Home>Furniture & Design>Interior Design Trends>What Happens If Glass Stays In Your Skin


Interior Design Trends
What Happens If Glass Stays In Your Skin
Modified: February 18, 2024
Discover the potential risks and complications of leaving glass in your skin. Stay informed about the latest interior design trends and tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
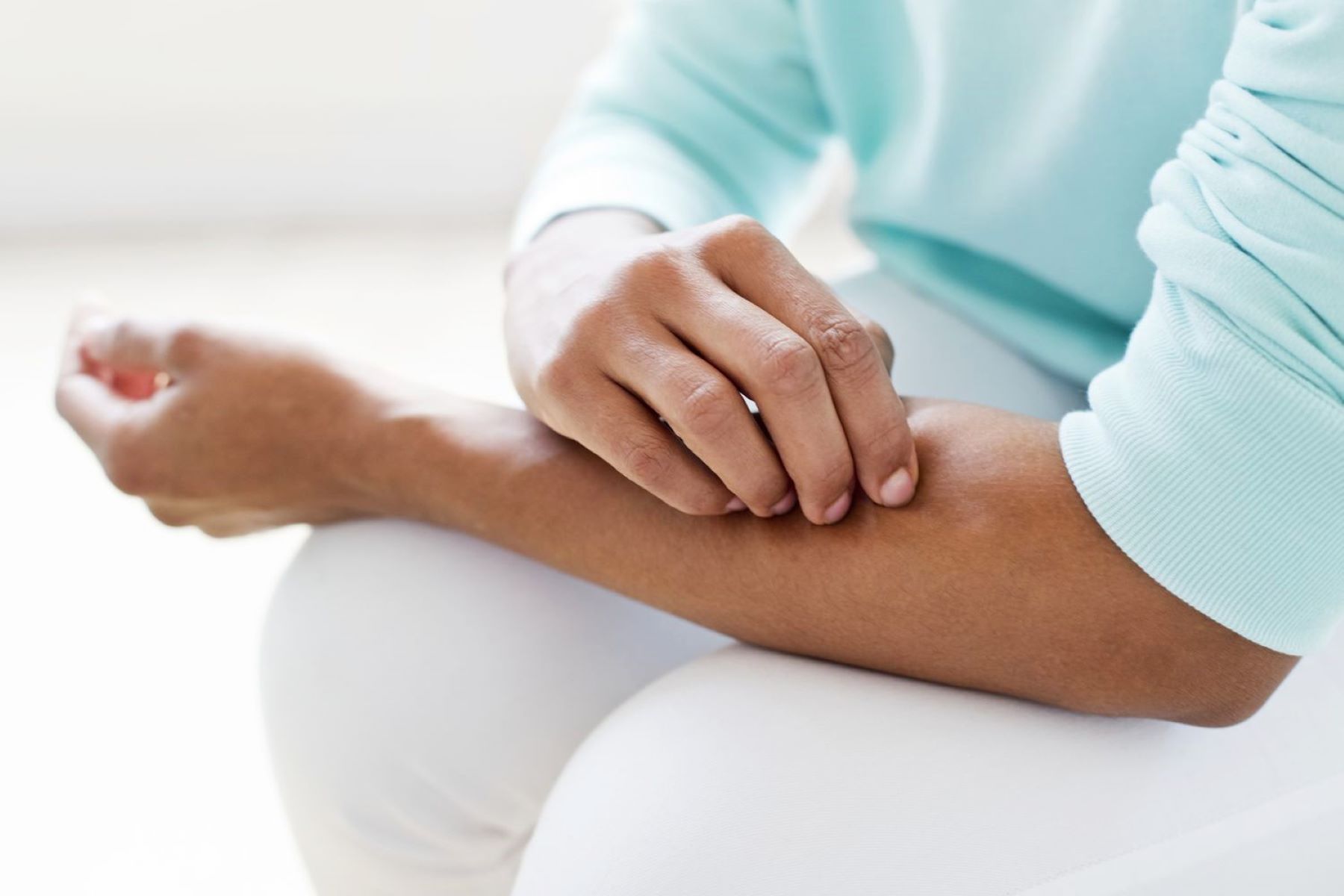
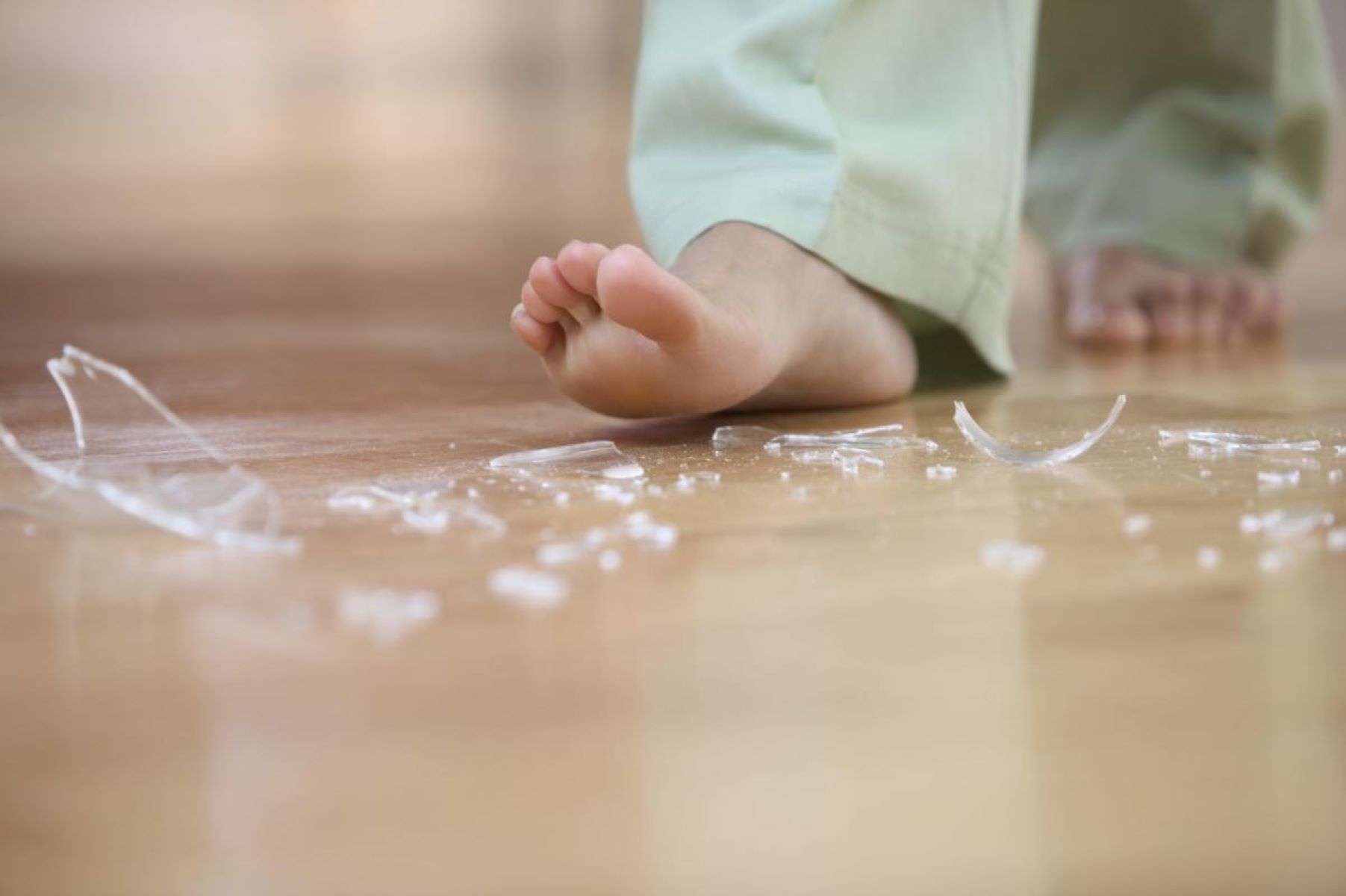
When glass becomes embedded in the skin, it can lead to discomfort, pain, and potential health risks. Whether it's a tiny shard from a broken glass or a larger piece from an accident, the presence of glass in the skin can be a cause for concern. Understanding how glass gets stuck in the skin, the potential risks and complications it poses, treatment options, and preventive measures is crucial for managing this issue effectively.
