Home>Technology>Home Entertainment Systems>How Do Television Networks Use Communication Satellites


Home Entertainment Systems
How Do Television Networks Use Communication Satellites
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover how television networks utilize communication satellites to enhance their home entertainment systems and provide a seamless viewing experience. Explore the benefits and advancements in this intriguing field.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Television networks have revolutionized the way we consume entertainment, bringing the world of movies, shows, and sports directly into our living rooms. Behind the scenes, these networks rely on advanced technology to ensure seamless transmission of content to viewers across the globe. Communication satellites play a vital role in this process, enabling television networks to reach a wide audience efficiently and reliably.
In this article, we will explore the importance of communication satellites in television networks and how they are used to deliver high-quality programming to viewers worldwide. We will delve into the broadcasting of television signals, satellite television distribution networks, direct-to-home (DTH) satellite services, and the integration of satellites with cable television. Additionally, we will discuss the challenges faced by satellite communication in television networks and offer a glimpse into the future of this industry.
So, let’s embark on a journey through the fascinating world of television networks and communication satellites, and discover the intricate mechanisms that bring entertainment to our screens.
Key Takeaways:
- Communication satellites are vital for global TV coverage, ensuring high-quality, reliable signals, and flexibility for networks to adapt to changing demands and provide backup during critical broadcasts or emergencies.
- Despite challenges, the future of TV networks and satellites looks promising, with advancements in technology enabling high-definition content, interactive viewing experiences, integration with the internet, and potential live event coverage from space.
Read more: How To Start A Television Network
Importance of Communication Satellites in Television Networks
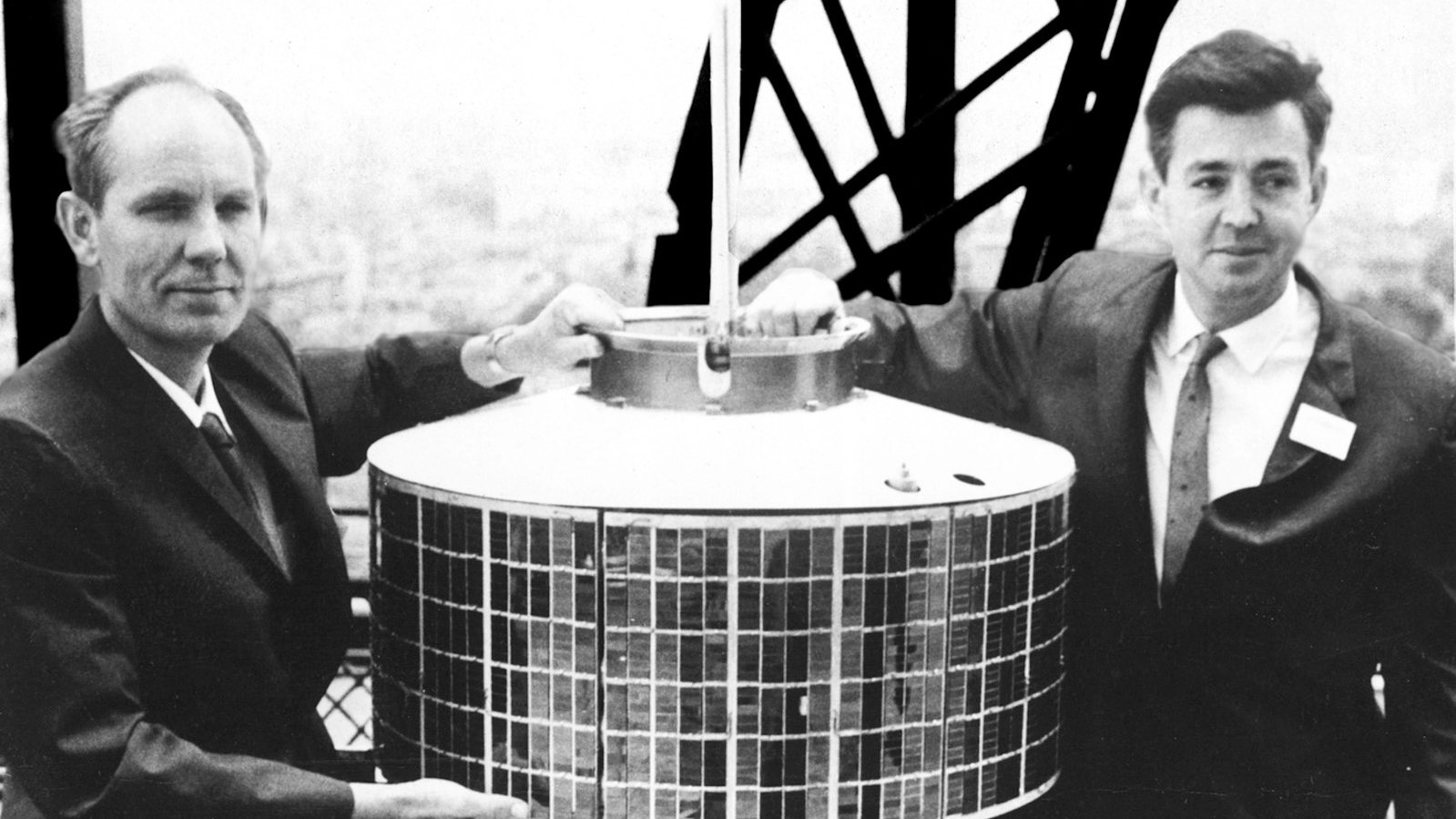
Communication satellites play a crucial role in television networks, facilitating the distribution of television signals worldwide. These satellites act as relay stations in space, receiving signals from the broadcasting stations on the ground and transmitting them to receivers in homes or cable headends. Here are some key reasons why communication satellites are essential in the television industry:
