

Articles
What Is a CPU Fan
Modified: August 24, 2024
Discover the importance of CPU fans and how they play a crucial role in keeping your computer cool. Read our informative articles to learn more.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
A CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of a computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. As the CPU works, it generates heat. If this heat is not adequately managed, it can cause the CPU to overheat and malfunction, leading to system instability and potential hardware damage. This is where the CPU fan comes into play.
A CPU fan is a crucial component in a computer system that helps to cool down the CPU by dissipating the excess heat. It is designed to maintain a safe operating temperature for the CPU, ensuring smooth and efficient performance. Without a functional CPU fan, the CPU could overheat within minutes, leading to system crashes or even permanent damage.
The importance of a CPU fan cannot be overstated, especially in high-performance computers or systems that undergo intensive tasks such as gaming, video editing, or running advanced software. In these situations, the CPU generates a significant amount of heat that needs to be efficiently managed to prevent thermal throttling or a complete system shutdown.
Not only does a CPU fan keep the CPU cool, but it also contributes to the overall stability and longevity of the computer system. By preventing the CPU from overheating, it helps to enhance system performance and reliability, ensuring that the computer can handle demanding tasks without compromising its functionality.
The CPU fan serves several important functions. Firstly, it removes the hot air that accumulates around the CPU, preventing the temperature from rising to dangerous levels. Additionally, it promotes airflow within the computer case, helping to maintain an optimal operating temperature for all components, including the CPU, motherboard, RAM, and GPU.
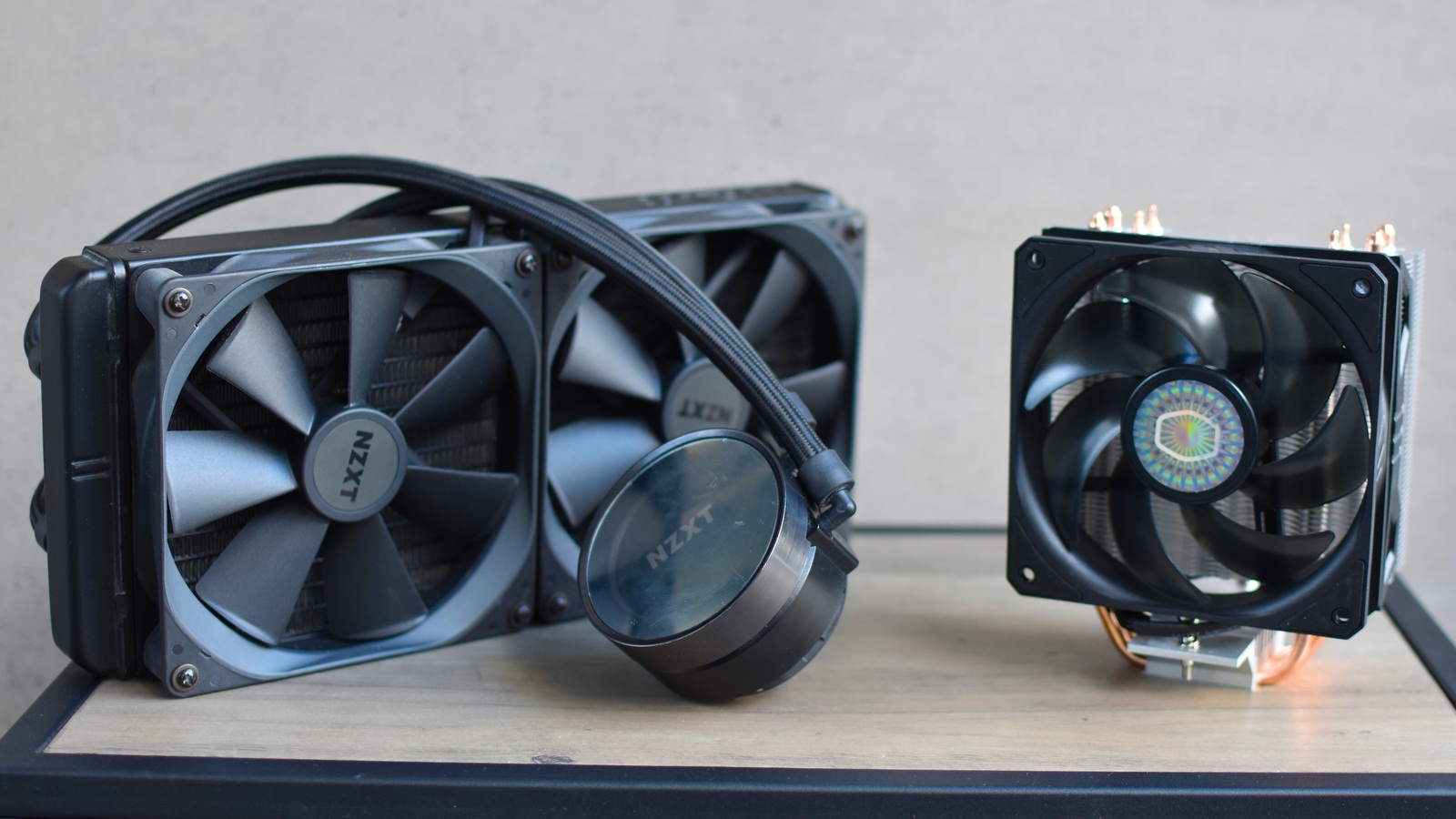
There are several types of CPU fans available on the market, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common type is the air-cooled CPU fan, which utilizes a combination of heatsinks and fans to dissipate heat. Liquid-cooled CPU fans, on the other hand, use a closed-loop liquid cooling system to cool the CPU more efficiently. Both types have their pros and cons and can be selected based on specific requirements and preferences.
