

Articles
How To Store Medications
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn how to store medications properly to maintain their effectiveness and ensure your safety. Our articles provide helpful tips and guidance for proper medication storage.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to storing medications, proper care and attention are crucial. Whether you’re dealing with over-the-counter drugs or prescription medications, understanding how to store them correctly is essential to maintain their effectiveness and ensure your safety.
Improper storage conditions can lead to a degradation in the potency of medications or, in some cases, even render them ineffective. Additionally, storing medications inappropriately can create potential safety hazards, especially if they fall into the wrong hands, such as children or pets.
In this article, we will explore best practices for medication storage, including temperature and humidity control, proper packaging and labeling, organizing and storing medications, and guidelines for medication disposal. By following these guidelines, you can help ensure both the effectiveness and safety of your medications.
Let’s dive in and learn more about how to store medications properly.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper medication storage is crucial for maintaining effectiveness and safety. Understanding storage requirements, choosing the right location, and controlling temperature and humidity are essential for preserving medication potency.
- Safe and proper medication disposal is vital to protect public health and the environment. Following disposal guidelines, utilizing take-back programs, and removing personal information before disposal are key practices for responsible medication management.
Read more: How To Store Insulin
Understanding Medication Storage Requirements
Medications can be sensitive to environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure. The storage requirements may vary depending on the type of medication, so it is essential to understand these requirements to maintain their efficacy.
One crucial factor to consider is temperature. Certain medications, such as insulin or antibiotics, may require refrigeration to keep them stable. On the other hand, some medications are sensitive to extreme cold and should not be stored in the refrigerator. It is essential to check the prescription label or consult with your pharmacist to determine the appropriate storage temperature for your medications.
Humidity is another crucial factor to consider. Excessive moisture can cause medication to deteriorate, lose effectiveness, or even become contaminated. Therefore, it is generally recommended to store medications in a dry environment, away from areas such as the bathroom or kitchen sink, where humidity levels can be high.
Light exposure can also impact the stability of certain medications. Some medications are light-sensitive and can become less effective or even break down when exposed to direct sunlight or bright artificial light. It is advisable to store these medications in opaque containers or keep them in a dark, cool place, such as a cabinet or drawer.
Additionally, it is essential to take note of any specific storage instructions provided with the medication. Some medications may require special storage considerations, such as keeping them in a sealed container or protecting them from freezing temperatures. Always read the package insert, consult with your healthcare provider, or ask your pharmacist if you have any questions or concerns.
By understanding the specific storage requirements of your medications, you can ensure their stability and effectiveness, providing you with the intended benefits when you need them.
Choosing the Right Storage Location
Selecting the appropriate storage location for your medications is essential to maintain their integrity and safety. Here are some factors to consider when choosing the right storage location:
1. Keep medications out of reach of children and pets: Choose a storage location that is not easily accessible to children or pets. High cabinets or lockable drawers are good options to prevent accidental ingestion or tampering.
2. Avoid areas prone to extreme temperature fluctuations: Medications should be stored in a location where the temperature remains relatively consistent. Avoid areas near windows, radiators, or heating vents, as they may expose medications to excessive heat or cold.
3. Consider the storage conditions required for specific medications: Different medications have varying storage requirements. Some may need to be kept at room temperature, while others may require refrigeration. Be sure to read the label or consult with your pharmacist to determine the appropriate storage conditions for each medication.
4. Protect medications from light exposure: Light-sensitive medications should be stored in a dark environment. Choose a storage location away from direct sunlight or bright artificial light sources. Keeping medications in opaque containers or using amber-colored prescription bottles can provide additional protection.
5. Avoid storing medications in the bathroom: The bathroom is typically not an ideal location for medication storage due to the high levels of humidity and temperature fluctuations caused by showers or baths. Consider alternative storage areas, such as a bedroom or kitchen cabinet.
6. Secure medications to prevent accidental spills or falls: It is important to keep medications organized and secure to minimize the risk of accidental spills or falls. Use shelves, bins, or organizers to keep medications upright and prevent them from mixing together.
By choosing the right storage location, you can maintain the effectiveness and safety of your medications, ensuring that they are readily available when needed.
Temperature and Humidity Control
Proper temperature and humidity control are critical in maintaining the effectiveness and stability of medications. Here are some guidelines to help you ensure the optimal storage conditions for your medications:
1. Room temperature storage: Most medications are recommended to be stored at room temperature (around 68-77°F or 20-25°C). This temperature range helps preserve the integrity and effectiveness of the medications. Avoid exposing medications to extreme temperatures or fluctuations, as this can impact their potency.
