Home>Articles>Why One Of The 2 Prongs Of An Electrical Cord Are Bigger Than The Other


Articles
Why One Of The 2 Prongs Of An Electrical Cord Are Bigger Than The Other
Modified: October 28, 2024
Discover the reason why one of the prongs on an electrical cord is larger than the other in this informative article on electrical cords. Learn about the functionality and safety measures in place.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Have you ever wondered why one of the 2 prongs of an electrical cord is bigger than the other? It’s a curious observation, and you may have pondered the reasoning behind it. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of electrical cords and delve into the reasons why one prong is larger than the other.
Electrical cords are an essential part of our modern lives. We rely on them to power our electronic devices, appliances, and lighting fixtures. Whether it’s a laptop charger, a toaster, or a desk lamp, these cords provide the vital connection between our electrical devices and the power outlet.
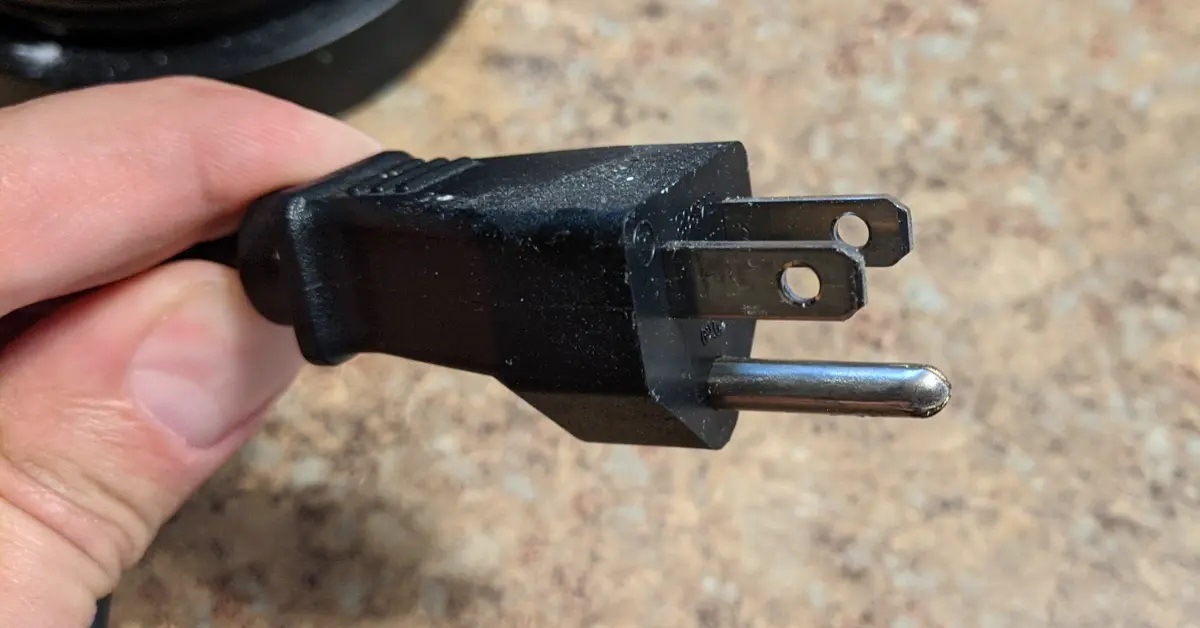
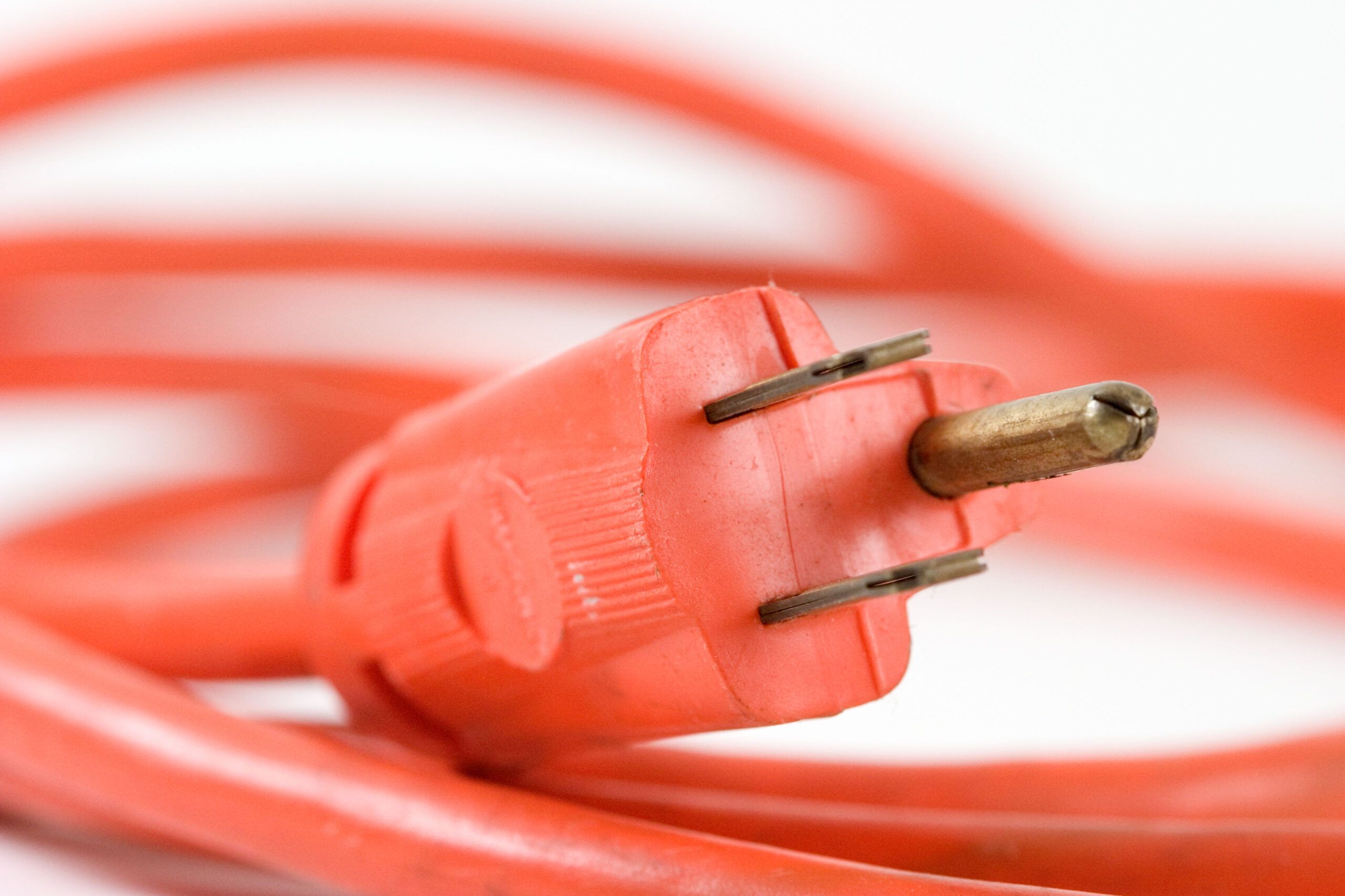
When you take a closer look at an electrical cord, you’ll notice that it has two prongs – one larger and one smaller. These prongs are designed to fit into the corresponding slots of an electrical outlet. But why are they different in size? Is there a specific purpose behind it, or is it purely a design choice? Let’s find out.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the size difference in the prongs of an electrical cord provides insight into the intricate design of electrical systems, ensuring proper connections and minimizing electrical hazards.
- Different types of electrical plugs are used worldwide, and understanding their compatibility is crucial for safe and reliable electrical connections, especially when traveling internationally.
Read more: Why Is Some Grass Darker Than Others
Understanding Electrical Cords
Before we dive into the details, let’s first understand the basic anatomy of an electrical cord. An electrical cord consists of three primary components – the conducting wires, the insulation, and the plug.
The conducting wires are usually made of copper or aluminum and are responsible for carrying the electrical current from the power source to the device. These wires are typically color-coded – the black or red wire is the “hot” wire that carries the current, the white wire is the neutral wire that completes the circuit, and the green or bare wire is the ground wire that provides a safe path for excess electrical energy.