Global Coverage: One of the main advantages of communication satellites is their ability to provide global coverage. Unlike terrestrial-based transmission systems that have limited reach, satellites can broadcast signals to remote and inaccessible areas, reaching viewers in rural communities, ships, and airplanes. This makes television accessible to a vast and diverse audience across the globe.
Signal Quality and Reliability: Communication satellites ensure high-quality and reliable transmission of television signals. Since satellite signals travel through space, they are not as susceptible to interference from obstacles like tall buildings or geographical barriers. This results in a more stable signal, delivering clear and uninterrupted content to viewers.
Bandwidth Efficiency: Television networks transmit vast amounts of data, including high-definition video, audio, and interactive services. Communication satellites offer significant bandwidth efficiency, allowing networks to deliver a wide range of channels and content simultaneously. This efficient use of bandwidth enables broadcasters to cater to diverse viewer preferences and offer a more engaging television experience.
Flexibility and Scalability: With communication satellites, television networks have the flexibility to adapt to changing demands and rapidly expand their reach. Satellites provide scalability, enabling broadcasters to add or remove channels, increase or decrease coverage areas, and even introduce new services without major infrastructure upgrades. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in the dynamic and competitive television industry.
Global Event Coverage: Communication satellites play a critical role in live event coverage, such as major sports tournaments, award shows, or breaking news. Satellites allow networks to broadcast these events in real-time to millions of viewers worldwide, ensuring that everyone can experience the excitement and thrill of the moment simultaneously.
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Communication satellites offer a reliable backup and disaster recovery solution for television networks. In the event of a terrestrial transmission failure or natural disaster, broadcasters can quickly switch to satellite transmission, ensuring uninterrupted service to viewers. This redundancy is crucial, especially during critical broadcasts or emergency situations.
In summary, communication satellites are integral to the functioning of television networks, providing global coverage, ensuring signal quality and reliability, offering bandwidth efficiency, enabling flexibility and scalability, facilitating global event coverage, and serving as a backup and disaster recovery solution.
