Home>Data Storage>Random Access Memory>RAM Vs. ROM: 12 Major Differences To Know
Random Access Memory
RAM Vs. ROM: 12 Major Differences To Know
Modified: December 6, 2023
Instantly clear up confusions regarding RAM vs. ROM as we walk you through the major differences between these two types of storage.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
One of the most misunderstood terms in the technological world is RAM and ROM. Most people often confuse the two terms with each other. In this article, you will learn more about the types of RAM and ROM, similarities between RAM and ROM, and most importantly the differences between RAM vs ROM.
12 Differences Between RAM And ROM
| RAM | ROM |
|---|---|
| Inserted in a slot on the motherboard, comes in the form of a thin rectangular chip | Mainly an optical drive constructed with magnetic tapes |
| Non-permanent: contents, information, and data stored can be modified, rewritten, or deleted as the case may be | Permanent: stored data can only be read but never modified or altered |
| Data-writing is a fast process | Data-writing is a slow process |
| Two primary sizes, whether it is used in a laptop or personal desktop computer | Different sizes of ROM which depend on its usage |
| Contents stored in RAM can be accessed directly by the central processing unit of the computer | The CPU can only access data and information stored on the ROM when the contents are transferred to the RAM |
| RAM mostly has a higher memory space. Most of the chips have storage capacity ranging from 1GB to 1 terabyte | Most ROM chips come with between 4GB to 8GB storage capacity |
| Volatile memory: All contents stored in RAM are lost when the device is turned off. | Non-volatile memory: Data or contents stored on it save even when the device is off.
ROM is a non-volatile type of device memory. Data or contents stored on it save even when the device is off.
ROM is a non-volatile type of device memory. Data or contents stored on it save even when the device is off.
|
| The primary memory in most electronic devices is the RAM. It mostly comprises of DIMM modules, SRAM (CPU cache) and DRAM.
The primary memory in most electronic devices is the RAM. It mostly comprises of DIMM modules, SRAM (CPU cache) and DRAM. |
During bootstrapping operation, ROM is responsible for storing instructions.
Mainly used in firmware such as UEFI, BIOS, Medical devices, RFID tag, microcontrollers, and other devices where permanent memory operation is necessary. |
| More expensive | Relatively inexpensive |
| The speed of the central processing unit increases when you increase the speed of RAM.
The speed of the central processing unit increases when you increase the speed of RAM.
|
When the speed of ROM increases, it increases and boosts the overall speed of your personal computer also. |
| The major types of RAM include DDR, SRAM, SDRAM, and DRAM. | The major types of ROM memory include PROM, Mask ROM, EPROM, and EEPROM. |
| Used in everyday devices such as computers, phones and tablets | Mainly used in firmware such as UEFI, BIOS, Medical devices, RFID tag, microcontrollers, and other devices where permanent memory operation is necessary. |
What Is RAM (Random Access Memory)?
RAM is an acronym that stands for Random Access Memory. It is a kind of computer memory that houses application programs, in-use data, and operating system (OS) so that the processor of the device can easily access them. Its main function is storing data currently being used by the Central Processing Unit of the computer.
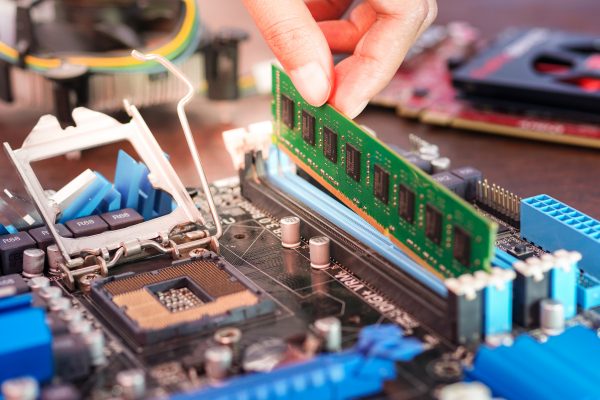
RAM is a prominent hardware component in most electronic devices like desktop computers, tablets, laptops, and smartphones. In personal computers, RAM is installed as a memory module. While in smartphones and tablets, you can hardly remove it as it is usually integrated into the device. The name Random Access, as associated with RAM, comes from the fact that memory address termed storage location can easily be accessed. You can use RAM in storing data only when the device is on.
Types Of RAM
There are basically two major types of RAM. These are the static RAM (SRAM) and Dynamic RAM (DRAM).
1. DRAM: This is mostly used as the main memory in a computer system. Each DRAM memory consists of a capacitor, and a transistor assembled an integrated circuit. Bits of data is mostly stored in the capacitor unit. For DRAM to retain data and contents effectively, it must be refreshed every millisecond.