The conducting wires are then surrounded by insulation, which is typically made of a plastic or rubber material. The insulation serves two crucial purposes: it protects us from coming into direct contact with the live wires, preventing electric shocks, and it prevents the wires from coming into contact with each other, avoiding short circuits.
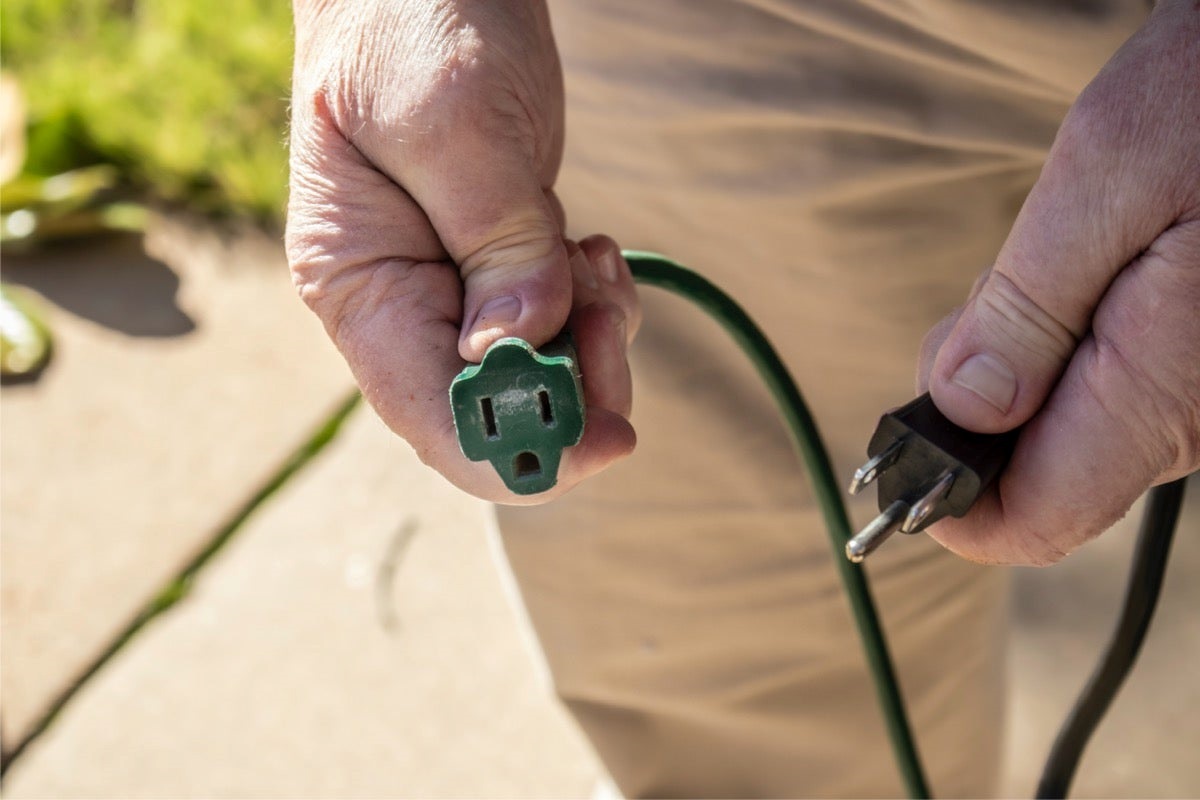
At the end of the cord, we have the plug, which is responsible for connecting the cord to the electrical outlet. The plug consists of two prongs and sometimes an additional grounding prong. It’s these prongs that have the noticeable size difference. But why?
Now that we have a basic understanding of electrical cords, let’s explore the purpose behind the size difference in the prongs.
The Purpose of Prongs
The prongs of an electrical cord serve a vital purpose in ensuring a proper and secure connection between the cord and the electrical outlet. Each prong has a specific function:
1. The Larger Prong: Also known as the “hot” prong or the “live” prong, the larger prong is responsible for carrying the electrical current from the power source to the device. It is typically connected to the “hot” wire, which is the wire that carries the current from the power source. The larger prong is designed to fit into the larger slot in the outlet, which is connected to the “hot” wire of the electrical system.