Broadcasting of Television Signals via Communication Satellites
The broadcasting of television signals via communication satellites is a complex process that involves the transmission of video, audio, and data from the source to the end viewer. Let’s explore the steps involved in this fascinating journey:
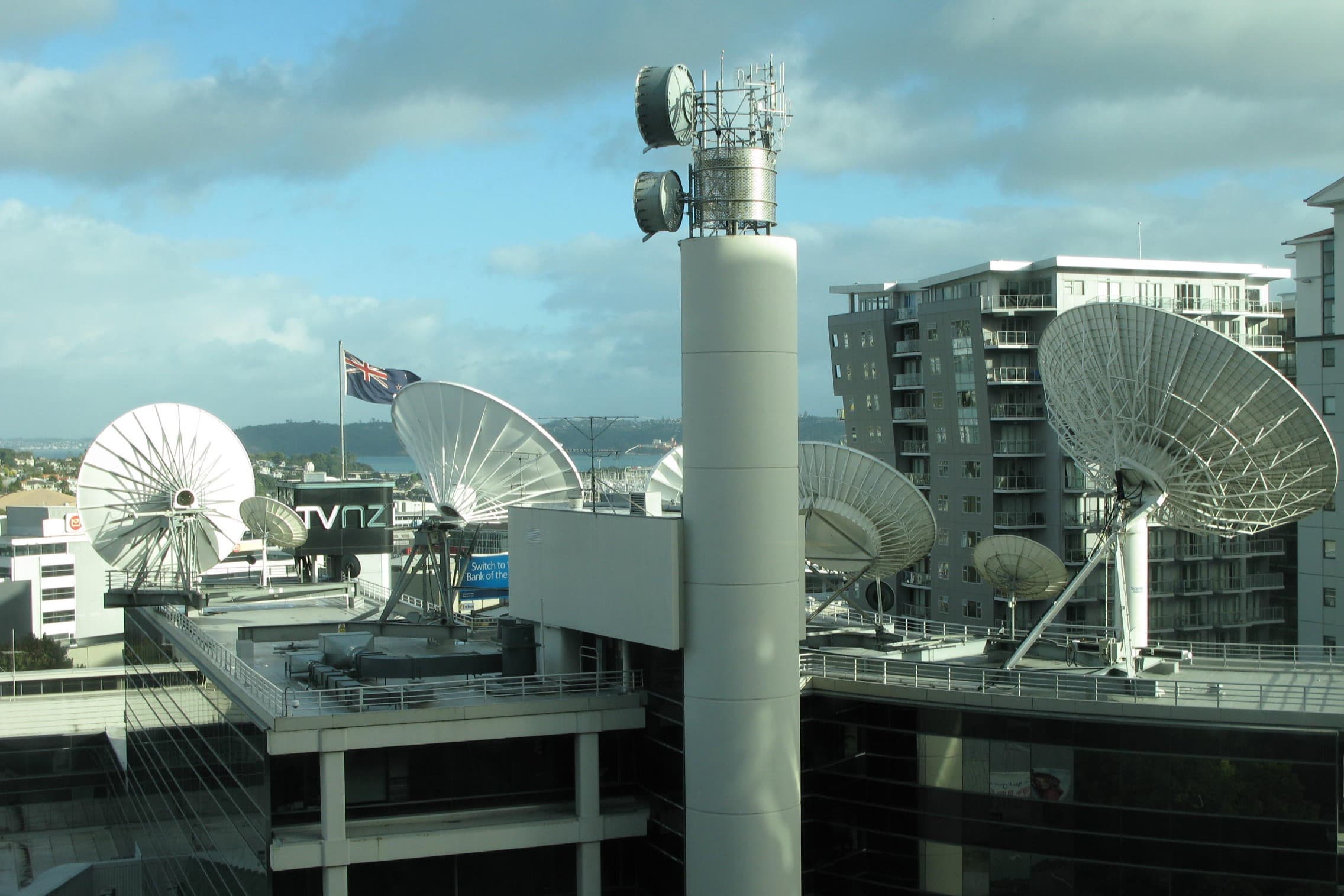
Up-linking: The first stage in broadcasting television signals via communication satellites is up-linking. This involves sending the television signals from the broadcasting station to the communication satellite. Specialized equipment, known as an Earth station or teleport, is used to transmit the signals to the satellite. The signals are then received by the satellite’s transponders, which convert and amplify them for transmission back to Earth.
Transmission: Once the television signals have been up-linked to the satellite, they are transmitted through space to the coverage area. Communication satellites orbit the Earth in geostationary or medium-Earth orbits, ensuring a consistent position relative to the Earth’s surface. This allows for continuous coverage of a specific region or multiple regions, depending on the satellite’s capabilities.
Down-linking: The down-linking process involves receiving the transmitted signals from the satellite back on Earth. Satellite dishes, commonly known as receiving antennas, are used to capture the signals and send them to the receiving station. These antennas are designed to pick up the satellite’s specific frequency and polarization, ensuring accurate reception.
