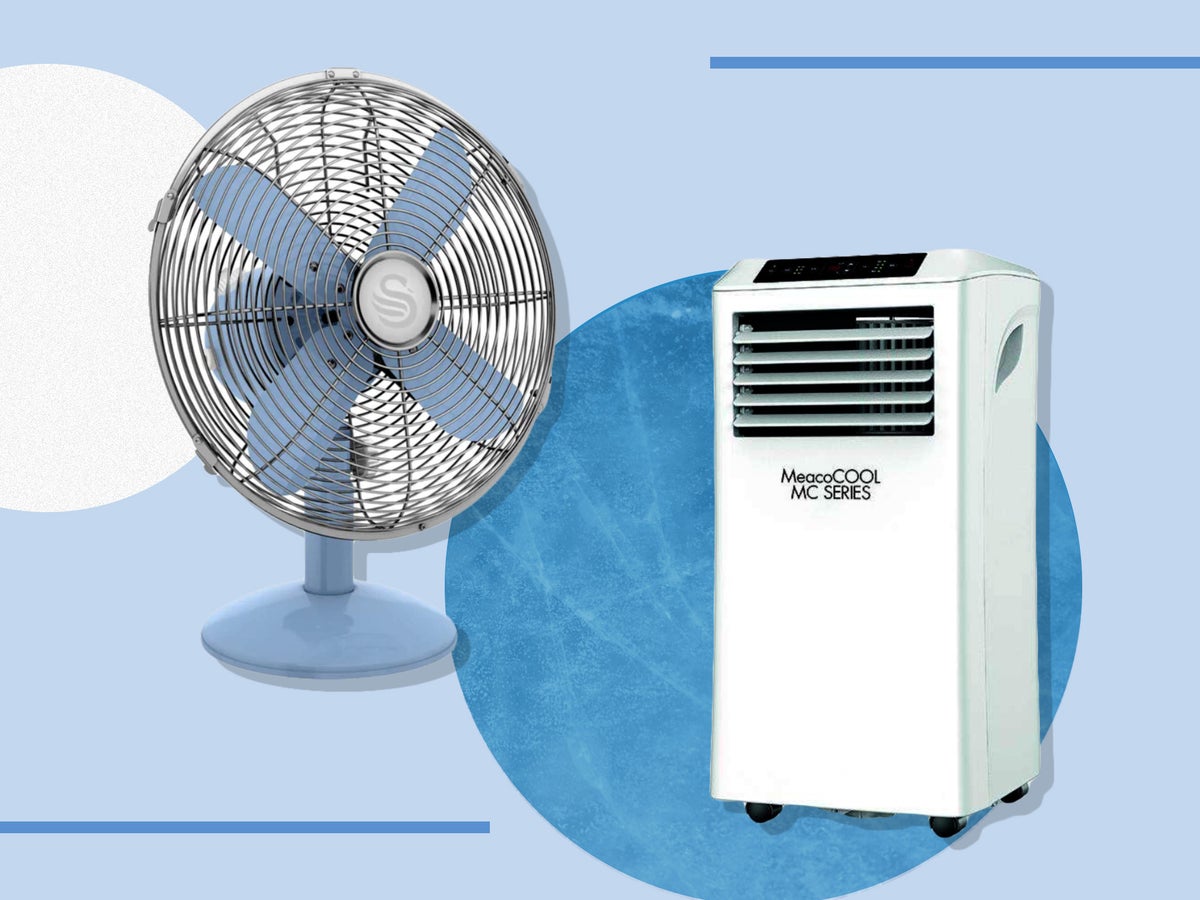


Articles
What Uses More Electricity Ac Or Fan
Modified: November 1, 2024
Discover the energy consumption comparison between AC and fans in this informative article. Find out which one uses more electricity and make informed decisions for your home.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to staying cool during hot summer months or reducing humidity levels in your home, two popular options are air conditioners (ACs) and fans. Both of these appliances provide relief from the heat, but have distinct differences in terms of energy consumption. If you’re wondering which device uses more electricity, it’s essential to evaluate their efficiency and understand the factors that contribute to energy usage.
