Home>Furniture & Design>Interior Design Trends>What Happens To Recycled Glass


Interior Design Trends
What Happens To Recycled Glass
Modified: March 24, 2024
Discover the latest interior design trends with recycled glass. Learn about the sustainable and stylish options for your home.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Recycled glass is a versatile and sustainable material that plays a crucial role in the circular economy. As environmental consciousness continues to grow, the significance of recycling glass has become increasingly evident. Glass recycling not only conserves natural resources but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with glass production. Understanding the journey of recycled glass, from collection to repurposing, sheds light on its immense value and the positive implications for the planet.
Glass, a timeless and elegant material, has been utilized for centuries in various forms, from exquisite art pieces to everyday containers. However, the disposal of glass products poses a significant challenge due to its non-biodegradable nature. This is where the concept of recycling comes into play, offering a sustainable solution to mitigate the accumulation of glass waste in landfills and oceans.
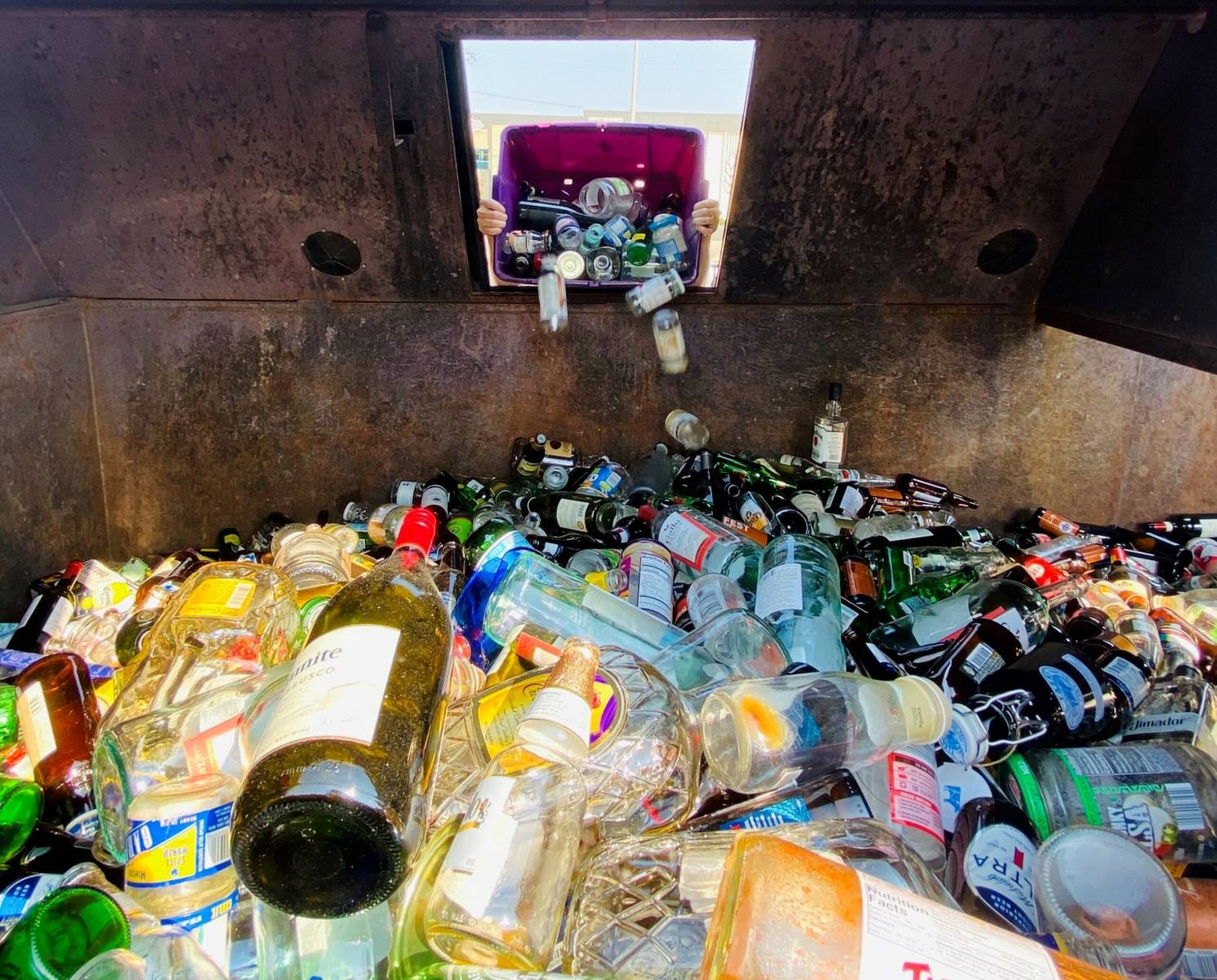
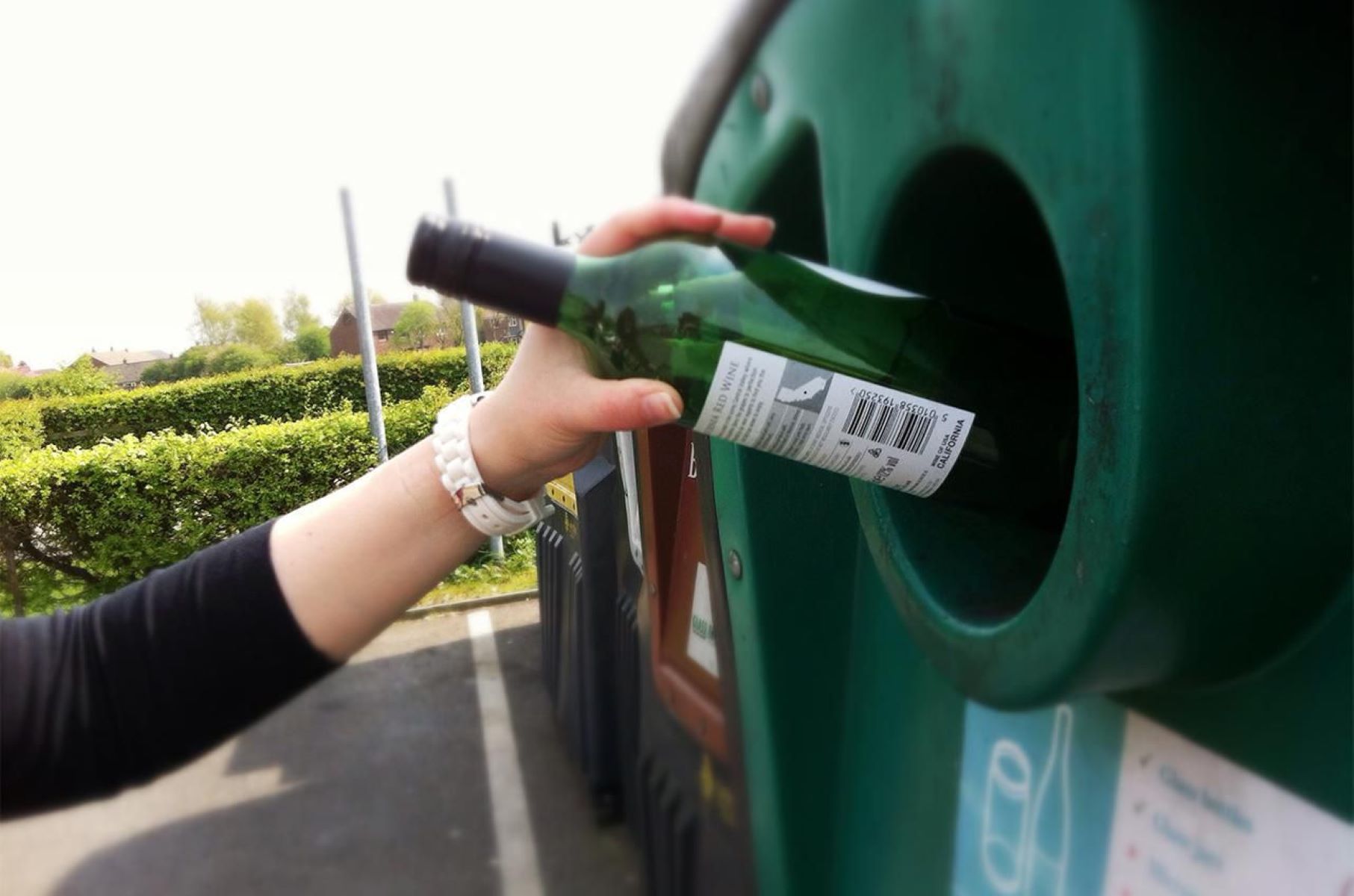
The process of recycling glass involves meticulous sorting, cleaning, and crushing of discarded glass items. Once the glass is collected from recycling bins or designated centers, it undergoes a thorough inspection to remove any contaminants, such as plastic or metal, ensuring the purity of the glass cullet, which is the term for crushed glass ready for recycling. This meticulous sorting process is essential to maintain the quality and integrity of the recycled glass.
