
Articles
How To Store A Magnet
Modified: January 7, 2024
Discover the best way to safely store your magnets with our helpful articles. Keep your collection organized and protected for years to come.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to storing magnets, there are certain considerations you need to keep in mind to ensure their longevity and effectiveness. Magnets are fascinating objects that can be found in various sizes and strengths, from small fridge magnets to powerful rare earth magnets used in industries.
Understanding how to properly store magnets is crucial to maintain their magnetic properties and avoid any potential hazards. Whether you’re a hobbyist or using magnets for industrial or scientific purposes, this comprehensive guide will provide you with valuable insights on how to store magnets correctly.
In this article, we will discuss the factors that can affect magnet storage, the necessary preparations before storing magnets, suitable storage containers, ideal storage locations, and tips to prevent magnet demagnetization and maintain safe distances between magnets. We will also cover the storage of different types of magnets, including rare earth magnets and ferromagnetic materials.
So, if you’re ready to learn the ins and outs of magnet storage, let’s dive right in!
Key Takeaways:
- Proper storage of magnets is crucial to maintain their magnetic properties, effectiveness, and longevity. Understanding factors like temperature, moisture, and magnetic interactions is key to ensuring optimal magnet performance.
- Preparing magnets for storage, choosing suitable storage containers, and maintaining safe distances between magnets are essential for preserving their integrity and preventing unintended interactions or damage. Following specific guidelines for different types of magnets, such as rare-earth magnets and ferromagnetic materials, ensures their longevity and effectiveness.
Understanding Magnets
Before we delve into the details of storing magnets, it’s important to have a basic understanding of how magnets work. Magnets have two poles, commonly known as the north and south poles. These poles exhibit attracting and repelling forces when they come in contact with each other.
Magnets are made up of tiny magnetic domains, which are groups of atoms that align their magnetic fields in the same direction. When these domains align, they create a magnetic field that extends outwards from the magnet. The strength of a magnet is determined by the alignment and density of these domains.
There are different types of magnets, with varying strengths and magnetic properties. The most common types are permanent magnets and electromagnets. Permanent magnets, as the name suggests, retain their magnetic properties over a long period of time. They are made from materials such as ferrite, alnico, and rare earth metals like neodymium and samarium cobalt.
Electromagnets, on the other hand, are temporary magnets that require an electric current to produce a magnetic field. They are created by winding a wire coil around a ferromagnetic core, such as iron or steel, and passing an electric current through the coil to generate the magnetic field.
The strength of a magnet is typically measured by its magnetic field, which is usually expressed in units of gauss or tesla. The larger the value, the stronger the magnetic field. Strong magnets, such as neodymium magnets, can have magnetic fields that are thousands of times greater than the Earth’s magnetic field.
Now that we have a better understanding of how magnets work, let’s proceed to explore the factors that can impact magnet storage.
Factors Affecting Magnet Storage
Several factors can affect the storage of magnets and their overall performance. Understanding these factors is crucial for maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of magnets. Let’s take a look at some key considerations:
1. Temperature: Temperature plays a significant role in magnet stability. Extreme heat or cold can impact the magnetic properties of magnets. High temperatures can cause magnets to lose their magnetism, while extremely low temperatures can cause them to become brittle and more susceptible to damage.
2. Moisture and Humidity: Magnets, especially those made from iron or steel, are prone to rust or corrosion when exposed to moisture or high humidity levels. This can lead to a reduction in their magnetic strength and can even cause them to deteriorate over time.
3. Mechanical Stress: Magnets are sensitive to mechanical stress such as impact, vibration, and pressure. Excessive force or rough handling can cause the magnetic domains to shift, affecting the overall magnetic properties of the magnet.
4. Magnet-to-Magnet Interaction: When magnets come into contact with each other, they can attract or repel one another. These forces can cause magnets to chip, crack, or lose their magnetism if they collide with too much force.
5. Magnetic Fields: Continuous exposure to strong magnetic fields can demagnetize or weaken magnets over time. It’s essential to store magnets away from objects that generate strong magnetic fields, such as electrical equipment, electronic devices, and other magnets.
6. Shielding: Some magnets, especially rare earth magnets, can be highly reactive to magnetic fields. It’s crucial to store them in non-magnetic containers or wrap them in materials like mu-metal or soft iron to shield them from external magnetic forces.