Decoding and Distribution: Once the television signals have been down-linked, they need to be decoded and distributed to viewers. At the receiving station, the signals are sent through a process called demodulation, which converts them back into a format compatible with television sets or other receiving devices. The decoded signals are then distributed through various means, such as cable networks, direct-to-home (DTH) satellite services, or internet-based streaming platforms.
Viewer Reception: At the viewer’s end, the decoded television signals are received and displayed on their television sets or devices. This is done through a receiver, commonly known as a set-top box, that connects to the television and allows viewers to access and tune in to the desired channels. The set-top box decodes the signals and passes them on to the television for display.
The broadcasting of television signals via communication satellites offers numerous advantages. It allows for the simultaneous transmission of multiple channels, provides global coverage, overcomes geographical limitations, and ensures the delivery of high-quality and reliable content to viewers around the world.
Overall, the broadcasting of television signals via communication satellites involves a series of interconnected processes, from up-linking and transmission to down-linking, decoding, and viewer reception. This seamless integration of technology enables television networks to reach a wide audience and deliver an immersive viewing experience.
Satellite Television Distribution Networks
Satellite television distribution networks are integral to the functioning of television networks, enabling the efficient delivery of content to viewers around the world. These networks consist of a complex system of communication satellites, up-link and down-link stations, and distribution platforms. Let’s take a closer look at how satellite television distribution networks operate:
Satellites: Communication satellites are at the core of satellite television distribution networks. These satellites are strategically positioned in space to cover specific regions or multiple regions, depending on their orbital characteristics. They receive up-linked television signals from broadcasting stations on Earth and retransmit them back to Earth, allowing for wide-scale distribution of content.
Up-link Stations: Up-link stations, also known as Earth stations or teleports, are responsible for transmitting television signals from the broadcasting stations to the communication satellites. These stations are equipped with specialized equipment, such as high-power transmitters, antennas, and modulators, to ensure the efficient transfer of signals to the satellites. Up-link stations are typically located in geographically advantageous positions to maximize signal coverage.
Down-link Stations: Down-link stations, also known as receiving stations, capture the transmitted signals from the satellites and bring them back to Earth. These stations are equipped with large satellite dishes, or receiving antennas, that are designed to pick up the specific frequency and polarization of the satellite signals. The down-link stations play a crucial role in ensuring the accurate reception of television signals for further processing and distribution.
Distribution Platforms: Once the television signals have been down-linked, they are sent to distribution platforms for further processing and delivery to viewers. These distribution platforms can include cable television networks, direct-to-home (DTH) satellite services, or internet-based streaming platforms. Each platform has its own infrastructure and technology to ensure efficient distribution of content to end users.
Cable Television Networks: Cable television networks receive the down-linked signals from the satellite distribution network and distribute them to subscribers through cable wires. Cable companies provide a wide range of channels and package options, offering viewers a vast selection of content. Cable television networks offer the advantage of providing local programming and offering additional services such as internet and telephone bundles.
Direct-to-Home (DTH) Satellite Services: DTH satellite services deliver television signals directly to the viewer’s home via a small satellite dish and set-top box. These services eliminate the need for a cable connection, making them suitable for areas where cable infrastructure is limited or unavailable. DTH services offer a wide selection of channels and often provide high-definition (HD) and even Ultra HD (4K) content.
Internet-based Streaming Platforms: With the rise of internet connectivity, streaming platforms have become increasingly popular for distributing television content. These platforms utilize the internet to deliver on-demand streaming of television shows, movies, and other forms of entertainment. They often require a subscription and can be accessed through various devices such as smartphones, smart TVs, and streaming media players.
Satellite television distribution networks have revolutionized the way television content is delivered to viewers. With their wide coverage, signal reliability, and flexibility, these networks have allowed television networks to reach global audiences and provide a diverse range of programming choices. Whether through cable networks, DTH services, or streaming platforms, satellite television distribution networks continue to shape the future of television distribution.