2. Refrigeration: Some medications, such as certain types of antibiotics, insulin, or certain eye drops, require refrigeration to maintain their stability. Check the medication label or consult your pharmacist to determine if refrigeration is necessary. When storing medications in the refrigerator, make sure they are properly sealed in airtight containers or packaging to prevent exposure to moisture.
3. Avoid freezing temperatures: Freezing temperatures can cause certain medications to lose their effectiveness or even become unsafe to use. It is important to check the storage instructions for each medication and avoid storing them in areas that can freeze, such as the freezer compartment of a refrigerator or extremely cold garages or basements.
4. Humidity control: Excessive humidity can impact the stability and effectiveness of medications. It is recommended to store medications in dry environments and avoid areas such as the bathroom, where humidity levels can be high. Consider using desiccant packets or moisture-absorbing products in your medication storage area to help control humidity.
5. Traveling with medications: When traveling, especially to hotter or more humid climates, take extra precautions to protect your medications. Use insulated bags or coolers with ice packs to maintain the appropriate temperature. Avoid leaving medications in a hot car or exposed to direct sunlight.
6. Temperature monitoring: Consider using a thermometer or temperature monitoring device in your medication storage area to ensure that the temperature remains within the recommended range. This can help you identify any potential issues and take necessary actions to maintain optimal storage conditions.
Remember, following temperature and humidity control guidelines is crucial to preserve the potency and safety of your medications. By providing the proper storage conditions, you can ensure that your medications remain effective and ready for use when needed.
Proper Packaging and Labeling
Proper packaging and labeling of medications are essential steps in ensuring their safety and effectiveness. Here are some guidelines for proper packaging and labeling:
1. Original packaging: It is recommended to keep medications in their original packaging whenever possible. The original packaging typically includes important information such as the medication name, dosage instructions, expiration date, and lot number. It also provides a protective barrier against light, moisture, and external contaminants.
2. Labeling: If you transfer medications from their original packaging to another container, ensure proper labeling. Clearly label the container with the medication name, dosage instructions, and expiration date. This will help you easily identify the medication and its intended use, reducing the chances of any confusion or medication errors.
3. Child-resistant containers: Use child-resistant containers for medications, especially if there are children in the household. These containers are designed to be difficult for children to open, reducing the risk of accidental ingestion or exposure.
4. Medication information: Keep a record of important medication information, such as the name, dosage, prescribing healthcare provider, and any potential side effects or special instructions. This information can be useful for reference purposes and when discussing medications with healthcare professionals.
5. Store separately: Store medications separately based on their properties and intended use. For example, keep prescription medications separate from over-the-counter medications, and store medications for different family members separately to avoid confusion.
6. Expiration dates: Check the expiration dates on medication packaging regularly. Expired medications may not be as effective as they should be and should be safely disposed of following proper guidelines (discussed later in this article).