By taking these factors into account, you can ensure a proper storage environment for your magnets. In the next section, we’ll discuss the necessary preparations before storing magnets.
Preparing for Storage
Before you store your magnets, there are a few essential preparations you should undertake to ensure their longevity and performance. Follow these steps to adequately prepare your magnets for storage:
1. Clean the Magnets: Remove any dust, dirt, or debris from the surface of the magnets. Use a soft cloth or brush to gently clean them. Avoid using abrasive materials that could scratch or damage the magnets.
2. Inspect for Damage: Check the magnets for any signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or uneven surfaces. Damaged magnets may have compromised magnetic properties, so it’s important to address any issues before storage.
3. Demagnetize if Necessary: If you need to demagnetize a magnet before storage, you can gradually heat it or expose it to a strong magnetic field that is opposite to its own polarity. However, be cautious as improper demagnetization can permanently affect the magnet’s magnetic properties.
4. Handle with Care: When handling magnets, be careful to avoid dropping or slamming them together. The impact can cause damage to the magnets and affect their magnetic properties.
5. Keep Magnetic Fields in Mind: Ensure that you are working in an environment away from strong magnetic fields or objects that could interfere with the magnetism of your magnets. This includes keeping them away from electronic devices, electrical wires, and other magnets.
6. Label and Document: It’s a good practice to label your magnets or keep a record of their specifications, such as size, material, and magnetic strength. This information will come in handy when you retrieve or use them in the future.
By taking these preparatory steps, you are setting the stage for proper magnet storage. In the next section, we will explore suitable storage containers for your magnets.
Proper Cleaning and Inspection
Before storing magnets, it is crucial to clean and inspect them thoroughly to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Follow these steps to properly clean and inspect your magnets:
1. Gather the necessary cleaning supplies: Prepare a soft cloth or brush, mild soap, and warm water. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could damage the magnets.
2. Remove any dirt or debris: Use the soft cloth or brush to gently remove any dirt, dust, or debris from the surface of the magnets. Be careful not to scratch or damage the magnets during the cleaning process.
3. Clean the magnets: Fill a basin or sink with warm water and add a small amount of mild soap. Dip the magnets into the soapy water and gently scrub them using the cloth or brush. Pay close attention to any hard-to-reach areas or crevices.
4. Rinse thoroughly: After cleaning the magnets, rinse them thoroughly with clean water to ensure that no soap residue remains. Make sure to remove all traces of soap to prevent any potential buildup on the surface of the magnets.
5. Dry the magnets: Use a soft, dry cloth to gently pat the magnets dry. Avoid using excessive force or heat to dry them, as this can damage the magnets. Allow the magnets to air dry completely before storing them.
6. Inspect for any damage: After cleaning, carefully examine the magnets for any signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or uneven surfaces. If you notice any damage, it is essential to address it before storing the magnets.
7. Check the magnetic strength: Test the magnetic strength of the magnets by bringing them near metal objects or other magnets. If you notice a significant decrease in their attracting force, it may indicate a loss of magnetism and should be noted for future reference.
By following these cleaning and inspection steps, you can ensure that your magnets are in optimal condition before storing them. In the next sections, we will explore suitable storage containers and locations for your magnets.