When choosing a CPU fan, there are certain characteristics to consider. A good CPU fan should have efficient cooling capabilities, low noise levels, a durable design, and compatibility with the CPU socket on your motherboard. It is also important to select a fan that matches the thermal requirements of your CPU.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the functions and types of CPU fans, discuss the characteristics of a good CPU fan, offer tips on selecting the right CPU fan for your system, provide guidance on the installation and maintenance of CPU fans, and troubleshoot common CPU fan issues. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of CPU fans and their vital role in keeping your computer cool and functioning optimally.
Key Takeaways:
- The CPU fan is a critical component that prevents overheating, maintains system stability, and enhances overall performance by effectively dissipating heat and promoting optimal operating temperatures for the CPU and other components.
- Choosing the right CPU fan involves considering factors such as compatibility, cooling performance, noise levels, form factor, durability, and budget. Proper installation, maintenance, and timely troubleshooting are essential for ensuring efficient cooling and prolonged system longevity.
Read more: How to Replace a CPU Fan
Definition of CPU Fan
A CPU fan is a device specifically designed to cool down the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer. The CPU is one of the most essential components of a computer system, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. As the CPU carries out these tasks, it generates heat. Without proper cooling, this heat can accumulate and cause the CPU to overheat, leading to system instability, performance degradation, or even permanent damage.
A CPU fan works by dissipating the excess heat produced by the CPU, ensuring that it operates within safe temperatures. It accomplishes this by moving air across heatsinks or heat pipes that are attached to the CPU. The airflow generated by the fan helps to transfer the heat away from the CPU and into the surrounding environment, preventing the CPU from overheating.
