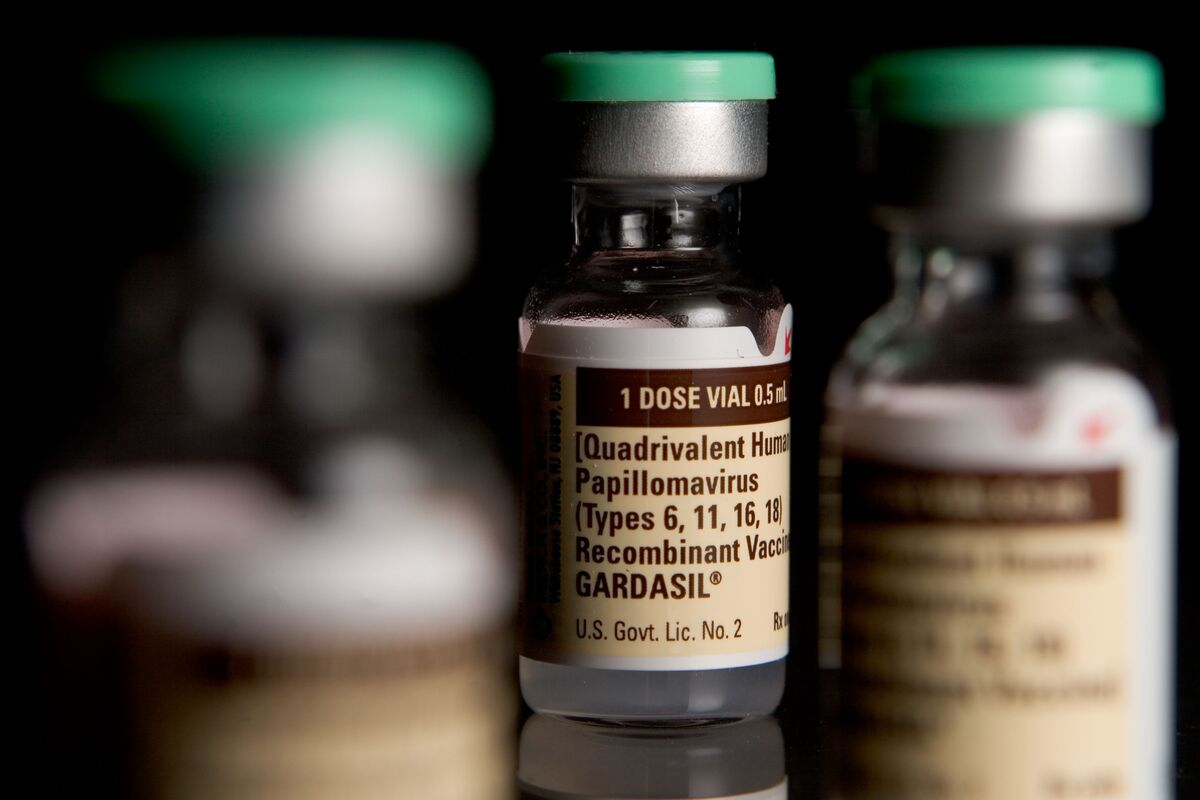
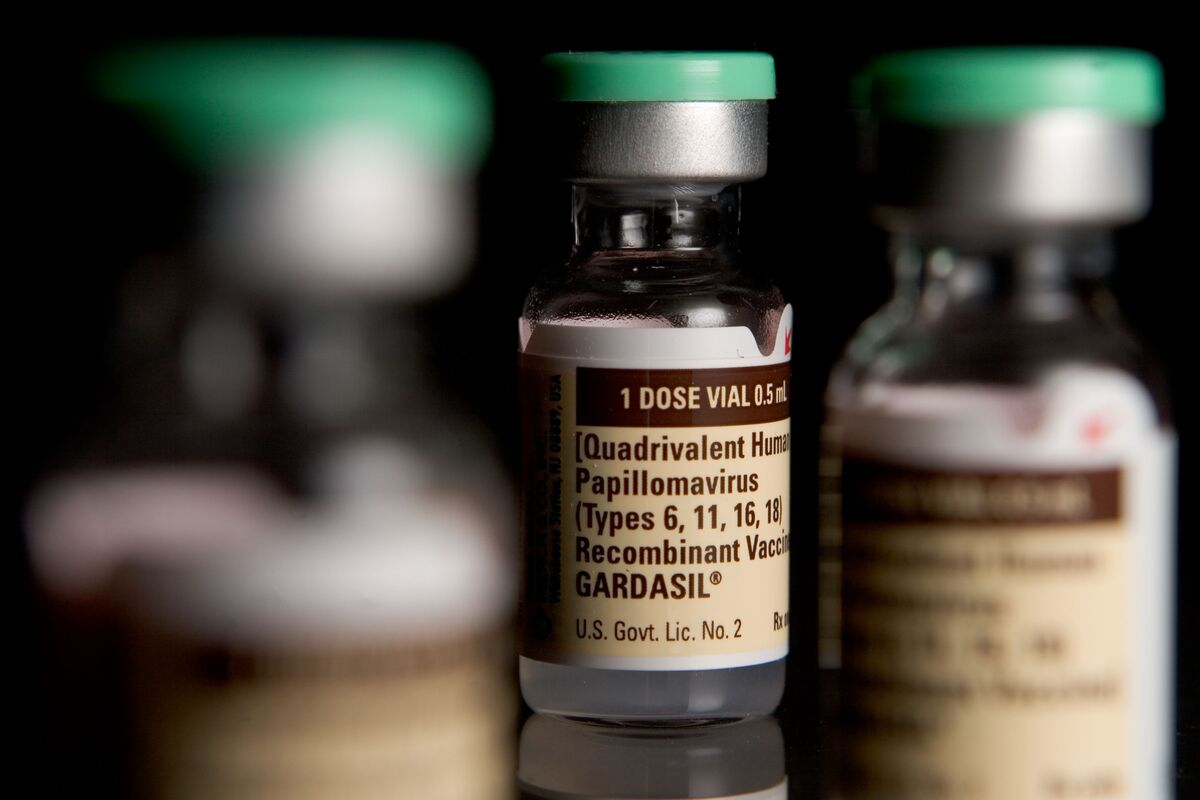
Articles
How To Store Gardasil
Modified: February 20, 2024
Learn how to store Gardasil safely and effectively with these informative articles. Discover best practices and tips for keeping your vaccine in optimal condition.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Gardasil is a well-known vaccine that provides protection against several strains of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), a common sexually transmitted infection. This vaccine has been proven to be highly effective in preventing HPV-related diseases, including cervical, vulvar, vaginal, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers, as well as genital warts.
When it comes to the storage of Gardasil, proper handling and storage conditions are crucial to maintain its effectiveness. Improper storage can lead to a reduction in potency, rendering the vaccine less effective in providing the necessary protection against HPV.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of storing Gardasil correctly and provide you with essential guidelines to ensure its quality and efficacy. By following these recommendations, healthcare providers can confidently administer the vaccine, knowing that it will offer the maximum benefit to their patients.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper storage of Gardasil, including maintaining the recommended temperature range of 2°C to 8°C, is crucial to ensure the vaccine’s potency and effectiveness in protecting against HPV-related diseases.
- Training staff on storage procedures, monitoring temperature fluctuations, and maintaining proper storage documentation are essential components of effective vaccine management for Gardasil.
Read more: How To Store Store-Bought Bread
Understanding Gardasil