Read more: How To Fix Magnetic Blinds
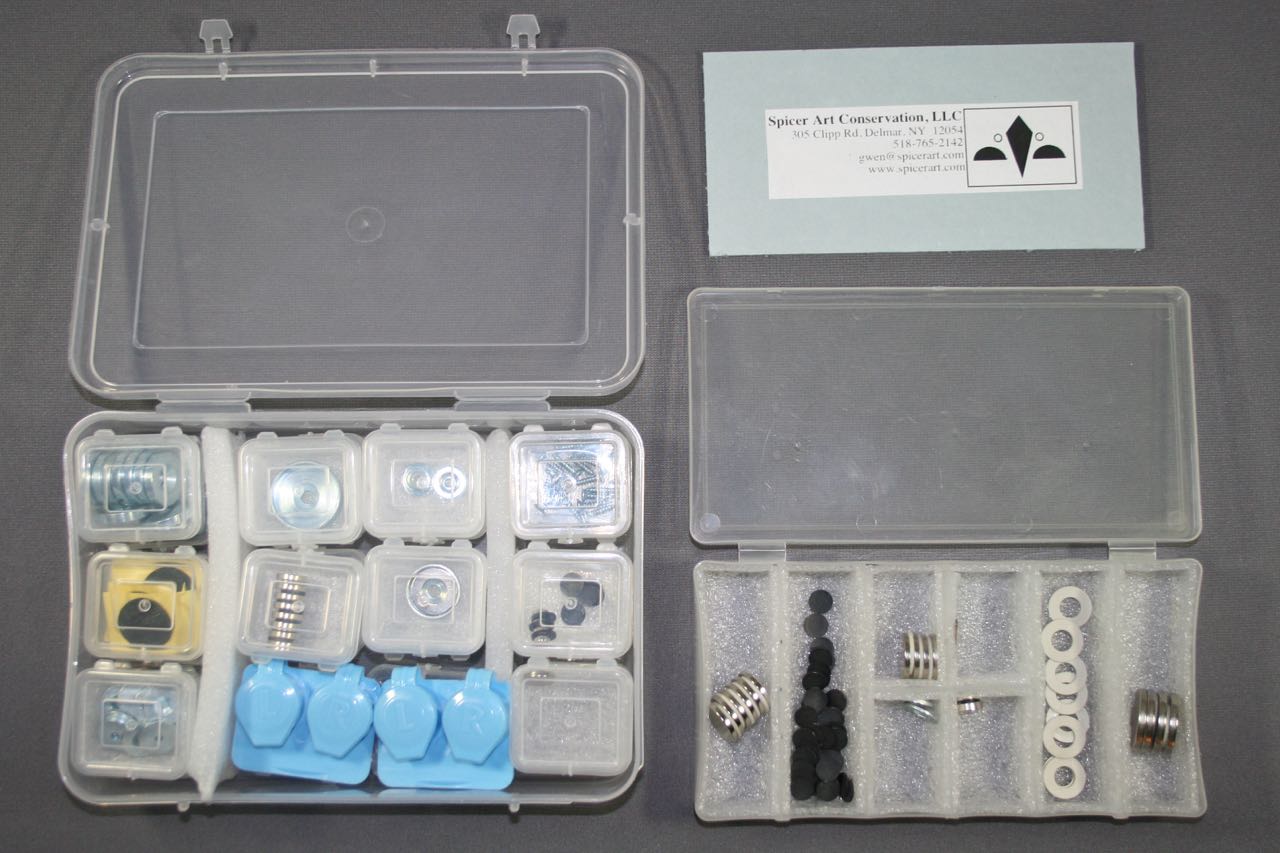
Choosing Suitable Storage Containers
Choosing the right storage containers for your magnets is essential to protect them from external factors and ensure their longevity. Here are some factors to consider when selecting suitable storage containers:
1. Non-magnetic materials: Opt for containers made of non-magnetic materials such as plastic, glass, or wood. Avoid using metal containers, as they can interfere with the magnetism of the stored magnets.
2. Size and shape: Select containers that provide enough space for your magnets, allowing them to be stored without touching or colliding with each other. Consider the size and shape of your magnets to ensure a proper fit within the containers.
3. Individual compartments: If you have multiple magnets, consider using containers that have individual compartments. This will prevent magnets from attracting or repelling each other and causing damage.
4. Cushioning material: Use cushioning materials such as foam, felt, or soft fabric to line the containers. This provides an extra layer of protection and minimizes the risk of scratches or damage to the magnets during storage.
5. Sealable containers: Choose containers that have tight-sealing lids or closures to prevent dust, moisture, or humidity from entering and affecting the magnets. This will help maintain the integrity of the magnets over time.
6. Transparent containers: Consider using transparent containers, such as plastic storage boxes with clear lids. This allows you to easily identify the magnets without the need to open or disturb the storage containers.
7. Labeling: Label the storage containers with specific information about the magnets they hold, such as magnet type, size, and magnetic strength. This will help you easily locate the desired magnets when needed.
Remember to store your magnets in a location away from strong magnetic fields, electronic devices, or other potential sources of interference. By choosing the right storage containers, you can ensure the safety and protection of your magnets for years to come.
Best Storage Locations
Choosing the right storage location for your magnets is crucial to maintain their magnetic properties and prevent any potential damage. Here are some guidelines for selecting the best storage locations:
1. Dry and Cool Environment: Ideally, store your magnets in a dry and cool environment. Moisture and high humidity can potentially cause rust or corrosion, which can degrade the magnets’ performance over time. Avoid areas prone to leaks, excessive condensation, or high levels of humidity.
