Home>Articles>How To Prevent Your Motor Housing From Becoming Energized

Articles
How To Prevent Your Motor Housing From Becoming Energized
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn about common electric motor problems that can cause the motor housing to become energized. Read articles on how to troubleshoot and fix these issues.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Electric motors are an essential component in various industries and applications. They play a crucial role in powering machinery and equipment, making them vital for smooth operations. However, like any complex mechanical system, electric motors can experience problems that need to be addressed promptly to ensure optimal performance and safety.
One significant issue that can arise with electric motors is the energization of the motor housing. When this occurs, the motor housing becomes electrically charged, posing significant risks to personnel, equipment, and the overall operation of the facility.
Key Takeaways:
- Regular maintenance and inspection of electric motors are crucial for optimal performance, safety, and longevity. Proactive maintenance helps identify and resolve potential issues early, minimizing downtime and ensuring reliability.
- Proper grounding systems and effective electrical insulation are essential for preventing motor housing energization and minimizing electrical hazards. Regular inspections and adherence to safety standards are key to maintaining a safe working environment.
Read more: How To Slope Drainage From Your House
Understanding Electric Motor Problems
Before we delve into the reasons that can cause the motor housing to become energized, let’s explore some common electric motor problems that can lead to this issue.
1. Faulty Insulation: Electrical insulation is critical for preventing the flow of current through unintended parts of the motor. If the insulation deteriorates due to age, overheating, or mechanical stress, it can result in stray current reaching the motor housing.
2. Grounding Issues: A lack of proper grounding or a faulty grounding system can contribute to the motor housing becoming energized. The purpose of grounding is to provide a safe path for electrical faults to be redirected away from the motor and into the ground, preventing energization of the housing.
3. Improper Installation: Incorrect installation of the motor or improper wiring can lead to electrical imbalances, resulting in the housing becoming energized. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and consult qualified electricians during the installation process.
4. Damaged Components: Any damage to the motor’s internal components, such as wiring, terminals, or connectors, can compromise the integrity of the electrical system and increase the risk of the motor housing becoming energized.
Addressing electric motor problems promptly is of utmost importance. Failure to do so can lead to severe consequences, including safety hazards, equipment damage, and legal and compliance issues. In the next section, we will look at the risks and dangers associated with an energized motor housing.
What Causes the Motor Housing to Become Energized?
There are several factors that can cause the motor housing to become energized. Let’s take a closer look at each of these causes:
- Electrical Faults: Electrical faults such as short circuits, ground faults, or phase imbalances can cause an abnormal flow of current within the motor. This can result in the energization of the motor housing, exposing anyone who comes into contact with it to the risk of electric shock.
- Faulty Wiring or Connections: Poorly insulated or damaged wiring, loose connections, or improper grounding can contribute to an energized motor housing. These issues can create unintended electrical paths, allowing current to flow where it shouldn’t and increase the chances of the motor housing becoming energized.
- Malfunctioning Components: Defective components within the motor, such as capacitors, switches, or contactors, can cause the motor housing to become energized. A malfunctioning component can disrupt the proper flow and distribution of electrical current, leading to unsafe conditions.
- Lack of Maintenance: Neglecting regular maintenance can result in deteriorating insulation, loose connections, and other electrical issues that increase the likelihood of an energized motor housing. It is crucial to implement scheduled maintenance routines to identify and address potential problems before they escalate.
It is important to note that an energized motor housing poses significant risks and dangers that need to be addressed immediately. Ignoring or underestimating these risks can have severe consequences, as we will explore in the next section.
Common Electric Motor Problems
Electric motors are susceptible to a range of issues that can affect their performance and functionality. By understanding these common problems, you can be better prepared to identify and address them before they escalate. Here are some of the most prevalent electric motor problems:
- Overheating: Overheating is a common issue in electric motors and can be caused by various factors such as excessive load, inadequate cooling, or insulation failure. Excessive heat can lead to decreased motor efficiency, insulation breakdown, and premature motor failure.
- Electrical Overload: Electrical overload occurs when the motor is driven beyond its specified capacity. This can happen due to excessive load, voltage surges, or inadequate wiring. Electrical overload can cause overheating, insulation damage, and motor failure.