2. SRAM: This consists of about three to six transistors. It does not need to be updated regularly, like the DRAM, for it to store data effectively. In terms of speed, SRAM is faster compared to DRAM. However, it is a little bit expensive.
RAM As Volatile Memory
All contents stored on the RAM are wiped out when the device goes off. As soon as the device is on again or restarts, the applications and operating system load afresh. This means the operating system will load new data. It is on this premise that RAM is referred to as volatile memory.
The size of the RAM’s storage capacity in any device determines the space, the open application, and the operating system can utilize. If a device has a large RAM capacity, multiple programs can run simultaneously without frustrating slow down. On the other hand, once a device has consumed all the RAM storage capacity, the overall performance and speed of the device will be grossly affected. Hence, the overall speed/performance of any device is primarily determined by the available space remaining when the RAM is in use.
Top 3 Random Access Memory (RAM) Products
Premium CHOICE
What Is ROM (Read-Only Memory)?
ROM is a popular storage acronym for Read-Only Memory (ROM). It is a kind of storage standard that stores information/data on electronic devices or personal computers permanently.
The ROM contains all the programming operations needed for computer start-up. It houses all software and program instructions and perform large computer I/O tasks. Since ROM is Read-only, you cannot modify any data written on a ROM chip.
Mostly referred to as non-volatile memory, this means you can never erase any data stored on the ROM even if the computer system is off. There are many ROM chips, both on the expansion boards and the motherboard. These chips are mainly for the BIOS (basic input/output system), reading & writing to peripheral devices, boot up, and essential data management.
Another major area that uses ROM is firmware updates. A typical example of ROM is the type of cartridge mostly used for video games where one system can run multiple games.
ROM As Non-Volatile Memory
The reason why ROM is non-volatile is that all the data stored in it does not get erased even after you restart or shut down the computer system. On the other hand, RAM is referred to as volatile memory because all the contents in it get erased when you shut down or restart the computer.
When you are working with a desktop computer, and suddenly the power goes off, you will notice that even after you power the system again, you will not see the former stuff you were doing on the screen. This is because the memory was lost. It is volatile.
Types Of ROM
There are different types of ROM, but the major ones include PROM and EEPROM. Here’s a quick look:
1. PROM: This is an acronym that stands for Programmable Read-Only memory. It is a type of ROM that is programmed or written using a specific device.
2. EEPROM: An acronym for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory. It can store or delete instructions on specific circuits.
3. Mask ROM: This is a type of ROM where the integrated circuit manufacturer can only write or program instructions or contents.
4. EPROM: This acronym stands for Erasable Programmable Read-Only memory. It is used to store contents that can only be erased when the memory is exposed to UV light.
RAM Vs. ROM
Storage Capacity
A ROM memory chip is mostly referred to as a non-volatile medium of storage. It does not need a constant power supply to retain the contents stored in it. On the other hand, a RAM chip is referred to as a volatile storage medium. It loses all contents stored in it when the computer system is shut down. RAM is a temporary storage medium, while ROM is a permanent storage medium. The storage capacity for ROM ranges from 4 to 8 GB while that of RAM ranges from 1 to 256 GB.
Uses
A ROM memory chip is mainly used for the start-up process of computer devices, while the RAM chip is used mostly for the usual computer operations after the operating system has booted. For example, a RAM chip is used to temporarily store files like documents in MS Word while you are typing, contents on a game you are playing or images you are editing on Photoshop.
Volatile And Non- Volatile Memory
What Is Volatile Memory?

Volatile memory is mostly referred to as temporary memory. It is the memory hardware that stores contents quickly. The contents stored in the volatile memory are mechanically deleted once the system is turned off. Two significant examples of volatile memory include Cache Memory and RAM (Random Access Memory). It is economical and quick and you can easily access it.
What Is Non-Volatile Memory?
Non-volatile memory is a type of memory that stores data even when the system goes off. It is a static memory. The ROM (Read Only Memory) is a typical example of non-volatile memory. Non-volatile memory has a high impact on the storage capacity of the system.
Differences Between Volatile And Non-Volatile Memory
Here are the significant differences between volatile and non-volatile memory:
Data Retention
Volatile memory stores data until when the system is powered off while the data stored in ROM remains even when the system goes off.
Persistence
The data in volatile memory is not permanent, while the data in non-volatile memory is permanent.
Speed
In terms of speed, volatile memory is faster compared to non-volatile memory. The memory access speed in non-volatile memory is relatively low.
Data Transfer
The rate of data transfer in volatile memory is fast and easy. On the other hand, data transfer in non-volatile memory is relatively difficult.
