

Articles
What Do The Numbers On Fertilizer Mean
Modified: January 19, 2024
Discover what the numbers on fertilizer mean in this insightful article. Gain a better understanding of how to choose the right fertilizers for your plants.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to gardening and agriculture, fertilizers play a crucial role in providing the necessary nutrients for plants to thrive. However, understanding the numbers and terminology on fertilizer labels can be a daunting task for many. What do those numbers really mean? Why are they important? In this article, we will demystify the meaning behind the numbers on fertilizer labels and shed light on the importance of understanding them.
Imagine you’re strolling through the gardening section of a store, searching for the perfect fertilizer for your plants. You pick up a bag and notice a series of three bold numbers printed on it: 10-10-10. What do these numbers signify? Well, they are not just random digits. They represent the ratio of essential macronutrients contained in the fertilizer.
Understanding these macronutrient numbers is crucial because it allows you to choose the right fertilizer for your specific needs. Different plants have different nutrient requirements, and the balance of these nutrients is vital for their growth and overall health. By deciphering the numbers on fertilizer labels, you can ensure that your plants receive the nutrients they need to flourish.
Let’s dive deeper into the individual macronutrients and their respective numbers, starting with nitrogen.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the numbers on fertilizer labels and the importance of nutrient ratios is crucial for successful gardening and farming. It allows for tailored fertilization, balanced nutrition, and optimal plant growth.
- Soil testing is invaluable for customizing fertilization, adjusting soil pH, and addressing nutrient deficiencies. It empowers informed decisions, leading to healthier plants and sustainable gardening practices.