- Bearing Failure: Bearings are vital components that support the rotor and shaft of the motor. Over time, bearing wear and tear can occur, leading to increased friction, noise, and motor vibration. If not addressed promptly, bearing failure can cause the motor to seize or suffer significant damage.
- Excessive Vibration: Excessive vibration can be caused by various factors such as misalignment, unbalanced rotor, or worn-out bearings. Vibrations can result in increased noise, reduced performance, and potential motor damage if left unattended.
- Electrical Noise: Electrical noise can manifest as buzzing, humming, or other abnormal sounds produced by the motor. This noise can be caused by electromagnetic interference (EMI) or issues with electrical connections. Proper grounding and shielding can help mitigate electrical noise problems.
- Starting Problems: Motor starting problems can be attributed to issues with the starting capacitor, centrifugal switch, or power supply. Difficulty in starting can lead to motor stalling, increased power consumption, or intermittent operation.
- Insulation Breakdown: Insulation breakdown can occur due to excessive heat, moisture, chemical exposure, or mechanical stress. When insulation fails, the risk of short circuits and electrical hazards increases, and the motor becomes more prone to failures.
It is crucial to address these common electric motor problems promptly to prevent further damage and ensure the longevity and reliability of the motor. Regular maintenance, inspections, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines can help identify and resolve these issues effectively.
Importance of Fixing Electric Motor Problems
Fixing electric motor problems is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance, efficiency, and safety of operations. Failing to address these issues promptly can result in severe consequences that can impact personnel safety, equipment functionality, and overall productivity. Here are some reasons why fixing electric motor problems is of utmost importance:
- Prevents Costly Damages: Ignoring or delaying repairs can lead to more extensive damage to the motor and other connected components. The longer a problem persists, the more likely it is to escalate, resulting in costly repairs or even the need for motor replacement.
- Maximizes Energy Efficiency: Electric motors that are operating with problems such as overheating or excessive vibration are not running at their optimal efficiency. Fixing these issues ensures that the motor operates smoothly and efficiently, reducing energy consumption and minimizing operational costs.
- Improves Reliability: Addressing motor problems enhances the reliability of the motor, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns or failures. This is especially crucial in applications where downtime can lead to significant financial losses or safety concerns.
- Enhances Safety: A malfunctioning or energized motor housing presents severe safety hazards. Fixing electric motor problems helps reduce the risk of electrical shocks, fires, and other accidents that can harm personnel and damage property.
Risks and Dangers Associated with an Energized Motor Housing
An energized motor housing poses significant risks and dangers that should not be underestimated. Here are some of the potential hazards associated with an energized motor housing:
- Electric Shock Hazards: When the motor housing becomes energized, anyone who comes into contact with it can be exposed to electric shock. This can cause serious injury or even prove fatal, especially if the voltage is high.
- Fire Hazards: An energized motor housing increases the risk of electrical sparks or arcing, which can ignite flammable materials or surrounding equipment, leading to fires. The consequences can be devastating, including property damage, injuries, and loss of life.
- Equipment Damage: Electrical currents flowing through unintended paths due to an energized motor housing can damage connected machinery, control systems, or other electrical components. This can lead to costly repairs, production delays, or complete equipment failure.
- Personnel Safety: Personnel working in close proximity to an energized motor housing are at risk of electrical shock or other related injuries. Employers have a legal responsibility to provide a safe work environment and must take necessary measures to protect their employees from such hazards.
- Legal and Compliance Issues: Operating with an energized motor housing can lead to legal and compliance problems. Violations of electrical safety standards and regulations can result in penalties, fines, legal actions, and damage to the company’s reputation.
Given the risks and dangers associated with an energized motor housing, it is crucial to identify and resolve electric motor problems promptly to ensure the safety of personnel, protect equipment, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
Electric Shock Hazards
Electric shock hazards are a significant concern when dealing with an energized motor housing. Electric shocks occur when a person’s body becomes part of an electrical circuit, allowing current to pass through their body. Here are some key aspects to understand about electric shock hazards:
- Severity of Electric Shocks: The severity of an electric shock depends on various factors, such as the voltage level, duration of exposure, and the path the current takes through the body. Electric shocks can range from mild tingling sensations to severe burns, muscle contractions, cardiac arrest, or even death.
