Home>Garden Essentials>Learn How To Do Architectural Landscape Design


Garden Essentials
Learn How To Do Architectural Landscape Design
Modified: October 20, 2024
Learn how to create stunning architectural landscape designs for your garden with our comprehensive guide. Find expert tips and techniques to transform your outdoor space.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
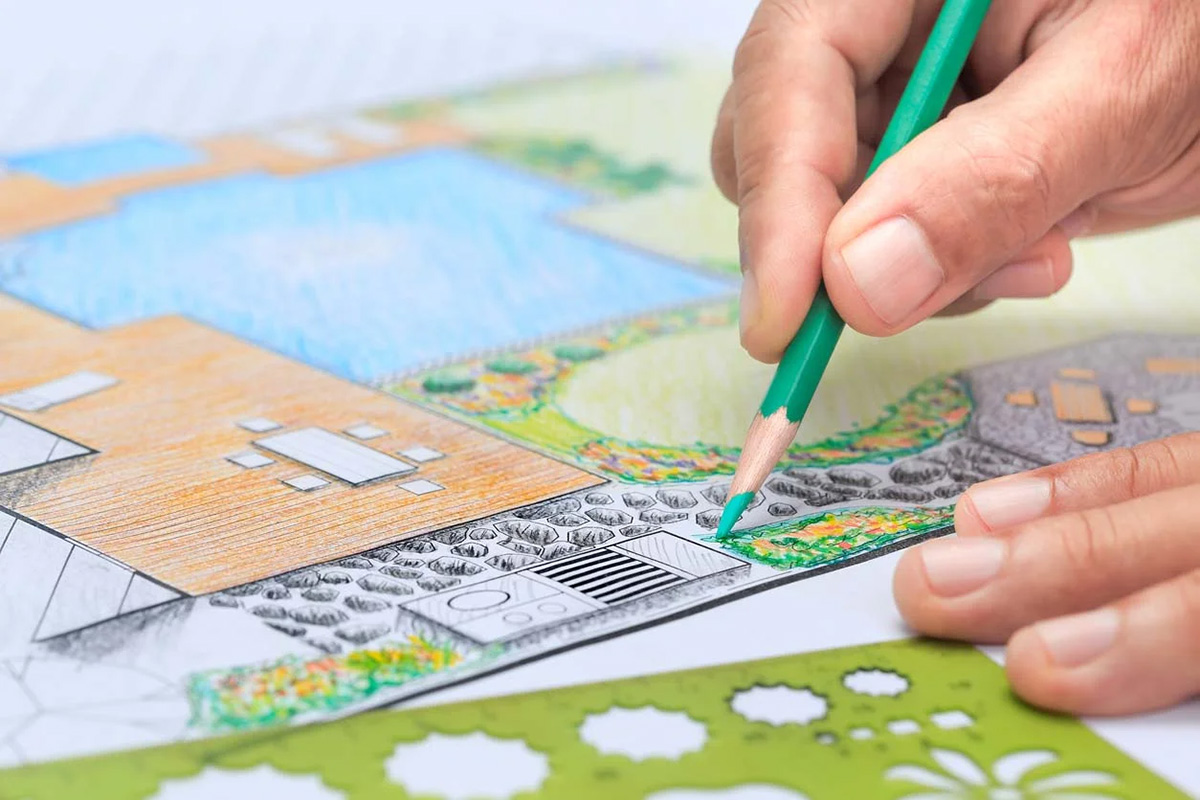
Welcome to the world of architectural landscape design! The art of creating beautiful and functional outdoor spaces has captivated the human imagination for centuries. From ancient gardens and grand estates to modern urban settings, landscaping has evolved to become an integral part of our living environment.
Architectural landscape design involves the careful planning, organization, and manipulation of outdoor spaces to achieve a harmonious blend of aesthetics and functionality. It takes into account various elements such as natural features, site analysis, vegetation, structures, colors, textures, and lighting to create a breathtaking and inviting landscape.
Whether you have a small backyard or a vast commercial property, understanding the principles and techniques of architectural landscape design can help you transform any space into a visually captivating and functional oasis. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the diverse aspects of this fascinating discipline and provide you with valuable insights to help you embark on your landscaping journey.
So, whether you’re a seasoned landscape designer looking to broaden your knowledge or a passionate homeowner ready to take on your own landscaping project, join us as we explore the world of architectural landscape design and uncover the secrets behind creating breathtaking outdoor spaces.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the natural features, climate, and context of a site is crucial for creating stunning outdoor spaces in architectural landscape design. It sets the foundation for informed and harmonious design decisions.
- By integrating structures, hardscapes, and lighting, designers can enhance the functionality and visual appeal of outdoor spaces. Thoughtful selection and placement of elements create captivating and usable landscapes.
Read more: How To Learn Construction
Understanding Architectural Landscape Design
Architectural landscape design is a multidisciplinary approach that combines elements of art, architecture, and horticulture to create visually appealing and functional outdoor spaces. It goes beyond simply planting flowers or arranging rocks; it’s about creating a harmonious relationship between the built environment and the natural world.
At its core, architectural landscape design involves carefully analyzing the site and its surroundings, considering factors such as topography, climate, soil conditions, and existing vegetation. By understanding these elements, designers can make informed decisions about the layout, materials, and plant choices to maximize the potential of the space.
One of the key principles of architectural landscape design is the concept of unity and harmony. A successful design seamlessly integrates the various components of the landscape, creating a cohesive and balanced composition. This can be achieved through careful consideration of color schemes, textures, and the use of repetition and rhythm throughout the space.
Another important aspect of architectural landscape design is the consideration of functionality. Outdoor spaces are not only meant to be visually pleasing but also practical and usable. Designers need to think about how people will interact with the space, whether it’s for relaxation, entertaining, or recreation. This involves careful planning of seating areas, pathways, and the integration of structures such as gazebos, pergolas, or outdoor kitchens.
Furthermore, sustainability and environmental consciousness are becoming increasingly important in architectural landscape design. Designers are encouraged to incorporate environmentally friendly practices such as using native plants, minimizing water usage, and implementing efficient irrigation systems. By embracing sustainable design principles, we can create landscapes that are not only visually stunning but also have a positive impact on the environment.
Overall, architectural landscape design is a blend of creativity, technical knowledge, and intuitive understanding of the natural world. It allows us to shape our outdoor spaces in a way that enhances our quality of life and connects us to the beauty of nature. Whether it’s a small backyard or a large public park, the principles of architectural landscape design can be applied to transform any space into a captivating and functional haven.
The Importance of Site Analysis
Before embarking on any architectural landscape design project, conducting a thorough site analysis is crucial. Site analysis is the process of understanding the characteristics and unique attributes of a specific location. It provides designers with valuable insights that shape the design decisions and ensure that the final outcome is not only visually appealing but also functional and sustainable.