Furthermore, the recycling process not only conserves energy but also reduces carbon emissions, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to glass production from raw materials. By repurposing glass, the demand for virgin materials diminishes, leading to a decrease in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, thereby contributing to a healthier and more sustainable planet.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of the glass recycling process, explore the diverse applications of recycled glass, and examine the environmental benefits and challenges associated with glass recycling. This comprehensive exploration will provide valuable insights into the multifaceted world of recycled glass and its pivotal role in shaping a greener and more sustainable future.
Key Takeaways:
- Recycled glass is a sustainable superhero, saving energy and reducing pollution. It transforms into new products like glass containers, insulation, and even beautiful art, making the planet greener and cleaner.
- Despite challenges like contamination and logistics, recycled glass is a versatile eco-warrior. It conserves energy, diverts waste, and promotes a circular economy, showing that even old glass can have a bright, sustainable future.
Read more: What Percentage Of Glass Is Recycled
The Recycling Process
The recycling process of glass is a meticulously orchestrated journey that transforms discarded glass items into valuable raw materials, ready to be repurposed into new products. This intricate process begins with the collection of glass from various sources, including recycling bins, drop-off centers, and commercial establishments. Once gathered, the glass undergoes a rigorous sorting process to eliminate any contaminants, such as plastic, metal, or ceramics, ensuring that only pure glass cullet remains.
Following the sorting stage, the glass cullet is thoroughly cleaned to remove any impurities or residues. This cleansing process is vital to maintain the quality and purity of the glass, as any remaining contaminants could compromise the integrity of the recycled material. Once cleaned, the glass cullet is crushed into small fragments, ready to be utilized in the production of new glass products.
The crushed glass undergoes further processing to refine its texture and size, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. This refined glass cullet serves as a versatile raw material, capable of being transformed into various products, including new glass containers, fiberglass insulation, and decorative glassware.
Moreover, the recycling process significantly reduces the energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with glass production from raw materials. By utilizing recycled glass, the demand for virgin materials diminishes, leading to a decrease in energy consumption and environmental impact. This sustainable approach not only conserves natural resources but also minimizes the accumulation of glass waste in landfills and oceans, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
In essence, the recycling process of glass embodies a harmonious blend of innovation and sustainability, offering a compelling solution to the challenges posed by glass waste. Through meticulous sorting, cleaning, and crushing, discarded glass is reborn as a valuable resource, ready to embark on a new journey as part of innovative and eco-conscious products. This transformative process underscores the profound potential of recycled glass in fostering a more sustainable and circular economy, where waste is repurposed into valuable assets, perpetuating a cycle of environmental responsibility and resource efficiency.