Gardasil is a vaccine that is specifically designed to prevent infections caused by certain strains of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection that can lead to various types of cancers and genital warts. The vaccine is primarily used to protect against HPV types 16 and 18, which are responsible for causing most cases of cervical cancer.
Since its introduction, Gardasil has proven to be highly effective in preventing HPV-related diseases. It contains virus-like particles (VLPs) derived from the outer shell of the HPV viruses, which stimulate an immune response without causing infection. This leads to the production of antibodies that provide protection against the targeted HPV strains.
Gardasil is administered via a series of injections, typically three doses over a period of six months. It is recommended for both males and females, usually between the ages of 9 and 26, although it can be administered to individuals up to age 45 in certain cases. The vaccine is most effective when given before individuals become sexually active and are exposed to the virus.
It is essential to note that Gardasil does not protect against all HPV types. However, by preventing infection with the targeted strains, it significantly reduces the risk of developing HPV-related diseases. Therefore, it is crucial to store Gardasil properly to ensure its full potency and efficacy.
Importance of Proper Storage
Proper storage of Gardasil is of utmost importance to ensure its potency and effectiveness. Vaccines, including Gardasil, are sensitive biological products that can be affected by improper storage conditions. If not stored correctly, the vaccine’s efficacy may be compromised, and it may not provide the intended protection against the targeted HPV strains.
When a vaccine is exposed to adverse storage conditions, such as improper temperatures or light exposure, there is a risk of degradation of the active ingredients. This can lead to a reduction in potency, rendering the vaccine less effective in stimulating the desired immune response. If administered in such a compromised state, the vaccine may not provide the level of protection needed to prevent HPV-related diseases.