- Effects on the Body: Electric shocks can cause a range of injuries and health effects. These include burns at the point of contact, internal organ damage, neurological damage, muscle spasms, respiratory difficulties, and even psychological trauma.
- Secondary Hazards: Electric shocks can also cause secondary hazards. When a person experiences an electric shock, they may lose control of their body or be thrown forcefully, leading to falls or other accidents. This can result in additional injuries or even fatalities.
To mitigate the risk of electric shock hazards associated with an energized motor housing, several precautions must be taken:
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Implementing proper lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures ensures that all power to the motor is isolated and cannot be energized during maintenance or repair work. This prevents accidental contact with live electrical parts.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers should wear appropriate PPE, such as insulated gloves, safety boots, and protective clothing, to provide an additional layer of protection. These items are designed to minimize the risk of electric shock and burns in case of an accidental contact.
- Training and Education: Proper training and education on electrical safety are essential for all personnel working with or around electric motors. This includes understanding basic electrical principles, recognizing potential hazards, and knowing how to respond in case of an emergency.
- Regular Inspections and Maintenance: Regular inspections and maintenance of electrical equipment, including motors, can help identify and address potential issues that might lead to an energized motor housing. This includes checking for damaged wiring, loose connections, or signs of insulation deterioration.
- Qualified Personnel: Only qualified and trained personnel should handle electrical work, maintenance, or repairs. They should have the necessary knowledge, skills, and experience to work safely with electrical systems and follow industry guidelines and standards.
By taking these precautions and prioritizing electrical safety measures, the risk of electric shock hazards associated with an energized motor housing can be significantly reduced. It is crucial to prioritize the safety of personnel and ensure that proper measures are in place to prevent accidents and injuries.
Fire Hazards
When dealing with an energized motor housing, fire hazards are a significant concern. Electrical malfunctions can lead to arcing, sparking, or overheating, which may ignite flammable materials, causing fires. Understanding the fire hazards associated with an energized motor housing is crucial for maintaining a safe work environment. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Potential Causes: Several factors can contribute to fire hazards in relation to an energized motor housing. These include electrical faults, loose connections, damaged insulation, overheating, and the presence of flammable substances in the surrounding environment.
- Severity of Fires: Fires caused by an energized motor housing can vary in severity, from small localized incidents to large-scale fires that can rapidly spread and cause significant damage. The consequences can include property damage, equipment destruction, injuries, and even loss of life.
- Fire Suppression Challenges: Dealing with fires involving energized electrical equipment presents unique challenges. Traditional firefighting methods, such as using water, may not be suitable as they can conduct electricity and pose additional risks. Therefore, specialized fire suppression methods, such as carbon dioxide or other non-conductive agents, should be utilized.
To mitigate the risk of fire hazards associated with an energized motor housing, several precautions must be taken:
- Proper Installation: Ensure that the motor is installed correctly, following manufacturer guidelines and industry standards. Proper wiring, grounding, and appropriate clearances are essential to minimize fire hazards.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Conduct regular maintenance and inspections of the motor to identify any potential electrical faults or issues that may increase the risk of fires. This includes checking for loose connections, damaged wiring, or signs of overheating.
- Fire Suppression Equipment: Install appropriate fire suppression equipment, such as fire extinguishers rated for electrical fires, in the vicinity of the motor housing. Ensure that employees are trained on how to use these fire suppression tools effectively and safely.
- Flammable Material Control: Keep flammable materials away from the motor housing and maintain proper storage procedures. This includes regular housekeeping to prevent the accumulation of flammable debris or substances near the motor.
- Emergency Response Planning: Develop and implement an emergency response plan that outlines the actions to be taken in the event of a fire. This includes evacuation procedures, emergency shutdown protocols, and communication strategies to ensure the safety of personnel.
By implementing these precautions and prioritizing fire safety measures, the risk of fire hazards associated with an energized motor housing can be significantly minimized. It is crucial to have a comprehensive fire safety plan in place and provide proper training to all personnel to respond effectively in case of a fire emergency.
Equipment Damage
An energized motor housing can pose a serious risk of equipment damage. Electrical currents flowing through unintended paths due to an energized motor housing can affect connected machinery, control systems, and other electrical components. This can lead to various types of equipment damage and operational disruptions. Here are some key aspects to consider regarding equipment damage:
- Electrical Overloads: An energized motor housing can cause electrical overloads in connected equipment, exceeding their designed capacity. Excessive current flow can damage sensitive components, such as circuit boards, fuses, or transformers, compromising the overall functionality of the equipment.