The human skin, while resilient, is not impervious to injury. Accidental contact with glass, such as broken bottles or windows, can result in fragments becoming lodged in the skin. This can occur during everyday activities, household chores, or in more serious situations, such as car accidents or industrial mishaps. The presence of glass in the skin can lead to irritation, inflammation, and infection if not addressed promptly and properly.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of how glass becomes stuck in the skin, the potential risks and complications associated with this issue, available treatment options, and effective preventive measures to minimize the likelihood of glass-related skin injuries. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these aspects, individuals can equip themselves with the knowledge needed to address and mitigate the impact of glass in the skin.
Understanding the implications of glass in the skin is essential for promoting skin health and overall well-being. By exploring the causes, risks, and solutions related to this issue, individuals can make informed decisions and take proactive steps to safeguard their skin from the potential harm posed by embedded glass fragments. Let's embark on this insightful journey to unravel the complexities of dealing with glass in the skin and empower ourselves with the knowledge to address this concern effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Glass in the skin can cause pain, infection, and delayed healing. Prompt treatment by a professional is crucial to minimize risks and ensure optimal recovery.
- Preventing glass-related skin injuries involves safe handling, protective gear, and regular inspection. By promoting safety and awareness, we can create a healthier environment.
How Glass Gets Stuck in the Skin
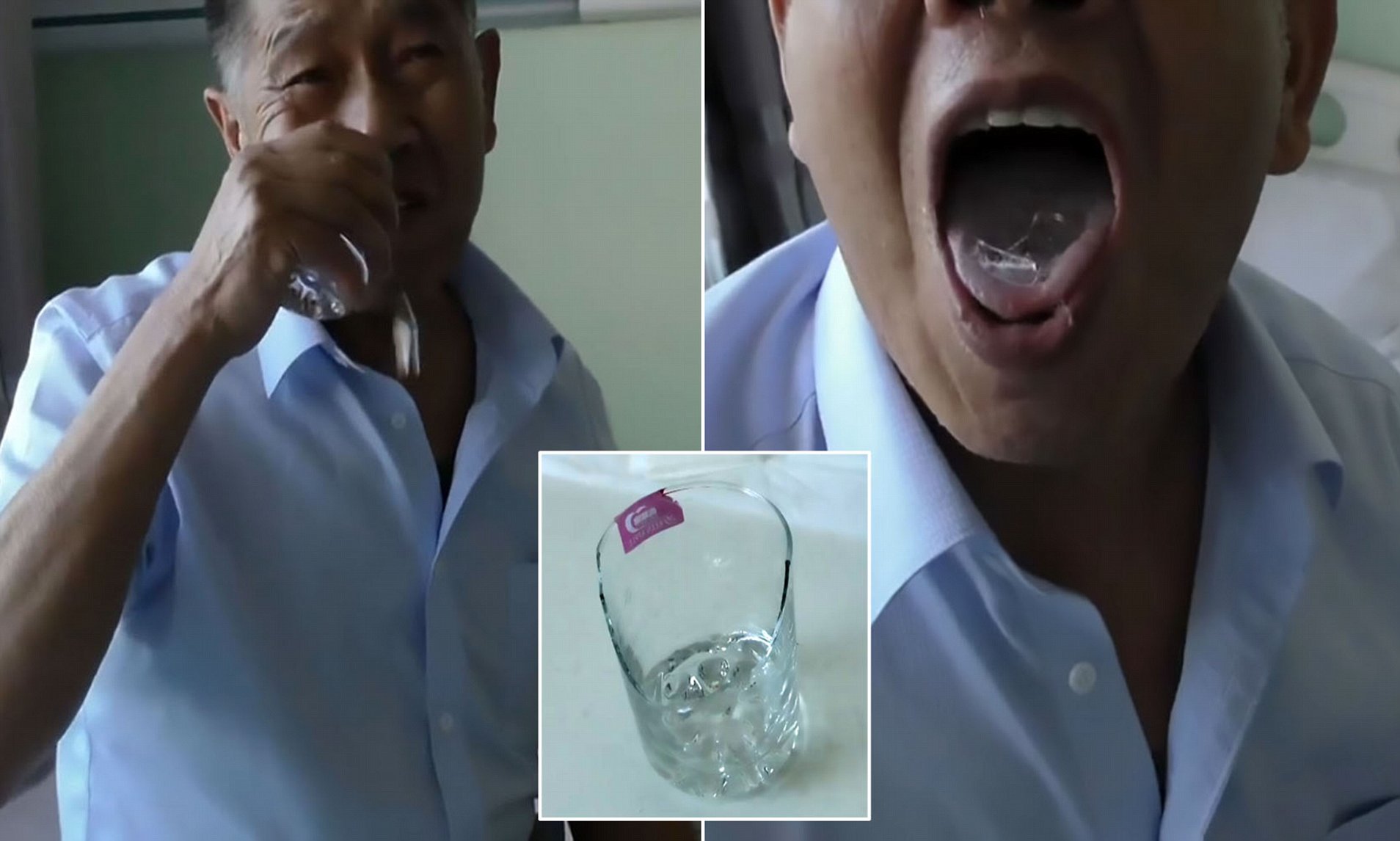
Glass can become embedded in the skin through various scenarios, often as a result of accidental contact or exposure. When glass breaks, it can produce sharp and jagged edges that have the potential to penetrate the skin upon contact. This can occur during everyday activities, such as handling broken glassware, cleaning up shattered glass, or walking barefoot in areas where glass fragments are present. Additionally, high-impact incidents, such as car accidents or industrial mishaps, can lead to larger glass fragments becoming lodged in the skin.
The skin's outermost layer, known as the epidermis, serves as a protective barrier against external elements. However, when the skin comes into contact with glass, especially sharp or pointed pieces, it can result in the glass penetrating the epidermis and becoming embedded in the underlying layers of the skin. The force and angle of contact, as well as the size and shape of the glass fragment, play significant roles in determining how deeply the glass becomes lodged in the skin.