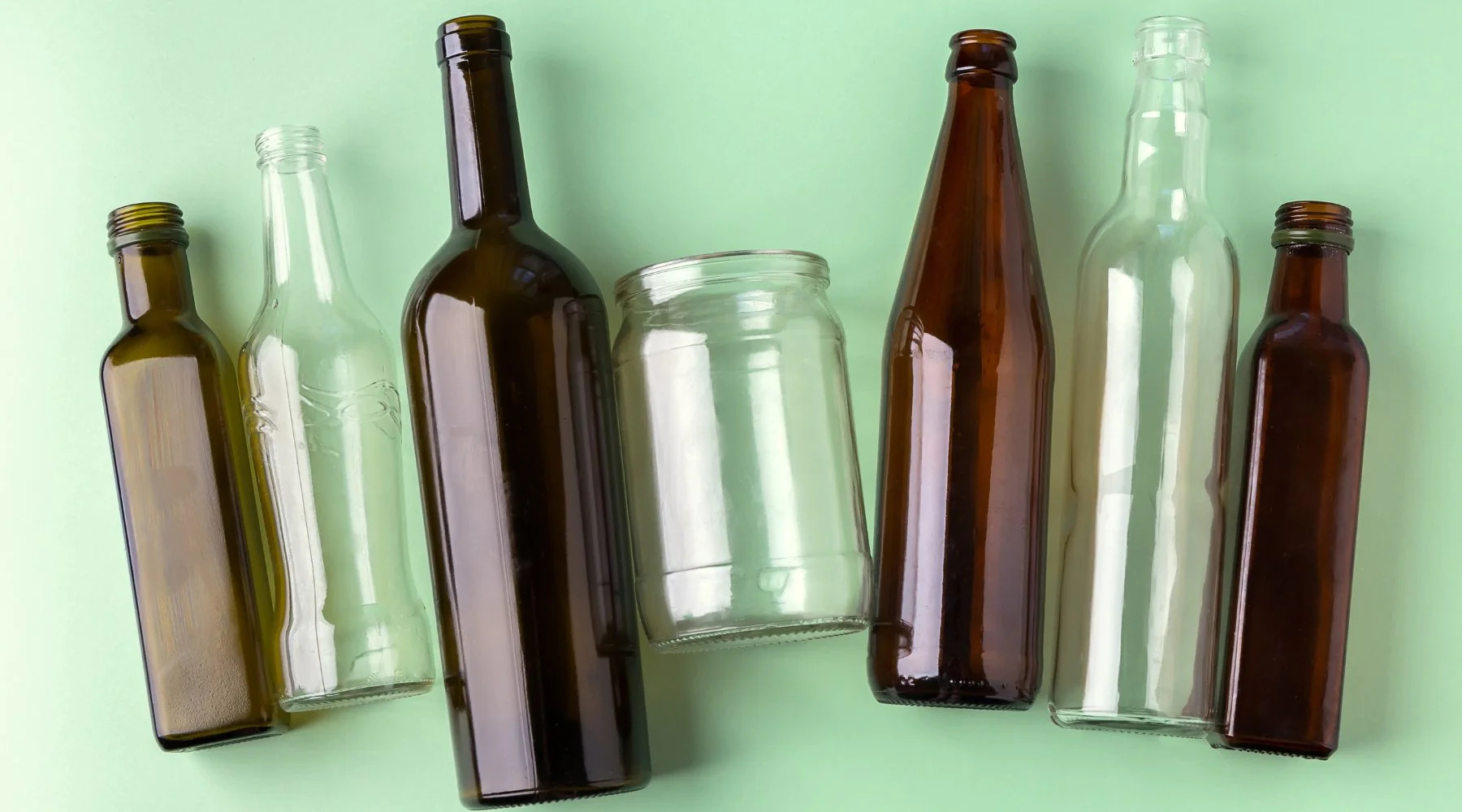
Uses for Recycled Glass
Recycled glass, also known as cullet, serves as a remarkably versatile raw material, finding applications across diverse industries and creative endeavors. Its adaptability and eco-friendly properties make it an attractive choice for manufacturers and artisans seeking sustainable alternatives. The following are some prominent uses for recycled glass:
-
Glass Manufacturing: One of the primary applications of recycled glass is in the production of new glass items. The high-quality cullet obtained from the recycling process can be melted and molded into new glass containers, bottles, and jars. By incorporating recycled glass into the manufacturing process, the demand for virgin materials is reduced, leading to energy savings and a decreased environmental footprint.