Direct-to-Home (DTH) Satellite Services
Direct-to-Home (DTH) satellite services have revolutionized the way viewers access television content, offering a convenient and versatile alternative to traditional cable television. DTH satellite services deliver television signals directly to the viewer’s home via a small satellite dish and a set-top box. Let’s explore the features and advantages of DTH satellite services:
Equipment: To access DTH satellite services, viewers need a satellite dish and a set-top box. The satellite dish is installed outdoors to capture the satellite signals, while the set-top box is connected to the television to decode and display the received signals. The set-top box often comes with advanced features like electronic program guides, interactive services, and high-definition (HD) or even Ultra HD (4K) video capabilities.
Wide Range of Channels: DTH satellite services offer a vast selection of channels, catering to a diverse range of viewer preferences. From local and regional channels to international networks, DTH services provide access to an extensive lineup of TV shows, movies, sports, news, and more. Viewers have the freedom to choose from various channel packages and customize their subscription to suit their interests.
High-Quality and Digital Broadcasting: DTH satellite services provide high-quality, digital broadcasting to viewers. By directly receiving signals from satellites, DTH services bypass terrestrial infrastructure limitations and potential signal degradation. This results in a clear and crisp picture quality, enhanced audio, and an immersive viewing experience.
Interactive and Value-Added Services: DTH satellite services often offer a range of interactive features and value-added services. These can include electronic program guides that provide detailed program information and allow viewers to schedule recordings or set reminders. Some DTH services also offer video-on-demand (VOD) options, allowing viewers to access movies and TV shows at their convenience. Interactive services like games, sports betting, and shopping are also commonly available.
Flexibility and Customization: DTH satellite services provide viewers with flexibility and customization options. Subscribers can choose from different channel packages based on their preferences and budget. They can also add premium channels or pay-per-view events for specific content, further tailoring their viewing experience. DTH services enable viewers to have control over the channels they want to watch without being tied to fixed cable bundles.
Rural and Remote Access: DTH satellite services offer a practical solution for viewers in rural and remote areas where cable infrastructure may be limited or unavailable. By utilizing satellites, DTH services can reach these areas efficiently, providing television access to communities that might otherwise struggle to receive traditional cable services. This helps bridge the digital divide and ensure equal access to entertainment and information.
DTH satellite services have transformed the television landscape, offering viewers a convenient and customizable way to access their favorite content. With high-quality broadcasting, a wide range of channels, interactive features, and flexible subscription options, DTH services continue to gain popularity among viewers worldwide.
Television networks use communication satellites to transmit their programming to a wide audience. This allows for global coverage and reach, making it an essential tool for broadcasting companies.
Read more: What Is The CW Television Network?
Cable Television and Satellites
Cable television and satellites have become closely intertwined, working together to provide viewers with a vast array of programming options and improved access to television content. Let’s delve into the relationship between cable television and satellites:
Signal Distribution: Cable television relies on a network of cables to transmit television signals from the cable operator’s headend to subscribers’ homes. In the traditional cable setup, the broadcast signals are received by the cable operator, who then distributes the signals via coaxial or fiber optic cables to different neighborhoods and households. However, satellites play a significant role in this process by facilitating the distribution of television signals to cable operators.
Satellite Feeds for Cable Operators: To provide a wide range of channels to subscribers, cable operators often rely on satellite feeds. These satellite feeds deliver a large number of channels to the cable operator’s headend, which is then distributed through the cable network to subscribers. Satellite feeds allow cable operators to expand their channel offerings beyond what is available through terrestrial broadcasts, ensuring a more diverse and comprehensive content lineup.
Remote Content Delivery: Satellites are particularly useful for cable operators serving remote or geographically challenging areas, where installing and maintaining a robust cable infrastructure can be impractical or cost-prohibitive. In such cases, cable operators can utilize satellite signals to receive and distribute television content to subscribers in these remote regions, bridging the gap and extending cable services to areas where it would otherwise be difficult to deploy.
Premium and Pay-Per-View Content: Satellites also play a role in delivering premium and pay-per-view content to cable television subscribers. Cable operators can receive premium channels, such as HBO or Showtime, via satellite feeds, allowing them to offer these channels as part of their service packages. Satellites enable cable operators to securely receive and distribute encrypted content, ensuring that subscribers have access to exclusive programming and events.
Backup and Redundancy: Satellites serve as a backup and redundancy solution for cable television operators. In case of terrestrial transmission issues or outages due to natural disasters or technical glitches, cable operators can switch to satellite feeds as a temporary solution, ensuring uninterrupted service to subscribers. The backup capability provided by satellites helps maintain service reliability and ensures that viewers can continue enjoying their favorite shows even during challenging situations.