Proper storage not only helps maintain the vaccine’s potency, but it also ensures the safety of patients. Vaccines that are stored incorrectly may be at risk of contamination, which can compromise the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine. Patients rely on healthcare providers to administer safe and effective vaccines, so proper storage practices are essential to meet these expectations.
Additionally, healthcare providers who administer vaccines are subject to regulatory requirements and guidelines. These guidelines outline the specific storage conditions that must be adhered to in order to maintain vaccine potency and ensure patient safety. Failure to comply with these guidelines can lead to regulatory penalties, as well as potential legal and ethical consequences.
In summary, proper storage of Gardasil is crucial to maintain the vaccine’s potency, ensure patient safety, and comply with regulatory requirements. By following recommended storage practices, healthcare providers can confidently administer Gardasil, knowing that it will provide the maximum benefit and protection against HPV-related diseases.
Recommended Storage Requirements
To maintain the potency and effectiveness of Gardasil, it is vital to store the vaccine under appropriate conditions. The manufacturer provides specific guidelines for storage requirements, and it is essential to follow these recommendations to ensure the vaccine’s quality and efficacy.
The recommended storage temperature for Gardasil is 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). This temperature range corresponds to the standard refrigerator temperature. Storing the vaccine within this range helps maintain its potency and stability.
It is important to note that fluctuations in temperature can affect the vaccine’s efficacy. Exposure to temperatures outside the recommended range, especially freezing temperatures or temperatures above 8°C (46°F), can lead to a loss of potency. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor the temperature consistently and take necessary measures to prevent temperature excursions.
In addition to temperature requirements, it is essential to protect Gardasil from light exposure. The vaccine should be stored in its original packaging, which provides protection from light. Exposure to direct sunlight or fluorescent light can degrade the vaccine’s potency over time.
Furthermore, it is crucial to prevent the vaccine from freezing. Freezing can cause damage to the vaccine’s structure and render it ineffective. To avoid freezing, it is important to store Gardasil away from the freezer compartment of the refrigerator and ensure that the temperature is consistently maintained above freezing levels.
Considering the importance of maintaining proper storage conditions, it is recommended to use vaccine refrigerators specifically designed for storing vaccines. These refrigerators should be equipped with a reliable thermometer and a temperature alarm system to monitor and notify any temperature deviations.
Regular temperature monitoring is crucial to ensure that the vaccine remains within the recommended temperature range. Temperature logs should be maintained to record the daily temperatures and provide a comprehensive record of storage conditions. This documentation helps identify any temperature excursions and can assist in assessing the vaccine’s viability.
By adhering to these recommended storage requirements, healthcare providers can have confidence in the quality and effectiveness of the Gardasil vaccine. Providing optimal storage conditions is crucial to ensure that the vaccine retains its potency and delivers the desired protection against HPV-related diseases.
Selecting the Storage Location
Choosing the right storage location for Gardasil is an important step in ensuring the vaccine’s potency and efficacy. The storage location should provide the necessary environmental conditions to maintain the recommended temperature range, protect against light exposure, and prevent freezing.
The ideal storage location for Gardasil is a dedicated vaccine refrigerator. These refrigerators are specifically designed to meet the storage requirements of vaccines, including maintaining the recommended temperature range of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Vaccine refrigerators are equipped with features such as temperature controls, alarms, and reliable thermometers to ensure consistent monitoring and maintenance of proper storage conditions.
If a dedicated vaccine refrigerator is not available, an alternative option is a pharmaceutical or medical-grade refrigerator. These refrigerators are also designed to maintain the recommended temperature range and generally offer reliable temperature control and monitoring features.
Regardless of the type of refrigerator used, it is important to ensure that it is in good working condition and regularly calibrated to maintain accurate temperature readings. Thermometers should be placed in a designated area within the refrigerator, away from the walls and door, to ensure accurate temperature measurements.
It is crucial to ensure that the storage location is away from sources of heat or direct sunlight. Placing the refrigerator in a well-ventilated area, away from windows or heating vents, will help maintain a stable temperature and protect the vaccine from light exposure.
In addition to the storage location itself, it is important to consider the accessibility and security of the area. The storage location should be easily accessible to authorized personnel responsible for storing and administering the vaccine. At the same time, it should be secured to prevent unauthorized access, ensuring the safety and integrity of the vaccine supply.
Lastly, it is important to promote good storage practices among staff members responsible for handling and storing the vaccine. Proper training should be provided to ensure that all personnel are knowledgeable about the recommended storage requirements and understand the importance of maintaining proper storage conditions.
By carefully selecting the storage location and adhering to recommended storage practices, healthcare providers can ensure that Gardasil is stored in optimal conditions, retaining its potency and efficacy for maximum protection against HPV-related diseases.
