

Articles
When Was The Chimney Invented
Modified: August 22, 2024
Discover the fascinating history of chimney invention in this captivating collection of articles. Uncover the origins and evolution of this integral architectural feature.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
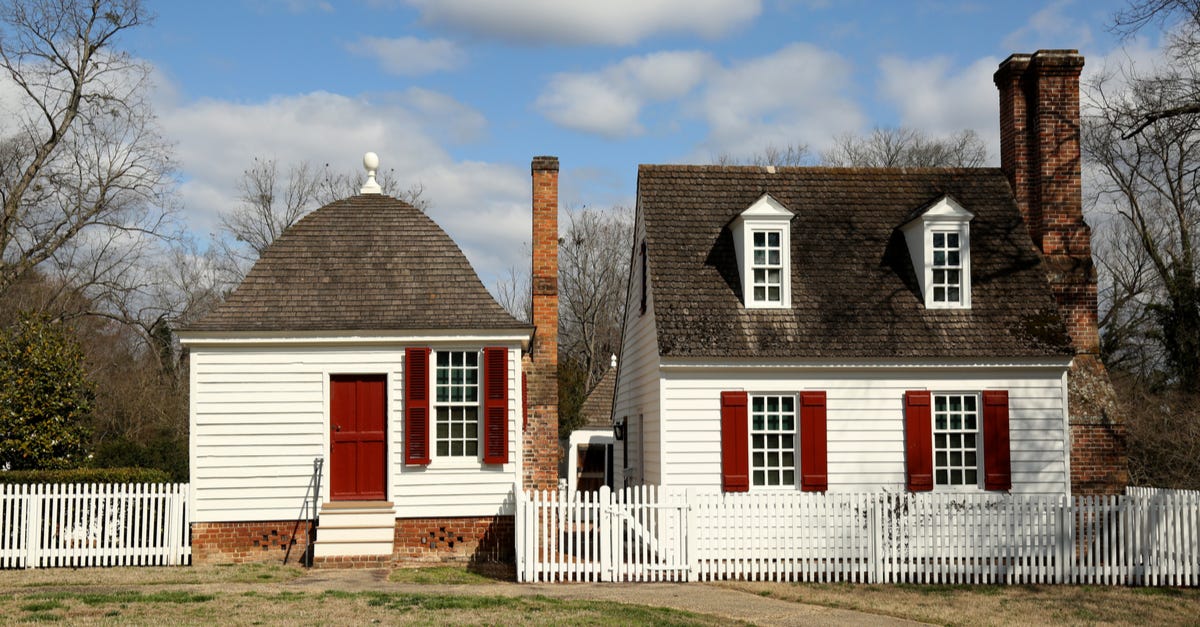
Fire has been a fundamental element for human survival and comfort since the beginning of time. From ancient civilizations huddling around open fires to the modern central heating systems of today, the evolution of fire and heating methods has been remarkable. One significant invention that revolutionized the way we harness and distribute heat is the chimney.
The chimney, a vertical structure designed to carry smoke and gases away from a living space, has a long and fascinating history. Its invention not only improved ventilation and prevented smoke-related health issues but also contributed to the architectural and aesthetic developments of homes throughout the centuries.
In this article, we will delve into the origins and development of the chimney, exploring its rich history from its early beginnings to its relevance in modern times. By understanding the chimney’s evolution, we can appreciate its impact on various aspects of human civilization and the comfort it has provided for countless generations.
Key Takeaways:
- The invention and evolution of chimneys have significantly impacted human civilization, providing essential functions such as improving ventilation, reducing health risks, and adding architectural beauty to homes and buildings.
- From ancient Roman innovations to modern advancements, chimneys have adapted to changing technologies and design preferences, remaining relevant and widely used for venting gases, maintaining indoor air quality, and enhancing the overall aesthetics of buildings.
Read more: When Was The Bathtub Invented
Early History of Fire and Heating
Fire has been central to human survival and warmth since prehistoric times. The ability to control fire not only provided protection from predators but also offered heat, light, and culinary possibilities. In the early days, our ancestors would gather around open fires, seeking warmth and security in their primitive shelters.
As societies advanced, so did methods of heating. Ancient civilizations, such as the Greeks and Romans, developed more sophisticated heating systems. The Greeks used central heating in their public buildings, such as bathhouses, by directing the heat from fires through a complex network of underground channels. The Romans, renowned for their engineering prowess, developed an intricate system called a hypocaust. This underfloor heating system allowed hot air to circulate beneath the floors, providing warmth to their luxurious villas and public spaces.
Including subtitle ‘Early Chimney Designs’
As heating methods evolved, so did the need for better ventilation. Early chimney designs started to emerge, although not in the form we recognize today. These early chimneys consisted of simple holes or vents in the walls or roofs of buildings, allowing smoke to escape. While these primitive vents served the purpose of removing smoke, they did little in terms of effectively channeling and controlling the airflow.
Additionally, early chimneys often lacked proper insulation, resulting in constant heat loss. Despite their limitations, these early chimney designs were an important step towards the development of more sophisticated structures that would come later.