Technology Integration: Technological advancements have allowed for seamless integration between cable television networks and satellites. Cable headends can receive, process, and distribute satellite feeds alongside terrestrial broadcasts, offering a wide variety of channels to subscribers. Viewers can easily access satellite-delivered content through their cable connection, enjoying the benefits of both cable television infrastructure and satellite distribution.
Overall, the intersection between cable television and satellites has enhanced the reach, versatility, and content availability in the television industry. By leveraging satellites for signal distribution, cable operators are able to offer a wider selection of channels, deliver premium content, ensure remote access, provide backup solutions, and integrate seamlessly with evolving technologies.
Satellite Communication Challenges in Television Networks
While satellite communication plays a vital role in television networks, there are several challenges that broadcasters and operators face when utilizing satellite technology. These challenges can impact signal quality, cost, and overall performance. Let’s explore some of the key challenges in satellite communication for television networks:
Signal Latency: One of the primary challenges in satellite communication is signal latency, or the delay in signal transmission due to the long-distance traveled by the signals between the Earth and the satellite. This latency can result in a noticeable delay between the broadcast and its reception by viewers. While advancements have reduced latency, it still remains a challenge, especially in live broadcasts and interactive services where real-time communication is critical.
Weather Interference: Satellite signals are susceptible to interference from adverse weather conditions such as rain, snow, or atmospheric disturbances. Heavy rain or storms can cause attenuation or signal degradation, affecting signal quality and potentially leading to service interruptions. Broadcasters have to carefully consider the satellite’s coverage and the weather conditions in their target regions to mitigate the impact of weather interference.
Bandwidth Limitations: Television networks require significant bandwidth to transmit multiple channels, high-definition content, and other data-intensive services. However, satellites have limited bandwidth capacity, and allocating sufficient bandwidth for television broadcasts can be a challenge. As the demand for higher-quality content and interactive services increases, broadcasters must carefully manage their bandwidth usage and explore compression and encoding technologies to optimize the available capacity.
Cost and Infrastructure: Satellite communication involves considerable costs, including the launch and maintenance of satellites, ground station equipment, and transmission fees. Building and operating a satellite network requires significant investment, making it a barrier for small broadcasters or those with limited resources. Additionally, establishing ground stations and maintaining them can be challenging, particularly in remote or underdeveloped regions where infrastructure is limited.
Orbital Congestion: The number of active satellites in space has been steadily increasing, leading to orbital congestion. This congestion poses challenges for satellite communication as it can result in signal interference or the need for satellite operators to carefully manage their satellite positions to avoid collisions. The increasing number of satellites also raises concerns regarding spectrum allocation and coordination to prevent signal overlap or interference.
Regulatory and Licensing Requirements: Broadcasting via satellites requires adherence to regulatory and licensing requirements set by national and international authorities. Obtaining the necessary licenses and permissions can be a complex process, involving compliance with various regulations and standards. Navigating these bureaucratic processes can be time-consuming and costly for broadcasters, particularly when operating in multiple countries with different regulatory frameworks.
Security and Piracy: Satellite communication systems face security threats such as signal piracy and unauthorized access to content. Encryption techniques and digital rights management systems are used to protect satellite signals, but sophisticated piracy methods still pose challenges. Ensuring secure transmission and preventing unauthorized distribution of content are ongoing challenges that television networks must address.
Despite these challenges, satellite communication continues to play a crucial role in television networks, enabling global coverage and wide content distribution. Broadcasters and operators are constantly innovating and working towards overcoming these hurdles to ensure reliable and high-quality satellite communication in the television industry.
Future of Television Networks and Communication Satellites
The future of television networks and communication satellites is set to be dynamic and transformative as advancements in technology continue to shape the industry. Let’s explore some exciting developments and trends that will impact the future of television networks and satellite communication:
High-definition and Ultra HD Content: As consumer demand for higher visual quality increases, television networks will continue to focus on delivering high-definition (HD) and Ultra HD (4K and 8K) content. Communication satellites will play a crucial role in transmitting the large data requirements of these formats, ensuring viewers can enjoy immersive and visually stunning experiences in the comfort of their homes.