Read more: How To Store Basil From Grocery Store
Storing Gardasil in a Refrigerator
When it comes to storing Gardasil, refrigeration is the preferred method to maintain the vaccine’s potency and effectiveness. Storing the vaccine in a dedicated vaccine refrigerator or a pharmaceutical-grade refrigerator ensures that it remains within the recommended temperature range of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Here are some essential guidelines for storing Gardasil in a refrigerator:
- Designate a specific area: Allocate a designated area within the refrigerator for storing the vaccine. This area should be easily visible and accessible, with enough space to accommodate the vaccine vials.
- Organize the storage: Arrange the vaccine vials in a way that allows for proper air circulation and avoids overcrowding. This prevents temperature fluctuations and ensures that the vaccine remains at a consistent temperature.
- Keep away from walls and doors: Place the vaccine vials away from the walls and door of the refrigerator. This helps to maintain a stable temperature, as these areas are more prone to temperature fluctuations.
- Avoid the freezer compartment: Do not store the vaccine in the freezer compartment of the refrigerator. The freezing temperatures can damage the vaccine and render it ineffective. Ensure that the vaccine vials are kept at a temperature above freezing at all times.
- Protect from light: Make sure that the vaccine vials are stored in their original packaging or in a container that provides protection from light. Exposure to direct sunlight or fluorescent light can degrade the vaccine’s potency over time.
- Monitor temperature regularly: Check the temperature of the refrigerator regularly to ensure that it remains within the recommended temperature range. This can be done using a reliable thermometer placed in the designated vaccine storage area. Keep a temperature log to record daily readings and identify any temperature excursions.
- Address temperature excursions promptly: If a temperature excursion is detected, take immediate action to bring the refrigerator temperature back to the recommended range. This may involve adjusting the temperature settings, relocating the vaccine vials, or repairing any equipment issues. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific instructions on addressing temperature excursions.
By following these guidelines, healthcare providers can ensure that Gardasil is stored properly in a refrigerator, maintaining its potency and efficacy. Regular temperature monitoring and proper handling of the vaccine vials are crucial to ensure that patients receive a vaccine that is safe and effective in preventing HPV-related diseases.
Storing Gardasil in a Freezer
While refrigeration is the preferred method for storing Gardasil, there may be situations where storing the vaccine in a freezer becomes necessary. It is important to note that freezing temperatures can potentially damage the vaccine, so extreme caution must be exercised when considering this storage option.
If storing Gardasil in a freezer is required, here are some important guidelines to follow:
- Use an appropriate freezer: Ensure that the freezer used for storing Gardasil is of high quality and maintains a stable temperature. Medical-grade freezers or ultra-low temperature freezers are recommended, as they are designed to provide consistent and reliable freezing conditions.
- Check the temperature: Set the freezer temperature to maintain a consistent freezing temperature of -15°C to -25°C (-4°F to -13°F). It is important to regularly monitor the freezer temperature to ensure it remains within this range. Use a calibrated thermometer to accurately measure the temperature.
- Use proper storage containers: Store Gardasil vials in appropriate containers that can withstand freezing temperatures. Ensure that the vials are tightly sealed to prevent any moisture or air from entering and potentially compromising the vaccine’s effectiveness.
- Protect from light: Just like storing in a refrigerator, it is important to protect Gardasil from light exposure. Keep the vaccine vials in their original packaging or in opaque containers that provide ample light protection.
- Prevent cross-contamination: If storing Gardasil alongside other items in the freezer, ensure that there is no risk of cross-contamination. Keep the vaccine in a separate, well-labeled section of the freezer to avoid any accidental mix-ups.
- Monitor for temperature fluctuations: During the freezing process or when accessing the freezer, there may be slight temperature fluctuations. Regularly monitor the freezer temperature and minimize the duration and frequency of opening the freezer to maintain the required freezing conditions.
- Thawing and using frozen Gardasil: When it comes time to use the frozen Gardasil, safely thaw the vials in a refrigerator or under cold running water. Do not use any other methods such as microwaving or leaving them at room temperature, as these can compromise the vaccine’s integrity. Once thawed, promptly administer the vaccine following the appropriate protocols.
Storing Gardasil in a freezer should only be considered as a last resort and under exceptional circumstances. Refrigeration remains the preferred method for maintaining the vaccine’s potency and efficacy.
It is important to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and regulatory requirements to determine if freezing Gardasil is an approved storage option. Proper temperature monitoring, correct packaging, and careful handling are essential to ensure that the vaccine remains safe and effective for use.
