Home>Data Storage>Read Only Memory>Is ROM Volatile Or Nonvolatile? (What Are The Differences?)

Read Only Memory
Is ROM Volatile Or Nonvolatile? (What Are The Differences?)
Modified: December 6, 2023
Find out if Read-Only Memory (ROM) is volatile or non-volatile and learn the differences between these two types of memory.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Are you finding it difficult to determine whether ROM is volatile or non-volatile? And are you wondering about the differences between the two? This article provides you with relevant information that will help you answer these questions and much more. More storage ideas below!
What Is ROM?

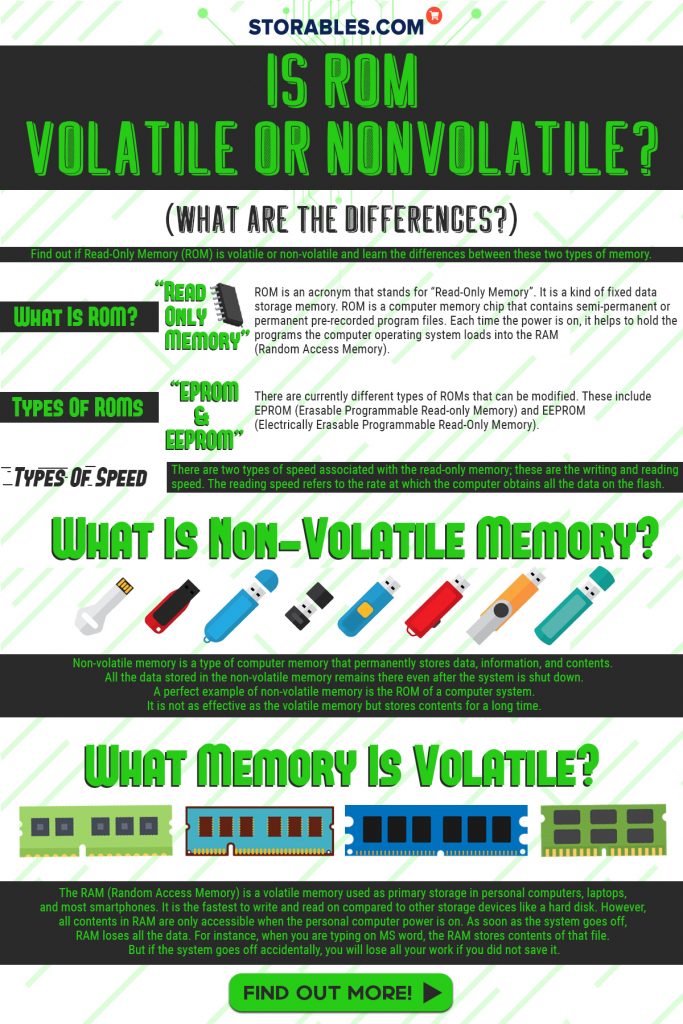
ROM is an acronym that stands for “Read-Only Memory”. It is a kind of fixed data storage memory. ROM is a computer memory chip that contains semi-permanent or permanent pre-recorded program files. Each time the power is on, it helps to hold programs that the computer operating system loads into the RAM (Random Access Memory).
Read-only memory is a mask type of computer memory – the oldest of its kind. All contents stored in it are permanent and can never be modified. However, since its invention in 1956, it has undergone several changes.
Types Of ROMs

There are currently different types of ROMs that can be modified. These include EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-only Memory) and EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory).
EPROM is a type of erasable ROM that can be adjusted more than once. However, if you want to write new data on an EPROM, you will need a special programmer circuit. EPROMs are designed with a quartz window which enables them to be erased under a powerful UV light. On the other hand, the EEPROM has a structure that is similar to that of the EPROM, but is more efficient in the sense that it can both be rewritten and erased electrically.
Types Of Speed
There are two types of speed associated with the read-only memory, namely writing speed and reading speed. Reading speed refers to the rate at which the computer obtains all the data on the flash. Writing speed, on the other hand, refers to the rate at which data is written over the memory.
ROM is used to store BIOS (basic input/output system), reading & writing to peripheral devices, boot up, and essential data management. It acts as a computer security check system. Every program run on the computer must first pass through a routine before it can access any hardware component.
Difference Between Volatile Non Volatile Memory