Read more: What Do The Numbers On A Fertilizer Bag Mean
Understanding Fertilizer Labels
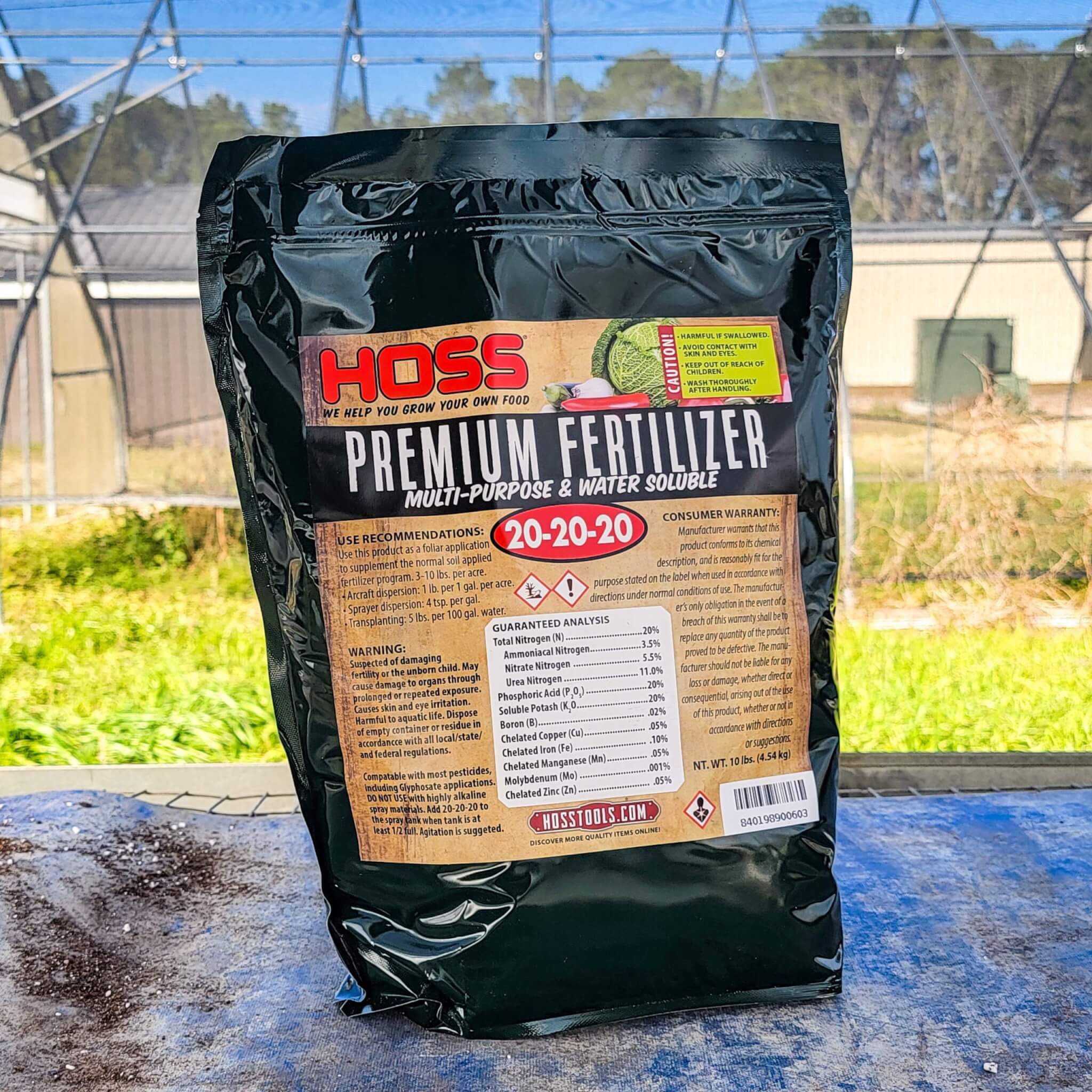
When you look at a fertilizer label, you will notice a series of three numbers separated by hyphens, such as 10-10-10 or 5-10-5. These numbers represent the percentage of three essential macronutrients that are present in the fertilizer: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). They are expressed in the form of N-P-K.
The ratio of these macronutrients indicates the relative amount of each nutrient in the fertilizer. For example, in a fertilizer with a ratio of 10-10-10, each nutrient is present in equal proportions: 10% nitrogen, 10% phosphorus, and 10% potassium. In another fertilizer with a ratio of 5-10-5, there is less nitrogen but more phosphorus and potassium.
These macronutrients play crucial roles in plant growth and development. Nitrogen is responsible for promoting leaf and stem growth, phosphorus stimulates root development and flower production, and potassium enhances overall plant health, including disease resistance and water retention. The specific needs of your plants will determine the ideal N-P-K ratio.
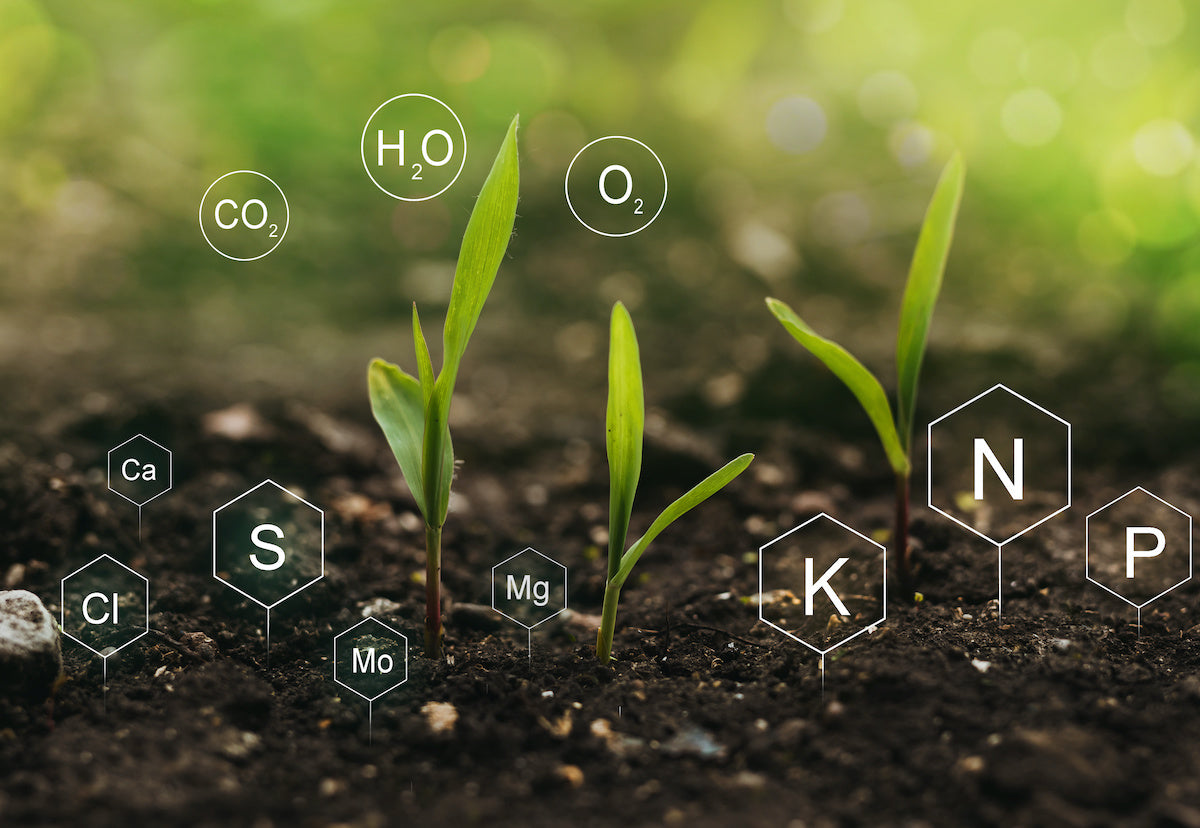
But what about the secondary and micronutrients? While nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are the primary macronutrients, there are secondary nutrients like calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S), as well as micronutrients like iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), and others. These nutrients are necessary for plant growth, albeit in smaller quantities.
Now that we have a general understanding of the macronutrients and their ratios, let’s delve into each nutrient individually, starting with nitrogen.
Macronutrient Numbers
When interpreting fertilizer labels, the macronutrient numbers provide valuable information about the nutrient content and ratio in the product. Let’s take a closer look at each of these macronutrients and understand their significance.
Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen is a crucial nutrient for plant growth, as it is involved in the synthesis of proteins, chlorophyll, and other essential compounds. It promotes vigorous vegetative growth, lush green foliage, and enhances overall plant vigor. Fertilizers with higher nitrogen content are often used for leafy plants like lettuce, spinach, and grass. However, excessive nitrogen can lead to excessive vegetative growth with weak stems, making plants more susceptible to diseases and pests. It is important to strike a balance when using nitrogen-based fertilizers.
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus contributes to vital processes like photosynthesis, energy transfer, and root development. It is particularly important during the early stages of plant growth and flowering. Phosphorus stimulates root growth, ensuring strong and healthy root systems. It also plays a significant role in flower and fruit production. Fertilizers with higher phosphorus content are often recommended for plants that require strong root development, such as tomatoes, carrots, and flowering plants.
Read more: What Do The Numbers Mean In Ryobi Drill
Potassium (K)
Potassium is involved in many physiological processes within plants, including regulating water uptake and retention, improving disease resistance, and enhancing overall plant health. It is essential for the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of plants. Fertilizers with higher potassium content are commonly used for enhancing drought tolerance and overall plant resilience. Plants like citrus trees, roses, and potatoes benefit from potassium-rich fertilizers.
Understanding the macronutrient numbers on fertilizer labels can help you select the right fertilizer for your specific gardening needs. However, it’s crucial to remember that the nutrient requirements of plants can vary, and conducting a soil test is recommended to determine the specific nutrient needs of your soil. This brings us to the next important point: the ratio of nutrients in fertilizers.
Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen is one of the three essential macronutrients that plants need to thrive. It plays a vital role in supporting plant growth, as it is a key component in the production of proteins, enzymes, chlorophyll, and other fundamental compounds. This essential nutrient is responsible for promoting lush green foliage and vigorous vegetative growth.
When it comes to fertilizers, nitrogen is often represented by the first number in the N-P-K ratio. For example, in a fertilizer with a ratio of 10-10-10, the first 10 represents the percentage of nitrogen present in the product. This means that 10% of the fertilizer is composed of nitrogen.
So why is nitrogen so important for plants? Let’s take a closer look at its various functions:
- Promotes Leaf Growth: Nitrogen is essential for leaf development. It stimulates the production of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for the green color in plants. Chlorophyll captures light energy and converts it into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis. Adequate nitrogen levels ensure healthy and robust leaf growth.
- Influences Plant Structure: Nitrogen is involved in cell division and elongation, which determines the overall structure of the plant. It contributes to the formation of new cells and helps plants grow taller and stronger. Insufficient nitrogen can lead to stunted growth and smaller leaves.
- Enhances Protein Synthesis: Proteins are essential for various plant functions, including enzymatic reactions, structural support, and nutrient transport. Nitrogen is a key component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. By providing an ample supply of nitrogen, plants can synthesize proteins and carry out vital biological processes.
- Affects Photosynthesis: Nitrogen plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. It is an integral part of the chlorophyll molecule, which captures sunlight and facilitates the production of glucose and oxygen. Adequate nitrogen levels ensure efficient photosynthesis and robust plant growth.
- Impacts Plant Health and Immunity: Nitrogen is involved in the synthesis of various defense compounds, such as phytoalexins and enzymes, which help plants ward off diseases and pests. Additionally, it promotes a strong and healthy plant immune system, allowing plants to withstand environmental stresses.
While nitrogen is essential for plant growth and vitality, it’s important to use it judiciously. Excessive nitrogen application can lead to an imbalance in nutrient uptake, causing plants to become more susceptible to diseases and pests. Overfertilization can also result in nutrient runoff, negatively impacting the environment. It is essential to follow recommended application rates and consider factors like soil type, plant species, and growth stage when applying nitrogen-based fertilizers.
By understanding the role of nitrogen and its impact on plant growth, you can make informed decisions when choosing fertilizers and ensure optimal nutrient supply for your plants.
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus is a vital macronutrient that plays a crucial role in supporting plant growth and development. It is represented by the second number in the N-P-K ratio on fertilizer labels. For example, in a fertilizer with a ratio of 10-20-10, the second number, 20, indicates the percentage of phosphorus present in the product.
Phosphorus is involved in various essential processes within plants. Let’s explore the significance of phosphorus and its functions:
- Root Development: Phosphorus is essential for the growth and development of roots. It promotes root cell division and elongation, leading to a well-established and robust root system. Strong roots allow plants to efficiently absorb water, nutrients, and anchorage, thereby supporting overall plant health and stability.
- Energy Transfer: Phosphorus plays a vital role in energy transfer within plants. It is a key component of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule responsible for storing and transporting energy within cells. ATP is required for various metabolic processes, including photosynthesis, respiration, and nutrient uptake.
- Flower and Fruit Production: Phosphorus is important for reproductive growth in plants. It is involved in flower and fruit development, promoting the formation of healthy blooms and ensuring successful pollination. Adequate phosphorus levels can result in abundant flowers and high-quality fruits.
- Resilience to Environmental Stress: Phosphorus contributes to enhancing plants’ resilience to environmental stresses. It helps plants cope with temperature fluctuations, drought conditions, and other adverse environmental factors. Phosphorus aids in the synthesis of various stress-related compounds and enhances plant defense mechanisms.
- Nutrient Transport: Phosphorus plays a vital role in nutrient uptake and transport within plants. It is involved in the conversion of inorganic phosphorus into organic forms that can be readily used by plants. Phosphorus facilitates the movement of nutrients from the roots to other parts of the plant, ensuring proper nutrient distribution.
