Home>Gardening & Outdoor>Landscaping Ideas>Why Can’t You Eat Grass


Landscaping Ideas
Why Can’t You Eat Grass
Modified: March 26, 2024
Discover why eating grass is not a good idea and explore landscaping ideas for a healthier outdoor space. Learn about the potential risks and benefits.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
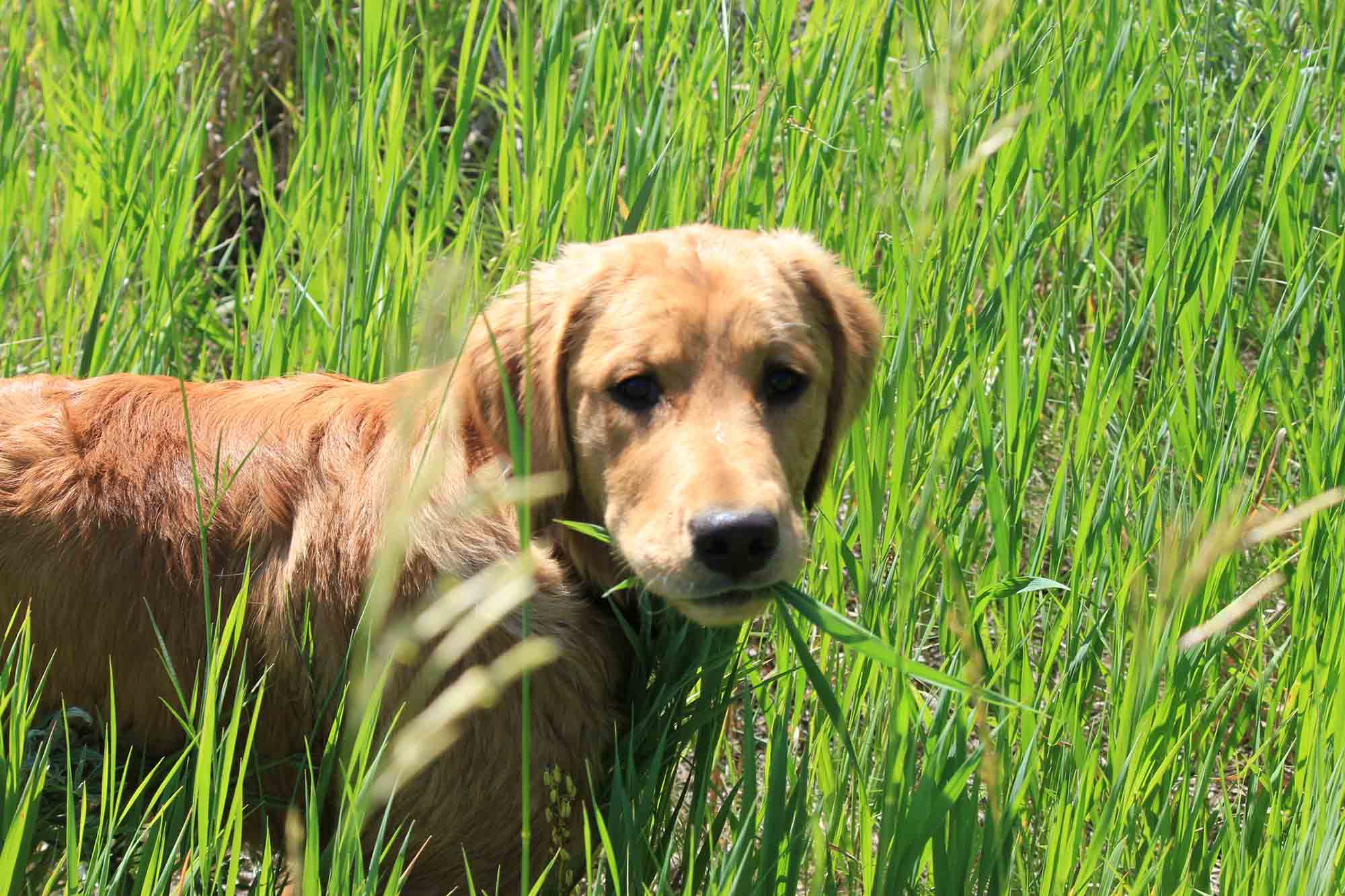
Have you ever wondered why your furry friend, your beloved pet, seems to have an insatiable urge to munch on the lush, green grass in your backyard? It's a common sight for pet owners, but have you ever stopped to ponder the reasons behind this peculiar behavior? In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of why animals, particularly our domesticated companions, are drawn to grass and why it's not a suitable dietary option for them.