One of the primary purposes of site analysis is to understand the site’s natural features. This includes examining the topography, soil conditions, drainage patterns, and existing vegetation. The topography of the site will influence the placement and layout of various elements, while the soil conditions will determine plant selection and irrigation needs. By understanding these natural features, designers can make informed decisions that work in harmony with the site’s existing conditions.
Site analysis also involves considering the site’s microclimate and macroclimate. The microclimate refers to the unique climate conditions specific to a small area, such as temperature variations, wind patterns, and sunlight exposure. Understanding the microclimate helps designers determine appropriate plant choices and the placement of structures to optimize comfort and functionality in the landscape. On the other hand, macroclimate refers to the broader climate conditions of the region, such as average temperature, rainfall, and seasonal changes. Considering the macroclimate helps designers select plants that are well-suited to thrive in the local environment.
Furthermore, site analysis takes into account the site’s existing infrastructure and utilities. This includes identifying the location of utility lines, irrigation systems, and any existing structures that need to be integrated into the design. Taking these factors into consideration ensures that the final design works seamlessly with the existing infrastructure and minimizes the need for costly renovations or disruptions.
In addition to natural and built features, site analysis also considers the site’s context and surroundings. This involves examining the neighboring properties, architectural styles, and the overall character of the area. By understanding the context, designers can create a design that complements the existing surroundings and adds value to the overall aesthetic of the neighborhood or space.
Overall, site analysis is a critical step in the architectural landscape design process. It sets the foundation for a successful design by providing designers with a comprehensive understanding of the site’s unique attributes and challenges. By considering the natural features, climate conditions, infrastructure, and context of the site, designers can create a design that is not only visually pleasing but also functional, sustainable, and harmonious with its surroundings.
Principles of Architectural Landscape Design
Architectural landscape design is guided by a set of principles that help create visually appealing and functional outdoor spaces. These principles serve as a framework for designers to develop their designs and ensure a cohesive and harmonious outcome. Let’s explore some of the key principles that govern architectural landscape design:
- Unity and Harmony: Unity refers to the sense of oneness and coherence in a design. It is achieved by creating a harmonious relationship between various elements in the landscape. This can be accomplished through the use of consistent materials, colors, and textures throughout the space. By creating a sense of unity, the design feels cohesive and visually pleasing.
- Balance: Balance is the distribution of visual weight or elements within a design. It can be achieved through symmetrical or asymmetrical arrangements of plants, structures, or other landscape features. A balanced design feels stable and visually appealing, creating a sense of equilibrium.
- Proportion and Scale: Proportion and scale refer to the relationship between different elements in the design. It involves considering the size, shape, and visual weight of each element to create a visually pleasing composition. Proper proportion and scale ensure that elements within the landscape harmonize with one another and the overall space.
- Rhythm and Repetition: Rhythm creates a sense of movement and flow within the design. It can be achieved through the repetition of plants, patterns, or structural elements. By incorporating rhythm and repetition, the design feels dynamic and visually captivating.
- Focal Points: Focal points are key elements in the landscape that draw attention and create visual interest. They serve as a focal point in the design and help guide the viewer’s gaze. Focal points can be created through the use of large plants, sculptures, water features, or other eye-catching elements.
- Emphasis and Contrast: Emphasis and contrast help create visual interest and hierarchy within the design. They involve highlighting specific elements or creating contrasting elements to draw attention. This can be done through the use of color, texture, or size variations.
- Functionality and Practicality: While aesthetics are important, architectural landscape design also prioritizes functionality and practicality. The design should consider how people will interact with the space and ensure that it serves its intended purpose. This involves thoughtful planning of seating areas, pathways, and the integration of structures that enhance usability and enjoyment of the outdoor space.
- Sustainability and Environmental Consciousness: In today’s world, designing with sustainability in mind is crucial. Architectural landscape design embraces practices such as using native plants, implementing efficient irrigation systems, and minimizing water usage. By designing with sustainability in mind, we can create landscapes that are not only visually appealing but also have a positive impact on the environment.
By applying these principles, designers can create visually stunning and functional outdoor spaces that enhance the overall quality of life. Each principle plays a crucial role in guiding the design decisions and ensures a harmonious and captivating landscape design.
Types of Plants and Vegetation
Plants and vegetation are vital components of architectural landscape design, adding beauty, color, texture, and life to outdoor spaces. There is a wide variety of plant species available, each with its unique characteristics and requirements. Let’s explore some popular types of plants and vegetation commonly used in landscape design:
- Trees: Trees are an essential part of any landscape design, providing shade, visual interest, and vertical structure. They come in various sizes, shapes, and foliage types, ranging from deciduous trees that lose their leaves in the fall to evergreen trees that retain their foliage throughout the year. Trees can be used as focal points, to frame views, or to create a canopy-like ambiance.
- Shrubs: Shrubs are versatile plants that can serve various purposes in landscape design. They can be used for privacy screening, creating a border or hedge, or adding structure and texture to the garden. Shrubs come in different sizes and foliage types, offering a range of colors and textures to enhance the visual appeal of the landscape.
- Perennials: Perennials are plants that live for more than two years, often flowering during specific seasons. They add bursts of color and texture to the landscape and are typically easier to maintain than annuals. Examples of perennials include roses, lavender, daylilies, and daisies. They can be used in flower beds, borders, or as accents throughout the landscape.
- Grasses: Ornamental grasses are popular in landscape design due to their versatility and low-maintenance nature. They add movement, texture, and visual interest to the landscape, especially when they sway with the wind. Grasses come in various heights, colors, and textures, offering a wide range of options for designers to incorporate into their designs.
- Groundcovers: Groundcovers are low-growing plants that spread horizontally, covering the ground and suppressing weeds. They are ideal for filling in gaps, preventing erosion, and providing a uniform look to the landscape. Groundcovers come in a variety of foliage types and colors, such as creeping thyme, sedum, or creeping juniper.
- Climbing Plants: Climbing plants are excellent for adding vertical interest and texture to structures such as walls, fences, or pergolas. They can provide privacy, shade, or simply add a touch of elegance to the landscape. Examples of climbing plants include ivy, wisteria, and climbing roses.
- Native Plants: Native plants are species that naturally occur in a specific region and have adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. They are often recommended for landscape design due to their resilience and ability to support local wildlife. Using native plants promotes biodiversity and helps create a sustainable and environmentally-friendly landscape.
When selecting plants for architectural landscape design, it’s crucial to consider factors such as climate, sun exposure, soil conditions, and maintenance requirements. By choosing a variety of plants that complement one another and the overall design, you can create a visually stunning and diverse landscape that thrives year-round.