While phosphorus is essential for plant growth, it’s crucial to use it responsibly. Excessive phosphorus application can lead to nutrient imbalances, environmental pollution, and water contamination. Additionally, phosphorus availability can be affected by soil pH, temperature, and other factors. Conducting a soil test can help determine the phosphorus levels in your soil and guide you in making appropriate fertilizer application decisions.
By understanding the role of phosphorus and its impact on plant growth and development, you can make informed choices when selecting fertilizers and ensure optimal nutrient supply for your plants’ specific needs.
Potassium (K)
Potassium is an essential macronutrient that plays a critical role in supporting plant health and growth. Represented by the third number in the N-P-K ratio on fertilizer labels, potassium is necessary for maintaining optimal plant functions. For instance, in a fertilizer with a ratio of 10-20-10, the third number, 10, indicates the percentage of potassium present in the product.
Let’s explore the significance of potassium and its various roles in plant growth:
- Water Regulation: Potassium facilitates water regulation within plants, helping them effectively manage water uptake and retention. It regulates the opening and closing of stomata, small pores on the leaf surface responsible for gas exchange and transpiration. Adequate potassium levels enable plants to maintain proper water balance, enhancing their tolerance to drought conditions.
- Enzyme Activation: Potassium is involved in the activation of several enzymes essential for various metabolic reactions within plants. These enzymes play key roles in photosynthesis, respiration, protein synthesis, and many other biochemical processes. Potassium acts as a cofactor, ensuring that these enzymes function optimally and maintain proper plant functioning.
- Enhanced Nutrient Uptake: Potassium plays a crucial role in improving the uptake and transportation of other essential nutrients within plants. It promotes the efficient absorption of nitrogen, phosphorus, and other micronutrients. Potassium also enhances nutrient translocation, ensuring their proper distribution to different plant parts and supporting overall plant health.
- Strengthened Cell Walls: Potassium contributes to the formation of strong cell walls in plants. It improves cell rigidity and structural integrity, making plants more resistant to diseases, pests, and environmental stressors. Adequate potassium levels lead to stronger stems and overall plant durability.
- Reduced Disease Susceptibility: Potassium is known to enhance plant resistance against diseases and pests. It fortifies plant cell walls, making it more difficult for pathogens to invade. Potassium also stimulates the production of defense compounds within plants, boosting their immune response and reducing disease susceptibility.
It’s important to note that the availability and uptake of potassium can be influenced by factors such as soil pH, temperature, and nutrient interactions. Conducting a soil test can provide valuable insights into the potassium levels in your soil and guide you in determining the appropriate fertilizer application rates.
By understanding the significance of potassium and its impact on plant health and growth, you can make informed decisions when selecting fertilizers and ensure that your plants receive the necessary potassium to thrive.
Secondary and Micronutrients
While nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are the primary macronutrients required in larger quantities by plants, there are also secondary nutrients and micronutrients that play crucial roles in plant growth and development. These nutrients are required in smaller amounts but are equally essential for optimal plant health.
Let’s take a closer look at the secondary and micronutrients and their importance:
Secondary Nutrients
The three secondary nutrients are calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S). While these nutrients are not required in the same quantities as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, they are still vital for plant growth and function.
- Calcium (Ca): Calcium is necessary for cell wall formation, root development, and overall plant structure. It helps to strengthen plant tissues, reducing the risk of diseases and enhancing plant resilience.
- Magnesium (Mg): Magnesium is a central component of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis. It is crucial for energy production, enzyme activation, and the overall green color of plants.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur is involved in protein synthesis, enzyme activation, and the production of essential compounds like vitamins and amino acids. It assists in the formation of plant proteins, which are crucial for growth and development.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients, also known as trace elements, are essential elements required in very small amounts by plants. While their concentrations may be low, their absence or deficiency can have significant negative impacts on plant growth and health.
- Iron (Fe): Iron is vital for chlorophyll synthesis, electron transport, and enzyme functions. It plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, enabling plants to convert sunlight into energy for growth and development.