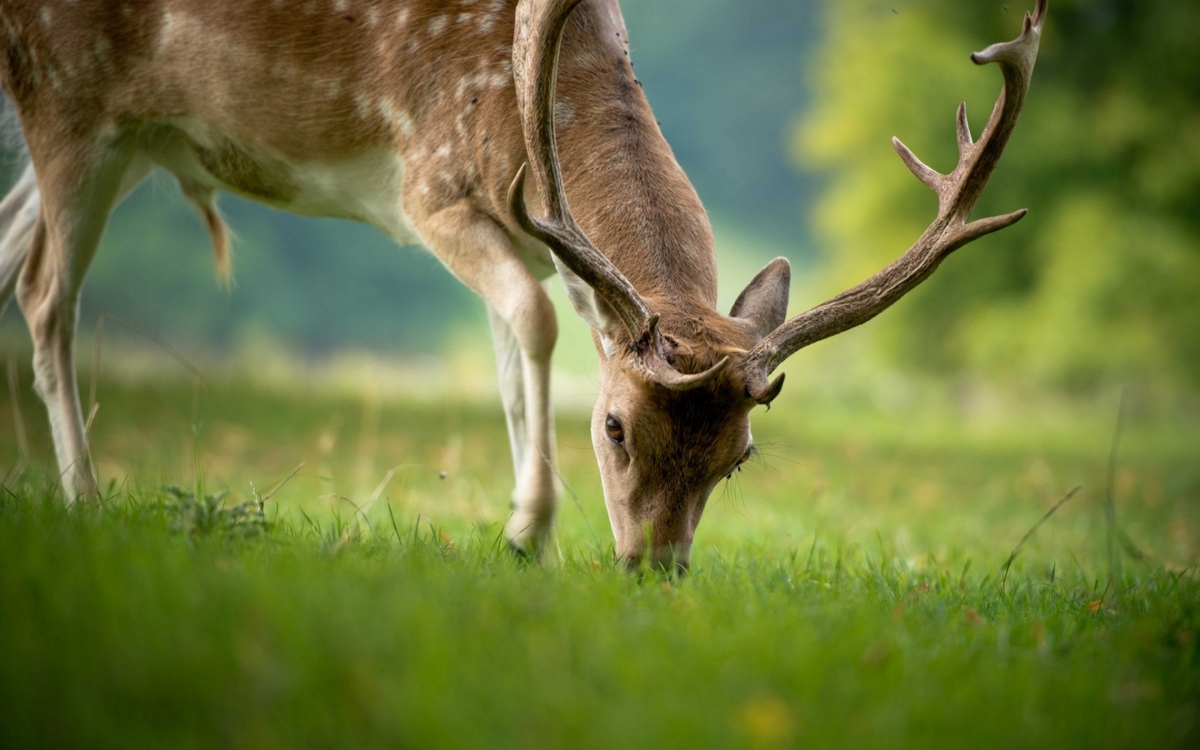
The act of grazing on grass is not limited to domestic pets; wild animals such as deer, rabbits, and elephants also partake in this seemingly odd behavior. While it may appear harmless or even natural, there are important considerations to explore regarding the nutritional content of grass, the differences in digestive systems between animals and humans, the presence of toxic substances in certain grasses, evolutionary adaptations, and ethical concerns related to this behavior.
Join us on this enlightening journey as we uncover the reasons behind this behavior and gain a deeper understanding of why our pets and other animals feel compelled to nibble on the verdant blades beneath their paws.
Key Takeaways:
- Animals eat grass due to evolutionary instincts, but it’s not a suitable diet. Grass lacks essential nutrients and can be toxic, so pet owners should provide balanced, safe diets for their furry friends.
- Grass consumption by animals is a complex behavior influenced by nutrition, digestion, evolution, and ethics. Understanding these factors helps us care for our pets’ well-being and natural instincts responsibly.
Read more: Why Cant You Recycle Pizza Boxes
Nutritional Content of Grass
Grass, the ubiquitous green carpet that covers much of the earth’s surface, is a complex and diverse plant species with a surprising array of nutritional components. While it may seem like a simple and unassuming snack for animals, grass contains a variety of nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients are essential for the growth and sustenance of the plant itself, but the question arises: are they equally beneficial for the animals that consume them?
Carbohydrates are a primary component of grass, providing a source of energy for animals. However, the cellulose content in grass, which is indigestible for many animals, limits the availability of these carbohydrates. Proteins, on the other hand, are crucial for muscle development and overall bodily functions. Grass does contain proteins, but the quality and quantity may not always meet the nutritional needs of animals, especially those that are primarily carnivorous.
Fats, vitamins, and minerals are also present in varying degrees in different types of grass. While these nutrients are essential for overall health, the availability and digestibility of these components can vary widely based on the species of grass and the digestive capabilities of the animal consuming it.
It’s important to note that the nutritional content of grass can fluctuate depending on factors such as soil composition, climate, and the stage of growth. As a result, the suitability of grass as a dietary option for animals is not straightforward and requires a deeper understanding of their specific nutritional requirements.