2. Low Dust and Debris: Minimize exposure to dust and debris, as they can accumulate on the magnets’ surfaces and interfere with their magnetic strength. Choose storage locations that are relatively clean or consider covering the containers to provide additional protection.
3. Away from Direct Sunlight: Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can lead to temperature fluctuations, which may affect the magnetic properties of the stored magnets. Find a storage location away from windows or consider using opaque containers to shield the magnets from sunlight.
4. Controlled Temperature: Aim for a stable and controlled temperature for your storage location. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can impact the magnets’ magnetic properties. Avoid areas that experience frequent temperature fluctuations or extreme temperature conditions.
5. Secure and Stable: Ensure that the storage location is secure and stable, minimizing the risk of accidental falls or movements that could damage the magnets. Avoid storing magnets in areas prone to vibrations or physical disturbances, as these can impact their alignment and magnetism.
6. Away from Electronics: Keep your magnets away from electronic devices, including computers, televisions, and mobile phones. These devices can produce electromagnetic fields that may interfere with the magnetic properties of the magnets. Maintain a safe distance to avoid any unwanted interactions.
7. Consider Special Requirements: Certain types of magnets may have specific storage requirements. For example, if you have rare earth magnets, they may require extra caution due to their stronger magnetic fields. Be sure to follow any recommended guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
By selecting the best storage location for your magnets, you can ensure their longevity and optimal performance. In the next sections, we will discuss how to keep magnets away from electronics and prevent magnet demagnetization.
Keeping Magnets Away from Electronics
When storing magnets, it is crucial to keep them away from electronics to prevent any interference or damage. Electronic devices can generate electromagnetic fields that can affect the magnetic properties of the stored magnets. Here are some key considerations to keep magnets away from electronics:
1. Safe Distance: Maintain a safe distance between magnets and electronic devices. The exact distance may vary depending on the strength of the magnets and the sensitivity of the electronic equipment. However, a general guideline is to keep a distance of at least several inches or centimeters.
2. Magnetic Shielding: For stronger magnets or in cases where proximity to electronics cannot be avoided, consider using magnetic shielding materials. Materials like mu-metal or soft iron can absorb or redirect magnetic fields, reducing the potential impact on nearby electronic devices.
3. Keep Magnets and Electronics Separate: Store magnets in a different location from electronic devices, especially those with sensitive components like hard drives, credit cards, or pacemakers. It is important to avoid direct contact or close proximity that could potentially cause damage or disruption to the electronics.
4. Optimal Storage Distance: Different electronic devices have varying levels of susceptibility to magnetic fields. It is advisable to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or research the specific electronic device to determine the optimal storage distance for magnets.
5. Non-Magnetic Storage Containers: Store magnets in non-magnetic containers, such as plastic or wood, to minimize the risk of magnetic fields affecting nearby electronics. Avoid storing magnets in metal containers as they can amplify the magnetic fields and potentially interfere with electronic devices.
6. Handle Magnets with Care: When handling magnets near electronic devices, exercise caution to prevent accidental contact or collision. Dropping or placing magnets directly onto electronic devices can cause damage to their internal components.
7. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: If you are unsure about the potential impact of magnets on specific electronic devices, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or contact their customer support for advice. They can provide specific recommendations based on the device’s specifications.
By keeping magnets away from electronics and following these guidelines, you can minimize the risk of interference or damage to electronic devices while ensuring the integrity of the stored magnets. Next, we will explore measures to prevent magnet demagnetization.
Store magnets in a cool, dry place away from heat and direct sunlight to prevent them from losing their magnetism. Keep them away from electronic devices and credit cards to avoid interference.
Preventing Magnet Demagnetization
Preventing magnet demagnetization is essential to maintain the magnetic properties and effectiveness of your magnets. Demagnetization can occur due to various factors, such as exposure to high temperatures, strong magnetic fields, or physical impacts. Here are some measures to prevent magnet demagnetization:
1. Temperature Control: Avoid exposing magnets to extreme temperatures. High temperatures can cause magnets to lose their magnetism or weaken their magnetic fields. Similarly, rapid temperature changes can also negatively affect their magnetic properties. Store magnets in a cool and stable environment to minimize the risk of demagnetization.
2. Magnetic Field Exposure: Keep magnets away from strong magnetic fields or magnetic materials. Continuous exposure to such fields can weaken or demagnetize magnets over time. Store magnets in a location that is isolated from other magnets, electrical devices, or sources of strong magnetic fields.
