Home>diy>Building & Construction>Who Is A Foreman In Construction


Building & Construction
Who Is A Foreman In Construction
Modified: January 6, 2024
A construction foreman is a vital role in building construction projects. Learn about their responsibilities and how they oversee the site and crew.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
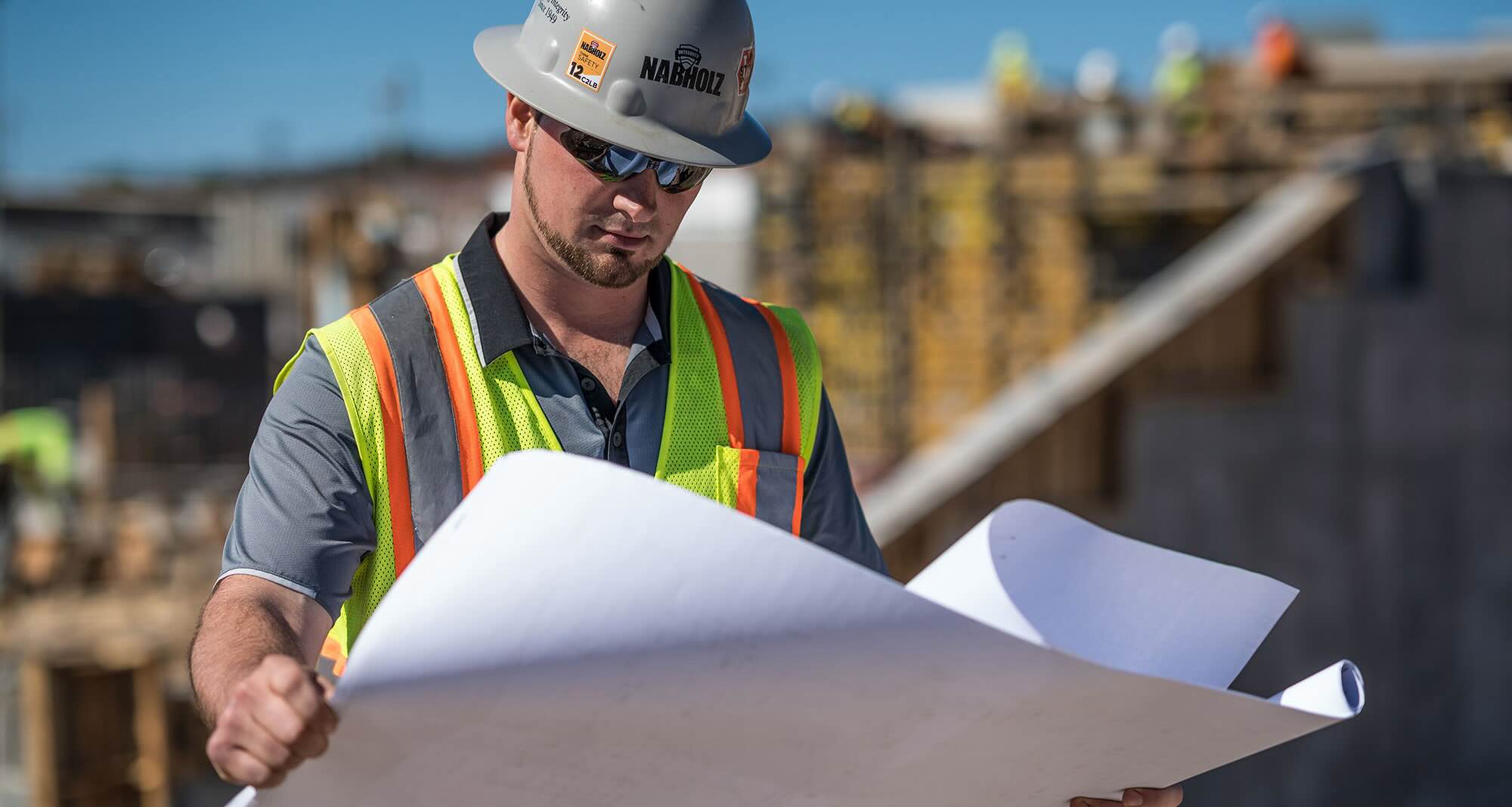
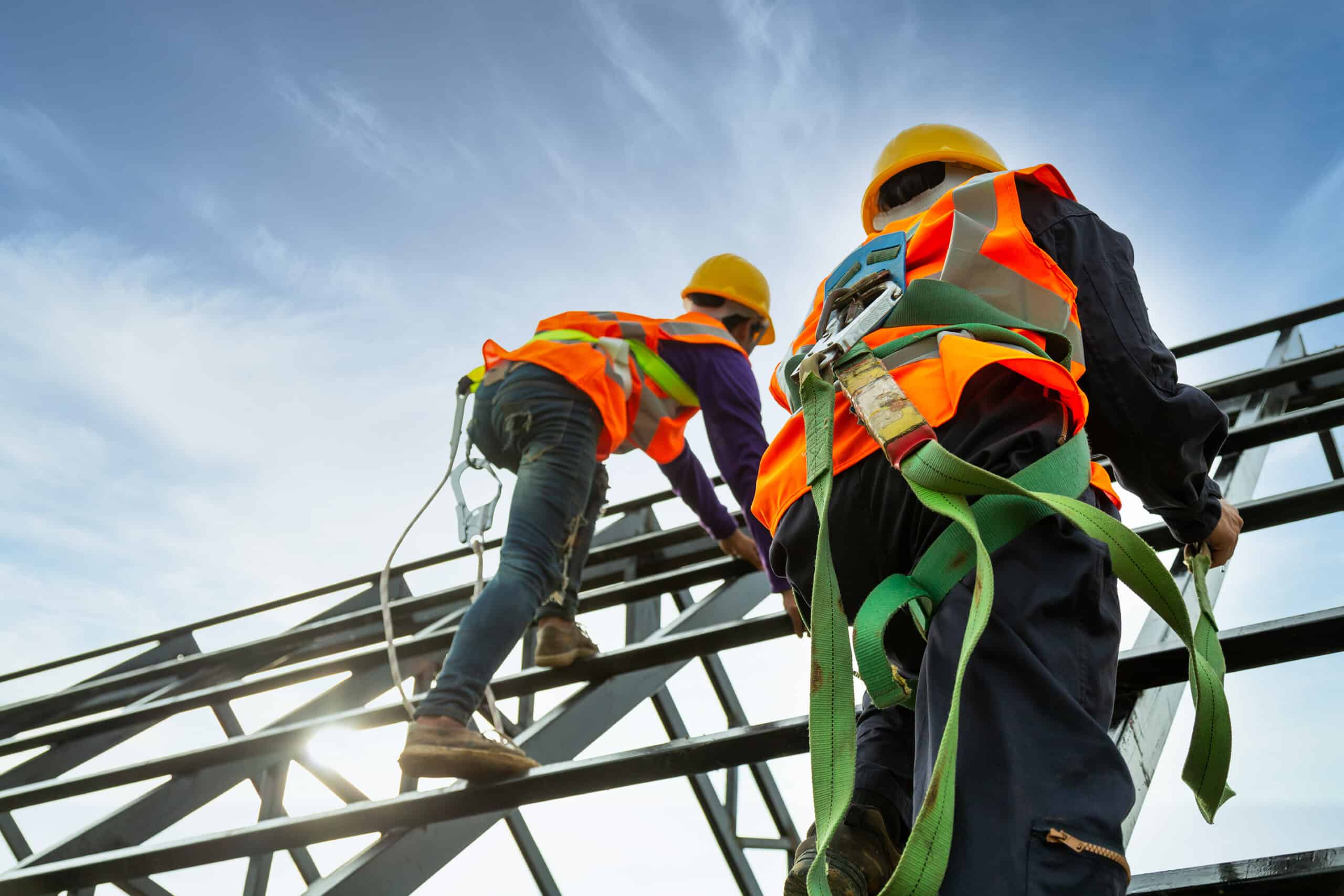
When it comes to the successful completion of a construction project, the role of a foreman is pivotal. A foreman acts as the backbone of the construction site, overseeing and coordinating the work of various tradespeople and ensuring that everything is on track.
A foreman is responsible for managing the day-to-day operations on a construction site, from coordinating schedules and supervising workers to handling safety protocols and resolving any issues that may arise. It is a demanding and challenging role that requires a unique blend of technical expertise, leadership skills, and the ability to adapt and problem-solve in a fast-paced environment.
In this article, we will explore the role, skills, qualifications, and responsibilities of a foreman in the construction industry. Whether you are considering a career as a foreman or simply want to gain a better understanding of the importance of this position, this article will provide you with valuable insights into the world of construction management.
Key Takeaways:
- A foreman in construction plays a pivotal role in overseeing project execution, enforcing safety regulations, and fostering a collaborative work environment. Their diverse skill set and adaptability are essential for project success.
- Continuous learning and professional development are crucial for foremen to stay updated with industry advancements, enhance leadership abilities, and meet the evolving demands of the construction industry.
Read more: How To Be A Foreman In Construction
Role of a Foreman in Construction
A foreman plays a crucial role in the construction industry, acting as a bridge between the project manager or construction supervisor and the workers on the ground. Their primary responsibility is to ensure that the work is carried out efficiently, safely, and according to the project plan.
First and foremost, a foreman is responsible for coordinating and supervising the activities of the construction site. This includes assigning tasks to workers, monitoring progress, and ensuring that deadlines are met. They need to have a deep understanding of the project plans, specifications, and blueprints to accurately communicate instructions to the team.