Digestive System Differences
One of the fundamental reasons why animals, particularly domestic pets, are often drawn to grass is rooted in the differences between their digestive systems and those of herbivorous creatures. Unlike herbivores with specialized digestive systems designed to break down and extract nutrients from plant matter, the digestive systems of carnivorous and omnivorous animals, including cats, dogs, and even humans, are not as well-equipped to derive significant nutritional value from grass.
Herbivores have evolved complex digestive systems that facilitate the breakdown of cellulose, the main structural component of plant cell walls. Ruminants, such as cows and sheep, possess multi-chambered stomachs and a symbiotic relationship with microorganisms that aid in the fermentation and digestion of cellulose. Hindgut fermenters, like horses and rabbits, have an enlarged cecum where microbial fermentation occurs, enabling them to extract nutrients from fibrous plant material.
In contrast, the digestive tracts of carnivores and omnivores are shorter and less efficient at breaking down cellulose. While some plant matter may pass through their digestive systems relatively intact, the nutrients within are not as readily accessible. This fundamental difference in digestive physiology means that the nutritional benefits derived from grass consumption by non-herbivorous animals are limited at best.
Furthermore, the ingestion of grass by non-herbivorous animals can lead to challenges in digestion and potential gastrointestinal issues. The fibrous nature of grass can cause irritation to the digestive tract and may even lead to vomiting, which is a common behavior observed in pets after consuming grass. This further underscores the disparity between the digestive capabilities of herbivores and non-herbivores when it comes to processing plant material.
Understanding these digestive system variances sheds light on why animals are instinctively drawn to grass, yet it also emphasizes the importance of providing them with a diet that aligns with their specific nutritional needs and digestive physiology.
Toxic Substances in Grass
While grass may appear innocuous and wholesome, it’s essential to recognize that not all varieties of grass are benign, especially when it comes to the consumption by animals. Certain grasses contain toxic substances that can pose significant health risks to pets and other animals. Understanding these potential hazards is crucial for pet owners and individuals responsible for the well-being of animals.
One of the most prevalent toxic substances found in grass is mycotoxins, which are produced by fungi that can colonize grass under specific environmental conditions. Mycotoxins can be harmful when ingested by animals, leading to a range of adverse effects, including gastrointestinal distress, liver damage, and neurological symptoms. Additionally, some grasses contain naturally occurring compounds, such as alkaloids and glycosides, which can be toxic to animals when consumed in sufficient quantities.
Another concern is the potential for contamination of grass with pesticides, herbicides, or other chemical agents. Lawns and grassy areas in urban and suburban environments are often treated with various chemicals to control pests and promote growth. When animals graze on these treated surfaces, they may inadvertently ingest these harmful substances, leading to poisoning and detrimental health outcomes.
It’s important for pet owners to be vigilant and mindful of the types of grasses present in their surroundings and to be aware of any potential chemical treatments applied to these areas. This awareness can help prevent accidental exposure to toxic substances and mitigate the associated health risks for their pets.
Furthermore, for individuals responsible for the care of livestock or animals in agricultural settings, knowledge of toxic grasses and proactive pasture management practices are essential for safeguarding the well-being of these animals. This includes identifying and removing toxic grass species from grazing areas and implementing measures to prevent the growth and spread of harmful fungi and weeds.
By recognizing the presence of toxic substances in certain grasses and taking proactive steps to mitigate the associated risks, we can better protect the health and safety of our beloved pets and other animals that may encounter these potentially hazardous plants.
Grass contains cellulose, which is difficult for humans to digest. It can cause stomach discomfort and may not provide the necessary nutrients. Stick to foods that are easier for your body to process.
Evolutionary Adaptations
The innate inclination of animals to consume grass, despite potential digestive challenges and the presence of toxic substances, can be attributed to evolutionary adaptations that have persisted over millennia. Understanding the evolutionary context of this behavior provides valuable insights into the biological and ecological factors that drive animals to engage in grass consumption.
For herbivorous animals, the consumption of grass is a fundamental aspect of their dietary and ecological niche. Over the course of evolution, herbivores have developed specialized anatomical and physiological adaptations that enable them to effectively utilize grass as a primary food source. These adaptations include specialized teeth and jaw structures for grinding and masticating fibrous plant material, as well as complex digestive systems optimized for the breakdown and fermentation of cellulose-rich vegetation.
While non-herbivorous animals may not possess the same degree of specialized adaptations for grass consumption, the instinctual attraction to grass can be traced back to ancestral behaviors and ecological interactions. In the wild, animals may seek out specific types of grasses or plants to supplement their diets with essential nutrients, aid in digestion, or even as a means of self-medication to alleviate certain health issues.