Origins of the Chimney
The true origins of the chimney as we know it today can be traced back to ancient Rome. The Roman Empire was not only famous for its impressive architectural marvels but also for its innovation in heating systems. One of their most significant contributions was the creation of the “domus,” a type of residential housing that included a central heating system with a chimney-like structure.
The domus featured a central open space called the atrium, which served as the main living area. A hole in the roof, called the compluvium, allowed smoke from the central hearth to escape. Over time, the compluvium evolved into a more sophisticated structure known as the smoke flue. This flue, constructed using bricks and tiles, directed the smoke upwards and out of the building, effectively creating a chimney-like structure.
As the Roman Empire expanded, knowledge of their heating systems spread to other regions, including Northern Europe. However, with the fall of the Roman Empire, the technology and understanding of advanced heating systems and chimneys were lost for centuries.
Including subtitle ‘Rediscovery and Development’
It wasn’t until the medieval period that chimneys began to re-emerge in Western Europe. As more permanent structures were built, the need for improved ventilation and heating became crucial. The medieval chimneys were often constructed using stone or rubble, and their main purpose was to allow smoke to escape from the building.
During this period, chimneys were integrated into the great halls of castles and manor houses. These large, imposing structures were not only functional but also symbolized the wealth and status of their owners. Roaring fires would be lit in the hearths, with the chimneys carrying away the smoke and ensuring a more pleasant and healthier living environment.
However, early medieval chimneys lacked the design sophistication we associate with chimneys today. They were often oversized, with wide flues that allowed for significant heat loss. Moreover, chimney sweeps were not yet common, resulting in the accumulation of soot and the increased risk of chimney fires.
Medieval and Renaissance Chimneys
During the medieval and Renaissance periods, chimney design and construction underwent significant advancements. The need for more efficient heating systems, combined with the emergence of skilled craftsmen and tradesmen, led to the refinement of chimney architecture.
Including subtitle ‘Architectural Features’
Medieval chimneys were typically made of stone, with their design characterized by a square or rectangular shape. These chimneys integrated seamlessly into the architecture of castles and manor houses, becoming an integral part of the overall aesthetic appeal. Chimneys were often tall and slender, rising above the rooftops in a distinctive manner.
One notable architectural feature of these chimneys was the addition of corbels. Corbels were projecting supports placed underneath the chimney’s upper structure, allowing for better stability and weight distribution. These corbelled chimneys added a touch of elegance to the buildings, serving both functional and decorative purposes.
Another feature of medieval chimneys was the inclusion of smaller flues within the chimney structure. These smaller flues, called smoke escapes or smoke jacks, allowed the smoke to escape from individual rooms, preventing it from traveling throughout the entire building. This advancement improved the efficiency of the heating system and reduced the risk of smoke inhalation in different parts of the house.
With the arrival of the Renaissance period, chimney design became even more elaborate and ornate. Chimneys began to feature decorative elements such as carved stone or marble, intricate patterns, and decorative caps or finials. These embellishments added a touch of elegance and sophistication to the overall aesthetic of the buildings.
Including subtitle ‘Chimney Sweeps’
During this time, the role of chimney sweeps also became more prominent. Chimney sweeps were skilled individuals who specialized in cleaning chimneys and preventing the accumulation of soot and debris. Their services were essential in maintaining the efficiency and safety of chimneys, as well as reducing the risk of chimney fires.
The occupation of a chimney sweep became widely recognized and respected. In some areas, chimney sweeps even had their own annual festivals and celebrations, reflecting the importance of their profession.
Medieval and Renaissance chimneys marked a significant step forward in heating technology and architectural design. These chimneys not only improved heating efficiency but also added a touch of grandeur and elegance to the buildings they were integrated into. The advancements in chimney architecture during this time laid the foundation for the modern chimneys we are familiar with today.
The chimney was invented in ancient Rome, around 1st century AD. It was used to vent smoke and gases from indoor fires, improving air quality and fire safety.
The Advancements in Chimney Design
The evolution of chimney design continued to progress, with significant advancements during the Industrial Revolution and beyond. During this time, technological innovations and changes in society resulted in new materials, improved construction techniques, and a better understanding of chimney physics.
Including subtitle ‘Influence of Industrial Revolution’
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the 18th century, brought about a wave of technological advancements that impacted chimney design. The increased use of coal as a fuel source for heating and industrial processes resulted in a more significant demand for efficient chimney systems.
One of the most significant developments during this time was the invention of the chimney stack. The chimney stack, also known as a chimney pot or chimney flue, replaced the traditional open chimney top. This simple addition had a profound effect on chimney draft efficiency and reducing the risk of downdrafts caused by inclement weather conditions.
Including subtitle ‘Important Features’
Another important feature that emerged during this period was the inclusion of a damper in chimneys. The damper is a metal plate or valve within the chimney that can be opened or closed to control the airflow. This innovation allowed homeowners to regulate the heat output more effectively and prevent heat loss when the fireplace was not in use.
With the advent of new construction materials, such as brick, concrete, and metal, chimney design became more versatile and adaptable. These materials offered better insulation and durability, allowing for the construction of taller and more intricately designed chimneys.