Read more: How Hard Is It To Learn CAD
Considering Environmental Factors
In architectural landscape design, it is vital to consider environmental factors to create sustainable and eco-friendly outdoor spaces. By understanding and addressing these factors, designers can minimize the negative impacts on the environment and create landscapes that thrive and contribute positively to the surrounding ecosystem. Let’s explore some key environmental factors to consider in landscape design:
- Climate: Climate is a crucial factor that directly influences the success and longevity of a landscape design. Consider the average temperature, rainfall patterns, and seasonal changes in your region. Choose plants that are well-adapted to the local climatic conditions to ensure their survival and reduce water usage. Incorporate shading elements, such as trees and pergolas, to provide relief from excessive heat and protect delicate plants.
- Water Management: Water scarcity is a significant concern in many regions. Implementing efficient water management practices is essential for a sustainable landscape design. Consider installing a drip irrigation system that targets specific areas and reduces water waste. Collect and reuse rainwater through rain barrels or cisterns. Use mulch to retain moisture in the soil and reduce evaporation. Select native or drought-tolerant plants that require less water once established.
- Soil Conditions: Soil quality directly impacts plant health and growth. Test the soil pH and composition to determine its nutrient content and drainage capacities. Amend the soil as needed to ensure optimal conditions for plant growth. Consider using organic or natural fertilizers to promote healthy soil and reduce chemical runoff into water sources.
- Ecological Balance: Landscapes have the potential to support biodiversity and ecological balance. Incorporate native plant species that provide food and habitat for local wildlife such as birds, butterflies, and bees. Avoid using pesticides and herbicides that can harm beneficial insects and disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem. Create diverse micro-habitats, such as rock piles or small ponds, to attract a variety of wildlife.
- Energy Efficiency: Designing outdoor spaces that contribute to energy efficiency is vital. Incorporate shade-providing elements such as trees, trellises, or pergolas to reduce the need for excessive air conditioning. Design the layout to harness natural ventilation and airflow, minimizing the use of artificial cooling systems. Consider the orientation of structures to maximize sunlight exposure in winter and provide shade in summer.