Another crucial aspect of a foreman’s role is resource management. They are responsible for ensuring that all necessary materials, tools, and equipment are available and in good working condition. They must also ensure that there is an adequate number of skilled workers on-site to complete the required tasks.
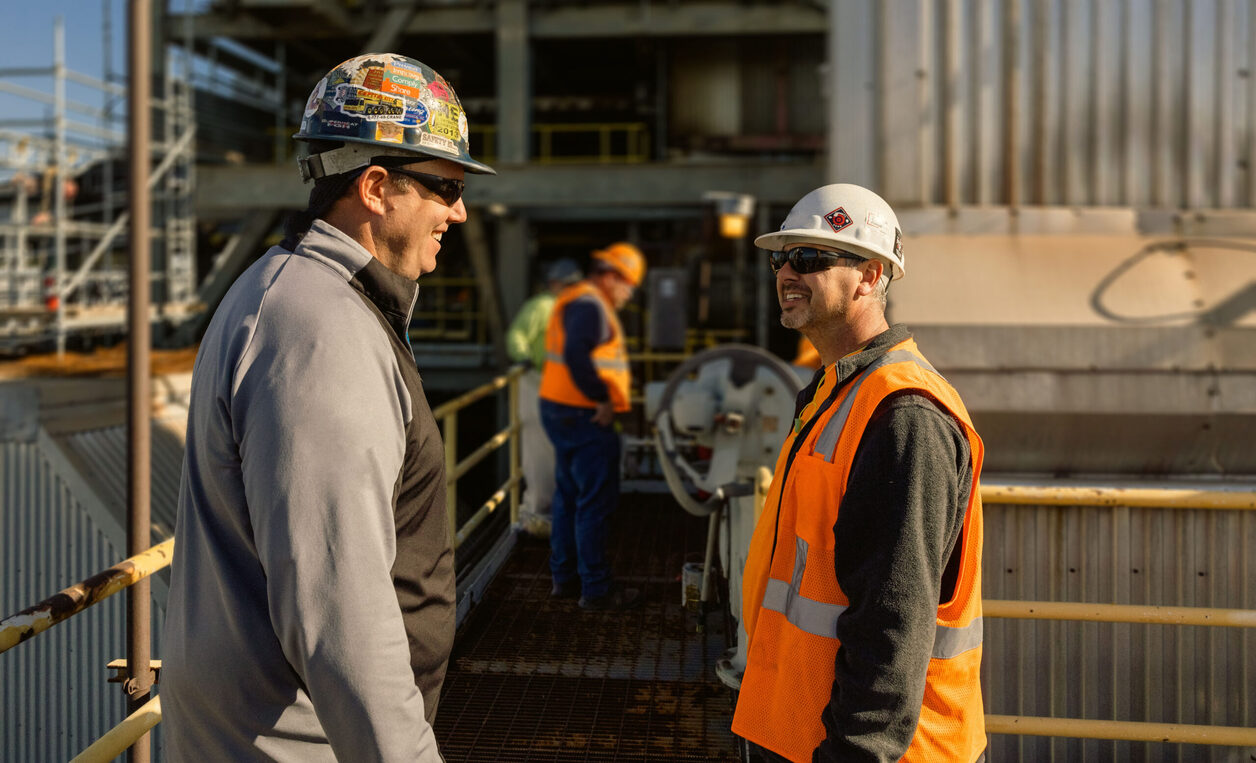
Communication is a key skill for a foreman as they act as a liaison between workers, management, and clients. They need to effectively convey project information, resolve conflicts, and maintain a positive and productive working environment.
A foreman must also enforce safety regulations and promote a culture of safety on the construction site. They conduct regular safety inspections, ensure that workers are following proper safety procedures, and address any safety concerns immediately. Safety is of utmost importance in the construction industry, and a competent foreman can significantly reduce accidents and ensure the well-being of the entire team.
In addition to managing day-to-day operations, a foreman is also responsible for keeping accurate records of work progress, materials used, and personnel on-site. This information is crucial for reporting to the project manager and client, as well as for future reference and analysis.
Overall, the role of a foreman in construction is multifaceted. They are not only responsible for efficient project execution but also for fostering a collaborative and safe working environment. A skilled and experienced foreman can greatly contribute to the success of a construction project and play a vital role in ensuring its timely completion.
Skills and Qualifications Required for a Foreman
Being a foreman in construction requires a unique set of skills and qualifications. In addition to technical knowledge, a successful foreman possesses strong leadership abilities, excellent communication skills, and the ability to adapt to changing situations. Let’s take a closer look at the key skills and qualifications required for this role.
Technical Expertise: A foreman should have a solid understanding of the construction process, including knowledge of various trades, building codes and regulations, and reading blueprints. They must be able to interpret project plans and specifications, as well as assess the quality of work to ensure it meets industry standards.