3. Magnetic Shielding: Use magnetic shielding materials, such as mu-metal or soft iron, to protect magnets from external magnetic fields. These materials can help redirect or absorb magnetic fields, reducing the risk of demagnetization.
4. Proper Handling: Handle magnets with care to prevent physical impacts that can lead to demagnetization. Dropping or colliding magnets together can disrupt the alignment of their magnetic domains, causing a loss of magnetism. Avoid rough handling and store them in a secure manner to minimize the risk of damage.
5. Magnetize Using Correct Techniques: If you need to magnetize or remagnetize a magnet, ensure that you use the appropriate techniques and equipment recommended for the specific magnet type. Incorrect magnetization procedures can negatively impact the magnet’s magnetic properties.
6. Avoid Mechanical Stress: Magnets are sensitive to mechanical stress. Avoid bending, twisting, or subjecting them to excessive pressure. Mechanical stress can lead to changes in the magnetic domains, resulting in reduced magnetism or complete demagnetization.
7. Store Rare Earth Magnets in Proper Conditions: Rare earth magnets, such as neodymium magnets, are particularly susceptible to demagnetization. Store them away from other magnets, high temperatures, and strong magnetic fields. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the proper storage and handling of these magnets.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can effectively preserve the magnetic properties of your magnets and ensure their long-term performance. In the next section, we will discuss maintaining safe distances between magnets to avoid undesirable interactions.
Read more: How To Install Magnetic Door Lock
Maintaining Safe Distances between Magnets
Maintaining safe distances between magnets is crucial to prevent unintended interactions, collisions, or damage. When magnets come into contact with each other, they can attract or repel, leading to potential hazards or disruption. Here are some guidelines for maintaining safe distances between magnets:
1. Keep Similar Pole Magnets Apart: Similar pole magnets, that is, two north poles or two south poles, will repel each other. It is important to store them separately to avoid unintended attraction or damage. Place a barrier or sufficient distance between them to prevent accidental contact or collision.
2. Avoid Stacking Magnets: Stacking magnets on top of each other can lead to potential hazards. The magnets can attract or repel with a considerable force, leading to their sudden separation or even causing injury. Store magnets in single layers or use dividers or non-magnetic materials to keep them separated.
3. Use Individual Compartments: When storing multiple magnets, consider using storage containers with individual compartments. This ensures that each magnet has its own designated space, preventing direct contact or unwanted interactions. Individual compartments help maintain safe distances and minimize the risk of damage.
4. Label or Mark Pole Orientation: To avoid confusion and unintended reactions, label or mark the pole orientation of the magnets. Indicate the north and south poles clearly to ensure proper alignment when handling or storing the magnets. This will help you maintain safe distances and minimize the risk of attracting or repelling magnets unintentionally.
5. Consider Magnet Size and Strength: Take into account the size and strength of the magnets when determining safe distances. Stronger magnets with higher magnetic fields may require larger safe distances to prevent unwanted interactions. Larger magnets may also require more space to maintain safe distances between them.
6. Be Mindful of Surrounding Objects: Consider the presence of other magnetic or sensitive objects in the vicinity of your magnets. Certain items, such as credit cards, electronics, or mechanical watches, can be affected by strong magnetic fields. Maintain safe distances between magnets and these objects to avoid any unintended consequences or damage.
7. Consult Manufacturer Guidelines: Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or recommendations for specific magnets, especially if they have unique properties or requirements. Some magnets may require specific safe distances or precautions based on their composition, size, or strength.
By following these guidelines and maintaining safe distances between magnets, you can reduce the risk of unintended interactions, collisions, or damage. In the next sections, we will discuss the storage of different types of magnets, including rare-earth magnets and ferromagnetic materials.
Storing Different Types of Magnets
When it comes to storing different types of magnets, it’s important to consider their unique properties and requirements. Magnets can vary in composition, strength, and susceptibility to external factors. Let’s explore the specific considerations for storing two common types of magnets: rare-earth magnets and ferromagnetic materials.
Storing Rare-Earth Magnets:
Rare-earth magnets, such as neodymium magnets, are known for their exceptional strength and magnetic properties. However, they are also more prone to demagnetization than other types of magnets. Here are some tips to store rare-earth magnets:
1. Keep Them Separated: Store rare-earth magnets separately from other types of magnets. Their strong magnetic fields can potentially interfere with or demagnetize nearby magnets.