Interactive and Personalized Viewing: Television networks are embracing interactive and personalized viewing experiences to cater to individual viewer preferences. With advancements in satellite technology, broadcasters can offer interactive features, such as personalized recommendations, interactive advertising, and real-time interactive shows. Communication satellites will enable seamless two-way communication between broadcasters and viewers, enhancing engagement and customization.
Internet Integration: The integration of television networks with the internet will continue to shape the future of the industry. Hybrid models that combine traditional broadcasting with internet-based streaming are becoming increasingly popular. Communication satellites will facilitate the delivery of internet-based streaming services, allowing viewers to access on-demand content and live broadcasts seamlessly, regardless of their geographic location.
5G and Next-Generation Networks: The advent of 5G technology brings new possibilities for television networks and communication satellites. 5G networks promise faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity, enabling broadcasters to deliver content efficiently and at higher quality. Communication satellites will complement 5G networks by extending coverage to remote and underserved areas, ensuring universal access to television content.
Advancements in Compression Technologies: Compression technologies like High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) and its successor, Versatile Video Coding (VVC), will enable more efficient use of bandwidth and facilitate the transmission of higher quality content over communication satellites. These advancements will allow broadcasters to deliver immersive content while optimizing satellite capacity, ultimately enhancing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of television distribution.
Emergence of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites: The emergence of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations, such as SpaceX’s Starlink, brings new opportunities for television networks. LEO satellites operate closer to the Earth, resulting in lower latency and higher data rates. This technology could potentially provide enhanced satellite internet services to support streaming platforms and could present new distribution options for television networks when integrated with ground-based infrastructure.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics: The integration of AI and data analytics into television networks will revolutionize content recommendations, targeted advertising, and audience analytics. By leveraging communication satellite data, broadcasters can gather valuable insights about viewer preferences and behavior, enabling them to deliver personalized content and enhance the viewer experience.
Space Tourism and Live Event Coverage: The rise of space tourism and private space exploration could open up opportunities for live event coverage from space. With the capability to transmit signals from spacecraft, communication satellites could play a role in bringing viewers breathtaking experiences, such as live broadcasts from space missions or space tourism ventures.
Overall, the future of television networks and communication satellites holds immense potential for innovation and growth. Advancements in technology, integration with the internet, the emergence of new satellite constellations, and the adoption of AI and data analytics will shape the way content is delivered and experienced. As the industry continues to evolve, television networks and communication satellites will work hand in hand to provide viewers with engaging, personalized, and high-quality content, transcending boundaries and revolutionizing the way we consume entertainment.
Conclusion
The integration of communication satellites into television networks has transformed the way we consume entertainment, providing global coverage, high-quality content, and a diverse range of programming options. Communication satellites play a critical role in broadcasting television signals, facilitating the distribution of content to viewers worldwide.
We have explored the importance of communication satellites in television networks, highlighting their global coverage capabilities, signal quality and reliability, bandwidth efficiency, flexibility, and scalability. Communication satellites have enabled television networks to reach a wide and diverse audience, overcoming geographical limitations and offering a seamless viewing experience.
We have also examined satellite television distribution networks, which rely on communication satellites, up-link and down-link stations, and various distribution platforms. Cable television and direct-to-home (DTH) satellite services have revolutionized the way viewers access television content, offering a wide range of channels, high-quality broadcasting, interactive features, and customization options.
While there are challenges in satellite communication, including signal latency, weather interference, bandwidth limitations, infrastructure costs, and regulatory requirements, advances in technology continue to address these issues. The future of television networks and communication satellites promises even more exciting developments, including high-definition and Ultra HD content, interactive and personalized viewing experiences, integration with the internet, advancements in compression technologies, the emergence of low Earth orbit satellites, AI and data analytics, and potential live event coverage from space.
In conclusion, communication satellites are an indispensable component of the television industry, bridging distances and connecting viewers to a wide world of entertainment. As technology continues to evolve, satellite communication will play a pivotal role in delivering high-quality content, enhancing viewer engagement, and shaping the future of television networks. With ongoing advancements, we can expect television networks and communication satellites to provide an even more immersive, personalized, and accessible television experience for audiences around the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Do Television Networks Use Communication Satellites
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Do Television Networks Use Communication Satellites”