Leadership Abilities: As a foreman, you will be leading a team of workers, so strong leadership skills are essential. You should be able to inspire and motivate your team, delegate tasks effectively, and provide guidance and support when needed. Strong decision-making skills are also crucial, as you will often need to make quick and informed decisions to keep the project moving forward.
Communication Skills: Effective communication is vital for a foreman. You will need to clearly convey instructions, project details, and safety procedures to your team. Additionally, you will need to communicate with project managers, clients, and subcontractors, so excellent verbal and written communication skills are a must.
Adaptability and Problem-Solving: Construction projects can be unpredictable, and unexpected challenges may arise. A good foreman should be able to adapt to changing circumstances and come up with creative solutions. The ability to think critically and problem-solve on the spot is a valuable asset in this role.
Organizational Skills: The ability to plan and organize work efficiently is crucial for a foreman. You should be able to manage schedules, coordinate resources, and prioritize tasks effectively. Good organizational skills help ensure that the project stays on track and that deadlines are met.
Safety Consciousness: Safety is paramount in the construction industry. A foreman should have a deep understanding of safety regulations and protocols and be committed to ensuring a safe working environment. This includes conducting regular safety inspections, enforcing safety procedures, and addressing any potential hazards promptly.
Experience and Education: While formal education is not always a requirement, many employers prefer candidates with a high school diploma or equivalent. Relevant certifications, such as those in construction management or occupational safety, can also be beneficial. Experience in the construction field, typically gained through working as a tradesperson or in a similar supervisory role, is highly valued.
Interpersonal Skills: Building positive relationships with your team, subcontractors, and clients is essential for a foreman. Strong interpersonal skills, such as the ability to communicate effectively, listen actively, and resolve conflicts, are critical in maintaining a productive and harmonious work environment.
In summary, being a successful foreman requires a combination of technical knowledge, leadership abilities, effective communication skills, adaptability, and a commitment to safety. By honing these skills and gaining relevant experience, you can excel in this critical role in the construction industry.
Responsibilities of a Foreman in Construction
A foreman has a wide range of responsibilities on a construction site. They are responsible for overseeing and managing various aspects of the project to ensure its successful completion. Let’s delve into the key responsibilities of a foreman in construction.
Supervision and Coordination: One of the primary responsibilities of a foreman is to supervise and coordinate the work of the construction site. This includes assigning tasks to workers, monitoring progress, and ensuring that work is being carried out in accordance with project plans and specifications.
Resource Management: A foreman is responsible for efficiently managing the resources on the construction site. This includes ensuring that all necessary materials, tools, and equipment are available and in good working condition. They must also manage the allocation of workforce, ensuring that there are enough trained and skilled workers to complete the tasks at hand.
Quality Control: Maintaining high-quality work is essential in any construction project. A foreman is responsible for ensuring that the work being carried out meets the required standards and specifications. They must conduct regular inspections, address any issues or deficiencies, and ensure that quality control measures are implemented throughout the project.
Safety Compliance: Safety is a top priority on any construction site. A foreman plays a crucial role in enforcing safety regulations and protocols to maintain a safe working environment. They must ensure that workers are following proper safety procedures, conduct regular safety inspections, and address any safety concerns immediately.
Communication: Effective communication is vital for a foreman. They need to effectively convey project details, instructions, and safety procedures to their team members. They are also responsible for communicating with project managers, clients, and subcontractors, providing progress updates, and addressing any concerns or issues that may arise.
Problem-Solving: Construction projects often come with unexpected challenges and problems. A foreman needs to have strong problem-solving skills to identify and resolve issues efficiently. They must be able to think critically, make informed decisions, and propose viable solutions to keep the project on track.
Recordkeeping and Documentation: A foreman is responsible for maintaining accurate records of work progress, materials used, and personnel on-site. These records are crucial for reporting to project managers and clients, as well as for future reference. They must also ensure that all necessary documentation, such as permits and licenses, is up to date and compliant.
Team Management: As a foreman, you are responsible for managing and leading a team of workers. This includes providing guidance and support to team members, resolving conflicts, and fostering a positive and productive work environment. Leading by example and motivating the team is an essential aspect of a foreman’s responsibilities.
Project Planning and Organization: A foreman plays a key role in project planning and organization. They must have a thorough understanding of the project scope, timelines, and milestones. They need to develop work schedules, coordinate with subcontractors, and ensure that all tasks are properly sequenced and coordinated to meet project deadlines.
In summary, the responsibilities of a foreman in construction are diverse and demanding. From supervising and coordinating work to ensuring safety compliance and maintaining quality control, a foreman plays a crucial role in the successful completion of a construction project.
Communication and Leadership Skills for a Foreman
Effective communication and strong leadership skills are essential for a foreman in the construction industry. As a foreman, you are responsible for managing a team of workers and ensuring that projects are completed efficiently and successfully. Let’s explore the importance of communication and leadership skills in this role.