- Waste Management: Proper waste management is essential for maintaining a sustainable landscape. Utilize composting practices to reduce the amount of organic waste sent to landfills. Implement recycling bins in outdoor spaces to encourage proper waste disposal. Consider using recycled or reclaimed materials for hardscape elements such as paths, patios, or retaining walls.
- Light Pollution: Light pollution not only affects human health but also disrupts the natural behavior and cycles of wildlife. Use outdoor lighting fixtures that are energy-efficient and properly shielded to minimize light pollution. Consider motion-sensor lighting to reduce unnecessary energy consumption and provide adequate lighting only when needed.
By considering these environmental factors in architectural landscape design, we can create outdoor spaces that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also promote sustainability and harmony with the natural world. Sustainable design practices contribute to the preservation of resources, support biodiversity, and create landscapes that can be enjoyed for generations to come.
When designing an architectural landscape, consider the natural elements of the site such as sunlight, wind patterns, and existing vegetation. These factors will help you create a sustainable and visually appealing design.
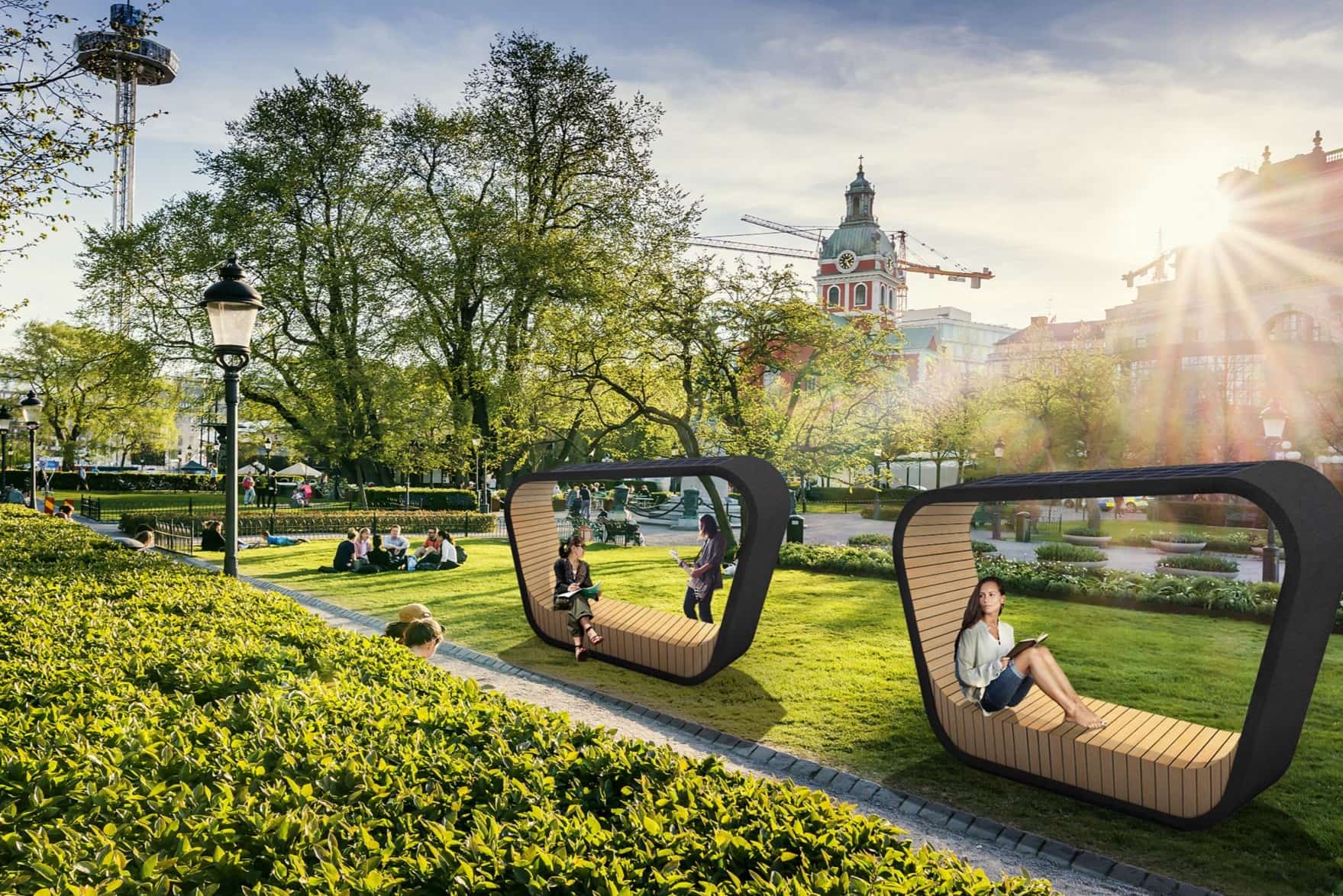
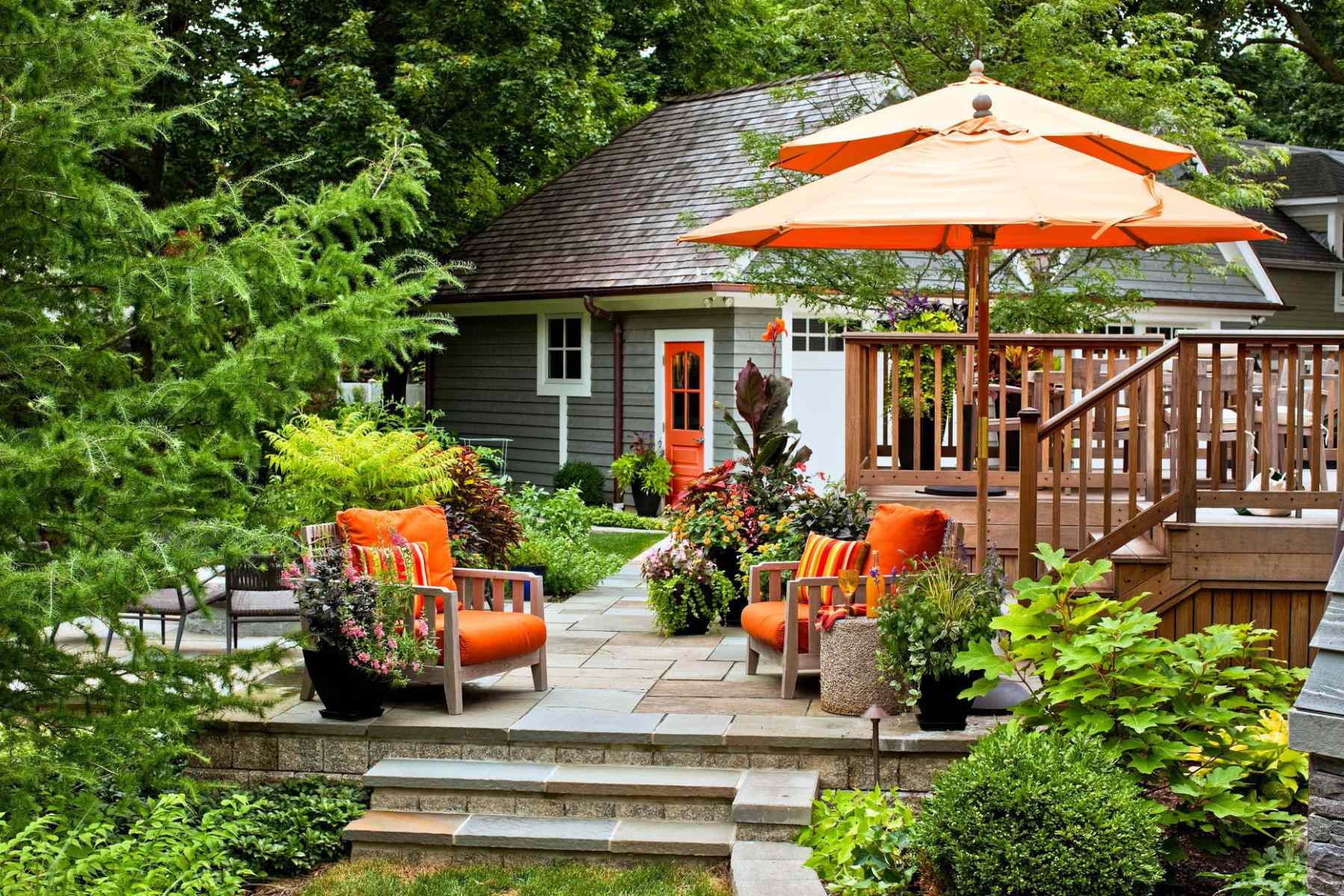
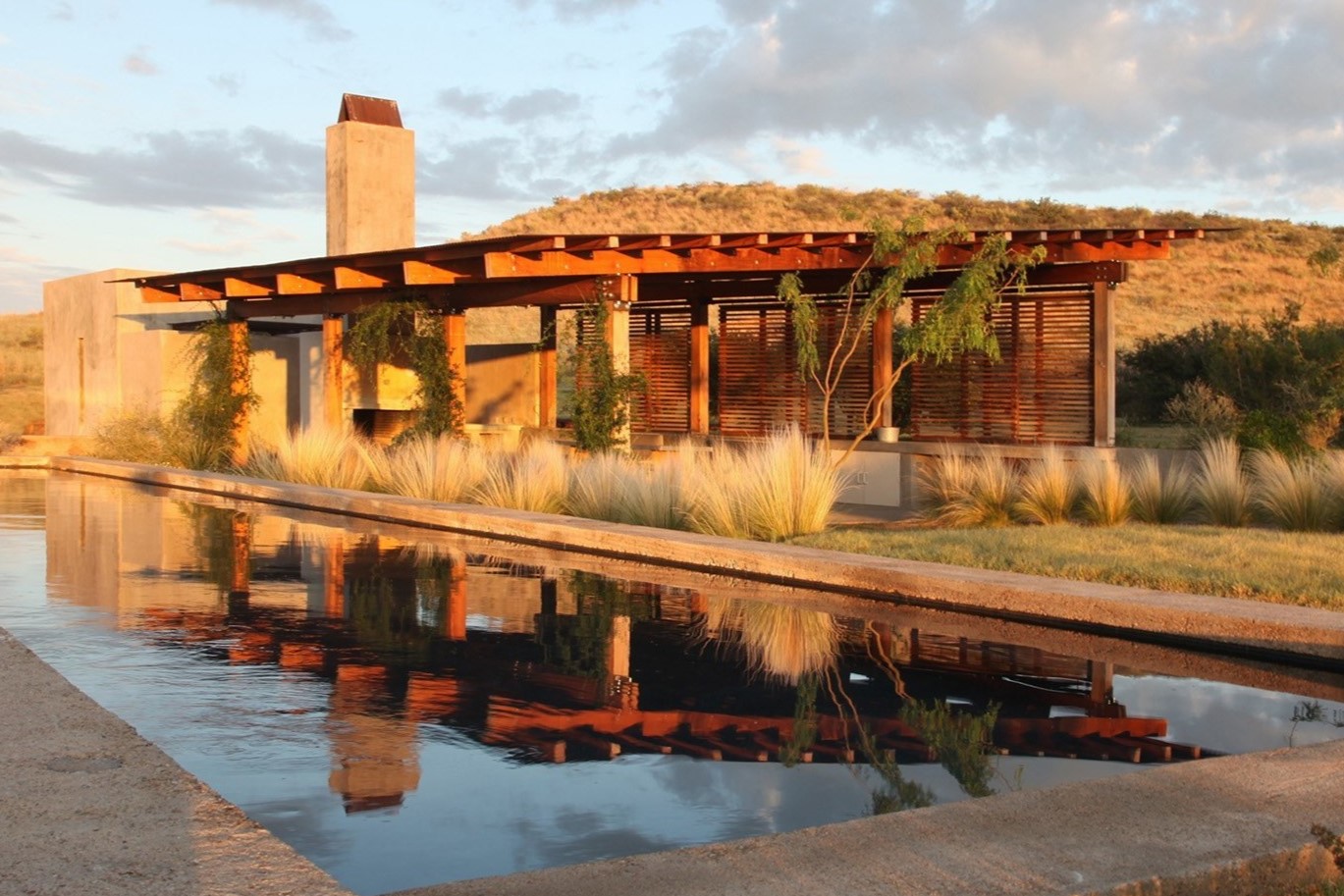
Integrating Structures and Hardscapes
Structures and hardscapes play a crucial role in architectural landscape design, providing functional and visually appealing elements that enhance the overall aesthetic and functionality of outdoor spaces. By effectively integrating structures and hardscapes into the landscape, designers can create cohesive and harmonious designs. Let’s explore how to integrate structures and hardscapes in landscape design:
- Pathways and Walkways: Pathways and walkways provide guidance and create a sense of flow within the landscape. Incorporate materials such as pavers, flagstones, or gravel to create visually appealing paths that lead visitors through the outdoor space. Consider the width and layout of the pathways to accommodate easy movement while maintaining a visually pleasing design. Enhance pathways with lighting fixtures to ensure safety and usability during nighttime.