Storing Gardasil at Room Temperature
Storing Gardasil at room temperature is generally not recommended, as the vaccine is most stable when kept within the recommended temperature range of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in a refrigerator. However, there may be situations where refrigeration is not readily available, and storing the vaccine at room temperature becomes the only option. In such cases, it is important to follow certain guidelines to minimize the risk of compromising the vaccine’s potency and effectiveness.
Here are some important considerations for storing Gardasil at room temperature:
- Temperature range: Choose a storage area with a stable room temperature between 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F). It is crucial to prevent exposure to extreme temperatures, such as excessive heat or cold, as they can degrade the vaccine’s potency.
- Protect from light: Ensure that the vaccine vials are stored in their original packaging or in containers that provide protection from light. Direct sunlight or exposure to fluorescent light can degrade the vaccine over time.
- Monitor temperature regularly: Regularly check the room temperature to ensure that it remains within the recommended range. An ambient temperature monitoring device can be used to provide accurate readings and prompt action if the temperature exceeds the acceptable limits.
- Time limitations: If storing Gardasil at room temperature becomes necessary, it is important to minimize the duration of storage. Aim to use the vaccine as soon as possible and avoid unnecessary delays in administration.
- Temperature excursions: If there is an unexpected temperature fluctuation or if the temperature exceeds the acceptable range, take immediate action to address the issue. Contact the vaccine manufacturer or your healthcare provider for guidance on the appropriate steps to ensure the vaccine’s integrity.
- Thawing frozen vaccine: If you have previously stored Gardasil in the freezer and need to thaw it for room temperature storage, follow the recommended thawing process carefully. Thaw the vials in a refrigerator or under cold running water, and once thawed, promptly transfer them to room temperature storage.
- Discard expired vaccines: Regularly check the vaccine vials for expiration dates. Expired vaccines should be discarded according to proper procedures and should not be stored or used.
It is important to note that storing Gardasil at room temperature should be seen as a temporary solution. Refrigeration remains the preferred method to maintain the vaccine’s potency and ensure its effectiveness. If refrigeration becomes available, the vaccine should be transferred to the appropriate storage conditions as soon as possible.
Ultimately, it is crucial to consult the vaccine manufacturer’s guidelines and local regulations to determine if storing Gardasil at room temperature is permitted and suitable for your specific situation. Proper temperature monitoring and careful handling are key to preserving the vaccine’s quality and efficacy.
Store Gardasil in the refrigerator between 2-8°C (36-46°F) and protect from light. Do not freeze. Keep the vaccine in its original packaging until ready for use.
Avoiding Improper Storage Methods
Proper storage methods are essential to maintain the potency and effectiveness of Gardasil. Avoiding improper storage practices is crucial in ensuring the vaccine’s quality and efficacy. Here are some important recommendations to follow:
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures: Gardasil should not be exposed to extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold. High temperatures can accelerate degradation, while freezing temperatures can damage the vaccine’s structure. Store the vaccine within the recommended temperature range of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) to maintain its potency.
- Do not store in a household refrigerator: It is important not to store Gardasil in a household refrigerator that is used for storing food and other items. The temperature control in these refrigerators may not be consistent or reliable enough to maintain the required temperature range for the vaccine.
- Avoid storage in vaccine carriers or coolers: While vaccine carriers and coolers are useful for transporting vaccines, they are not suitable for long-term storage. These containers may not provide the necessary temperature control and insulation to maintain the proper storage conditions for Gardasil.
- Avoid storing with food or beverages: Do not store Gardasil alongside food items or beverages. This is to prevent any contamination or improper handling that may impact the vaccine’s safety and effectiveness.
- Do not store near heat sources: Keep Gardasil away from heat sources such as heaters, radiators, or heat-emitting equipment. Exposure to excessive heat can compromise the vaccine’s potency and effectiveness.
- Avoid re-freezing previously frozen vaccines: Once Gardasil has been thawed from frozen storage, it should not be refrozen. Freezing and thawing cycles can cause damage to the vaccine’s structure. Use the vaccine promptly after thawing, and if unused, discard any remaining doses following proper disposal protocols.
- Prevent exposure to light: Protect the vaccine from direct sunlight and fluorescent light exposure. Keep the vaccine vials in their original packaging or in containers that provide sufficient light protection to maintain Gardasil’s potency.
- Do not use if compromised or expired: Discard Gardasil if the vials appear damaged, if the seal is broken, or if it has reached the expiration date. Using compromised or expired vaccines can compromise their effectiveness and pose a safety risk to patients.
By avoiding these improper storage methods and adhering to the recommended storage guidelines, healthcare providers can ensure that Gardasil remains in optimal condition. Following proper storage practices is essential to guarantee the vaccine’s integrity and efficacy, providing patients with the maximum protection against HPV-related diseases.