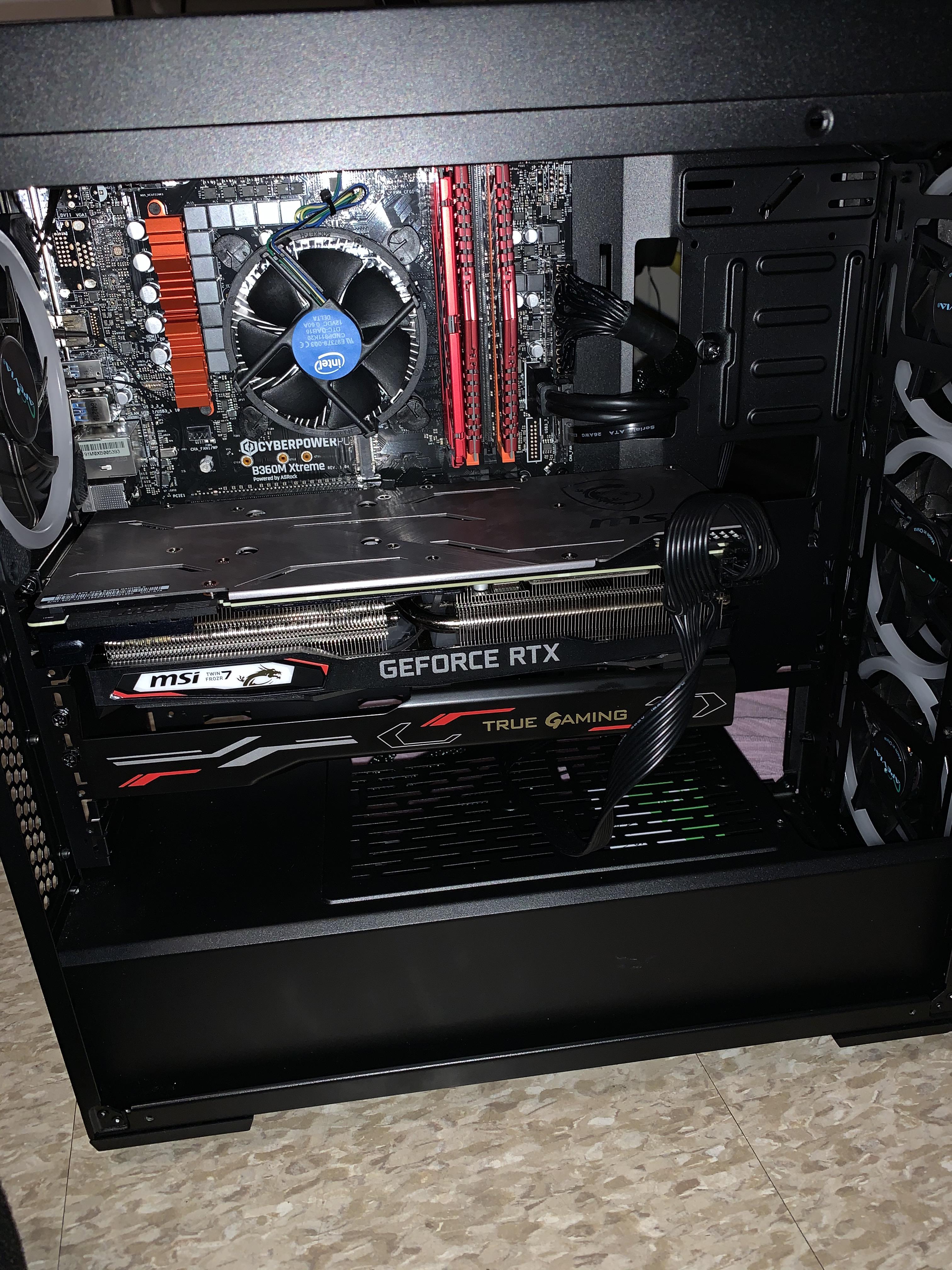
CPU fans are typically attached directly to the CPU socket on the motherboard. They are positioned in close proximity to the CPU, allowing for efficient heat transfer. In some cases, the CPU fan is secured to the heatsink with mounting brackets or clips, while in other instances, it may be integrated into an all-in-one cooling solution, such as a liquid cooling system.
Most CPU fans are powered by the computer’s power supply unit (PSU) or the motherboard itself. They are usually controlled by the system’s BIOS or via specialized software, which adjusts the fan speed based on the CPU temperature. This allows the fan to spin faster when the CPU is under heavy load and produce more airflow, effectively cooling the CPU more efficiently.
In addition to cooling the CPU, some CPU fans also contribute to overall case ventilation. By creating airflow within the computer case, they help to expel hot air and draw in cool air, maintaining a suitable operating temperature for all components inside the system.
The design and specifications of CPU fans can vary widely depending on the intended use, system requirements, and personal preferences. Factors such as fan size, airflow capacity, noise level, and power consumption should be considered when selecting a CPU fan.