Data Stored
Volatile memory stores all data of programs currently run by the Central Processing Unit. Similarly, all frequently used data is also stored in volatile memory. On the other hand, non-volatile memory stores the data of the necessary booting process of the computer. It also saves all data and media files that are programmed for permanent storage.
Read more: What Does ROM Mean And Why Do You Need It?
Impact
Memory like RAM generally affect the performance of the computer while non-volatile memory does not have any significant impact on it. Instead, the latter affects the storage capacity of the system.
Speed
Volatile memories are among the fastest and most efficient. They contain data of the most frequently used programs. You can easily access all data stored in the volatile memory. The rate at which the CPU accesses data stored in non-volatile memory is slower compared to its volatile counterpart.
What Is Volatile Memory?
Volatile memory is a type of computer memory that stores data temporarily. Usually referred to as temporary memory, its contents are only present when the computer system’s power is running. As soon as the system is switched off, all stored information will be lost.
Due to its temporary nature, volatile memory only stores the most frequently used data, and the data of all running programs on the computer processor. It is efficient, fast and easily accessible. Volatile memory has a direct influence on the performance of the computer. The more volatile data you have, the more effective the performance of your computer system will be.
Why ROM Is Non-Volatile?

Read-only memory is a non-volatile storage solution. This is because you cannot erase or modify it when the computer system is turned off. Computer manufacturers write codes on the ROM chip, and users cannot alter or interfere with it. But there are modern types of ROMs which can actually be deleted or modified despite the fact that they are non-volatile.
ROM stores contents, data, and information in semiconductor memory chips, e.g. floating-gate memory cells comprising of floating-gate metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors MOSFETs, including flash storage memory storage like SSD (solid-state drives), NAND flash and ROM chips such as EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable ROM), EPROM (erasable programmable ROM). It can also be referred to as traditional non-volatile disk storage.
Read more: RAM Vs. ROM: 12 Major Differences To Know
Electrically Addressed Storage
Another key attribute that makes ROM non-volatile is the fact that it is an electrically addressed storage. Non-volatile memories are classified based on their write mechanism. Mask ROMs are mostly used to store large volumes of data that do not need to be modified or updated after manufacture. Programmable ROMs can be changed after manufacture.
ROM also refers to the part of the computer system that is in-built and is required for the smooth running of the operating system. In the case of a computer, it is located on the motherboard. It generally helps with data transfer and memory space management, and is programmed and locked such that it cannot be modified. This is the basis upon which is referred to as non-volatile memory.
What Is Non-Volatile Memory?

Non-volatile memory is a type of computer memory that permanently stores data, information, and contents. All data stored in the non-volatile memory remains there even after the system is shut down. A perfect example of non-volatile memory is the ROM of a computer system. It is not as effective as the volatile memory but stores contents for a long time.
You can find all the necessary system information and programs in non-volatile memory e.g. boot process information, BIOS, and start-up information. When it comes to access, non-volatile memory is slower compared to the volatile memory. Non-volatile memory influences the computer’s storage capability. The greater the amount of non-volatile memory, the more the permanent storage space you will have.
Types Of Volatile Memory And Non Volatile Memory

The most common examples of volatile memory include cache and RAM, while the most common examples of non-volatile memory include read-only memory (ROM), flash memory, ferroelectric RAM, and magnetic storage devices (such as floppy disks, hard disk drives, and magnetic tape), optical discs and most traditional computer storage methods like punctured cards and paper tape.
What Memory Is Volatile?

RAM (Random Access Memory) is a type of volatile memory that is used as primary storage in personal computers, laptops, and most smartphones. It is the fastest to write and read on compared to storage devices like a hard disk. However, all contents in RAM are only accessible when the personal computer power is on. As soon as the system goes off, RAM loses all its data. For instance, when you are typing on MS word, the RAM stores contents of that file. But if the system is switched off by accident, you will lose all your work if you did not save it.
Volatile memory is mostly the best choice for primary storage. This is because it offers the fastest means of data storage compared to other options. Volatility helps to protect and secure valuable information as it will be wiped away once the system is shut down.
Most of the widely used RAMs are volatile in nature. There are two main types, namely static and dynamic RAM:
Frequently used as the main memory in a computer system, each DRAM memory consists of a capacitor and a transistor assembled an integrated circuit. The capacitor unit mostly stores bits of data. For DRAM to retain data effectively, you must refresh it every millisecond.
This consists of about three to six transistors. Unlike the DRAM, it does not need to be updated regularly in order to store data effectively. In terms of speed, SDRAM is faster compared to DRAM. However, it is a bit more expensive than the latter.
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.



0 thoughts on “Is ROM Volatile Or Nonvolatile? (What Are The Differences?)”