Clear and Effective Communication: Communication is the backbone of any successful construction project. A foreman must be able to communicate clearly and effectively to convey project details, instructions, and safety protocols to their team. They should have strong verbal communication skills to articulate tasks, expectations, and any changes that may occur during the project. Additionally, they should be proficient in written communication to document project progress, provide updates to project managers and clients, and maintain clear and accurate records.
Active Listening: In addition to communicating effectively, a foreman should possess excellent listening skills. Active listening allows a foreman to understand the concerns, ideas, and feedback from workers. By actively listening, a foreman can establish a positive and collaborative working environment, foster trust and respect, and make informed decisions based on the input received from the team.
Empathy and Interpersonal Skills: Building strong relationships with team members, subcontractors, and clients is essential for a foreman. Empathy and interpersonal skills play a crucial role in forming these connections. A foreman should have the ability to understand and relate to the needs and challenges of their team members. By showing empathy, they can create a supportive work environment and effectively address any conflicts or issues that may arise.
Leadership Abilities: Effective leadership is vital for a foreman. They should have the ability to motivate, inspire, and guide their team to achieve project goals. Strong leadership skills involve setting clear expectations, providing direction and guidance, and recognizing and celebrating the achievements of the team. A good leader leads by example, demonstrating professionalism, dedication, and a strong work ethic.
Conflict Resolution: Construction projects often involve various challenges and conflicts. A foreman should possess excellent conflict resolution skills to address disagreements or disputes that may arise within the team. They should be able to listen to different perspectives, mediate conflicts, and find amicable solutions that uphold the best interests of the project and the team.
Team Building: A successful foreman understands the importance of teamwork and focuses on building a cohesive and collaborative team. By fostering a positive work environment, encouraging open communication, and creating opportunities for professional growth, a foreman can develop a strong and unified team.
Adaptability: In the construction industry, unexpected changes are common. A foreman should have the ability to adapt quickly to these changes and make sound decisions to keep the project on track. They should be flexible, resourceful, and able to adjust plans and strategies as needed.
In summary, communication and leadership skills are fundamental for a foreman in the construction industry. By effectively communicating with their team, actively listening, demonstrating empathy, and exhibiting strong leadership abilities, a foreman can create a positive work environment, foster collaboration, and ensure the success of construction projects.
Read more: Who Made George Foreman Grill
Safety Regulations and Protocols for a Foreman
Ensuring the safety of all workers on a construction site is a top priority for a foreman. They play a critical role in enforcing safety regulations and protocols to prevent accidents, injuries, and fatalities. Let’s explore the important safety regulations and protocols that a foreman must adhere to:
Familiarity with Safety Standards: A foreman should have a thorough understanding of local, state, and federal safety standards and regulations. This includes knowledge of OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) guidelines, industry best practices, and any specific safety requirements for the construction project at hand.
Safety Planning and Risk Assessment: Before work commences, a foreman must conduct a comprehensive safety planning process. This involves identifying potential hazards, assessing risks, and implementing controls and preventive measures to mitigate those risks. They should continuously review and update the safety plan as the project progresses.
Implementing Safety Training: A foreman is responsible for ensuring that all workers receive proper safety training. This includes orientation for new workers, training sessions for specific tasks or equipment usage, and regular briefings on safety protocols. They must verify that workers understand the safety procedures and have the necessary knowledge and skills to perform their tasks safely.
Supervising Safety Procedures: A foreman must closely monitor the adherence to safety procedures on the construction site. This includes conducting regular safety inspections, observing work activities, and intervening if workers are not following proper safety protocols. They should promptly address any unsafe actions or conditions and take corrective measures to mitigate risks.
Providing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): A foreman should ensure that appropriate personal protective equipment, such as hard hats, safety goggles, gloves, and protective clothing, is provided to workers. They should emphasize the importance of wearing PPE and monitor compliance to maintain a safe working environment.
Emergency Preparedness: A foreman should have plans in place for emergency situations, such as fires, natural disasters, or medical emergencies. They should train workers on emergency procedures, including evacuation routes and first-aid protocols. Additionally, a foreman should communicate with emergency services and maintain up-to-date contact information for immediate response when needed.
Safety Communication: Effective safety communication is crucial for a foreman. They should regularly reinforce safety messages and reminders during toolbox talks, team meetings, and daily briefings. Clear and concise communication of safety procedures, hazards, and any changes or updates is essential to ensure that all workers are aware and informed.
Documentation and Reporting: A foreman must maintain accurate records of safety inspections, incidents, near misses, and safety-related training. They should promptly report any workplace accidents, injuries, or hazardous conditions to project managers, clients, and relevant authorities as per legal requirements.
Leading by Example: A foreman should demonstrate a commitment to safety by following safety protocols themselves. They should serve as role models for their team, adhering to safety regulations and encouraging others to do the same. Leading by example reinforces the importance of safety and fosters a culture of safety consciousness on the construction site.