ACs are designed to cool the air by removing heat and moisture from an enclosed space. They work by using a refrigeration cycle, where warm air is drawn in, cooled through a coil, and then released back into the room. On the other hand, fans do not have a cooling mechanism. They function by circulating air, creating a breeze, and providing a sense of coolness through evaporative cooling.
Energy consumption is a significant concern for many households, not only due to the impact on their electric bills but also the environmental footprint. Understanding the energy usage of ACs and fans can help you make more informed decisions about which cooling option is the most suitable for your needs. In this article, we will compare the energy consumption of ACs and fans and explore the factors that influence their energy efficiency.
Key Takeaways:
- Air conditioners (ACs) consume more electricity than fans due to their cooling mechanism and compressor operation. However, newer energy-efficient AC models can help reduce environmental impact and lower energy costs.
- Fans are a more energy-efficient cooling option compared to ACs, providing localized comfort with significantly lower electricity consumption. Factors such as size, speed settings, and motor efficiency influence fan energy usage.
Read more: What Uses More Gas Windows Or AC
Energy Consumption of an AC
Air conditioners are known for their ability to provide effective cooling in even the hottest conditions. However, this convenience comes at a cost, both financially and in terms of energy usage.
An AC’s energy consumption is primarily determined by its cooling capacity, expressed in British Thermal Units (BTUs), and its efficiency rating, known as the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER). Higher BTU and SEER ratings indicate greater cooling power and improved energy efficiency.
When an AC is turned on, it uses electricity to power the compressor, which actively removes heat from the indoor air. The more heat that needs to be removed to reach the desired temperature, the more electricity the AC will consume. Therefore, factors such as the size of the room, insulation levels, and outdoor temperature can significantly impact the energy consumption of an AC unit.
Additionally, the settings on the AC unit, such as temperature and fan speed, also affect energy usage. Lowering the temperature and increasing the fan speed will result in higher energy consumption. It’s important to find a balance between comfort and energy efficiency to minimize electricity usage.
It’s worth mentioning that newer AC models are more energy-efficient than older ones. If you have an older AC unit, it might be wise to consider upgrading to a newer model that has better energy-saving features. Look for AC units with the Energy Star label, which signifies that they meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
In general, ACs consume more electricity compared to fans due to the cooling mechanism and the power required to operate the compressor. However, advancements in technology have led to the development of energy-efficient AC units that are designed to reduce environmental impact and lower energy costs.
Energy Consumption of a Fan
Fans are a popular and cost-effective option for cooling homes, offices, or other indoor spaces. They provide a refreshing breeze that can make the room feel cooler, even without actually lowering the temperature. As a result, fans tend to have significantly lower energy consumption compared to ACs.
The energy consumption of a fan primarily depends on its size, speed settings, and motor efficiency. Generally, larger fans will consume more electricity than smaller ones. However, fans are known for their low power requirements, especially when compared to AC units.
Electric fans work by using an electric motor to rotate blades, which move the air in the room. This movement creates a cooling effect by increasing evaporation from the skin, which helps to dissipate heat and creates a sense of coolness. The energy consumption of a fan is directly related to the power rating of the motor. Higher wattage motors will consume more electricity.
In terms of energy efficiency, it’s important to note that fans do not lower the temperature of the room. They simply circulate the air, providing a cooling effect through increased air movement. This means that fans are most effective at providing comfort in a small, enclosed space rather than cooling a large area.
Fans also have adjustable speed settings, allowing users to choose between high, medium, or low speeds. Higher speeds consume more energy as the motor works harder to rotate the blades at a faster rate. Conversely, using the fan at lower speeds can help reduce energy consumption without compromising on comfort.
Some modern fan models also come equipped with additional features such as timer functionalities and programmable settings. These features can help further reduce energy consumption by allowing users to automate the fan’s operation based on their preferences and specific cooling needs.
Overall, fans are a more energy-efficient cooling option than AC units. They are a viable choice for individuals who want to stay cool while minimizing energy consumption and reducing electricity costs. Incorporating ceiling fans or portable fans into your cooling strategy can be an effective way to improve comfort without the high energy usage associated with air conditioners.