Read more: How To Store Arrows
Checking the Expiration Date
Checking the expiration date of Gardasil is a crucial step in ensuring the vaccine’s efficacy and safety. The expiration date indicates the period during which the vaccine is guaranteed to remain effective if stored properly. Using an expired vaccine can compromise its potency and render it less effective in providing the desired protection against HPV.
Here are some important guidelines for checking and managing the expiration dates of Gardasil:
- Ensure proper vaccine rotation: Implement a system for vaccine rotation to ensure that older stock is used before newer stock. This practice helps prevent the use of expired vaccines and ensures that the vaccine supply remains up to date.
- Regularly review vaccine inventory: Conduct routine checks of your vaccine inventory to identify and remove any expired or soon-to-be expired vials of Gardasil. This should be done in accordance with local regulations and guidelines to ensure proper disposal of expired vaccines.
- Inspect packaging and labels: Examine the packaging and labels of Gardasil vials to locate the expiration date. The expiration date is typically printed on the vial or the outer packaging. Ensure that the packaging is intact and the seal is unbroken before using the vaccine.
- Follow manufacturer’s guidelines: Adhere to the specific recommendations provided by the vaccine manufacturer regarding expiry dates and storage conditions. The manufacturer’s guidelines should be readily available and followed meticulously to ensure the vaccine’s quality and efficacy.
- Utilize a reliable inventory management system: Implement an inventory management system that includes monitoring the expiration dates of all vaccines, including Gardasil. This ensures diligent tracking and enables timely vaccine administration before expiration.
- Train staff on expiry date management: Provide proper training to healthcare personnel responsible for vaccine management regarding the importance of checking and managing vaccine expiration dates. This helps instill a culture of vigilance and ensures adherence to proper storage and inventory practices.
- Discard expired vaccines appropriately: When vaccines, including Gardasil, reach their expiration dates, they should be promptly discarded according to proper disposal protocols. Consult local regulations or reach out to waste management authorities for guidance on safe and responsible disposal.
By consistently checking the expiration date, managing the vaccine inventory effectively, and following proper disposal procedures, healthcare providers can ensure that patients receive Gardasil that is within the designated shelf life, providing the intended protection against HPV-related diseases.
Monitoring Temperature Fluctuations
Monitoring temperature fluctuations is a critical aspect of maintaining the potency and efficacy of Gardasil. Fluctuations outside the recommended temperature range of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) can compromise the vaccine’s effectiveness. It is essential to consistently monitor and address any temperature deviations to ensure the vaccine’s integrity.
Here are some important guidelines for monitoring temperature fluctuations:
- Use a reliable temperature monitoring system: Implement a temperature monitoring system that provides accurate and real-time temperature readings. This can include digital thermometers, data loggers, or temperature monitoring devices specifically designed for vaccine storage. Choose a system that suits your needs and budget while ensuring reliable and consistent monitoring of the refrigerator temperature.
- Regularly check and record temperatures: Conduct routine temperature checks at least twice daily to ensure that the refrigerator remains within the recommended temperature range. Record these temperatures in a designated logbook or digital tracking system to maintain a comprehensive record of temperature monitoring.
- Respond promptly to temperature deviations: If a temperature deviation is noticed, take immediate action to investigate and address the cause of the fluctuation. Common causes of temperature excursions include power outages, equipment malfunctions, or doors left ajar. Promptly rectify the issue and return the temperature to the proper range.
- Develop a temperature excursion protocol: Establish a documented protocol for handling temperature excursions. This should include steps to follow when a deviation occurs, such as notifying appropriate personnel, documenting the event, conducting temperature checks, and taking corrective action.
- Consider temperature monitors with alarms: Invest in temperature monitoring devices that provide audible and visual alarms to alert staff when the temperature goes outside the recommended range. These alarms help ensure that temperature excursions are detected promptly, allowing for immediate intervention and mitigation.
- Perform routine maintenance and calibration: Regularly schedule maintenance and calibration of refrigeration units to ensure their reliability and accuracy. Calibration should be performed by qualified technicians to ensure the temperature readings are precise.
- Train staff on temperature monitoring: Properly train staff members responsible for monitoring temperature fluctuations. They should be educated on the importance of temperature monitoring, how to use the monitoring devices correctly, and how to respond to temperature excursions in accordance with established protocols.
By diligently monitoring temperature fluctuations, healthcare providers can promptly detect and address any deviations, thereby maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of Gardasil. Regular monitoring and appropriate interventions ensure that patients receive a vaccine that is safe and capable of providing optimal protection against HPV-related diseases.