-
Fiberglass Production: Recycled glass cullet is utilized in the manufacturing of fiberglass insulation, a crucial component in the construction and automotive industries. The finely crushed glass particles are spun into fibers and used to create insulation materials that offer thermal efficiency and soundproofing properties. By integrating recycled glass into fiberglass production, the industry contributes to sustainable building practices and energy conservation.
-
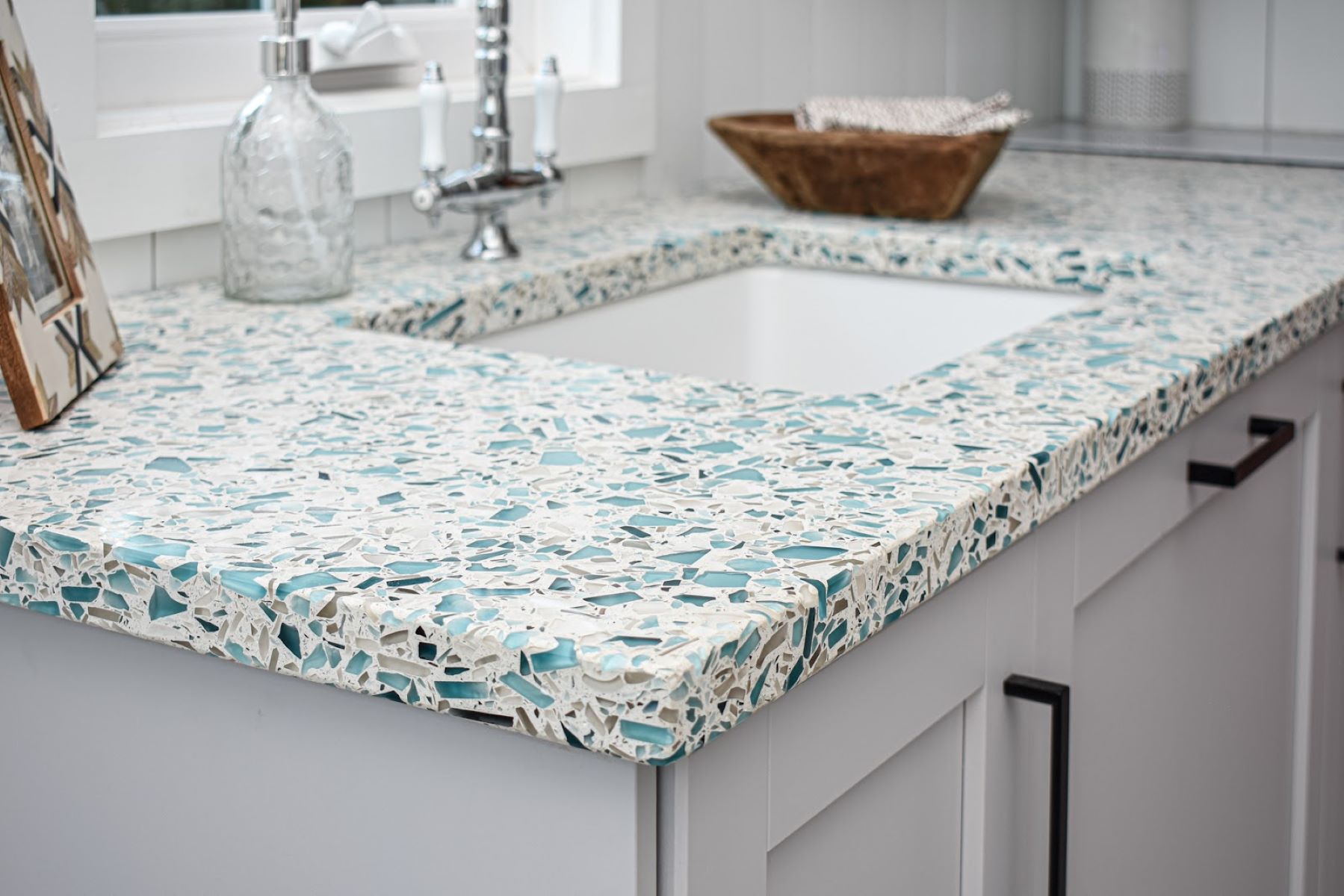