2. Avoid Direct Contact: Prevent rare-earth magnets from directly touching each other or other ferromagnetic materials. The strong attraction between these magnets can lead to collisions or damage.
3. Use Non-Magnetic Separators: In case you need to store multiple rare-earth magnets together, utilize non-magnetic separators, such as foam blocks or plastic dividers. This will create safe distance and minimize the risk of unintended interactions.
4. Shielding: Consider using magnetic shielding materials, such as mu-metal or soft iron, to protect rare-earth magnets from external magnetic fields. These materials can help redirect or absorb magnetic fields that may weaken or demagnetize the magnets.
Storing Ferromagnetic Materials:
Ferromagnetic materials, such as iron or steel, can retain their magnetism even after they have been magnetized. Proper storage is crucial to maintain their magnetic properties and prevent unintended magnetic effects. Here are some guidelines for storing ferromagnetic materials:
1. Shield from External Magnetic Fields: Protect ferromagnetic materials from exposure to strong or fluctuating magnetic fields. Store them away from magnets, electrical devices, or other sources of magnetism that can affect their magnetic properties.
2. Prevent Moisture and Rust: Ferromagnetic materials are susceptible to rust or corrosion when exposed to moisture. Ensure a dry storage environment and consider using desiccants or anti-rust products to inhibit the formation of rust or corrosion.
3. Lubrication: Apply a thin layer of lubrication, such as oil or grease, to ferromagnetic materials to prevent rust and maintain their magnetic properties. This is particularly important for tools or equipment made from ferromagnetic materials.
4. Store Flat and Stable: Store ferromagnetic materials in a flat and stable position to avoid warping or deformation. Keeping them properly supported and secure will help maintain their integrity and prevent any damage.
Remember to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or guidelines specific to the type of magnet or material you are storing. By following these tips, you can ensure the longevity, effectiveness, and safety of different types of magnets. In the next section, we will conclude our discussion.
Read more: How To Use Magnetic Stud Finder
Storing Rare Earth Magnets
Rare-earth magnets, such as neodymium magnets, are known for their exceptional strength and magnetic properties. However, they are also more prone to demagnetization than other types of magnets. Proper storage is crucial to maintain the integrity and effectiveness of rare-earth magnets. Here are some guidelines for storing rare-earth magnets:
1. Keep Them Separated: Store rare-earth magnets separately from other types of magnets. Due to their strong magnetic fields, they can potentially interfere with or demagnetize nearby magnets. Keeping them separate minimizes the risk of unintended interactions.
2. Avoid Direct Contact: Prevent rare-earth magnets from directly touching each other or other ferromagnetic materials. The strong attraction between these magnets can lead to collisions, chipping, or damage. Use non-magnetic spacers or separators to maintain a safe distance between the magnets.
3. Use Non-Magnetic Storage Containers: Store rare-earth magnets in non-magnetic containers such as plastic or glass. These materials will provide insulation from external magnetic fields and minimize the risk of demagnetization. Avoid using metal containers, as they can amplify the magnetic fields and potentially interfere with the magnets.
4. Shielding: Consider using magnetic shielding materials to provide additional protection for rare-earth magnets. Mu-metal or soft iron can help redirect or absorb external magnetic fields, reducing the risk of demagnetization. Wrap the magnets in these materials or place them in shielded containers for added security.
5. Avoid Temperature Extremes: Rare-earth magnets are sensitive to temperature changes. High temperatures can cause them to lose their magnetism or weaken their magnetic fields. Avoid exposing them to extreme heat or direct sunlight. Store them in a temperature-controlled environment, preferably at room temperature.
6. Keep Them Dry: Moisture can lead to rust or corrosion, which can degrade the magnets’ performance. Store rare-earth magnets in a dry environment and consider using desiccant packs to absorb any excess moisture. Ensure that the containers are tightly sealed to prevent the entry of moisture.
7. Handle with Care: Rare-earth magnets are very strong and can cause injuries when mishandled. Always handle them with caution, wearing protective gloves if necessary. Avoid placing them near sensitive body parts or electronic devices, as their strong magnetic fields can cause harm or interference.
Following these guidelines will help ensure the longevity and effectiveness of rare-earth magnets. Remember to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or guidelines specific to the magnets you are storing. With proper storage, your rare-earth magnets will remain powerful and reliable for your desired applications.