Overall, a CPU fan is a fundamental component in any computer system that ensures the CPU’s temperature remains within safe limits. By effectively cooling the CPU, it helps to maintain system stability, improve performance, and prolong the lifespan of the computer.
Importance of CPU Fan
The CPU fan plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and longevity of a computer system. Its importance cannot be overstated, especially as CPUs continue to become more powerful and generate increasing amounts of heat. Here are some key reasons why the CPU fan is so important:
- Temperature Regulation: The primary function of a CPU fan is to regulate the temperature of the CPU. As the CPU performs complex operations, it generates heat. If this heat is not effectively dissipated, the CPU can overheat, leading to system instability and potential damage. The CPU fan keeps the temperature in check by dissipating the excess heat and maintaining safe operating temperatures for the CPU.
- Prevention of Thermal Throttling: When a CPU exceeds its optimal operating temperature, it enters a state known as thermal throttling. In this state, the CPU slows down its clock speed to reduce heat generation, which severely affects system performance. A properly functioning CPU fan prevents thermal throttling by keeping the CPU temperature within safe limits, allowing the CPU to operate at its full potential.
- System Stability: Overheating can cause system crashes, freezes, and unexpected shutdowns. By keeping the CPU temperature under control, the CPU fan helps to maintain system stability and prevents these disruptive occurrences. This is particularly important during resource-intensive tasks such as gaming, video editing, or running demanding software.
- Hardware Protection: Excessive heat can not only harm the CPU but also other critical components such as the motherboard, RAM, and graphics card. By dissipating heat, the CPU fan indirectly protects these components by creating an environment with optimal operating temperatures. This helps to prevent component failure, extend their lifespan, and ensure the overall reliability of the computer system.
- Boosts Performance: When the CPU operates at higher temperatures, it may automatically reduce its clock speed to prevent overheating. This reduction in clock speed, known as thermal throttling, can significantly impact system performance. By keeping the CPU temperature low, the CPU fan enables the CPU to maintain its maximum clock speed, resulting in improved performance and faster processing times.
- Noise Reduction: While CPU fans are not completely silent, they help to dissipate the heat efficiently, resulting in lower fan speeds. A well-designed and properly functioning CPU fan can keep noise levels to a minimum, providing a quieter computing experience.
In summary, the CPU fan is a vital component in a computer system that ensures the CPU operates within safe temperature ranges. By regulating the temperature, it protects the CPU and other components from damage, enhances system stability, improves performance, and prolongs the lifespan of the computer system. Investing in a high-quality CPU fan is essential for any computer enthusiast or individual looking to maximize the reliability and functionality of their system.
Functions of CPU Fan
The CPU fan serves several important functions in a computer system, all of which contribute to maintaining the overall performance, stability, and longevity of the system. Here are the key functions of a CPU fan:
- Heat Dissipation: The primary function of a CPU fan is to dissipate the heat generated by the CPU. As the CPU performs calculations and executes instructions, it generates heat as a byproduct. The CPU fan works in conjunction with heatsinks or heat pipes to transfer the heat away from the CPU and into the surrounding environment. This prevents the CPU from overheating and ensures that it remains within safe operating temperatures.
- Airflow Creation: By spinning its blades, the CPU fan creates airflow around the CPU and within the computer case. This airflow helps to remove hot air that accumulates around the CPU and other components. It also facilitates the movement of cool air from outside the case, providing fresh air to the CPU and aiding in overall heat dissipation. The circulation of air is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures for all system components.
- Case Ventilation: In addition to cooling the CPU, the CPU fan also contributes to overall case ventilation. The airflow generated by the fan helps to expel hot air from the case and draw in cool air from outside. This helps to maintain suitable operating temperatures for other components, such as the motherboard, RAM, and graphics card. Proper case ventilation is essential for system stability and prevents the buildup of heat that could negatively impact performance.
- Noise Reduction: While not its primary function, the CPU fan can also help to reduce noise levels in the system. Modern CPU fans are designed to operate quietly, utilizing technologies such as fan blades with optimized shapes and rubber dampeners to minimize vibrations and noise. By efficiently dissipating heat, the CPU fan can operate at lower speeds, resulting in quieter operation during normal system use.