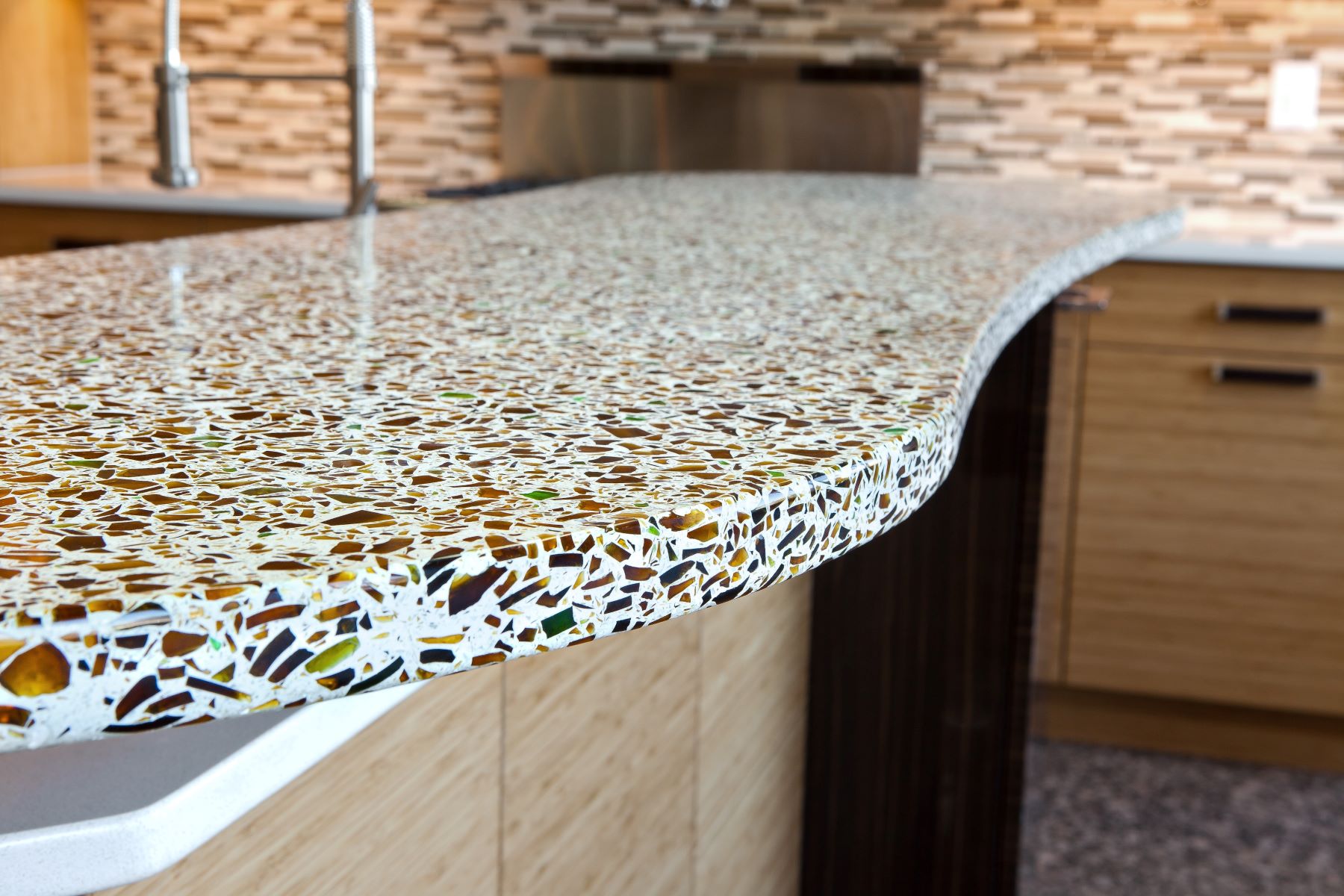
Decorative Applications: Recycled glass is widely employed in the creation of decorative and artistic pieces, including countertops, tiles, and mosaic artworks. Its unique texture and vibrant colors make it an appealing choice for interior designers and architects seeking sustainable and visually captivating materials. From stunning kitchen countertops to intricate mosaic installations, recycled glass adds a touch of eco-elegance to various design projects.