- Voltage Spikes: Electrical faults in the motor can generate voltage spikes that can propagate through the electrical system, affecting other connected equipment. These spikes can cause damage to electronic components, such as microprocessors or sensors, leading to malfunction or complete failure.
- Short Circuits: An energized motor housing increases the risk of short circuits, which can cause damage to wiring, connectors, or other electrical connections. Short circuits can result in the equipment shutting down, malfunctioning, or even causing electrical fires.
- Mechanical Damage: In some cases, an energized motor housing can create mechanical stresses that can affect the physical integrity of connected equipment. Vibrations, heat, or electrical and magnetic fields can physically damage parts of the machinery, resulting in premature wear, misalignment, or mechanical failures.
To mitigate the risk of equipment damage associated with an energized motor housing, several precautions must be taken:
- Proper Wiring and Grounding: Ensure that the wiring and grounding systems are properly installed and maintained. This includes using correctly sized cables, following proper wiring practices, and implementing effective grounding techniques to minimize the risk of electrical faults.
- Protective Devices: Install protective devices, such as surge protectors or voltage regulators, to protect connected equipment from voltage spikes or electrical surges. These devices help prevent damage to sensitive electronic components and maintain stable operating conditions.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of connected equipment to identify any signs of damage or abnormalities. This includes visual inspections, thermal imaging, or using diagnostic tools to detect potential issues before they escalate and cause significant damage.
- Maintain Effective Maintenance Practices: Implement a regular maintenance schedule for both the motor and connected equipment. This includes lubrication, cleaning, calibration, and other preventive maintenance tasks to ensure optimal performance and minimize the risk of mechanical or electrical failures.
- Implement Backup Systems: Consider implementing backup systems or redundancy in critical equipment to ensure continuity of operations in the event of a failure. This can involve redundant power supplies, backup generators, or fail-safe mechanisms to minimize downtime and prevent severe disruptions.
By following these precautions and implementing proper maintenance and protection measures, the risk of equipment damage associated with an energized motor housing can be significantly reduced. Regular inspections, adherence to safety guidelines, and preventive maintenance practices are essential in protecting connected equipment and ensuring uninterrupted operation.
Read more: How To Prevent Grass From Growing
Personnel Safety
Ensuring personnel safety is of utmost importance when dealing with an energized motor housing. The risks associated with an energized motor housing can result in serious injuries or even fatalities. Implementing proper safety measures and providing comprehensive training is essential to protect personnel. Here are some key aspects to consider regarding personnel safety:
- Electric Shock Hazards: An energized motor housing poses a significant risk of electric shock to personnel. It is essential for all individuals working in the vicinity of the motor to be aware of the potential dangers and understand how to safely interact with energized equipment.
- Training and Education: Providing proper training and education is crucial to ensure that personnel have the knowledge and skills to work safely with electric motors. This includes understanding electrical safety principles, recognizing hazards, and knowing how to respond in case of an emergency.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Personnel should be equipped with appropriate personal protective equipment, including insulated gloves, safety glasses, and arc flash-rated clothing. PPE provides an additional layer of protection and minimizes the risk of injuries in case of accidental contact or electrical incidents.
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Implementing lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures is essential to ensure that power to the motor is isolated during maintenance or repair work. LOTO procedures help prevent accidental energization and protect personnel from unexpected electrical hazards.
- Regular Equipment Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the motor and associated equipment to identify any signs of damage, deterioration, or potential hazards. This includes checking for loose connections, worn-out insulation, or other issues that may endanger personnel safety.
Emphasizing a safety-centric culture and encouraging open communication regarding safety concerns is vital. Personnel should feel comfortable reporting any potential hazards or incidents to ensure prompt resolution and continuous improvement of safety practices.
It is also essential to comply with relevant safety regulations and standards. Employers have a legal responsibility to provide a safe working environment and must ensure that personnel are trained and equipped to work safely with energized motors.
By prioritizing personnel safety and implementing proper safety measures, the risk of injuries and accidents associated with an energized motor housing can be significantly reduced. Regular training, effective communication, and the commitment to maintaining a safe work environment are key to protecting personnel from potential hazards.