- Patios and Outdoor Living Spaces: Patios and outdoor living spaces are essential for creating functional areas for relaxation, entertainment, and socializing. Consider the placement and size of patios in relation to the surrounding landscape elements. Incorporate materials such as stone, concrete, or wood to create a visually appealing and durable foundation. Integrate seating areas, dining spaces, or outdoor kitchens to enhance usability and provide comfort for outdoor gatherings.
- Retaining Walls and Terraces: Retaining walls and terraces are utilized to manage slopes and create usable spaces in challenging terrain. They can add visual interest and provide structural integrity to the landscape. Choose materials that complement the overall design, such as stone, brick, or wood. Consider incorporating planting pockets within the walls or terraces to soften their appearance and promote a seamless integration with the surrounding vegetation.
- Gazebos and Pergolas: Gazebos and pergolas add vertical elements and architectural interest to the landscape. They provide shaded areas and can serve as focal points or gathering spots within the outdoor space. Consider the placement and size of gazebos or pergolas to ensure they fit harmoniously within the overall composition. Enhance these structures with climbing plants or vines to create a natural and visually appealing effect.
- Water Features: Water features such as fountains, ponds, or waterfalls can create a tranquil and soothing atmosphere in the landscape. Consider the size and location of water features to ensure they don’t overwhelm the space or clash with other design elements. Incorporate materials that complement the overall aesthetic, such as stone or glass. Water features can attract wildlife, provide a focal point, and add a sense of serenity to the outdoor space.
- Structural Sculptures and Art Installations: Structural sculptures and art installations can add a unique and artistic touch to the landscape design. Consider incorporating sculptures or art pieces that reflect the theme or style of the outdoor space. Place them strategically to create visual interest and guide the viewer’s gaze. Explore materials such as metal, glass, or stone to add a modern or contemporary element to the landscape.
- Outdoor Lighting: Outdoor lighting is crucial for creating ambiance, safety, and extending the usability of outdoor spaces into the evening hours. Integrate lighting fixtures strategically to highlight focal points, pathways, and architectural features. Use different lighting techniques, such as uplighting, downlighting, or accent lighting, to create a visually appealing and functional lighting design. Consider energy-efficient options, such as LED lighting, to minimize energy consumption.
By thoughtfully integrating structures and hardscapes into the landscape design, designers can create visually captivating and functional outdoor spaces. The careful selection of materials, placement, and integration ensures that these elements harmonize with the overall composition, enhancing the beauty and usability of the landscape.
Effective Use of Colors and Textures
The use of colors and textures plays a vital role in architectural landscape design, adding depth, visual interest, and a sense of harmony to the outdoor space. By skillfully combining colors and textures, designers can create captivating and visually appealing landscapes. Let’s explore how to effectively use colors and textures in landscape design:
- Color Theory: Understanding color theory is essential in creating a harmonious color scheme. Consider the emotions and mood you want to evoke in the outdoor space. Cool colors, such as blues and greens, create a sense of calm and serenity, while warm colors, such as reds and yellows, evoke energy and vibrancy. Use complementary colors (those opposite on the color wheel) to create contrast and visual interest, or analogous colors (those next to each other on the color wheel) for a harmonious and soothing effect.
- Seasonal Interest: Consider the changing seasons and plan for a variety of colors and textures throughout the year. Incorporate plants with foliage that changes color in different seasons, such as deciduous trees or shrubs. Choose perennials that bloom at different times to ensure a continuous display of flowers throughout the year. By planning for seasonal interest, the landscape will have visual appeal no matter the time of year.
- Textures: Incorporating different textures in the landscape design adds depth and visual interest. Combine the textures of various plant foliage, such as smooth leaves, feathery ferns, or coarse grasses. Use materials with varying textures, such as rough stones, smooth pebbles, or weathered wood, for hardscape elements. Balancing contrasting textures can create a visually pleasing and dynamic composition.
- Focal Points: Colors and textures can be used to create focal points that draw attention and add visual interest to the landscape. Use vibrant or contrasting colors in plantings or structures to highlight specific areas. Incorporate plants or structures with unique textures that stand out from the surrounding elements. By creating focal points, you can guide the viewer’s gaze and create a visually captivating design.
- Repetition and Rhythm: Repetition of colors and textures creates a sense of unity and rhythm in the landscape design. Use repetition to create visual harmony by incorporating the same colors or textures in multiple areas throughout the outdoor space. This repetition creates a cohesive and harmonious design that leads the eye and creates a sense of rhythm.
- Contrast: Contrast in color and texture can add visual impact and create focal points within the landscape. Intentionally juxtapose plants or hardscape elements with contrasting colors or textures to create visual interest. For example, pairing dark foliage with bright flowers or smooth stones with textured plants can add drama and create a visually striking composition.
- Consider the Surroundings: When selecting colors and textures, consider the surrounding architecture, landscape features, and the overall character of the area. Choose colors and textures that complement and enhance the existing elements. For example, if the architecture of the surrounding buildings has a warm color palette, consider incorporating plants or hardscape elements with similar warm hues.
- Balance: Achieving balance is crucial in effectively using colors and textures in landscape design. Balance can be achieved by distributing colors and textures evenly throughout the outdoor space, creating a sense of equilibrium. Consider the visual weight of different colors and textures when designing the layout. A well-balanced design ensures that no single element overwhelms the overall composition.
By understanding and employing the effective use of colors and textures, designers can create visually captivating landscapes that evoke emotions, enhance the overall aesthetic, and provide a harmonious connection to nature.