Maintaining Proper Storage Documentation
Documenting the storage conditions of Gardasil is an essential aspect of vaccine management. Proper documentation helps ensure accountability, traceability, and adherence to regulatory requirements. It provides a comprehensive record of the vaccine’s storage history and assists in identifying any issues or deviations that may affect the vaccine’s quality and efficacy.
Here are some important guidelines for maintaining proper storage documentation:
- Record the receipt of vaccines: Document the date of receipt of Gardasil vaccines, including the batch/lot number, quantity received, and expiration dates. This information helps track the vaccine inventory and facilitates timely use before expiration.
- Temperature monitoring records: Maintain a logbook or electronic system to record daily refrigerator temperature readings. Record the date, time, and temperature to provide a comprehensive history of temperature monitoring. This documentation aids in identifying any temperature excursions and allows for appropriate corrective actions to be taken.
- Temperature excursion reports: Document any instances of temperature excursions in a standardized report format. Include details such as the date, time, duration, reason, corrective actions taken, and any follow-up measures. This information helps evaluate the impact of the temperature fluctuation and provides a record of subsequent actions taken to mitigate potential risks.
- Inventory management: Maintain accurate records of vaccine inventory, including the quantity of Gardasil received, used, and remaining. Include information such as lot numbers, expiration dates, and any other relevant details. Regularly update this information to ensure proper tracking of vaccine stock and facilitate efficient rotation and usage.
- Expiry date tracking: Implement a system to track and monitor vaccine expiration dates. Record the expiry dates of Gardasil vials in a logbook or electronic system. Proactively manage expiring vaccines to ensure they are used before their expiration dates or properly discarded if expired.
- Documentation of equipment maintenance: Keep records of maintenance activities, repairs, calibrations, and any modifications made to refrigeration units. Documenting these actions helps ensure the proper functioning of the equipment and aids in regulatory compliance.
- Safe disposal documentation: Maintain documentation of proper disposal procedures for expired or unusable Gardasil vials. Follow disposal protocols mandated by regulatory authorities and record the disposal details, including the date and method of disposal.
- Keep records accessible: Store all storage documentation in a designated, secure location that is easily accessible to authorized personnel. This ensures that the information is readily available for audits, inspections, and reference purposes.
Proper storage documentation not only demonstrates compliance with regulatory requirements but also facilitates effective vaccine management and ensures patient safety. Maintaining accurate and organized records helps identify potential issues, prompt corrective actions, and ensure the integrity and efficacy of Gardasil throughout its lifespan.
Conducting Regular Inventory Checks
Regular inventory checks are a crucial component of proper vaccine management, including the storage of Gardasil. Conducting routine inventory checks helps ensure accurate stock control, timely usage of vaccines, and identification of any discrepancies or issues that may affect the vaccine’s availability and integrity.
Here are some important guidelines for conducting regular inventory checks:
- Establish a schedule: Set a regular schedule for inventory checks to ensure they are performed consistently. The frequency of the checks may depend on the volume of vaccines used and the storage capacity. Typically, monthly or quarterly checks are recommended.
- Verify inventory records: Compare the recorded vaccine quantities, lot numbers, and expiration dates with the physical stock on hand. This helps identify any discrepancies or errors in the inventory records that may affect vaccine availability or result in expired stock.
- Rotate vaccine stock: Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system to ensure proper vaccine rotation. Use older stock before newer stock to minimize the risk of vaccines expiring before they can be utilized.
- Check for damaged packaging: Inspect the packaging of Gardasil vials for any signs of damage, including torn or compromised seals, broken vials, or label discrepancies. Damaged packaging can affect the vaccine’s integrity, and any compromised vaccines should be properly disposed of following the appropriate protocols.
- Review expiration dates: Assess the expiration dates of the vaccines and identify any that are approaching expiration. Ensure that appropriate measures are taken to use or discard vaccines before they expire, following proper disposal procedures.
- Address stock discrepancies: If any discrepancies or irregularities are found during the inventory check, thoroughly investigate the cause and rectify the issue. This may involve documenting and reporting the discrepancy, updating records, investigating possible inventory theft or errors, or seeking guidance from appropriate authorities or supervisors.
- Update inventory records: Keep the vaccine inventory records up to date with accurate information, including quantities received, used, and remaining. This ensures transparency and helps track vaccine utilization and stock replenishment needs.
- Synchronize inventory with vaccine orders: Align the inventory check with vaccine orders to ensure accurate stock replenishment. This helps prevent stockouts or excess inventory and ensures a continuous supply of Gardasil.
Conducting regular inventory checks not only ensures proper stock management but also plays a vital role in maximizing vaccine availability and maintaining the quality and efficacy of Gardasil. By closely monitoring the vaccine inventory and proactively addressing any discrepancies or issues, healthcare providers can confidently administer Gardasil, knowing that the vaccine is readily available and meets the required standards.