-
Landscaping and Aggregate Uses: Crushed recycled glass finds applications in landscaping and construction projects as a sustainable alternative to traditional gravel and aggregate materials. Its use in landscaping and hardscaping projects not only adds a distinctive aesthetic appeal but also contributes to sustainable urban development by reducing the demand for natural resources.
-
Water Filtration Systems: The exceptional purity and hardness of recycled glass make it an ideal material for water filtration systems. The finely crushed glass particles are utilized in the production of filtration media, effectively removing impurities and contaminants from water. This application underscores the vital role of recycled glass in promoting clean and safe water resources.
-
Ceramics and Abrasives: Recycled glass cullet is incorporated into the manufacturing of ceramic tiles and abrasives, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional raw materials. Its use in ceramics production contributes to resource conservation and reduces the environmental impact associated with conventional ceramic manufacturing processes.
The diverse applications of recycled glass underscore its immense potential in fostering sustainable practices across various industries. From glass manufacturing to artistic endeavors, the utilization of recycled glass cullet embodies a commitment to environmental stewardship and resource efficiency. As the demand for eco-friendly materials continues to rise, recycled glass stands as a shining example of innovation and sustainability, offering a compelling solution to the challenges posed by glass waste.
Environmental Benefits
Recycled glass embodies a myriad of environmental benefits that significantly contribute to sustainable resource management and environmental conservation. By repurposing discarded glass items into valuable raw materials, the recycling process offers a host of advantages that resonate with the principles of environmental stewardship and circular economy.
Energy Conservation
The utilization of recycled glass cullet in the manufacturing of new glass products leads to substantial energy savings. When compared to the production of glass from raw materials, incorporating recycled glass into the manufacturing process reduces energy consumption by a significant margin. This energy conservation is attributed to the lower melting point of glass cullet, which requires less energy during the melting and molding stages. As a result, the demand for energy-intensive glass production from virgin materials diminishes, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient manufacturing process.
Read more: What Can Glass Be Recycled Into
Reduction of Carbon Emissions
The integration of recycled glass into various industries plays a pivotal role in reducing carbon emissions. By utilizing glass cullet in the production of new glass items, manufacturers decrease their reliance on virgin materials, thereby lowering the carbon footprint associated with glass production. This reduction in carbon emissions aligns with global efforts to mitigate climate change and promote eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Waste Diversion
Glass recycling serves as a fundamental strategy for diverting glass waste from landfills and oceans. By repurposing discarded glass items, the recycling process mitigates the accumulation of glass waste in landfill sites, reducing the strain on waste management systems and minimizing environmental pollution. Furthermore, the diversion of glass waste from oceans and water bodies helps safeguard marine ecosystems and aquatic life, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
Conservation of Natural Resources
The utilization of recycled glass cullet conserves natural resources, such as sand, soda ash, and limestone, which are essential components in traditional glass production. By incorporating recycled glass into the manufacturing process, the demand for these virgin materials decreases, leading to resource conservation and reduced environmental impact. This sustainable approach underscores the importance of recycled glass in preserving natural resources for future generations.
Circular Economy Principles
Recycled glass embodies the principles of a circular economy, where waste is repurposed into valuable resources, perpetuating a cycle of sustainability and resource efficiency. By transforming discarded glass items into high-quality cullet, the recycling process fosters a closed-loop system that minimizes waste generation and maximizes the utilization of existing resources. This circular approach aligns with the broader goal of creating a regenerative and sustainable economy, where materials are continuously recycled and repurposed, reducing the reliance on finite resources.
In essence, the environmental benefits of recycled glass underscore its pivotal role in promoting sustainable practices and mitigating the environmental impact of glass production and disposal. By conserving energy, reducing carbon emissions, diverting waste, and preserving natural resources, recycled glass stands as a beacon of environmental responsibility and resource efficiency, offering a compelling solution to the challenges posed by glass waste.