- Cooling of Motherboard Components: The airflow created by the CPU fan not only helps to cool the CPU itself but also aids in cooling other components on the motherboard. Components such as voltage regulators, chipset, and RAM modules can generate heat during operation. The airflow created by the CPU fan helps to direct cool air over these components, preventing overheating and ensuring their stable operation.
- Prevention of Thermal Throttling: One critical function of the CPU fan is to prevent thermal throttling. When the CPU temperature exceeds safe limits, it may automatically reduce its clock speed to reduce heat generation. This reduction in clock speed, known as thermal throttling, has a negative impact on system performance. By keeping the CPU temperature within safe ranges, the CPU fan enables the CPU to operate at its maximum clock speed, ensuring optimal performance without any performance degradation caused by thermal throttling.
In summary, the CPU fan plays a vital role in cooling the CPU, creating airflow within the system, maintaining optimal operating temperatures for all components, reducing noise levels, and preventing thermal throttling. Its functions are essential for system stability, performance, and the overall health of the computer system. By selecting a high-quality CPU fan and ensuring proper airflow within the system, users can ensure the reliable and efficient operation of their computers.
Types of CPU Fans
CPU fans come in several different types, each with its own design, cooling capabilities, and advantages. The choice of CPU fan type depends on factors such as the specific requirements of the computer system, thermal management needs, and personal preferences. Here are the most common types of CPU fans:
- Air-Cooled CPU Fans: Air-cooled CPU fans are the most widely used type of CPU cooling solution. They consist of a combination of a heatsink and one or more fans. The heatsink is typically made of metal, such as aluminum or copper, and is designed to absorb and distribute heat away from the CPU. The fan(s) attached to the heatsink helps to increase airflow, enhancing the heat dissipation process. Air-cooled CPU fans are relatively affordable, easy to install, and offer efficient cooling for most standard computer systems.
- Liquid-Cooled CPU Fans: Liquid-cooled CPU fans, also known as closed-loop liquid coolers, provide more efficient cooling compared to air-cooled solutions. They consist of a pump, radiator, liquid-filled tubes, and a CPU block with a copper or aluminum baseplate. The pump circulates liquid, typically a mixture of water and coolant, to carry heat away from the CPU. The heated liquid then passes through the radiator, where fans dissipate the heat into the air. Liquid-cooled CPU fans offer better cooling performance, lower noise levels, and are popular among high-performance gaming and overclocking enthusiasts.
- Passive CPU Coolers: Passive CPU coolers do not include an integrated fan. Instead, they rely on the natural convection of air for heat dissipation. These coolers consist of large, finned heatsinks that provide a large surface area for heat transfer. Passive CPU coolers are often used in fanless systems or in situations where low noise levels are a priority. While they can effectively cool moderate to low-power CPUs, they may not be suitable for high-performance systems or CPUs that generate a significant amount of heat.
- Top-Flow CPU Coolers: Top-flow CPU coolers, also known as downdraft coolers, feature a horizontal heatsink that spans across the CPU socket. The fan, usually positioned on top of the heatsink, blows air downwards towards the CPU and other motherboard components. This design provides efficient cooling while also directing airflow to cool other components on the motherboard, such as voltage regulators or RAM modules. Top-flow coolers are often compact and can be an excellent choice for systems with limited vertical space or for users looking for added motherboard component cooling.
- Low-Profile CPU Coolers: Low-profile CPU coolers are designed for systems with limited vertical clearance, such as compact form factors or small cases. They feature shorter heatsinks and low-profile fans to fit within space-constrained environments. While they may not provide the same level of cooling performance as larger CPU coolers, they are still capable of effectively cooling CPUs with lower power consumption.
Each type of CPU fan has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on factors such as thermal requirements, system constraints, budget, and personal preferences. Whether it’s air-cooled, liquid-cooled, passive, top-flow, or low-profile, selecting the appropriate type of CPU fan ensures efficient heat dissipation, optimal cooling performance, and the stability of the computer system.