In some cases, individuals may not immediately notice that glass has become stuck in their skin, especially if the penetration is shallow or if the affected area is not easily visible. This delayed awareness can occur when small glass particles adhere to the skin's surface or when larger fragments become embedded in areas such as the hands, feet, or limbs. The presence of glass in the skin can lead to discomfort, pain, and potential complications if not addressed promptly.
It's important to note that glass fragments can vary in size, from minuscule shards to larger pieces, and can exhibit different degrees of sharpness. This diversity in glass fragments contributes to the range of ways in which glass can become stuck in the skin. Whether it's a tiny shard from a broken glass or a larger piece from an accident, the potential for glass to become embedded in the skin underscores the importance of understanding how such incidents occur and the subsequent measures needed to address them effectively.
By comprehending the mechanisms through which glass becomes stuck in the skin, individuals can gain insight into the potential risks and complications associated with this issue, as well as the appropriate steps to take for treatment and prevention. This understanding forms the foundation for effectively managing and mitigating the impact of glass in the skin, promoting skin health and overall well-being.
Potential Risks and Complications
The presence of glass in the skin poses various risks and potential complications that can impact an individual's health and well-being. Understanding these implications is crucial for addressing the issue effectively and preventing further harm. When glass becomes embedded in the skin, it can lead to a range of adverse effects, including:
-
Inflammation and Irritation: Glass fragments lodged in the skin can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to redness, swelling, and discomfort in the affected area. The body's natural defense mechanisms may attempt to expel the foreign material, resulting in heightened sensitivity and localized irritation.
-
Infection: One of the most significant risks associated with glass in the skin is the potential for infection. The presence of foreign bodies, such as glass fragments, creates an entry point for bacteria and other pathogens. If not addressed promptly and properly, this can lead to localized infections, cellulitis, or abscess formation, posing a risk to overall health.