In summary, a foreman has the responsibility to enforce safety regulations and protocols to protect the well-being of workers on a construction site. By having a deep understanding of safety standards, planning and implementing safety measures, providing proper training and equipment, and promoting a culture of safety, a foreman plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of everyone involved in the construction project.
A foreman in construction is a supervisory role responsible for overseeing and coordinating the work of a construction crew. They ensure that work is completed safely, on time, and according to specifications.
Planning and Organizational Skills for a Foreman
Planning and organizational skills are essential for a foreman in the construction industry. A foreman is responsible for managing various aspects of a construction project and ensuring that everything is executed smoothly and efficiently. Let’s explore the importance of planning and organizational skills for a foreman:
Project Planning: A foreman plays a crucial role in project planning. They need to have a thorough understanding of the project scope, timelines, and milestones. By analyzing project requirements and specifications, a foreman can develop a comprehensive project plan that outlines the sequence of tasks, resource allocation, and deadlines.
Task Sequencing and Coordination: A foreman must carefully sequence and coordinate tasks to ensure smooth workflow and optimal resource utilization. This involves determining the order in which tasks are to be executed, considering dependencies, and coordinating with subcontractors to ensure seamless collaboration.
Resource Management: Efficiently managing resources is key to project success. A foreman needs to assess the materials, tools, and equipment required for each phase of the project. They should plan and allocate resources accordingly, ensuring they are available on-site when needed and used optimally to minimize delays and maximize productivity.
Scheduling and Time Management: A foreman is responsible for creating and managing project schedules. They must allocate time frames for each task, keeping in mind the overall project timeline. Effective time management is crucial for meeting deadlines, coordinating with subcontractors, and ensuring efficient progress throughout the project.
Team Coordination: A foreman needs to coordinate and communicate effectively with their team members. They must assign tasks, clarify instructions, and provide guidance and support as needed. Establishing a system of communication and clearly defining roles and responsibilities within the team helps ensure that work is coordinated and executed efficiently.
Problem-Solving and Adaptability: Construction projects often encounter unexpected challenges and changes. A foreman needs to have strong problem-solving skills and the ability to adapt quickly to new circumstances. They should be able to think critically, make informed decisions, and adjust plans or strategies to overcome obstacles and keep the project on track.
Documentation and Recordkeeping: A foreman plays a crucial role in maintaining accurate records of work progress, materials used, and personnel. This includes documenting any changes, issues, or delays that occur during the project. Proper documentation ensures transparency, facilitates project evaluation, and serves as a reference for future projects.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: As part of their planning responsibilities, a foreman must identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. This involves evaluating potential hazards, implementing safety measures, and communicating risk prevention protocols to the team. Proactive risk management helps minimize accidents, injuries, and disruptions to the project.
Attention to Detail: A foreman should have keen attention to detail to ensure that all aspects of the project are executed accurately. From reviewing project plans and specifications to monitoring the quality of work, attention to detail helps maintain high levels of craftsmanship and reduces the likelihood of errors or rework.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Construction projects can be dynamic and subject to changes. It is crucial for a foreman to be flexible and adapt to evolving circumstances. This includes adjusting schedules, reallocating resources, and effectively communicating changes to the team. Flexibility helps navigate unforeseen challenges and keeps the project moving forward.
In summary, planning and organizational skills are essential for a foreman in the construction industry. By effectively planning, coordinating tasks and resources, managing time, and staying organized, a foreman can ensure the efficient execution of the project and contribute to its overall success.
Conflict Resolution and Problem-Solving Abilities
Conflict and challenges are inevitable in the construction industry, and a foreman plays a vital role in addressing and resolving them. Conflict resolution and problem-solving abilities are essential skills for a foreman to maintain a productive work environment and ensure the successful completion of construction projects. Let’s explore the importance of these skills in the role of a foreman:
Identifying and Addressing Conflict: A foreman should have the ability to identify and address conflicts that arise on the construction site. Conflict can occur among team members, between workers and subcontractors, or even with clients. By actively identifying conflicts and addressing them promptly, a foreman can prevent escalation and maintain a harmonious work environment.
Active Listening and Empathy: Effective conflict resolution starts with active listening and empathy. A foreman should actively listen to all parties involved, understanding their perspectives and concerns. By demonstrating empathy, a foreman can foster open communication, build trust, and encourage collaboration in finding mutually satisfactory resolutions.
Mediation and Negotiation: A foreman often acts as a mediator between conflicting parties. They should have strong mediation and negotiation skills to facilitate constructive discussions and help resolve conflicts. By remaining impartial, actively facilitating dialogue, and assisting in finding compromises, a foreman can bring conflicting parties together and promote harmony and cooperation.
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making: Construction projects present various challenges and problems that require effective problem-solving skills. A foreman should be able to analyze complex situations, identify underlying issues, and propose practical solutions. They must make informed decisions swiftly while considering the impact on the project, resources, and timeline.