Characteristics of a Good CPU Fan
When selecting a CPU fan, it’s important to consider several characteristics to ensure efficient cooling and optimal performance. Here are the key characteristics of a good CPU fan:
- Effective Cooling Performance: A good CPU fan should have efficient cooling capabilities to effectively dissipate heat from the CPU. It should be capable of maintaining the CPU at safe operating temperatures, even under heavy loads. Look for CPU fans with high airflows (measured in cubic feet per minute, or CFM) and static pressure ratings, as these indicate their ability to move air and efficiently cool the CPU.
- Low Noise Levels: Noise can be a significant concern, especially for users who prioritize a quiet computing experience. A good CPU fan should operate with minimal noise. Look for CPU fans with low decibel (dB) ratings or features such as PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controls, which allow for dynamic fan speed adjustment based on the CPU temperature. Larger fans tend to be quieter since they can move the same amount of air at lower speeds.
- Durable Design: The durability of a CPU fan is crucial, as it ensures long-term reliability and reduces the risk of failure. Look for CPU fans with high-quality materials, such as metals for heatsinks and sturdy fan blades made of durable polymers or metals. Consider CPU fans with a reliable bearing system, such as ball-bearing or fluid dynamic bearings, which offer better longevity and quieter operation compared to sleeve bearings.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the CPU fan is compatible with your specific CPU socket on the motherboard. There are different socket types, such as Intel’s LGA (Land Grid Array) or AMD’s AM4 socket, and the CPU fan must be designed to fit your specific CPU socket. Check the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure compatibility.
- Easy Installation: A good CPU fan should be easy to install, whether it’s an air-cooled or liquid-cooled solution. Look for CPU fans that come with clear instructions and include the necessary mounting hardware. Consider pre-applied thermal paste or thermal pads, as they simplify the installation process and ensure proper thermal conductivity between the CPU and heatsink.
- Thermal Management Features: Some CPU fans offer additional features to enhance thermal management. Look for fans with built-in temperature sensors or thermal controls that can adjust fan speeds automatically based on the CPU temperature. This allows for optimal cooling performance without the need for manual adjustments.
It’s important to note that different CPU fan models may excel in different areas, and it’s essential to prioritize the characteristics that align with your specific needs and system requirements. Consider factors such as CPU power consumption, case airflow, and intended use to determine which characteristics are most important for your particular setup.
By choosing a CPU fan with effective cooling performance, low noise levels, durability, compatibility, easy installation, and additional thermal management features, you can ensure optimal cooling for your CPU and maintain a stable and reliable computer system.
How to Choose the Right CPU Fan
Choosing the right CPU fan is crucial for maintaining optimal temperatures, performance, and stability of your computer system. With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to find the perfect match. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a CPU fan:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the CPU fan is compatible with your CPU socket. Different CPUs use different socket types, such as Intel’s LGA (Land Grid Array) or AMD’s AM4 socket. Check the manufacturer’s specifications or your motherboard’s documentation for the appropriate CPU socket type.
- Cooling Performance: Consider the cooling performance requirements of your CPU. If you have a high-power CPU or engage in demanding tasks like gaming or video editing, you may need a CPU fan with higher cooling capacities. Look for CPU fans with higher airflow (measured in CFM) and static pressure ratings to ensure effective heat dissipation.
- Noise Levels: Determine the level of noise you are comfortable with. Some CPU fans are designed to operate quietly, while others prioritize maximum cooling performance. Look for CPU fans with lower decibel (dB) ratings or ones that offer fan speed control options like PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) to adjust noise levels to your preference.
- Form Factor and Clearances: Consider the available space in your computer case. Ensure that the CPU fan you choose fits within the height and width clearances of your case. Some CPU fans, such as low-profile or top-flow designs, are specifically designed for compact cases with limited space.
- Heat Dissipation Method: Decide whether you prefer an air-cooled or liquid-cooled CPU fan. Air-cooled CPU fans are more common and generally sufficient for most users. Liquid-cooled CPU fans offer better cooling performance but may require additional installation steps and maintenance.
- Reliability and Durability: Choose a CPU fan from a reputable brand known for producing reliable and durable cooling solutions. Read reviews and consider the warranty length provided by the manufacturer to ensure long-term satisfaction and peace of mind.
- Budget: Determine your budget for a CPU fan. Prices can vary based on the type of fan, brand, and additional features. Set a budget that aligns with your needs and prioritize essential features accordingly.