Factors Affecting Energy Consumption
When comparing the energy consumption of air conditioners (ACs) and fans, it’s important to consider the various factors that can influence their energy efficiency. These factors can play a significant role in determining the overall electricity usage of each appliance. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key factors that affect energy consumption:
- Room size and insulation: The size of the room being cooled or ventilated is a crucial factor. Larger rooms require more cooling power and therefore consume more energy. Additionally, the insulation of the room can impact energy consumption. Well-insulated spaces can retain cool air better, reducing the need for excessive cooling or fan usage.
- Temperature settings: The temperature at which the AC is set or the fan is operated directly affects energy consumption. Lowering the AC temperature or increasing the fan speed will result in higher energy usage. Find a balance that provides comfort without wasting energy.
- Outdoor temperature: The ambient temperature outside can influence the AC’s energy consumption. If it’s exceptionally hot, the AC will have to work harder to maintain the desired indoor temperature, leading to higher electricity usage. In mild weather, fans may be sufficient to provide comfort without the need for air conditioning.
- Efficiency of the appliance: The energy efficiency of both the AC and the fan is an important factor. Look for AC units with a high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) rating and fans with energy-efficient motors. Choosing appliances with better efficiency can contribute to lower energy consumption.
- Usage patterns and duration: The frequency and duration of use also impact energy consumption. If the AC or fan is used for extended periods or left on when not needed, it will result in higher electricity usage. Make a conscious effort to use these appliances only when necessary and consider utilizing timers to control operation times.
- Maintenance and cleanliness: Regular maintenance and cleaning of both ACs and fans are essential for optimal performance and energy efficiency. Clogged filters or dusty blades can restrict airflow, causing the appliances to work harder and consume more energy. Keep the appliances clean and follow manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance.
- Additional features and settings: Some AC models have additional features like energy-saving modes or programmable timers that can help reduce energy consumption. Similarly, fans with adjustable speed settings and timers can be utilized to optimize energy usage based on specific cooling requirements.
These factors can vary from one household to another, making it essential to consider your specific circumstances when evaluating energy consumption. By understanding these factors and making informed choices, you can minimize energy usage, save on electricity costs, and reduce the environmental impact of your cooling choices.
Air conditioning units typically use more electricity than fans. If you’re looking to save on energy costs, consider using a fan instead of running the AC constantly.
Comparison of AC and Fan Energy Consumption
When it comes to comparing the energy consumption of air conditioners (ACs) and fans, there are notable differences between the two appliances. In general, ACs consume more electricity compared to fans due to their cooling mechanism and the power required to operate the compressor.
An AC unit uses electricity to power the compressor, which actively removes heat and moisture from the indoor air. The more significant the cooling capacity and the lower the energy efficiency rating, the more electricity an AC will consume. ACs are designed to cool large spaces, making them suitable for whole-house or room cooling. However, their high energy consumption can result in higher electric bills.
Fans, on the other hand, have significantly lower energy consumption. They work by circulating air, creating a breeze that provides a cooling effect through increased air movement. Fans simply move the existing air in the room without actually lowering the temperature. Because of this, fans are most effective in smaller, enclosed spaces where they can create a localized sense of coolness.
The energy consumption of a fan depends on factors such as size, motor power, and speed settings. Larger fans generally consume more electricity than smaller ones, while higher speed settings result in increased energy usage. However, even at their highest speeds, fans consume considerably less power compared to AC units.
Additionally, advancements in technology have led to the development of energy-efficient AC units. Newer models with higher SEER ratings and energy-saving features are designed to reduce environmental impact and lower energy costs. Choosing an energy-efficient AC model can help mitigate the higher energy consumption associated with ACs.
It’s important to consider the specific cooling requirements and constraints of your space when deciding between an AC and a fan. If you need to cool an entire house or a larger room, an AC may be necessary to achieve the desired temperature. However, if you’re looking for localized cooling or on a budget, a fan can provide sufficient comfort with significantly lower energy usage.