Storing Ferromagnetic Materials
Ferromagnetic materials, such as iron or steel, possess magnetic properties and can retain their magnetism even after being magnetized. Proper storage of ferromagnetic materials is essential to preserve their magnetic properties and prevent unintended magnetic effects. Here are some guidelines for storing ferromagnetic materials:
1. Shield from External Magnetic Fields: Protect ferromagnetic materials from exposure to strong or fluctuating magnetic fields. Store them away from magnets, electrical devices, or other sources of magnetism that can interfere with their magnetic properties. Keep a safe distance from electromagnetic equipment like speakers or transformers.
2. Prevent Moisture and Rust: Ferromagnetic materials are susceptible to rust or corrosion when exposed to moisture. It is crucial to store them in a dry environment with low humidity. Use desiccant packs or silica gel to absorb any excess moisture. Additionally, apply a thin layer of rust-prevention oil or lubricant to protect them from rusting.
3. Store Flat and Stable: Place ferromagnetic materials in a flat and stable position to prevent warping or deformation. Avoid stacking them or placing heavy objects on top, as this can lead to permanent distortions. Provide adequate support and ensure they are stored securely to prevent accidental falls or damage.
4. Maintain Clean Surfaces: Before storing ferromagnetic materials, ensure that their surfaces are clean and free from dust, dirt, or debris. Use a soft cloth or brush to remove any contaminants that may interfere with their magnetic properties. Keeping them clean will help optimize their performance and longevity.
5. Proper Ventilation: While it is important to store ferromagnetic materials in a dry environment, it is also necessary to provide proper ventilation. Adequate airflow helps prevent the accumulation of moisture or the formation of condensation, which can contribute to rust or corrosion. Avoid tightly sealing containers unless using moisture-resistant ones.
6. Organize and Label: Organize your ferromagnetic materials in a systematic manner, such as grouping them by type, size, or application. This will make it easier to locate specific materials when needed. Additionally, label each storage container to identify the contents, saving time and effort in the future.
7. Handle with Care: When handling ferromagnetic materials, be cautious of their magnetic properties. Keep them away from sensitive electronic devices like computers, pacemakers, or credit cards, as strong magnetic fields can interfere with their operation. Wear protective gloves if necessary, and avoid direct contact with skin or body parts.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively store ferromagnetic materials and maintain their magnetic properties for long-lasting use. Always consult any specific recommendations or guidelines provided by the manufacturer for optimal storage conditions of the particular material you are working with.
Conclusion
Proper storage of magnets is crucial to maintain their magnetic properties, effectiveness, and longevity. By understanding the factors that can affect magnet storage and implementing the necessary precautions, you can ensure the optimal performance of your magnets. Here are the key takeaways from this comprehensive guide:
– Understanding the basics of magnets, including their poles, magnetic fields, and different types, helps in handling and storing them effectively.
– Factors like temperature, moisture, mechanical stress, and magnetic interactions can impact magnet storage.
– Preparing magnets for storage through proper cleaning, inspection, and demagnetization ensures their optimal condition.
– Choosing suitable storage containers, such as non-magnetic, individual compartments, helps protect magnets from damage and interference.
– Selecting the best storage locations, away from direct sunlight, humidity, and strong magnetic fields, guarantees their safety and performance.
– Keeping magnets away from electronics minimizes the risk of interference and potential damage to electronic devices.
– Preventing magnet demagnetization involves controlling temperature, shielding magnetic fields, and handling magnets with care.
– Maintaining safe distances between magnets prevents unintended interactions, collisions, or damage.
– Different types of magnets, such as rare-earth magnets and ferromagnetic materials, have specific storage considerations.
– Proper storage of rare-earth magnets involves keeping them separated, avoiding direct contact, and using non-magnetic containers and shielding materials.
– Storing ferromagnetic materials necessitates protecting them from external magnetic fields, preventing moisture and rust, and ensuring flat and stable storage.
By following these guidelines and considering the unique properties of each magnet type, you can ensure the integrity and longevity of your magnets for various applications, whether in industries, laboratories, or as simple everyday tools.
Remember to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or guidelines specific to your magnets, as they may have additional advice or requirements for proper storage. With the right storage practices, your magnets will remain powerful, reliable, and ready for use whenever you need them.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store A Magnet
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Store A Magnet”