Furthermore, the act of consuming grass can serve as a form of environmental exploration and enrichment for animals. In both domestic and wild settings, animals may graze on grass as a means of engaging with their surroundings, fulfilling behavioral instincts, or addressing sensory and oral stimulation needs. This behavior can be particularly pronounced in domestic pets, as they may exhibit grass consumption as a natural expression of their innate behaviors and instincts.
From an evolutionary perspective, the propensity of animals to consume grass reflects a complex interplay of biological, ecological, and behavioral factors that have been shaped by the dynamics of natural selection and environmental pressures. While this behavior may appear enigmatic or perplexing at times, it is a testament to the intricate web of evolutionary adaptations that underpin the behaviors and dietary preferences of animals across diverse species.
Read more: Why Is Puppy Eating Grass
Ethical Considerations
As we contemplate the phenomenon of animals consuming grass, it is essential to consider the ethical implications and responsibilities associated with the care and well-being of our animal companions. This encompasses a range of considerations, including the provision of a balanced and appropriate diet, the management of environmental exposures, and the promotion of animal welfare in diverse contexts.
One of the primary ethical considerations relates to the nutritional needs of animals and the role of grass in meeting those needs. While the consumption of grass may be a natural behavior for many animals, it is crucial for pet owners and caregivers to ensure that their animals receive a diet that is nutritionally complete and tailored to their specific dietary requirements. This entails providing high-quality commercial pet foods, supplemental nutrients, and appropriate dietary enrichment to support optimal health and well-being.
Furthermore, the ethical dimensions of grass consumption extend to the management of outdoor environments and the prevention of exposure to potential hazards. Pet owners and individuals responsible for animals must exercise diligence in identifying and mitigating the risks associated with toxic grasses, chemical contaminants, and other environmental threats that may compromise the safety and health of animals engaging in grass consumption.
Another ethical consideration pertains to the promotion of natural behaviors and environmental enrichment for animals. While the consumption of grass may present certain challenges and risks, it is important to recognize the value of allowing animals to engage in instinctual behaviors and explore their surroundings in a safe and controlled manner. This may involve creating designated outdoor spaces or providing access to pet-friendly grassy areas where animals can engage in grazing behaviors under supervision.
Moreover, ethical considerations encompass the broader context of animal welfare and the responsible stewardship of animals in various settings, including agricultural, domestic, and wildlife environments. This involves upholding standards of care, promoting humane treatment, and fostering a deep sense of empathy and respect for the well-being of animals, including their dietary preferences and natural behaviors.
By embracing these ethical considerations and integrating them into our practices and attitudes towards animal care, we can cultivate environments that prioritize the health, safety, and natural inclinations of our beloved animal companions, while upholding the principles of ethical and compassionate stewardship.
Conclusion
The enigmatic allure of grass consumption by animals encompasses a rich tapestry of biological, ecological, and ethical considerations that invite us to explore the complex interplay between dietary behaviors and the well-being of our animal companions. As we unravel the intricacies of this behavior, we gain a deeper appreciation for the innate instincts, evolutionary adaptations, and ethical responsibilities that shape our interactions with animals in diverse contexts.
From the nutritional content of grass to the digestive system differences between herbivorous and non-herbivorous animals, we are confronted with the fundamental physiological factors that influence the suitability of grass as a dietary option. The presence of toxic substances in certain grasses underscores the need for vigilance and proactive measures to safeguard the health of animals that may encounter these potential hazards in their environments.
Delving into the evolutionary adaptations that underpin the consumption of grass by animals unveils a compelling narrative of ecological interactions, ancestral behaviors, and the intricate web of biological imperatives that have shaped this behavior over time. This evolutionary perspective offers valuable insights into the innate inclinations and ecological roles of animals as they engage with their environments and dietary preferences.
Amidst these considerations, ethical responsibilities emerge as a guiding compass for promoting the holistic well-being and welfare of animals. From ensuring nutritionally complete diets to managing environmental exposures and fostering natural behaviors, ethical considerations underscore the imperative of conscientious care and stewardship in our interactions with animals.
As we navigate the complexities of grass consumption by animals, we are reminded of the profound connections that bind us to our animal companions and the imperative of embracing a compassionate and informed approach to their care. By honoring the multifaceted dimensions of this behavior and integrating them into our practices, we cultivate environments that prioritize the health, safety, and natural inclinations of animals, fostering a harmonious coexistence that celebrates the richness of the animal kingdom.
Ultimately, the enigma of grass consumption by animals invites us to embark on a journey of understanding, empathy, and responsible stewardship, as we seek to nurture the well-being and innate instincts of our cherished animal companions in a world where the verdant blades of grass hold both allure and complexity.
Frequently Asked Questions about Why Can't You Eat Grass
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Why Can’t You Eat Grass”