Read more: How Recyclable Is Glass
Challenges in Glass Recycling
Glass recycling, despite its numerous environmental and economic benefits, is not without its challenges. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial to further enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of glass recycling initiatives. Some of the key challenges in glass recycling include:
Contamination: One of the primary challenges in glass recycling is the presence of contaminants in the glass waste stream. Contaminants such as ceramics, stones, and non-recyclable plastics can compromise the quality and purity of the recycled glass cullet. Addressing contamination requires improved sorting and collection processes, as well as increased public awareness regarding the proper disposal of glass items.
Collection and Transportation: The collection and transportation of glass waste from various sources to recycling facilities present logistical challenges. Glass is heavy and can be cumbersome to handle, requiring specialized collection and transportation methods to ensure efficient and cost-effective recycling processes. Additionally, the decentralized nature of glass waste collection poses challenges in consolidating and transporting the material to recycling centers.
Market Demand and End Markets: The availability of consistent and viable end markets for recycled glass cullet is essential for sustaining glass recycling efforts. Fluctuations in market demand for recycled glass products can impact the economic viability of glass recycling programs. Developing stable and diverse end markets for recycled glass is crucial to ensure the continued success of glass recycling initiatives.
Technological Limitations: The recycling of certain types of glass, such as heat-resistant glassware and ceramics, presents technological challenges due to their unique chemical compositions and melting points. Innovations in glass recycling technologies are necessary to overcome these limitations and expand the range of glass items that can be effectively recycled.
Consumer Behavior and Participation: Encouraging widespread consumer participation in glass recycling programs remains a challenge. Educating the public about the importance of proper glass disposal and recycling, as well as promoting convenient and accessible recycling infrastructure, are essential for increasing recycling rates and reducing glass waste in landfills.
Economic Viability: The economic viability of glass recycling programs is influenced by factors such as transportation costs, processing expenses, and market prices for recycled glass. Balancing the costs of collection, sorting, and processing with the revenue generated from the sale of recycled glass products is a continual challenge for recycling facilities and municipalities.
Innovative strategies, technological advancements, and collaborative efforts among stakeholders are essential for overcoming these challenges and advancing the glass recycling industry. By addressing these obstacles, the glass recycling sector can further solidify its position as a cornerstone of sustainable waste management and resource conservation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey of recycled glass from collection to repurposing exemplifies the transformative power of sustainable practices in mitigating environmental impact and fostering resource efficiency. The recycling process, characterized by meticulous sorting, cleaning, and crushing, breathes new life into discarded glass items, paving the way for their reincarnation as valuable raw materials. This intricate process not only conserves energy and reduces carbon emissions but also contributes to the conservation of natural resources, aligning with the principles of a circular economy.
The diverse applications of recycled glass, spanning from glass manufacturing to decorative uses and water filtration systems, underscore its remarkable versatility and eco-friendly properties. By integrating recycled glass cullet into various industries, manufacturers and artisans embrace a sustainable approach that resonates with the growing demand for eco-conscious materials. Furthermore, the environmental benefits of recycled glass, including energy conservation, waste diversion, and the reduction of carbon emissions, underscore its pivotal role in promoting sustainable resource management and environmental stewardship.
However, the challenges in glass recycling, such as contamination, collection logistics, market demand, and technological limitations, necessitate innovative solutions and collaborative efforts to further enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of glass recycling initiatives. Addressing these challenges is essential to bolster the resilience and economic viability of glass recycling programs, ensuring their continued success in the pursuit of a greener and more sustainable future.
In essence, the journey of recycled glass encapsulates a narrative of resilience, innovation, and environmental responsibility. As the demand for sustainable materials continues to rise, recycled glass stands as a beacon of hope, offering a compelling solution to the challenges posed by glass waste. By embracing the principles of circularity and sustainability, the recycling of glass transcends mere waste management, emerging as a catalyst for positive change and a testament to the transformative potential of sustainable practices. Through collective action and unwavering commitment, the journey of recycled glass embodies a vision of a world where waste is repurposed, resources are conserved, and the planet thrives in harmony with human innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Happens To Recycled Glass
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Happens To Recycled Glass”