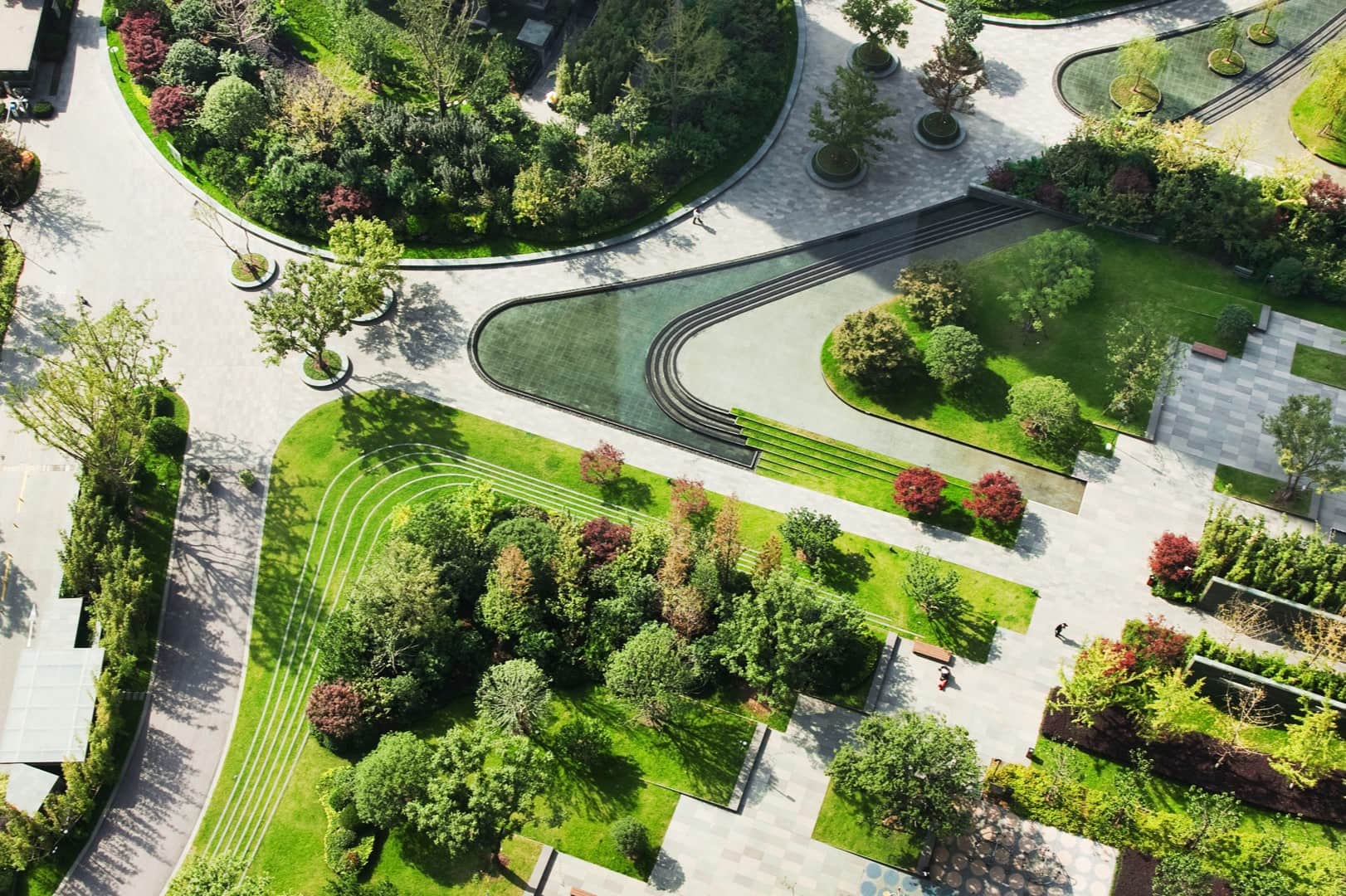
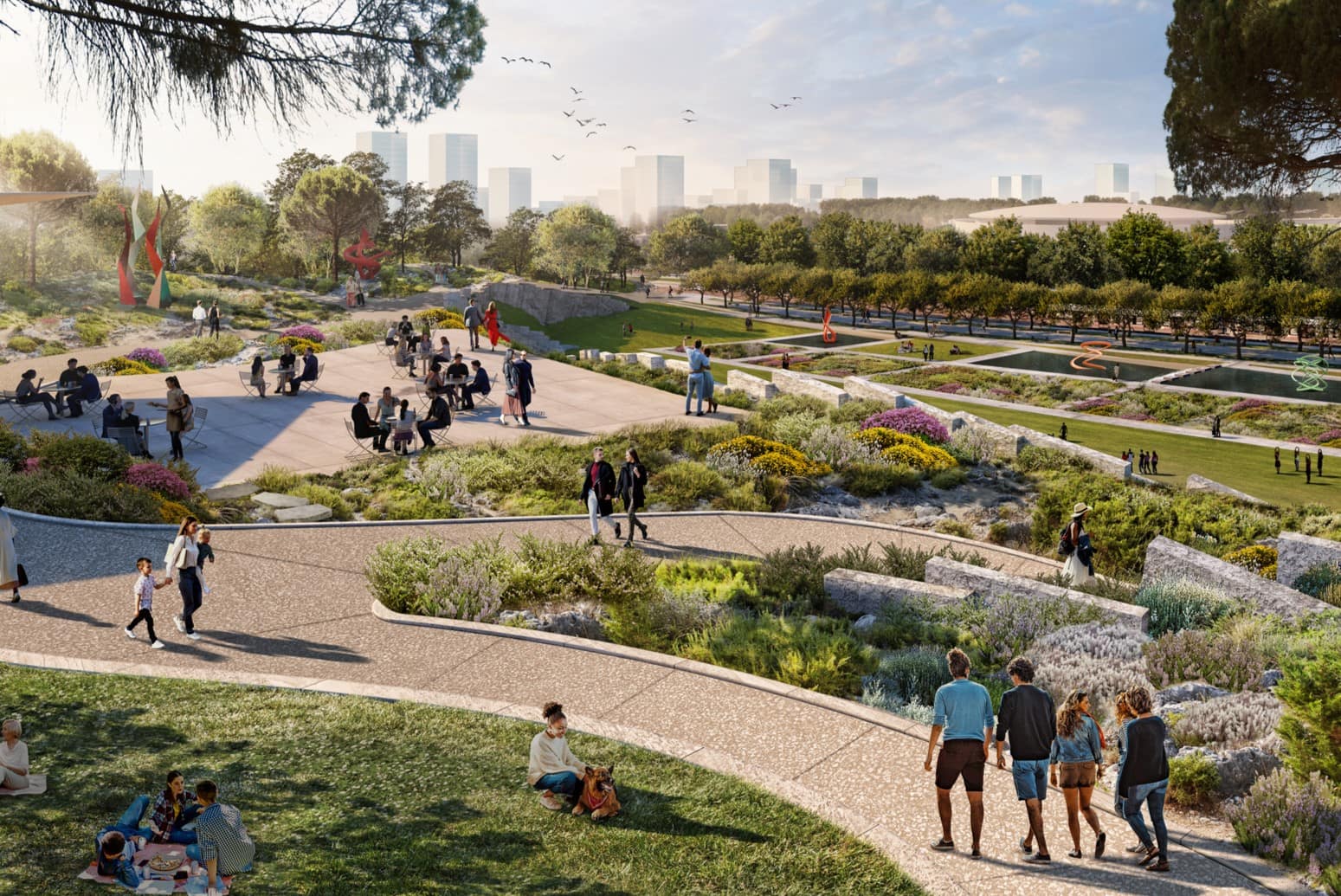
Creating Outdoor Spaces and Zones
In architectural landscape design, creating distinct outdoor spaces and zones allows for functionality, versatility, and a seamless integration of various activities within the landscape. By designing specific areas for relaxation, entertaining, or recreation, designers can enhance the usability and enjoyment of outdoor spaces. Let’s explore how to effectively create outdoor spaces and zones in landscape design:
- Functionality: Determine the primary functions and activities that will take place in the outdoor space. This could include seating and dining areas for socializing, a play area for children, a garden for relaxation, or a cooking area for outdoor cooking and entertaining. Understanding the specific needs and desires of the users will guide the design and layout of each outdoor space.