7. Prescription information: If you have any prescription medications stored, ensure that the prescription label is intact and legible, including the patient’s name, the prescribing healthcare provider’s name, and the prescription number. This information can be helpful for reference and in case further clarification is needed.
Proper packaging and labeling of medications contribute to their safe and effective use. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that you have accurate information about your medications and reduce the risk of any potential errors or accidents.
Store medications in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Avoid storing them in the bathroom or kitchen, as the humidity can degrade the medication. Keep them out of reach of children and pets.
Read more: How To Store Gardasil
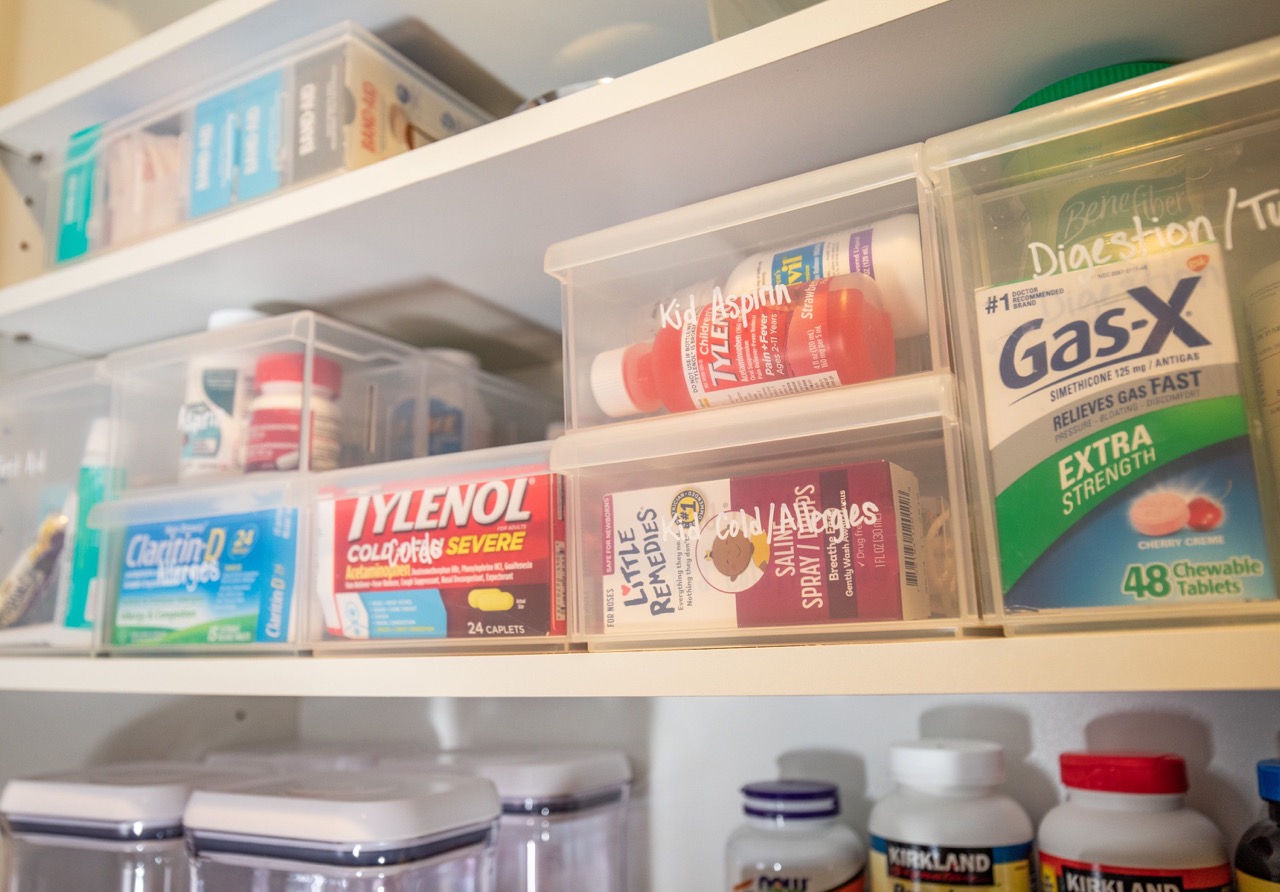
Organizing and Storing Medications
Proper organization and storage of medications are essential for easy accessibility and to maintain their integrity. Here are some tips to help you organize and store medications effectively:
1. Separate medications by type: Categorize medications based on their purpose, such as pain relievers, allergy medications, or vitamins. This will make it easier to locate specific medications when needed.
2. Use separate containers or compartments: Consider using pill organizers or separate containers for different medications. This helps prevent mix-ups and allows for easy access to specific medications at the right time.
3. Follow dosage instructions: Keep medications in their original packaging or clearly labeled containers with dosage instructions. This helps ensure that you take the correct dosage at the appropriate time.
4. Avoid storing medications near heat sources: Avoid storing medications near heat sources like stoves, radiators, or direct sunlight. High temperatures can degrade medications and reduce their effectiveness.
5. Secure medications from unauthorized access: If you have medications that need to be kept away from others, especially children or pets, store them in a lockable cabinet or drawer. This helps prevent accidental ingestion or tampering.
6. Keep medications out of the reach of children: Store medications in a location that is out of reach and out of sight of children. Ensure that child-resistant caps are properly closed, and consider using additional child safety locks if needed.
7. Regularly check expiration dates: Regularly go through your medication supply and discard any expired medications. Expired medications may not be as effective or could potentially be harmful if consumed.
8. Consider storage methods for different types of medications: Some medications, such as creams or ointments, may need to be stored in a cool place, while others may require specific temperature or humidity conditions. Be sure to read the storage instructions on the medication packaging or consult with your pharmacist.
By keeping your medications organized and stored properly, you can easily find what you need when you need it and ensure that they remain safe and effective for use.
Medication Storage Tips and Best Practices
Ensuring proper medication storage is crucial for maintaining efficacy and safety. Here are some essential tips and best practices to follow when storing medications:
1. Read storage instructions: Carefully read the packaging or prescription label for specific storage instructions provided by the manufacturer or healthcare provider. Follow these instructions to maintain the effectiveness of the medication.
2. Avoid sharing medications: Never share prescription medications with others, as it is unsafe and can lead to adverse reactions or unintended effects. Medications are prescribed based on individual needs and should be used only by the person they were prescribed for.
3. Store medications in their original containers: Whenever possible, keep medications in their original containers. These containers are designed to protect the medications from light, moisture, and external contaminants. They also provide essential information about the medication, such as dosage instructions and expiration dates.