2. The Smaller Prong: The smaller prong, also referred to as the “neutral” prong, is connected to the neutral wire of the electrical system. The neutral wire completes the circuit and carries the current back to the power source. The smaller size of this prong allows it to fit into the smaller slot in the outlet, which is connected to the neutral wire.
By having different-sized prongs, electrical cords ensure that they can only be inserted into an outlet in one specific orientation. This ensures that the hot and neutral wires are correctly connected and prevents the risk of electrical short circuits or improper grounding.
In addition to the size difference, some electrical plugs also have an additional prong, known as the grounding prong. This prong is usually located below the hot and neutral prongs and is designed to provide an additional level of safety. The grounding prong connects the electrical device to the ground wire in the electrical system, redirecting any excess electrical energy to the ground and preventing electrical shocks.
Now that we understand the purpose behind the size difference in the prongs, let’s explore the safety considerations that drove this design choice.
The Size Difference in Prongs
The size difference in the prongs of an electrical cord is not purely arbitrary. It is a deliberate design choice based on the electrical system’s wiring configuration and safety considerations.
The larger prong, often referred to as the “hot” or “live” prong, is designed to fit into the larger slot in the outlet, which is connected to the “hot” wire of the electrical system. The hot wire carries the current from the power source, whether it’s a power plant or a battery, to the electrical device. The larger size of the prong ensures a secure and firm connection that can handle the flow of electrical current.
The smaller prong, known as the “neutral” prong, is connected to the neutral wire of the electrical system. The neutral wire completes the circuit by carrying the current back to the power source. The smaller size of the prong allows it to fit into the smaller slot in the outlet, which is connected to the neutral wire. This ensures that the electrical current flows smoothly and completes the circuit without any interruptions.
The size difference in the prongs serves as a safety feature as well. It prevents the possibility of inserting the cord in reverse, where the smaller prong would be connected to the “hot” wire and the larger prong to the neutral wire. This would disrupt the electrical flow, potentially leading to short circuits, overheating, or other electrical hazards.
Furthermore, the size difference in the prongs also helps prevent accidental contact with live electrical parts. The larger prong, being the “hot” prong, is connected to the wire carrying the electrical current. By having a larger size, it is less likely to come into contact with other conductive surfaces or objects, reducing the risk of shock or electrocution.
It’s essential to note that the size difference in prongs may vary in different countries or regions. Some countries may have three-prong plugs, where an additional grounding prong is present. The grounding prong offers an extra safety measure by connecting the device to the ground wire, redirecting any excess electrical energy to the ground.
By understanding the reason behind the size difference in prongs, we can appreciate the thought put into the design of electrical cords and plugs, ensuring proper electrical connections and minimizing the risk of electrical hazards.
The larger prong on an electrical cord is the neutral prong, which is designed to ensure that the plug is inserted into the outlet in the correct orientation. This helps to maintain the polarity of the electrical circuit and ensure safety.
Safety Considerations
When it comes to electrical systems, safety is of utmost importance. The size difference in the prongs of an electrical cord plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety of both the user and the electrical device.
Here are some safety considerations associated with the size difference in prongs:
1. Polarity: The size difference helps maintain the proper polarity of the electrical connection. The larger prong, connected to the “hot” wire, fits into the larger slot in the outlet, while the smaller prong, connected to the neutral wire, fits into the smaller slot. This ensures that the electrical current flows in the correct direction, preventing potential electrical hazards.
2. Prevention of Short Circuits: The size difference in prongs reduces the risk of short circuits. If the prongs were the same size, there would be a possibility of inserting the cord into the outlet in reverse, connecting the “hot” wire to the neutral slot and vice versa. This could lead to a short circuit, causing damage to the electrical device or even starting a fire.
3. Electrical Shock Prevention: The larger prong, being connected to the “hot” wire, is designed to be inserted into the larger slot that carries the electrical current. By having a larger size, it reduces the chances of coming into accidental contact with other conductive surfaces or objects, minimizing the risk of electrical shock or electrocution.
4. Grounding: In some cases, electrical plugs may have an additional grounding prong. The grounding prong connects the electrical device to the ground wire in the electrical system. This helps redirect any excess electrical energy to the ground, providing an additional layer of protection against electrical shocks and reducing the risk of electrical fires.