-
Delayed Healing: The presence of glass in the skin can impede the natural healing process. It can disrupt the formation of new skin tissue, delay wound closure, and prolong the overall recovery period. This delay in healing can increase the risk of secondary complications and may necessitate more extensive treatment measures.
-
Tissue Damage: Sharp or jagged glass fragments can cause physical trauma to the surrounding tissues. This can result in lacerations, puncture wounds, or deeper tissue damage, depending on the size and nature of the embedded glass. Such tissue damage can lead to scarring, impaired function, and long-term discomfort if not managed appropriately.
-
Migration and Displacement: In some cases, glass fragments may shift within the skin over time, leading to changes in their position and depth. This can complicate the removal process and increase the risk of further tissue trauma. Additionally, migrated glass fragments can cause unexpected symptoms and challenges in treatment.
-
Psychological Impact: The presence of glass in the skin can have psychological implications, causing distress, anxiety, and discomfort. Individuals may experience heightened stress and concern about the potential consequences of the embedded glass, impacting their overall well-being and mental health.
-
Secondary Injuries: If glass fragments remain in the skin for an extended period, they can increase the risk of secondary injuries, such as accidental displacement, further tissue trauma, or exacerbation of existing complications. Addressing the issue promptly is essential for preventing such secondary injuries.
Understanding these potential risks and complications associated with glass in the skin underscores the importance of prompt and appropriate intervention. By recognizing these implications, individuals can prioritize seeking timely treatment and taking proactive measures to minimize the impact of embedded glass fragments on their skin and overall health.
If glass stays in your skin, do not try to remove it yourself. Seek medical attention to prevent infection and ensure safe removal.
Treatment Options
When dealing with glass embedded in the skin, prompt and effective treatment is essential to minimize the potential risks and complications. The choice of treatment options depends on various factors, including the size and depth of the embedded glass, the presence of associated injuries, and the risk of infection. Here are the primary treatment options for addressing glass in the skin:
-
Surface Extraction: For superficially embedded glass fragments, surface extraction may be sufficient. This involves carefully removing the visible portion of the glass using sterilized tweezers or forceps. Prior to extraction, the surrounding skin is thoroughly cleaned to minimize the risk of contamination. Once the visible glass is removed, the area is cleansed and dressed appropriately.
-
Sterile Dressings and Observation: In cases where the glass is shallowly embedded and the risk of infection is low, sterile dressings may be applied to the affected area. This approach allows for close observation of the wound to monitor for signs of infection or migration of the glass fragment. Regular dressing changes and careful monitoring are essential to ensure proper wound care.
-
Medical Evaluation and Imaging: When dealing with deeply embedded or larger glass fragments, seeking medical evaluation is crucial. Healthcare professionals may utilize imaging techniques, such as X-rays or ultrasound, to assess the depth and location of the glass within the skin. This information guides the appropriate course of action for safe and effective removal.
-
Surgical Removal: In cases where the glass is deeply embedded or located in sensitive areas, surgical removal may be necessary. This procedure is performed under sterile conditions by a qualified healthcare provider. It involves making a small incision to access and remove the glass fragment, followed by meticulous wound closure and post-operative care.
-
Antibiotic Treatment: If there is a concern for infection or if the glass fragment has been present for an extended period, antibiotic treatment may be prescribed. This helps prevent or address potential infections resulting from the presence of foreign material in the skin.
-
Follow-Up Care: Following the initial treatment, diligent follow-up care is essential to monitor the healing process, assess for signs of infection, and address any residual symptoms. Healthcare providers may recommend specific wound care measures and schedule follow-up appointments to ensure proper recovery.
It is important to note that self-removal of deeply embedded glass fragments is not recommended, as it can lead to further tissue trauma, increased risk of infection, and complications. Seeking professional medical evaluation and treatment is the safest and most effective approach for managing glass embedded in the skin.
By understanding the available treatment options and seeking appropriate care, individuals can address the presence of glass in the skin in a timely and comprehensive manner, minimizing the potential risks and promoting optimal healing and recovery.