- Manganese (Mn): Manganese is involved in enzyme functions, photosynthesis, and nitrogen metabolism. It contributes to the production of chlorophyll and helps regulate various plant growth processes.
- Zinc (Zn): Zinc is essential for plant growth and hormone regulation. It is involved in enzyme functions, DNA synthesis, and protein synthesis. Zinc is crucial for overall plant development and resilience to stress.
- Copper (Cu): Copper plays a role in enzyme functions, photosynthesis, and reproductive growth in plants. It assists in the formation of plant tissues and helps plants withstand environmental stresses.
- Boron (B): Boron is essential for cell wall synthesis, pollen development, and movement of sugars within plants. It contributes to proper carbohydrate metabolism and overall plant reproduction.
- Molybdenum (Mo): Molybdenum is involved in nitrogen fixation, enzyme functions, and the conversion of nitrate to ammonia within plants. It plays a crucial role in promoting healthy growth and efficient nitrogen utilization.
While secondary nutrients and micronutrients may be required in smaller quantities, their deficiencies can lead to various visible symptoms, including stunted growth, leaf discoloration, and reduced yield. Soil testing can help determine the availability of these nutrients in your soil and guide you in making informed fertilizer choices.
By considering the secondary nutrients and micronutrients in addition to the primary macronutrients, you can ensure a well-rounded nutrient supply for your plants, promoting their overall health and vitality.
Ratio of Nutrients
The ratio of nutrients refers to the relative proportions of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in a fertilizer. These ratios are indicated by the numbers on the fertilizer label, expressed as the N-P-K ratio. For example, in a fertilizer with a ratio of 10-10-10, there is an equal proportion of each nutrient, with 10% nitrogen, 10% phosphorus, and 10% potassium.
Understanding the ratio of nutrients is crucial because it determines the overall balance of essential elements that your plants receive. Different plants have varying nutritional needs, and the ideal nutrient ratio for one plant may differ from another.
Let’s explore how the ratio of nutrients affects plant growth and development:
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen promotes vegetative growth and lush foliage. If a plant requires more foliage development, a higher nitrogen ratio may be beneficial. Leafy vegetables like lettuce and spinach, for example, may benefit from higher nitrogen ratios.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus is crucial for root development and flower and fruit production. Plants that require strong root systems and abundant flowers or fruits, such as tomatoes or roses, may benefit from a higher phosphorus ratio.
- Potassium (K): Potassium enhances overall plant health, improves disease resistance, and aids in water regulation. Plants that require increased tolerance to drought or environmental stresses may benefit from a higher potassium ratio. Citrus trees and potatoes are examples of plants that benefit from higher potassium levels.
The specific nutrient ratio required by your plants can vary depending on factors such as plant species, growth stage, soil conditions, and environmental factors. To determine the optimal ratio for your plants, it is advisable to conduct a soil test. A soil test provides valuable information about the nutrient levels in your soil, allowing you to customize your fertilizer application to meet the specific needs of your plants.
It’s important to note that nutrient ratios can also be adjusted through organic amendments, such as compost or manure, or by using specific fertilizers targeted to address specific nutrient deficiencies.
Remember, achieving the right balance of nutrients is crucial for healthy plant growth. Over-application of fertilizers can lead to nutrient imbalances, which may negatively impact plant health and the environment. It’s best to follow recommended application rates and consider the specific needs of your plants when choosing fertilizer ratios.
By understanding the ratio of nutrients and tailoring your fertilizer application accordingly, you can provide your plants with the optimal nutrient balance they need to thrive and reach their full potential.
Importance of Soil Testing
Soil testing is an essential tool for any gardener or farmer to understand the specific nutrient needs of their soil and optimize plant growth. It involves analyzing the chemical composition of the soil to determine its pH level and the presence of macro and micronutrients. Here’s why soil testing is important:
1. Assess Nutrient Levels:
Soil testing helps determine the levels of essential nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and micronutrients, in the soil. By knowing the nutrient levels, you can make informed decisions about fertilizer application and choose the right blend of nutrients to meet your plants’ specific needs. This prevents over or under-fertilization, saving money and reducing the risk of nutrient imbalances.