Critical Thinking: Critical thinking is key when it comes to problem-solving. A foreman should have the ability to analyze information, evaluate options, consider potential risks and consequences, and make sound decisions. Critical thinking helps in identifying root causes of problems and finding innovative solutions.
Collaboration and Teamwork: Collaboration is crucial when addressing conflicts and solving problems. A foreman should foster a collaborative environment, encouraging teamwork and collective problem-solving. By involving the team members in problem-solving processes and considering their insights and suggestions, a foreman can tap into the collective knowledge and experience of the team, leading to more effective solutions.
Assertiveness and Diplomacy: A foreman needs to balance assertiveness and diplomacy when resolving conflicts and solving problems. They should assertively communicate expectations and address concerns, while also maintaining professionalism and diplomacy to preserve relationships and promote cooperation.
Continuous Improvement: Conflict resolution and problem-solving are skills that can be honed and improved over time. A foreman should be open to feedback, seek opportunities for personal growth, and continually learn from their experiences. By continuously improving their conflict resolution and problem-solving abilities, a foreman can become more effective in addressing conflicts and finding efficient solutions.
Preventive Measures: A proactive approach is essential in conflict resolution and problem-solving. A foreman should identify potential conflicts or problems in advance and implement preventive measures. By addressing underlying issues and establishing clear communication channels, procedures, and expectations from the outset, a foreman can minimize the likelihood of conflicts arising.
In summary, conflict resolution and problem-solving abilities are indispensable for a foreman in the construction industry. By effectively addressing conflicts, proactively solving problems, and fostering a collaborative and positive work environment, a foreman can enhance productivity, maintain team morale, and ensure the successful completion of construction projects.
Time Management and Decision-Making Skills
Time management and decision-making skills are crucial for a foreman in the construction industry. The ability to effectively manage time and make informed decisions is essential for maximizing productivity, ensuring project deadlines are met, and maintaining a smooth workflow. Let’s explore the importance of these skills in the role of a foreman:
Effective Time Allocation: Time management is critical for a foreman as they need to allocate and prioritize tasks to meet project deadlines. They should have the ability to create realistic and achievable schedules, considering factors such as the availability of resources and the complexity of tasks. Effective time management ensures that project milestones are achieved, minimizing delays and efficiently utilizing resources.
Task Prioritization: Prioritizing tasks is a key aspect of time management. A foreman should be able to identify critical tasks that require immediate attention and allocate resources accordingly. By prioritizing tasks, a foreman can ensure that the most important and time-sensitive activities are focused on, keeping the project on track.
Resource Optimization: Time management goes hand in hand with resource optimization. A foreman needs to allocate resources, including materials, manpower, and equipment, in an efficient and balanced manner. Effective resource allocation ensures that resources are utilized optimally, minimizing waste and maximizing productivity.
Proactive Planning and Scheduling: A foreman should have a proactive approach to planning and scheduling. They need to anticipate potential delays or challenges and make contingency plans to mitigate their impact. By proactively planning and scheduling, a foreman can minimize disruptions, maintain productivity, and keep the project on schedule.
Effective Decision-Making: Construction projects often require prompt decision-making. A foreman should have the ability to analyze information, evaluate options, and make informed decisions that align with project objectives. They should consider factors such as cost, safety, quality, and schedule when making decisions, ensuring that the best course of action is taken.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Decision-making skills are crucial when it comes to assessing and mitigating risks. A foreman should identify potential risks, analyze their impact on the project, and make decisions on implementing preventive measures. By proactively addressing risks, a foreman can minimize the likelihood of accidents, delays, and costly rework.
Adaptability and Flexibility: Construction projects are dynamic, with unexpected changes and challenges. A foreman should have the ability to adapt to changing circumstances and make quick decisions. They should be flexible and willing to adjust plans and strategies when necessary to maintain project timelines and achieve project goals.
Data Analysis and Problem-Solving: Decision-making often requires analyzing data and information to solve problems effectively. A foreman should have strong problem-solving skills, the ability to identify root causes, and the capacity to propose practical and innovative solutions. Data analysis helps in considering the impact of decisions on the project and making informed choices.
Confidence and Accountability: Effective decision-making requires confidence and accountability. A foreman should have confidence in their abilities and decisions, as well as the willingness to take responsibility for the outcomes of their decisions. Confidence instills trust and inspires team members, while accountability ensures that mistakes are acknowledged and lessons are learned.
Continuous Improvement: Time management and decision-making skills can always be refined and improved. A foreman should be open to feedback, actively seek opportunities for growth, and continuously learn from experiences. By striving for continuous improvement, a foreman can enhance their time management and decision-making abilities, becoming more effective in leading projects and achieving successful outcomes.
In summary, time management and decision-making skills are vital for a foreman in the construction industry. By effectively managing time, prioritizing tasks, making informed decisions, and adapting to changing circumstances, a foreman can ensure the efficient use of resources, maintain project schedules, and contribute to the overall success of construction projects.