- Layout and Flow: Create a logical and intuitive layout that allows for easy movement and flow between different outdoor spaces and zones. Consider the arrangement and proximity of each area, ensuring that there is a logical and convenient transition between them. Pathways, walkways, or natural features can serve as connectors to seamlessly link the different spaces.
- Privacy and Enclosure: Incorporate elements that provide privacy and enclosure within each outdoor space. This can include the strategic placement of hedges, fences, or trellises to screen the area from neighboring properties or busy streets. Privacy elements can create a sense of intimacy and seclusion, allowing users to feel more comfortable and relaxed in their outdoor environments.
- Seating and Gathering Areas: Designating comfortable seating and gathering areas is essential for socializing and relaxation. Consider the size and arrangement of seating elements such as benches, chairs, or outdoor sofas. Provide ample space for guests to gather and interact comfortably. Incorporate features like fire pits or outdoor fireplaces to create a cozy and inviting ambiance in seating areas.
- Outdoor Dining: Create a dedicated space for outdoor dining and entertaining. Design an area that can accommodate a dining table and chairs, or incorporate built-in seating with a dining counter. Consider the proximity to the indoor kitchen for convenience and ease of food preparation and serving. Provide shading options, such as pergolas or umbrellas, to shield the dining area from excessive sun exposure.
- Recreational Areas: Incorporate zones for recreational activities such as sports, games, or exercise. This can include a designated area for a playset, a lawn space for games like bocce or croquet, or a yoga or exercise space. Consider the appropriate placement and size of each recreational area to ensure usability and safety.
- Garden Zones: Designate separate areas for different types of gardens, such as flower gardens, vegetable gardens, or herb gardens. Each garden zone can have its unique character and planting scheme. Incorporate walking paths or stepping stones to navigate through the gardens and provide access for maintenance and enjoyment.
- Water Features: Create a focal point and a sense of tranquility by incorporating water features into specific outdoor spaces. This could include a small pond with a fountain, a cascading waterfall, or a reflection pool. Position water features near seating or meditation areas to enhance relaxation and provide a peaceful atmosphere.
- Shade and Shelter: Consider the necessary shade and shelter options within different outdoor spaces. Integrate structures such as pergolas, canopies, or umbrellas to provide shade from the sun during hot summer days. Designate areas with covered structures, such as gazebos or outdoor pavilions, for protection from rain or intense sunlight.
- Lighting: Incorporate outdoor lighting to create ambiance and extend the usability of outdoor spaces into the evening hours. Use a combination of task lighting, accent lighting, and ambient lighting to highlight specific features, ensure safety, and create a warm and inviting atmosphere. Illuminate pathways, seating areas, and focal points to provide functional and aesthetically pleasing lighting design.
By skillfully creating outdoor spaces and zones, designers can optimize functionality, provide versatile usage, and enhance the overall appeal and enjoyment of the landscape. Each space should fulfill a specific purpose while seamlessly integrating with the surrounding elements, providing a harmonious and well-organized outdoor environment.
Read more: How To Learn House Design
Elements of Lighting Design
In architectural landscape design, lighting plays a crucial role in enhancing the aesthetic appeal and functionality of outdoor spaces. Strategic lighting design can create ambiance, highlight key features, improve safety, and extend the usability of the landscape into the evening hours. Let’s explore the essential elements of lighting design in landscape architecture:
- Task Lighting: Task lighting focuses on providing illumination for specific activities or tasks within the outdoor space. This could include lighting for cooking areas, workspaces, or reading areas. Task lighting ensures visibility and functionality in targeted areas, allowing users to perform tasks with ease and precision.
- Accent Lighting: Accent lighting is used to highlight architectural features, focal points, or landscaping elements. By focusing a beam of light on specific areas, accent lighting creates visual interest and draws attention to specific elements. This can include illuminating trees, statuary, water features, or artwork. Accent lighting adds drama and depth to the landscape, creating focal points of interest.
- Ambient Lighting: Ambient lighting provides overall illumination to the outdoor space, creating a comfortable and inviting atmosphere. This can be achieved through the use of diffused lighting, such as lanterns, wall sconces, or overhead fixtures, that cast a soft and even glow. Ambient lighting ensures that the entire space is adequately lit, providing a warm and welcoming ambiance.
- Pathway Lighting: Pathway lighting is crucial for ensuring safety and guiding people through outdoor spaces. This can be accomplished through the use of various lighting fixtures such as bollards, step lights, or solar-powered pathway lights. Pathway lighting should be positioned to provide adequate illumination while maintaining a sense of aesthetics and harmony with the surrounding environment.
- Security Lighting: Security lighting is designed to deter intruders and improve visibility around the property. This includes lighting entrances, driveways, and dark corners or alleyways. Security lighting can be achieved through the use of motion-sensor fixtures or strategically placed floodlights.
- Color Temperature: Color temperature refers to the warmness or coolness of light and is measured in Kelvin (K). Designers can choose between warm white (around 2700K), which creates a cozy and intimate atmosphere, or cool white (around 5000K), which gives a more vibrant and natural appearance. The color temperature should be selected to complement the overall design aesthetic and desired ambiance of the outdoor space.
- Dimming and Controls: Incorporating dimming and controls allows for adjusting the intensity and mood of the lighting as needed. Dimming fixtures provide flexibility to create different lighting scenes and cater to various activities or occasions. Additionally, timers or smart control systems can be implemented to automate the lighting based on specific schedules or to integrate with home automation systems.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient lighting options, such as LED (Light Emitting Diode) fixtures, should be considered for landscape lighting. LEDs consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, resulting in reduced electricity usage and longer lifespan. Additionally, solar-powered fixtures can be utilized to harness renewable energy for outdoor lighting.