Ensure that the motor housing is properly grounded to prevent it from becoming energized. Regularly inspect and maintain the insulation of the motor windings to prevent electrical leakage.
Legal and Compliance Issues
Operating with an energized motor housing can lead to legal and compliance issues, as it poses significant safety risks and may violate electrical safety regulations and standards. It is crucial for organizations to comply with these regulations to protect employees, equipment, and the overall integrity of their operations. Here are some key aspects to consider regarding legal and compliance issues:
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Guidelines: OSHA provides guidelines and standards to ensure employee safety and prevent workplace accidents. Failure to comply with these guidelines can result in penalties, fines, potential legal actions, and damage to the company’s reputation.
- National Electrical Code (NEC) Compliance: The NEC establishes the minimum requirements for electrical installations, including grounding, wiring, and protection against electrical hazards. Compliance with the NEC is essential for preventing electrical accidents and maintaining a safe work environment.
- Electrical Safety Audits: Regular electrical safety audits can help identify potential issues with an energized motor housing, ensuring compliance with safety regulations. These audits involve evaluating the electrical systems, inspecting equipment, and verifying proper maintenance procedures.
- Employee Training: Employers are responsible for ensuring that employees receive proper training on electrical safety measures and procedures. This includes understanding electrical hazards, knowing how to work safely with energized equipment, and understanding emergency response protocols.
- Record Keeping: Proper documentation and record-keeping are crucial for demonstrating compliance with regulations. This includes maintaining records of maintenance inspections, training programs, safety audits, and any incidents or near misses related to the energized motor housing.
Identifying and Resolving Electric Motor Problems
Identifying and resolving electric motor problems is essential for maintaining safe and efficient operations. Here are some steps to help identify and resolve such problems:
- Visual Inspection of Motor Housing: Conduct a visual inspection of the motor housing to identify any visible signs of damage, loose connections, or insulation deterioration. Look for signs of overheating, such as discoloration or burning smells.
- Diagnostic Tests and Tools: Utilize diagnostic tests and tools, such as thermography, vibration analysis, or current measurements, to identify any underlying issues with the motor. These tests can reveal abnormalities, such as insulation breakdown, bearing wear, or electrical imbalances.
- Proper Maintenance and Repair Techniques: Ensure that maintenance and repair tasks are carried out by qualified individuals who have the necessary knowledge and skills. Follow manufacturer guidelines and use appropriate tools and techniques to address identified problems.
Addressing electric motor problems promptly is crucial to prevent further damage and ensure the longevity and functionality of the motor. By resolving these issues, organizations can maintain compliance with safety regulations, reduce the risk of accidents or injuries, and avoid costly legal consequences.
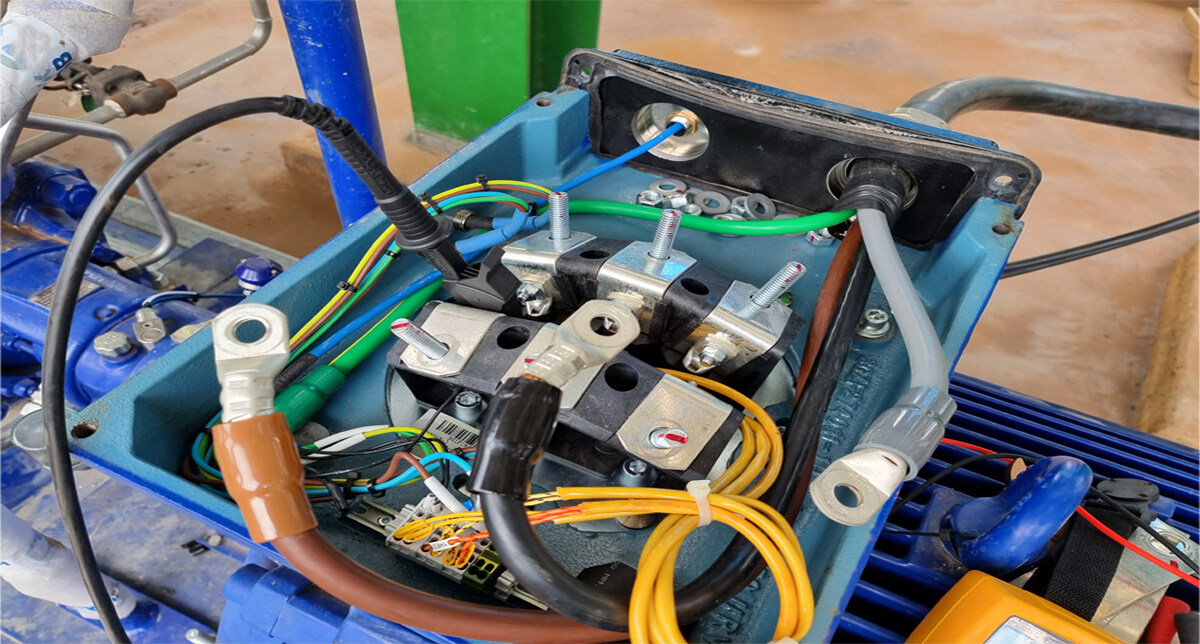
Visual Inspection of Motor Housing
Conducting a visual inspection of the motor housing is a crucial step in identifying potential issues and ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electric motors. Visual inspections allow for the early detection of visible signs of damage, wear, or deterioration that may lead to further problems if left unaddressed. Here are important considerations for a visual inspection of the motor housing:
- Physical Damage: Look for any signs of physical damage on the motor housing, such as cracks, dents, or corrosion. Physical damage can compromise the integrity of the housing, making it more susceptible to electrical hazards or insulation breakdown.
- Loose Connections: Check for any loose or disconnected wires, terminals, or connectors. Loose connections can lead to electrical arcing, overheating, or intermittent operation. Ensure all electrical connections are secure and properly tightened.
- Insulation Deterioration: Inspect the insulation material around the motor housing for any signs of deterioration, such as cracks, charring, or discoloration. Deteriorated insulation can lead to electrical faults, increased heat generation, or even short circuits.
- Overheating Indicators: Look for any indicators of overheating, such as discoloration or burning smells. Overheating can be a sign of excessive load, poor ventilation, or insulation breakdown, and it can lead to motor inefficiency, premature failure, and fire hazards.
- Proper Grounding: Verify that the motor housing is properly grounded. Grounding is essential for redirecting electrical faults and preventing the energization of the housing. Ensure that ground connections are securely attached and free from corrosion or other damage.
- Environmental Factors: Consider the environmental conditions surrounding the motor housing. Excessive dust, moisture, or exposure to chemicals can adversely affect the performance and longevity of the motor. Take preventive measures, such as installing protective covers or implementing proper ventilation, as needed.
A thorough visual inspection of the motor housing should be conducted regularly as part of routine maintenance and overall safety protocols. Document any observations, and promptly address any issues identified during the inspection. It is important to consult qualified professionals for more in-depth inspections or assessments, especially when dealing with large or complex motor systems.
By regularly performing visual inspections, organizations can effectively identify and address potential problems, improve the overall reliability and efficiency of electric motors, and ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations.
Diagnostic Tests and Tools
Diagnostic tests and tools play a vital role in identifying and pinpointing potential issues with electric motors. These tests provide valuable insights into the health and performance of the motor, allowing for targeted troubleshooting and effective problem resolution. Here are some diagnostic tests and tools commonly used for electric motor analysis:
- Thermography: Thermal imaging, also known as thermography, uses infrared cameras to detect variations in temperature. It helps identify overheated components, hot spots, or abnormalities within the motor. Thermography can reveal loose connections, insulation breakdown, or faulty bearings that may not be visible to the naked eye.
- Vibration Analysis: Vibration analysis involves using special sensors to measure the vibration levels of the motor. By analyzing vibration patterns, technicians can identify imbalance, misalignment, bearing wear, or other mechanical issues. Vibration analysis is useful for detecting potential failures and determining the necessary corrective actions.
- Current Analysis: Current analysis involves measuring and analyzing the current flow in the motor. By analyzing current signatures, technicians can detect electrical imbalances, phase issues, or abnormal operating conditions. Current analysis can help diagnose electrical faults, connection problems, or issues with the motor windings.
- Insulation Resistance Testing: Insulation resistance testing measures the electrical resistance of the insulation system in the motor. By applying a high-voltage DC test, technicians can determine the condition of the insulation and detect any degradation or moisture intrusion. Insulation resistance testing is crucial for assessing the overall health of the motor’s electrical insulation.