- Additional Features: Consider any additional features you may need, such as RGB lighting, software control, or temperature sensors. These features can enhance the aesthetics of your system or provide more advanced control over fan speeds and cooling performance.
Research different CPU fan models, compare specifications, and read user reviews to gather information about their performance, reliability, and user experiences. This will help you make an informed decision based on your specific requirements and preferences.
Ultimately, choosing the right CPU fan involves finding a balance between compatibility, cooling performance, noise levels, form factor, durability, and budget. By considering these factors and conducting thorough research, you can select a CPU fan that will effectively cool your CPU, fit within your system, and provide reliable and efficient cooling for optimal performance and longevity.
Installation and Maintenance of CPU Fan
Proper installation and maintenance of a CPU fan are essential for ensuring optimal cooling performance and longevity. Here are the steps to follow for installing and maintaining a CPU fan:
Installation:
- Gather the necessary tools: Before you start, ensure that you have the necessary tools, including a screwdriver (usually a Phillips-head) and thermal paste (if not pre-applied).
- Prepare the system: Shut down your computer and unplug it from the power source. Open the computer case and locate the CPU socket on the motherboard.
- Remove the old CPU fan (if applicable): If you are replacing an existing CPU fan, carefully disconnect the fan cables from the motherboard and remove any screws or clips securing the fan to the CPU socket or heatsink. Gently lift the old fan off the CPU.
- Prepare the CPU: Clean the surface of the CPU using a lint-free cloth or thermal paste remover to remove any residual thermal paste or debris. Ensure that the CPU surface is clean and dry.
- Apply thermal paste (if necessary): If your CPU fan does not come with pre-applied thermal paste, apply a small amount (pea-sized or rice-sized) in the center of the CPU surface. Use a spreading tool or the pressure from the CPU cooler to evenly distribute the thermal paste.
- Install the CPU fan: Gently align the CPU fan with the CPU socket, ensuring that the mounting holes on the fan align with the corresponding holes or hooks on the CPU socket. Secure the CPU fan in place using the provided screws or mounting mechanism. Apply gentle pressure to ensure proper contact between the CPU and the fan or heatsink.
- Connect the fan cables: Connect the fan cables to the appropriate fan headers on the motherboard. Refer to your motherboard’s manual for the specific headers designated for CPU fan connections.
- Close the computer case: Once the CPU fan is securely installed and connected, close the computer case and ensure that all screws or latches are properly secured.
Read also: 9 Best Cpu Cooling Fan for 2025
Maintenance:
- Clean the CPU fan periodically: Over time, dust and debris can accumulate on the fan blades and heatsink, reducing cooling efficiency. Regularly clean the CPU fan using compressed air or a soft brush to remove any dust or debris. Ensure that the computer is turned off and unplugged before cleaning.
- Check for fan operation: Periodically check that the CPU fan is operating smoothly and consistently. If you notice any unusual noises or decreased airflow, it may indicate a problem with the fan. In such cases, consider replacing the fan to ensure effective cooling.
- Monitor CPU temperatures: Use system monitoring software or BIOS utilities to monitor the CPU temperature periodically. Ensure that the CPU temperature remains within safe operating limits. If you notice consistently high temperatures, it may indicate inadequate cooling or a malfunctioning CPU fan. Take appropriate action to address the issue.
- Upgrade if necessary: As technology advances and CPU power increases, you may need to upgrade your CPU fan to keep up with the cooling demands. Monitor CPU temperatures and assess performance regularly to determine if an upgrade is necessary.
By following proper installation procedures, performing periodic maintenance, and monitoring CPU temperatures, you can ensure that your CPU fan operates effectively, keeps the CPU cool, and contributes to the overall performance and longevity of your computer system.
Tip: The CPU fan is a crucial component of a computer that helps to dissipate heat generated by the processor. It is important to regularly clean and maintain the CPU fan to ensure proper cooling and prevent overheating.