Preventing Glass from Getting Stuck in the Skin
Preventing glass from becoming embedded in the skin involves proactive measures to minimize the risk of accidental contact and exposure. By adopting preventive strategies and promoting safe practices, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of glass-related skin injuries. Here are essential guidelines for preventing glass from getting stuck in the skin:
-
Proper Handling and Disposal: When working with glass items, such as glassware, bottles, or decorative pieces, it is crucial to handle them with care. Avoiding rough or careless handling can help prevent breakage and the generation of sharp glass fragments. Additionally, proper disposal of broken glass ensures that potential hazards are minimized, reducing the risk of accidental contact.
-
Use of Protective Gear: In environments where the risk of glass breakage is higher, such as industrial settings or construction sites, the use of appropriate protective gear is essential. This may include gloves, safety goggles, or protective footwear designed to mitigate the impact of potential glass fragments and minimize the risk of skin injuries.
-
Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Periodic inspection of glass surfaces, such as windows, doors, and furniture, can help identify and address any existing cracks or damage. Timely repair or replacement of compromised glass reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakage and the subsequent risk of glass-related skin injuries.
-
Safe Cleanup Practices: In the event of glass breakage, thorough and safe cleanup practices are crucial. This includes using tools such as brooms, dustpans, and gloves to carefully collect and dispose of glass fragments. Additionally, thorough vacuuming of affected areas can help remove tiny glass particles, minimizing the risk of inadvertent skin contact.
-
Footwear Awareness: When walking in outdoor or potentially hazardous environments, wearing appropriate footwear provides a protective barrier against potential glass fragments. This is particularly important in areas where broken glass or debris may be present, reducing the risk of foot injuries and embedded glass.
-
Educational Initiatives: Promoting awareness and education about the risks associated with glass breakage and the importance of safe handling can empower individuals to take proactive measures. This can be achieved through workplace safety training, community outreach programs, and educational materials that emphasize the significance of preventing glass-related injuries.
By integrating these preventive measures into daily practices and promoting a culture of safety and awareness, individuals can effectively reduce the occurrence of glass-related skin injuries. Proactive efforts to prevent glass from becoming embedded in the skin contribute to a safer and healthier environment, minimizing the potential risks and complications associated with this issue.
Read more: What Happens If You Leave Glass In Your Foot
Conclusion
In conclusion, the presence of glass in the skin, whether from accidental contact or exposure, can lead to discomfort, pain, and potential health risks. Understanding how glass becomes embedded in the skin, the potential risks and complications it poses, available treatment options, and effective preventive measures is crucial for managing this issue effectively.
The process of glass becoming stuck in the skin can occur through various scenarios, ranging from handling broken glassware to experiencing high-impact incidents such as car accidents or industrial mishaps. The size, shape, and sharpness of glass fragments play significant roles in determining how deeply they become lodged in the skin, highlighting the diverse ways in which this issue can manifest.
The potential risks and complications associated with glass in the skin encompass inflammation, infection, delayed healing, tissue damage, migration, psychological impact, and secondary injuries. These implications underscore the importance of prompt and appropriate intervention to minimize the impact of embedded glass fragments on skin health and overall well-being.
When addressing glass embedded in the skin, prompt and effective treatment options include surface extraction, sterile dressings and observation, medical evaluation and imaging, surgical removal, antibiotic treatment, and diligent follow-up care. Seeking professional medical evaluation and treatment is essential, as self-removal of deeply embedded glass fragments is not recommended due to the potential for further tissue trauma and complications.
Preventive measures to minimize the risk of glass-related skin injuries involve proper handling and disposal of glass items, the use of protective gear in high-risk environments, regular inspection and maintenance of glass surfaces, safe cleanup practices, footwear awareness, and educational initiatives to promote safety and awareness.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of how glass becomes stuck in the skin, the potential risks and complications it poses, available treatment options, and effective preventive measures, individuals can equip themselves with the knowledge needed to address and mitigate the impact of glass in the skin. This understanding forms the foundation for effectively managing and promoting skin health and overall well-being.
In essence, by recognizing the implications of glass in the skin and taking proactive measures to address and prevent this issue, individuals can safeguard their skin from potential harm, promoting a safer and healthier environment for all.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Happens If Glass Stays In Your Skin
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Happens If Glass Stays In Your Skin”