during periods of extreme heat, drought, or cold, as the plants may be more susceptible to fertilizer burn.
Remember that prevention is key in avoiding fertilizer burn. By following these tips, you can ensure the optimal health and growth of your plants without the risk of fertilizer burn. Regular monitoring, adjusting, and providing proper care will help your plants thrive.
Now that you are equipped with the knowledge to prevent and fix fertilizer burn, you can confidently care for your plants and enjoy their flourishing beauty.
Continued:
Conclusion
Fertilizer burn can be a frustrating setback for any gardener or plant enthusiast. However, with the right knowledge and actions, you can fix and prevent fertilizer burn to ensure the health and vitality of your plants.
In this comprehensive guide, we have discussed the causes, signs, and symptoms of fertilizer burn. We have explored the steps to fix fertilizer burn, including stopping the application of fertilizer, watering the affected area, diluting the soil, applying activated charcoal or compost, monitoring and adjusting the watering routine, and reapplying fertilizer properly.
Additionally, we have provided prevention tips to help you avoid fertilizer burn in the future. By following these tips, such as reading and following instructions, using balanced fertilizers, and testing your soil, you can prevent fertilizer burn from occurring in the first place.
It is important to remember that plants have specific nutrient requirements and are prone to burn if those requirements are not met. Proper care and attention to their needs will lead to healthier and more resilient plants.
By staying vigilant, monitoring your plants regularly, and adjusting your practices as necessary, you can foster a thriving environment for your plants to grow and flourish.
Remember, each plant is unique, and finding the right balance of nutrients, water, and care requires observation and understanding. As you continue your journey in gardening, keep learning and experimenting to provide the best conditions for your plants’ success.
Now armed with the knowledge and steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently address and prevent fertilizer burn, leading to a garden filled with vibrant and flourishing plants.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Fix Fertilizer Burn
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Fix Fertilizer Burn”