In some cases, a combination of AC and fans can be an energy-efficient solution. For example, using an AC to cool the main living areas and utilizing fans to circulate the cooled air can help optimize energy consumption. Ceiling fans are particularly effective as they can generate a breeze that enhances the perceived coolness of the room.
Ultimately, the choice between an AC and a fan depends on various factors, including the size of the space, climate conditions, personal preferences, and energy efficiency goals. Evaluating these factors and understanding the energy consumption of both appliances can help you make an informed decision that balances both comfort and energy efficiency.
Additional Considerations
When comparing the energy consumption of air conditioners (ACs) and fans, there are some additional considerations to keep in mind to help you make an informed decision:
- Regional climate: The climate of your region plays a significant role in determining the cooling needs of your space. If you live in an area with intense heat or high humidity levels, an AC may be necessary to maintain a comfortable indoor environment. On the other hand, in milder climates, fans may be sufficient to provide the desired level of comfort.
- Health considerations: Some individuals may have specific health conditions, such as respiratory issues or allergies, that require cleaner air quality. ACs can help filter out pollutants and allergens, improving indoor air quality. However, fans can help with air circulation, preventing stagnant air and reducing the likelihood of mold or mildew growth.
- Noise levels: AC units tend to produce more noise compared to fans, especially when the compressor is running. If noise is a concern, fans are generally a quieter option, making them more suitable for bedrooms or offices where quiet operation is preferred.
- Installation and maintenance costs: AC units require professional installation and regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. These costs, along with higher energy consumption, should be factored into your decision. Meanwhile, fans are relatively inexpensive and require minimal installation and maintenance efforts.
- Aesthetic considerations: The appearance and design of the cooling appliance may also be important to consider. AC units are often more visible, while fans can be hidden in the ceiling or come in various stylish designs that complement the decor of the room.
- Sustainable cooling options: If environmental sustainability is a priority for you, considering alternative cooling options, such as evaporative coolers or ceiling fans, may be worth exploring. These options can provide efficient and eco-friendly cooling solutions with reduced energy consumption.
It’s important to weigh these additional factors alongside energy consumption to determine the best cooling option for your specific needs. Remember to consider the size of the space, climate conditions, personal preferences, and budget constraints when making a decision.
Ultimately, striking a balance between comfort, energy efficiency, and affordability is key. Finding the right combination of cooling technologies and strategies can help you create a comfortable environment while minimizing energy consumption and reducing your carbon footprint.
Conclusion
When comparing the energy consumption of air conditioners (ACs) and fans, it’s clear that there are significant differences between the two appliances. ACs are designed to cool entire rooms or even houses, utilizing a refrigeration cycle to remove heat and moisture from the air. Due to their cooling mechanism and the power required to operate the compressor, ACs consume more electricity compared to fans.
Fans, on the other hand, provide a refreshing breeze that creates a cooling effect through increased air movement. They consume significantly less power compared to ACs and are a more energy-efficient option for localized cooling. Fans are best suited for smaller, enclosed spaces, providing relief and comfort without drastically impacting energy consumption.
When considering the energy consumption of ACs and fans, it’s important to evaluate other factors as well. The size of the room, insulation levels, temperature settings, outdoor temperature, appliance efficiency, usage patterns, and maintenance all play a role in determining energy usage. Taking these factors into account enables you to make informed decisions that balance both comfort and energy efficiency.
In some cases, a combination of ACs and fans can be a suitable solution. ACs can be used for cooling main living areas or larger spaces, while fans can assist in distributing the cooled air and providing localized comfort. This hybrid approach can help optimize energy consumption and strike a balance between cooling effectiveness and cost.
Ultimately, the choice between an AC and a fan depends on your specific cooling requirements, climate conditions, budget, and environmental considerations. By evaluating these factors and understanding the energy consumption of both appliances, you can make a decision that meets your needs while minimizing energy usage and reducing your carbon footprint.
Remember, efficiency, comfort, and sustainability go hand in hand. Selecting energy-efficient appliances and adopting smart cooling strategies can not only keep you cool during the hot summer months but also contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Uses More Electricity Ac Or Fan
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Uses More Electricity Ac Or Fan”