CPU Access
Data and contents stored in volatile memory can be accessed by volatile memory easily while the data must be transferred non-volatile memory to volatile memory before the CPU can access it.
Storage
The storage capacity in volatile memory is low while volatile memory has a high storage capacity.
Impact
Volatile memory like RAM generally has an effect on the standard performance of the computer operation while non-volatile memory does not have any significant impact on the performance of the system but instead has an impact on the storage capacity of the system.
Cost
Volatile memory is generally expensive, depending on the memory capacity, while non-volatile memory cheaper compared to its non-volatile counterpart.
Processor
The processor in volatile memory direct access to the data stored on it, while the processor in non-volatile memory does not have direct access to contents stored.
Chips Location
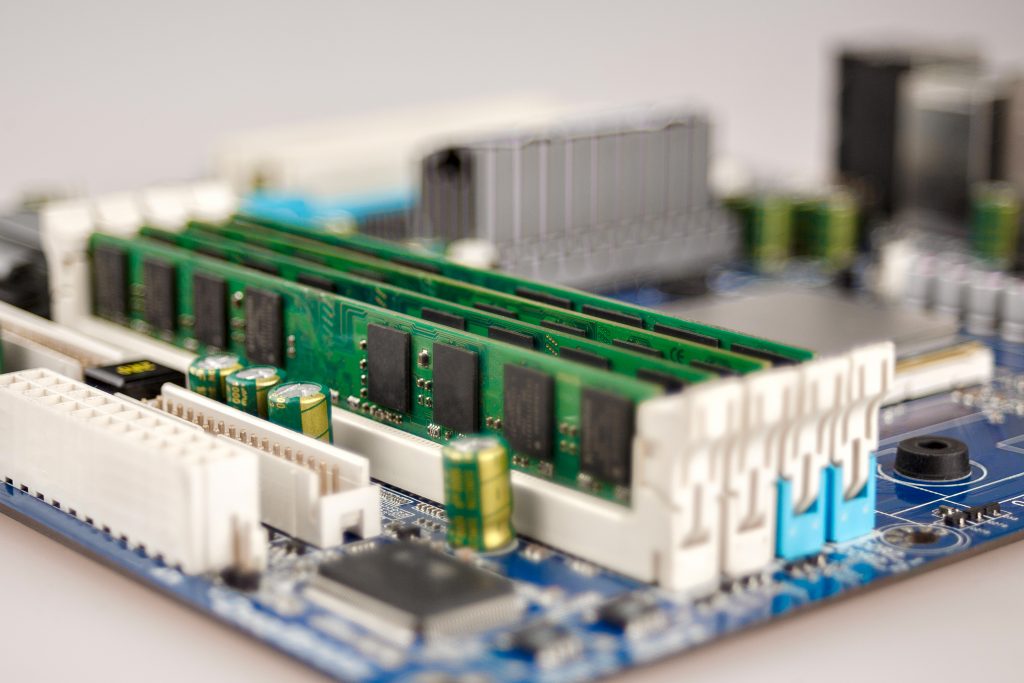
The volatile memory chip is located in a memory slot, while the non-volatile memory chip is usually found on the motherboard.
Having a sound knowledge and understanding of the main differences between RAM and ROM is paramount to understanding the basic operations of computer devices and other software devices. In this article, we were able to look at examples of RAM and ROM as well as the differences between the two types of storage. We hope the information shared has helped you understand these concepts better.
Frequently Asked Questions About RAM Vs. ROM
1) Can Data Be Recovered From RAM?
As RAM is a type of volatile memory, contents stored on it are erased within a period ranging from a few seconds to a few minutes after a computer/device is switched off. While this duration can be extended by lowering surrounding temperature/freezing the chip, these practices aren’t commonly carried out and do not guarantee zero data loss.
2) Is ROM Still Used?
Yes, it is. ROM is responsible for storing the start-up instructions for computers, and, as such, is still an essential computer of such terminals.
3) Which Is Better ROM Or RAM?
Both digital components serve vastly different functions and hence are equally good/important. While ROM is part of a computer’s firmware, RAM makes running computer programs and processes possible. Both ROM and RAM are required for a computer to work normally.
4) What Is The Difference Between RAM And ROM In Mobile?
While RAM affects the speed of a mobile phone, ROM determines the total amount of data it can store overall. Both RAM and ROM are crucial when it comes to ensuring that a phone works properly.
5) Why RAM Is Faster Than ROM?
RAM is more frequently accessed than ROM. While ROM may be designed to conserve power, RAM directly affects the speed of the entire computer.
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “RAM Vs. ROM: 12 Major Differences To Know”