5. International Compatibility: The size difference in prongs can also vary depending on the country or region. Different countries have different electrical systems and plug designs. This ensures that electrical cords manufactured for specific regions are compatible with the electrical outlets available in those areas, preventing users from using incompatible or unsafe electrical connections.
It is important to handle electrical cords and plugs with care and follow proper safety practices. Always make sure the electrical cord is in good condition, with no signs of fraying or damage. Insert the plug fully into the outlet, ensuring a secure connection. Avoid overloading outlets and using extension cords for prolonged periods.
By understanding and respecting the safety considerations associated with the size difference in prongs, we can ensure the safe and efficient use of electrical devices.
Different Types of Electrical Plugs
Electrical plugs come in various types and designs, each tailored to suit specific electrical systems and outlet configurations. Here are some of the different types of electrical plugs commonly used around the world:
1. Type A: This is the most common type of plug used in North America, Central America, and some parts of South America and Asia. It has two flat prongs, with the larger prong being the “hot” prong and the smaller prong the neutral prong.
2. Type B: Similar to the Type A plug, the Type B plug is also commonly used in North America and other regions. It features two flat prongs like the Type A, but with the addition of a grounding prong below. This grounding prong provides an extra level of safety.
3. Type C: The Type C plug, also known as the Europlug, is commonly used in Europe, Asia, and various other regions. It has two round pins and does not have an additional grounding prong. This plug is known for its compact size and compatibility with many outlets found worldwide.
4. Type D: The Type D plug, often called the Indian plug, is primarily used in India, Sri Lanka, and Nepal. It has three round pins in a triangular formation. The larger pin is the grounding pin, while the other two are the “hot” and neutral pins.
5. Type G: The Type G plug is commonly used in the United Kingdom, Ireland, and other countries in Europe, Africa, and Asia. It features three rectangular prongs in a triangular formation. The larger prong is the grounding prong, while the other two are the “hot” and neutral prongs.
6. Type I: The Type I plug is used in Australia, New Zealand, China, and Argentina, among other countries. It has two flat pins in a V-shape, with an additional grounding pin below. The angled shape of the pins prevents the plug from being inserted incorrectly.
7. Type J: This plug is used in Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It has three rounded pins in a linear formation, with a grounding pin at the center.
These are just a few examples of the different types of electrical plugs used worldwide. It’s important to note that the electrical devices and cords you purchase should match the type of plug used in your specific country or the region you plan to use them in.
When traveling internationally, it’s also essential to have the appropriate plug adapters or converters to ensure compatibility with the local electrical outlets. Using incorrect plugs can lead to improper connections, electrical hazards, or damage to your electrical devices.
By being aware of the different types of electrical plugs and understanding their compatibility, you can ensure safe and reliable electrical connections wherever you are.
Conclusion
Understanding why one of the two prongs of an electrical cord is bigger than the other provides insight into the intricacies of electrical systems and the importance of safety in their design. The larger prong, known as the “hot” prong, carries the electrical current, while the smaller prong, the neutral prong, completes the circuit. The size difference ensures the proper connection and prevents electrical hazards, such as short circuits and incorrect polarity.
The size difference in prongs also serves as a safety feature, reducing the risk of accidental contact with live electrical parts and minimizing the chances of electrical shocks or electrocution. Additionally, some electrical plugs have an extra grounding prong, further enhancing safety by redirecting excess electrical energy to the ground.
It is important to remember that different countries and regions have varying types of electrical plugs to suit their electrical systems. Understanding the different types of plugs and their compatibility is crucial when traveling or using devices from different regions to ensure safe and effective electrical connections.
By respecting safety considerations and using electrical cords and plugs correctly, we can prevent accidents, protect our electrical devices, and ensure a safe and efficient use of electricity in our daily lives.
In conclusion, the size difference in the prongs of an electrical cord is not just a design choice, but a deliberate feature that helps maintain proper electrical connections and enhances safety. It’s a testament to the thoughtful engineering behind electrical systems, ensuring our comfort, convenience, and, most importantly, our well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about Why One Of The 2 Prongs Of An Electrical Cord Are Bigger Than The Other
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “Why One Of The 2 Prongs Of An Electrical Cord Are Bigger Than The Other”