4. Keep medications out of direct sunlight: Exposure to direct sunlight can degrade certain medications and reduce their effectiveness. Store medications in a dark, cool place, such as a cabinet or drawer.
5. Follow proper medication disposal guidelines: When discarding medications, be mindful of proper disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination and misuse. Check with your local pharmacy or waste management authority for guidelines on how to safely dispose of unused or expired medications.
6. Keep a medication inventory: Maintain an up-to-date inventory of your medications, including the name of the medication, dosage, and expiration date. This will help you track when medications need to be refilled or replaced.
7. Store medications away from moisture and humidity sources: Moisture and high humidity can degrade medications and promote bacterial growth. Avoid storing medications in areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms or kitchen sinks.
8. Check for signs of degradation: Regularly inspect your medications for any signs of damage, such as discoloration, unusual odor, or changes in texture. If you notice any abnormalities, consult with your pharmacist or healthcare provider for guidance.
9. Keep medications away from extreme temperatures: Avoid exposing medications to extreme heat or cold, as it can impact their stability and effectiveness. Be cautious when traveling or storing medications in environments with fluctuating temperatures.
Following these medication storage tips and best practices will help ensure that your medications remain safe, potent, and effective throughout their intended shelf life.
Medication Disposal Guidelines
Proper disposal of medications is essential to protect public health and minimize the risk of misuse or environmental contamination. Here are some guidelines to follow when disposing of medications:
1. Check for take-back programs: Check if your local pharmacy, healthcare facility, or law enforcement agency offers medication take-back programs. These programs provide a safe and convenient way to dispose of unused or expired medications. They ensure proper disposal and prevent medications from falling into the wrong hands.
2. Follow specific disposal instructions: Some medications, especially controlled substances, may have specific disposal instructions provided by the prescribing healthcare provider or pharmacist. Follow these instructions carefully to ensure safe and proper disposal.
3. Do not flush medications unless instructed: In most cases, it is not recommended to flush medications down the toilet or drain unless specifically instructed to do so for certain medications. Flushing medications can contribute to water pollution and environmental damage. Check with local guidelines or specific medication instructions for proper disposal methods.
4. Remove personal information: Before disposing of medication packaging, ensure that all personal information, such as your name, address, and prescription details, is removed or obscured to protect your privacy and prevent potential misuse.
5. Dispose of medication in unappealing substances: To discourage accidental ingestion or intentional misuse, mix medication with an unappealing substance like kitty litter, coffee grounds, or used cooking oil. Seal the mixture in a plastic bag before disposing of it in the trash.
6. Do not share or give medications to others: Never share prescription medications with others, even if they have similar symptoms. Medications are prescribed based on individual needs and health conditions. Sharing medications can be dangerous and lead to unintended side effects or allergic reactions.
7. Dispose of sharps properly: If you use medications that require the use of needles and syringes, dispose of them in designated sharps containers. Do not throw them directly into the trash, as they can pose a risk of injuries to sanitation workers or others who handle the trash.
8. Educate yourself on local regulations: Be aware of any local or state regulations regarding medication disposal. Some areas may have specific guidelines or collection events for safe disposal of medications. Check with your local pharmacy or waste management authority for more information.
By following these medication disposal guidelines, you can help protect yourself, others, and the environment from the potential risks associated with the improper handling and disposal of medications.
Conclusion
Proper storage and disposal of medications are crucial components of maintaining their effectiveness and ensuring our safety. By understanding medication storage requirements, choosing the right storage location, controlling temperature and humidity, using proper packaging and labeling, organizing and storing medications appropriately, and following medication disposal guidelines, we can optimize the lifespan and potency of our medications while minimizing the risk of misuse or accidental ingestion.
Remember to carefully read medication labels and consult with healthcare professionals or pharmacists for any specific storage instructions. Storing medications in their original containers, away from direct sunlight, heat sources, and moisture, can help maintain their stability. Use child-resistant containers and store medications out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion or exposure.
Proper organization, such as categorizing medications and using separate containers or a pill organizer, can facilitate easy access and prevent confusion. Regularly checking expiration dates and safely disposing of unused or expired medications following recommended guidelines are essential practices to ensure the efficacy and safety of our medication supply.
Ultimately, by following these best practices for medication storage and disposal, we can have peace of mind knowing that our medications are stored correctly, easily accessible when needed, and disposed of safely to protect ourselves, others, and the environment. Our commitment to proper medication management not only ensures the best outcomes for our health but also contributes to broader public health and safety.
So, let’s prioritize proper medication storage and disposal, recognizing their importance in maintaining the integrity of our medications and promoting a healthy and safe environment for all.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Medications
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.




0 thoughts on “How To Store Medications”