Read more: How To Store Roux
Training Staff on Storage Procedures
Proper training of staff members is essential for ensuring the correct storage procedures of Gardasil. Thoroughly educating personnel on storage protocols helps maintain the integrity and effectiveness of the vaccine and reduces the risk of errors or mishandling. Here are some important aspects to consider when training staff on storage procedures:
- Provide comprehensive training: Offer initial and ongoing training to all staff members involved in the storage and handling of Gardasil. This includes healthcare providers, nurses, pharmacists, and any other personnel responsible for vaccine management.
- Explain storage requirements: Clearly explain the recommended storage temperature range of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for Gardasil. Emphasize the importance of maintaining this temperature range to preserve the vaccine’s potency and effectiveness.
- Demonstrate proper storage techniques: Show staff members how to correctly store Gardasil in a designated vaccine refrigerator or pharmaceutical-grade refrigerator. Demonstrate how to organize the vials, protect them from light, and monitor the temperature regularly.
- Emphasize the importance of proper handling: Train staff on proper handling procedures to prevent any damage to the vaccine vials. This includes avoiding excessive shaking or dropping of the vials and ensuring that the seal remains intact before use.
- Explain the potential consequences of improper storage: Educate staff members on the potential risks of improper storage, including the loss of vaccine potency and compromised patient safety. Highlight the impact of temperature excursions, exposure to light, or incorrect storage techniques on the vaccine’s effectiveness.
- Teach temperature monitoring techniques: Provide guidance on how to accurately monitor the refrigerator temperature using thermometers and temperature monitoring devices. Teach staff members to record the temperatures regularly and identify any temperature deviations.
- Train on proper documentation practices: Educate staff members on the importance of maintaining accurate storage documentation, including temperature logs, inventory records, and expiration date tracking. Instruct them on the proper use of logbooks or electronic systems for recording information.
- Reinforce expiry date management: Ensure that staff members understand the significance of regularly checking expiry dates and managing vaccine inventory accordingly. Train them to identify expiring vaccines and follow appropriate procedures for utilization or disposal.
- Encourage a culture of vigilance: Foster a culture of vigilance and accountability within the healthcare facility. Encourage staff members to report any storage or handling incidents, temperature excursions, or concerns regarding Gardasil to their superiors.
- Provide regular refreshers and updates: Conduct periodic training refreshers to reinforce knowledge and address any updates or changes in storage procedures or regulatory requirements. This ensures that staff members stay informed and maintain their competency.
By providing comprehensive training on storage procedures, healthcare facilities can ensure that all staff members involved in vaccine management understand the importance of proper storage and handling techniques for Gardasil. Well-trained staff members will be equipped to maintain the vaccine’s efficacy and protect patients from HPV-related diseases.
Conclusion
Proper storage of Gardasil is crucial to maintain its potency and effectiveness in providing protection against Human Papillomavirus (HPV). By following the recommended storage requirements and guidelines, healthcare providers can ensure that the vaccine remains safe and effective for administration to their patients. Understanding Gardasil and its importance in preventing HPV-related diseases sets the foundation for implementing the necessary storage procedures.
From selecting the appropriate storage location to monitoring temperature fluctuations and conducting regular inventory checks, each step plays a vital role in maintaining the vaccine’s integrity. Storing Gardasil in a dedicated vaccine refrigerator, between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F), ensures that it remains within the recommended temperature range.
Avoiding improper storage methods, such as exposure to extreme temperatures or light, helps protect the vaccine’s potency and prevent any potential safety risks. Regularly checking the expiration date and discarding expired vaccines is crucial in ensuring patients receive vaccines that are within their designated shelf life.
Monitoring temperature fluctuations, maintaining proper storage documentation, and training staff on storage procedures are essential components of effective vaccine management. Regular inventory checks help ensure accurate stock control and prompt identification of any issues or discrepancies in vaccine storage.
Properly trained staff members who understand the importance of adhering to storage protocols are critical to successful vaccine storage. Ensuring that staff members are knowledgeable about proper storage techniques, temperature monitoring, and documentation practices helps maintain a culture of vigilance and accountability within the healthcare facility.
In conclusion, by following the recommended storage requirements, conducting regular checks, and properly training staff, healthcare providers can ensure that Gardasil retains its potency, integrity, and effectiveness. This ensures optimal protection against HPV-related diseases for patients, contributing to the overall success of vaccination efforts in combating HPV. The commitment to proper storage procedures empowers healthcare providers to confidently administer Gardasil, knowing that the vaccine will provide the maximum benefit to those receiving it.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Gardasil
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “How To Store Gardasil”