Read more: What Does A Construction Foreman Do
Training and Development Opportunities for a Foreman
Continuous learning and professional development are crucial for a foreman in the construction industry. As the construction industry evolves, it is essential for foremen to stay updated with new technologies, industry best practices, and management techniques. Let’s explore the importance of training and development opportunities for a foreman:
Technical Skills Enhancement: The construction industry constantly evolves, with new technologies and techniques emerging. Training opportunities can enhance a foreman’s technical skills, such as construction methods, equipment operation, or specialized trades. Staying updated on the latest tools and technologies enables a foreman to effectively lead and manage the work team.
Supervisory and Leadership Training: Developing supervisory and leadership skills is essential for a foreman. Training programs in leadership, communication, team management, and conflict resolution can help enhance a foreman’s ability to motivate and inspire their team, effectively communicate with stakeholders, and resolve conflicts in a constructive manner.
Project Management: Many foremen aspire to take on broader project management roles. Training in project management methodologies, such as Agile or Lean construction, can provide the necessary skills and knowledge to plan, execute, and deliver successful construction projects.
Safety Training and Certifications: Safety is a top priority in construction, and foremen need to stay updated on safety regulations, protocols, and best practices. Pursuing training and certifications in occupational safety, emergency response, or specialized safety measures can enhance a foreman’s ability to enforce safety regulations and maintain a safe work environment for their team.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills: Strong communication and interpersonal skills are essential for effective leadership. Training in areas such as active listening, effective communication, negotiation, and public speaking can help a foreman enhance these skills, enabling better team collaboration, client interactions, and stakeholder management.
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Problem-solving and critical thinking are fundamental skills for a foreman. Training programs or workshops focused on problem-solving techniques, critical thinking, and decision-making can enhance a foreman’s ability to analyze complex situations, make informed decisions, and find innovative solutions to challenges encountered during construction projects.
Continuous Improvement Programs: Participating in continuous improvement programs, such as Lean construction or Six Sigma, allows foremen to gain knowledge and skills related to eliminating waste, improving processes, and optimizing resource utilization. These programs foster a culture of continuous improvement and enhance a foreman’s ability to identify and implement efficiency-enhancing measures.
Mentorship and Coaching: Engaging in mentorship or coaching programs can offer valuable guidance and support for a foreman’s professional development journey. Working with experienced mentors or coaches can provide insights, advice, and constructive feedback to help a foreman enhance their skills and grow as a leader in the construction industry.
Industry Events and Conferences: Attending industry events, conferences, and seminars allows foremen to stay updated on the latest trends, technologies, and best practices in the construction industry. These events provide valuable networking opportunities and the chance to learn from industry experts and peers.
Online Learning Resources: Online platforms and learning resources provide convenient and accessible opportunities for foremen to acquire new skills and knowledge. Online courses, webinars, and industry-specific forums can provide valuable insights and allow foremen to learn at their own pace.
Embracing training and development opportunities is crucial for a foreman’s professional growth, career advancement, and the overall success of construction projects. By continuously expanding their knowledge and skills, foremen can enhance their effectiveness as leaders, adapt to industry changes, and meet the evolving demands of the construction industry.
Conclusion
The role of a foreman in the construction industry is vital for the successful completion of projects. A foreman acts as the backbone of the construction site, overseeing the work of various tradespeople, ensuring safety protocols are followed, and coordinating tasks to meet project deadlines. To excel in this role, a foreman must possess a diverse range of skills and qualifications.
From technical expertise and leadership abilities to effective communication and problem-solving skills, a foreman must be well-rounded and adaptable. They must have a deep understanding of the construction process, be able to interpret project plans and specifications, and have the ability to lead and motivate their team.
Safety is of utmost importance in the construction industry, and a foreman plays a critical role in enforcing safety regulations and promoting a culture of safety on the construction site. They must also possess strong decision-making skills to address conflicts, make informed choices, and adapt plans as needed to keep the project on track.
Planning and organizational skills are essential for a foreman to ensure efficient project execution. They must be able to effectively allocate resources, create realistic schedules, and prioritize tasks to meet project milestones. Time management and the ability to make sound decisions are key to maintaining productivity and achieving project goals.
Continuous learning and professional development are crucial for a foreman to stay updated with industry advancements and enhance their leadership abilities. Training opportunities, industry events, and mentorship programs offer valuable avenues for foremen to expand their skills, improve their knowledge, and network with industry professionals.
In conclusion, the role of a foreman in construction is multifaceted and demanding. The success of a construction project often hinges on the expertise, leadership, and management skills of a capable foreman. By continually honing their skills, staying updated on industry trends, and effectively leading their team, a foreman can make a significant impact on the successful completion of construction projects and contribute to the growth of the construction industry as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions about Who Is A Foreman In Construction
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “Who Is A Foreman In Construction”