- Fixture Style and Placement: The style and placement of lighting fixtures should align with the overall design aesthetic of the landscape. Choose fixtures that complement the architectural style and blend harmoniously with the surrounding elements. Proper placement ensures that the fixtures provide optimal illumination without causing glare or disruption to the visual flow of the space.
- Safety and Compliance: It is essential to follow local safety guidelines and regulations when designing and installing outdoor lighting. Ensure that the fixtures are weather-resistant and suitable for outdoor use. Proper installation techniques, such as burying cables at appropriate depths and using waterproof connectors, should be employed for durability and safety.
By considering these elements of lighting design, landscape architects can create visually stunning, functional, and safe outdoor spaces. Lighting enhances the ambiance, highlights key features, and extends the usability of the landscape, allowing users to enjoy the beauty of their outdoor environment day and night.
Maintenance and Long-Term Care
Maintenance and long-term care are essential aspects of architectural landscape design to ensure that the outdoor space remains healthy, vibrant, and visually appealing over time. Proper maintenance practices help preserve the integrity of plants, structures, and hardscape elements, ensuring their longevity and minimizing the need for extensive renovations or replacements. Let’s explore some key considerations for maintenance and long-term care in landscape design:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the landscape to identify any issues or potential problems. Look for signs of damage, disease, or pest infestation in plants, as well as wear and tear in structures or hardscapes. Promptly address any issues to prevent them from escalating and causing further damage.
- Pruning and Trimming: Regular pruning and trimming of plants promote healthy growth, maintain desired shape and size, and prevent overcrowding. Trim dead or damaged branches, shape shrubs and trees, and remove any overgrown or diseased vegetation. Pruning should be done during the appropriate times of the year and following proper techniques to minimize stress on the plants.
- Watering and Irrigation: Proper watering and irrigation practices are crucial for plant health and survival. Understand the water requirements of different plant species and adjust watering schedules accordingly. Consider implementing efficient irrigation systems such as drip irrigation or smart controllers to optimize water usage and prevent overwatering or underwatering.
- Fertilization and Soil Amendments: Regularly assess the nutrient requirements of plants and amend the soil as needed. Use organic or slow-release fertilizers to provide necessary nutrients for plant growth. Monitor soil pH levels and adjust if necessary to create optimum growing conditions for plants. Be mindful of the potential environmental impact of fertilizers and use them according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- Weed and Pest Control: Implement a proactive approach to weed and pest control to prevent damage to plants and preserve the overall health of the landscape. Regularly remove weeds by pulling them out or using appropriate herbicides. Monitor for pests and employ integrated pest management techniques, such as using beneficial insects or targeted treatments, to control infestations without harming beneficial wildlife or pollinators.
- Mulching: Apply mulch around plants to conserve moisture, suppress weed growth, and regulate soil temperature. Mulch also adds an aesthetically pleasing layer to the landscape. Use organic mulch materials such as wood chips or compost, and replenish mulch as needed to maintain an adequate depth.
- Hardscape Maintenance: Regularly inspect and clean hardscape elements such as pathways, patios, or retaining walls. Remove debris, weeds, and moss that may accumulate in between pavers or cracks. Seal or repair any damaged or worn-out materials to maintain their structural integrity and visual appeal.
- Seasonal Care: Different seasons require specific care and attention in the landscape. Adjust maintenance practices based on seasonal needs, such as winterizing plants and protecting them from frost, preparing irrigation systems for cold weather, or planting seasonal flowers and bulbs. Regularly monitor and adjust maintenance practices to accommodate changes in weather or plant growth patterns throughout the year.
- Professional Guidance: Seeking professional guidance from a knowledgeable landscaper or horticulturist can provide valuable expertise and assistance in maintaining the landscape. They can offer insights on plant care, pruning techniques, pest management, and overall landscape maintenance strategies tailored to your specific needs and conditions.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Keep a record of maintenance activities, including watering schedules, fertilization applications, and any issues or observations throughout the landscape. This documentation helps track the health and progress of plants, identify patterns or recurring problems, and establish a comprehensive history of the landscape for future reference.
Maintenance and long-term care are ongoing commitments that require regular attention and investment of time and resources. By implementing proactive maintenance practices and caring for the landscape with diligence, you can ensure that your outdoor space remains healthy, visually appealing, and enjoyable for years to come.
Conclusion
Architectural landscape design combines creativity, knowledge, and attention to detail to create stunning and functional outdoor spaces. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have explored various aspects of architectural landscape design, from site analysis and understanding environmental factors to choosing plants, integrating structures, and incorporating lighting design. By applying these principles and techniques, you can transform any outdoor space into a captivating and inviting oasis.
The importance of site analysis cannot be underestimated, as it sets the foundation for a successful design. By understanding the site’s natural features, climate, and context, designers can make informed decisions that harmonize with the surroundings and optimize the potential of the space.
The principles of architectural landscape design, such as unity, harmony, balance, and functionality, guide designers in creating visually pleasing and cohesive outdoor environments. By considering the selection of plants and vegetation, taking into account their specific needs and characteristics, you can create diverse and thriving landscapes that change with the seasons.
Environmental factors play a crucial role in sustainable landscape design. Considering elements such as water management, ecological balance, and energy efficiency helps create landscapes that are in harmony with nature and contribute positively to the environment.
The integration of structures and hardscapes adds depth, structure, and functionality to the landscape. By carefully selecting and placing elements such as pathways, patios, water features, and lighting, designers can enhance the overall design and usability of outdoor spaces.
The effective use of colors and textures adds visual interest and creates focal points in the landscape. By understanding color theory, seasonal interest, and the balance between contrasting textures, you can evoke emotions and create a visually captivating design.
Creating outdoor spaces and zones allows for the utilization of different areas for specific purposes such as relaxation, entertainment, and recreation. By carefully designing seating areas, dining spaces, or recreational zones, you can maximize the potential of the outdoor space and tailor it to the needs and preferences of the users.
Lighting design is crucial in enhancing the ambiance, safety, and usability of the outdoor space. By incorporating elements such as task lighting, accent lighting, and pathway lighting, you can create a visually appealing and functional lighting design that extends the enjoyment of the landscape into the evening hours.
Maintenance and long-term care are essential to preserve the integrity and beauty of the landscape. By implementing regular inspections, proper pruning, watering, and fertilization practices, you can ensure that your landscape remains healthy, vibrant, and visually appealing for years to come.
In conclusion, architectural landscape design is an art form that integrates nature, functionality, and aesthetics. By understanding the principles, considering environmental factors, and employing thoughtful design techniques, you can create outdoor spaces that inspire, rejuvenate, and connect us to the beauty of the natural world. So, whether you’re designing a small backyard or a large public park, embrace the possibilities of architectural landscape design and embark on a journey to create captivating outdoor spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions about Learn How To Do Architectural Landscape Design
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “Learn How To Do Architectural Landscape Design”