2. Adjust Soil pH:
The pH level of the soil directly affects nutrient availability to plants. Soil testing allows you to determine the pH level, which can be acidic, neutral, or alkaline. By knowing the soil pH, you can adjust it if needed to create the optimal environment for plant growth. For example, acid-loving plants like blueberries prefer acidic soil, while most vegetables thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil.
3. Identify Nutrient Deficiencies or Toxicities:
Soil testing can reveal nutrient deficiencies or toxicities in the soil. Visual symptoms alone may not provide an accurate diagnosis of nutrient issues, as symptoms can vary for different nutrient deficiencies. By identifying specific nutrient imbalances through soil testing, you can address the deficiencies or excesses and prevent plant health problems before they become severe.
Read more: What Does Toaster Numbers Mean
4. Customize Fertilizer Application:
Based on soil test results, you can customize your fertilizer application to supply the exact amount of nutrients needed by your plants. This targeted approach saves money and minimizes the impact on the environment by reducing nutrient runoff. Soil testing also helps you choose the right type of fertilizer (organic or synthetic) and determine the appropriate timing of application.
5. Determine Soil Health:
Soil testing provides valuable insights into the overall health and fertility of your soil. It assesses important soil properties such as organic matter content, cation exchange capacity, and soil texture. Understanding these aspects helps you make informed decisions about soil amendments, organic matter application, and soil improvement practices to enhance soil health and optimize plant growth.
6. Monitor Changes Over Time:
Regular soil testing allows you to monitor changes in soil conditions over time. By keeping track of the nutrient levels and pH, you can track the effectiveness of your fertilization and soil management practices. Monitoring changes helps you make adjustments as needed, ensuring that your plants receive the appropriate nutrients for continuous healthy growth.
Overall, soil testing is invaluable for optimizing plant growth, improving crop yields, and maintaining the long-term health of your soil. By understanding the specific nutrient needs of your soil through soil testing, you can make informed decisions about fertilization, soil amendments, and soil management practices, leading to successful and sustainable gardening or farming endeavors.
Conclusion
Understanding the numbers on fertilizer labels and the importance of nutrient ratios is key to successful gardening and farming. The three primary macronutrients, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), play vital roles in plant growth and development. Nitrogen promotes lush foliage, phosphorus supports root development and flower production, while potassium enhances overall plant health and resilience.
Secondary nutrients, such as calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S), along with micronutrients like iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn), are also essential for optimal plant growth and vitality. Knowing the nutrient needs of your plants and the specific ratios required can help you select the right fertilizer and ensure balanced nutrition.
Soil testing is an invaluable tool in understanding the nutrient levels, pH, and overall health of your soil. This information allows you to customize your fertilization approach, adjust soil pH if needed, and address any nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. By tailoring your fertilizer application to meet the exact needs of your plants, you can optimize plant growth, save money, and reduce the environmental impact of excess fertilizers.
Regular soil testing and monitoring enable you to track changes in soil conditions over time and make necessary adjustments to your fertilization and soil management practices. It provides a comprehensive view of your soil’s health and fertility, empowering you to make informed decisions about soil amendments and improvement practices.
By combining a solid understanding of nutrient ratios, soil testing, and customized fertilizer application, you can create an ideal environment for your plants to thrive. Whether you’re an avid home gardener or a commercial farmer, optimizing nutrient supply and maintaining soil health will lead to healthier plants, better yields, and more sustainable gardening practices.
So don’t overlook the numbers on fertilizer labels or the importance of soil testing. Equip yourself with the knowledge and tools to unlock the full potential of your plants and cultivate a greener, more fruitful world.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Do The Numbers On Fertilizer Mean
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “What Do The Numbers On Fertilizer Mean”