Troubleshooting Common CPU Fan Issues
While CPU fans are designed to provide reliable cooling, they can sometimes encounter issues that affect their performance. Here are some common CPU fan issues and troubleshooting steps to resolve them:
1. Unusual Noise:
If you notice unusual noise coming from your CPU fan, it may indicate a problem. Here are some steps to troubleshoot the issue:
- Check for any obstructions near the fan blades or heatsink and remove them if present.
- Ensure that the fan is properly installed and securely connected to the motherboard.
- Clean the fan blades and heatsink from dust or debris that may be causing noise due to airflow obstruction.
- If the noise persists, the fan may be faulty and need to be replaced.
2. Insufficient Cooling:
If your CPU is running at higher temperatures than desired, it could indicate insufficient cooling. Here’s what you can do:
- Ensure that the CPU fan is spinning properly. Check the fan headers on the motherboard for proper connection.
- Clean the fan blades and heatsink from dust or debris that may hinder airflow and heat dissipation.
- If you are using an air-cooled CPU fan, consider upgrading to a more powerful fan or investing in a liquid cooling solution for better cooling performance.
- Verify that the CPU fan speed is appropriately set in the BIOS or through specific software. Adjust fan curves or enable automatic fan control to optimize cooling based on CPU temperatures.
Read more: How To Store CPU
3. Fan Not Spinning:
If the CPU fan is not spinning at all, it can lead to overheating and system instability. Follow these troubleshooting steps:
- Check the fan power connection to the motherboard. Ensure that it is securely connected to the correct fan header.
- Verify that the fan cables are not damaged or severed. Replace cables if needed.
- Check the BIOS settings to ensure that the CPU fan is enabled and properly configured.
- If the fan still does not spin, it may be faulty and require replacement.
4. Excessive Fan Speed:
If the CPU fan is running at excessively high speeds, it may result in unnecessary noise and increased wear on the fan. Try these troubleshooting steps:
- Check the fan speed settings in the BIOS or through specific software. Adjust the fan curves or enable automatic fan control to balance cooling performance and noise levels.
- Clean the fan blades and heatsink to ensure proper airflow and heat dissipation.
- If the problem persists, consider replacing the fan with a quieter model or one with better speed control capabilities.
If you encounter persistent issues with your CPU fan or if you are unsure about the cause of the problem, it is advisable to consult with a professional or contact the manufacturer for further assistance. Proper maintenance, troubleshooting, and timely resolution of CPU fan issues help ensure that your CPU stays cool, enhancing system performance and longevity.
Conclusion
The CPU fan plays a vital role in maintaining the temperature and performance of a computer’s central processing unit (CPU). By effectively dissipating heat and preventing overheating, the CPU fan ensures system stability, extends component lifespan, and enhances overall system performance.
We have discussed the definition and importance of a CPU fan, highlighting its crucial role in cooling the CPU and promoting system reliability. The CPU fan’s functions, including heat dissipation, airflow creation, case ventilation, and prevention of thermal throttling, were explored, showcasing its multi-faceted contributions to system performance.
In addition, we covered the different types of CPU fans, such as air-cooled, liquid-cooled, passive, top-flow, and low-profile options, providing the necessary information to help readers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and system constraints. The characteristics of a good CPU fan, including cooling performance, noise levels, durability, compatibility, ease of installation, and thermal management features, were discussed to guide users in selecting the right CPU fan for their system.
We also delved into the installation and maintenance of a CPU fan, emphasizing the importance of proper installation, periodic cleaning, monitoring CPU temperatures, and upgrading when necessary. By following these guidelines, users can ensure effective cooling, optimal performance, and prolonged longevity of their CPU fan and computer system as a whole.
Lastly, we provided insights into common CPU fan issues, such as unusual noise, insufficient cooling, fan not spinning, and excessive fan speed, along with troubleshooting steps to address these problems. Timely identification and resolution of these issues are crucial to maintain the smooth operation of the CPU fan and prevent further damage or system instability.
In conclusion, the CPU fan is an indispensable component for every computer system. It safeguards the CPU, promotes system stability, and ensures reliable performance. By understanding the importance of a CPU fan, choosing the right one, and properly maintaining it, users can create an optimal cooling environment for their CPU, prolong the lifespan of their system, and enjoy seamless computing experiences for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A CPU Fan
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is a CPU Fan”