Including subtitle ‘Reinforcement and Modern Innovations’
As architecture and construction techniques continued to develop, chimney reinforcement became a crucial aspect of design. Metal flues and liners were introduced to strengthen the chimney structure, improve fire safety, and prevent the degradation caused by the corrosive byproducts of combustion.
In recent years, several modern innovations have further improved chimney design. The implementation of damp-proofing materials has addressed issues related to water infiltration and damage. Additionally, the introduction of insulated chimneys and liner systems has significantly enhanced energy efficiency and reduced heat loss.
Furthermore, technology has made its way into chimney design. Advanced smoke detectors and carbon monoxide alarms provide an additional layer of safety, alerting homeowners to potential hazards and improving overall fire prevention.
The advancements in chimney design over time have resulted in safer, more efficient, and aesthetically pleasing structures. Chimneys have become an integral part of architectural design, adding charm and character to homes while providing comfort and functionality.
Read more: When Was HVAC Invented
Chimneys in Modern Times
In today’s modern world, chimneys continue to play a vital role in providing efficient heating and ventilation. Although many modern homes utilize alternative heating sources such as electric or gas-powered systems, chimneys still remain relevant and widely used.
Including subtitle ‘Function and Versatility’
Chimneys in modern times serve multiple purposes. They provide a way to safely vent gases and smoke generated from heating systems and fireplaces. Chimneys also play a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality by removing pollutants and ensuring proper ventilation.
Moreover, chimneys have evolved to accommodate a range of heating options. Wood-burning stoves, pellet stoves, and gas fireplaces are just a few examples of appliances that require a chimney for proper ventilation. These modern heating systems are designed to maximize energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Including subtitle ‘Design and Aesthetics’
Today’s chimney design focuses not only on functionality but also on aesthetics. Chimneys are often incorporated into the overall architectural design of homes and buildings, enhancing their visual appeal. Modern chimneys can be sleek and minimalist, or they can feature unique shapes and materials that complement the style of the structure.
Additionally, chimneys can be fitted with various accessories and finishes to further enhance their appearance. Decorative chimney caps, custom stone or brickwork, and even built-in lighting can add an element of personalization and individuality to the chimney design.
Including subtitle ‘Maintenance and Safety’
Maintaining and ensuring the safety of chimneys is of utmost importance. Regular chimney inspections and cleanings by professional chimney sweeps are recommended to remove built-up creosote, debris, and potential blockages. This not only improves the performance of the chimney but also reduces the risk of chimney fires and carbon monoxide poisoning.
Moreover, chimney safety features have become more advanced in modern times. Chimney liners and insulation help to prevent heat transfer and condensation, maintaining optimal performance and prolonging the lifespan of the chimney. Additionally, the installation of chimney caps can prevent birds, debris, and rainwater from entering the chimney, further protecting the structure.
Including subtitle ‘Emerging Technologies’
As technology continues to advance, new innovations are being introduced to improve chimney functionality and enhance safety. Smart chimney monitoring systems, for example, can connect to home automation networks and provide real-time information on chimney conditions, including temperature, draft, and air quality.
Furthermore, eco-friendly practices are being incorporated into chimney design. The development of clean-burning technologies, such as catalytic converters and high-efficiency particulate filters, aims to reduce emissions and minimize the environmental impact of burning fossil fuels.
Chimneys in modern times have evolved to meet the changing needs and demands of a technologically advanced society. Whether for heating, ventilation, or as an architectural focal point, chimneys continue to play a significant role in our homes and buildings, combining functionality, design, and safety.
Conclusion
The invention and development of chimneys have had a profound impact on the way we harness and distribute heat. From their humble beginnings as simple vents to the intricate and aesthetically pleasing structures we see today, chimneys have evolved alongside human civilization.
Throughout history, chimneys have provided essential functions, from improving ventilation and reducing health risks associated with smoke to enhancing heating efficiency and adding architectural beauty to homes and buildings. They have stood the test of time, adapting to changing technologies, materials, and design preferences.
From the ancient Romans’ use of the domus and smoke flues to medieval and Renaissance chimneys integrated into grand castles and manor houses, the design and functionality of chimneys have continued to evolve. The Industrial Revolution brought about significant advancements, including the introduction of chimney stacks and dampers to improve efficiency and control airflow. In modern times, chimneys have become versatile, accommodating a range of heating options and serving as design features that enhance the overall aesthetics of buildings.
Despite the emergence of alternative heating systems, such as electric and gas-powered options, chimneys remain relevant and widely used. They continue to provide essential functions in venting gases and smoke, maintaining indoor air quality, and adding character and charm to architectural designs.
Maintaining and ensuring the safety of chimneys through regular inspections and cleanings, as well as the implementation of advanced technologies and safety features, is crucial for their optimal performance and longevity.
In conclusion, the invention and evolution of chimneys have greatly contributed to the comfort, safety, and architectural beauty of our homes and buildings. As we continue to advance technologically and environmentally, chimneys will likely undergo further innovation to meet the changing demands of the modern world. Through it all, chimneys will remain a symbol of warmth, functionality, and timeless elegance.
Frequently Asked Questions about When Was The Chimney Invented
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “When Was The Chimney Invented”