- Power Quality Analysis: Power quality analysis focuses on evaluating the quality of the electrical power supplied to the motor. It helps identify voltage spikes, harmonics, frequency variations, or other power anomalies that may affect motor performance or cause damage. Power quality analysis ensures that the motor receives stable and clean power, minimizing the risk of electrical issues.
It is important to note that diagnostic tests and tools should be used by qualified professionals who have the necessary training and expertise. These professionals can interpret the test results accurately and make informed decisions regarding repairs, maintenance, or replacements.
Regularly conducting diagnostic tests on electric motors can provide crucial insights into their condition and help identify potential issues before they become severe. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention, minimizes downtime, improves performance, and extends the lifespan of the motor. Additionally, utilizing diagnostic tests and tools ensures compliance with safety regulations and enhances overall reliability and efficiency in motor-driven systems.
Proper Maintenance and Repair Techniques
Proper maintenance and repair techniques are crucial for ensuring the longevity, performance, and safety of electric motors. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major problems, while effective repair techniques ensure that any faults or failures are promptly and correctly resolved. Here are some important considerations for proper maintenance and repair of electric motors:
- Scheduled Maintenance: Implement a regular maintenance schedule for the motor, following manufacturer guidelines and recommendations. This includes tasks such as lubrication, cleaning, and inspection of key components to ensure proper functioning and prevent premature wear and tear.
- Component Inspection: Inspect motor components, such as bearings, seals, brushes, and belts, for signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. Replace any worn-out or damaged components promptly to prevent further damage to the motor and ensure optimal performance.
- Proper Lubrication: Ensure that the motor is properly lubricated according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Lubrication helps reduce friction, heat, and wear, extending the lifespan of the motor. Use the appropriate lubricants and follow recommended intervals for reapplication.
- Electrical Connections: Regularly check electrical connections, such as terminals, connectors, and wiring, to ensure they are secure and free from damage. Loose or corroded connections can lead to increased resistance, heat buildup, and potential ignition sources. Tighten or replace any faulty connections as necessary.
- Cleaning and Dust Removal: Keep the motor and its surrounding environment clean to prevent the accumulation of dust, dirt, or debris. Regularly clean the motor’s external surfaces, cooling fans, and air vents to ensure proper airflow and to prevent overheating.
- Following Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance and repair processes. Manufacturers often provide detailed instructions on inspection procedures, maintenance intervals, and specific techniques that should be followed to ensure the motor’s optimal performance and longevity.
It is important to note that maintenance and repair tasks should be performed by qualified personnel who have the necessary knowledge, training, and expertise. They should have a good understanding of electrical systems and safety procedures to work safely with energized equipment.
Preventive Measures for Motor Housing Energization
Preventive measures play a crucial role in mitigating the risk of motor housing energization, ensuring the safety of personnel and the integrity of electrical systems. By implementing these measures, the likelihood of an energized motor housing is significantly reduced. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Electrical Insulation: Insulation plays a vital role in preventing the flow of current to unintended parts of the motor. Regularly inspect the motor’s insulation for signs of deterioration, such as cracks or discoloration, and promptly repair or replace any damaged insulation to maintain its effectiveness.
- Grounding Systems: Implement a robust grounding system to redirect electrical faults and prevent the energization of the motor housing. Ensure that ground connections are properly installed, securely attached, and regularly inspected to maintain their effectiveness.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspection: Implement a comprehensive maintenance and inspection program to identify and address potential issues that can lead to motor housing energization. This includes routine inspections of electrical connections, insulation, grounding systems, and other critical components.
- Proper Installation: Follow proper installation procedures to ensure that the motor is installed correctly and according to manufacturer guidelines. It includes proper wiring, correct sizing of conductors, and adherence to electrical code requirements to minimize the risk of electrical faults that may lead to an energized motor housing.
By implementing these preventive measures, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of motor housing energization, enhancing personnel safety, protecting equipment, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations and standards. Regular maintenance, inspections, and adherence to proper installation practices are essential for preventing potential hazards and maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of electric motors.
Electrical Insulation
Electrical insulation is a critical component in electric motors that helps prevent the flow of current to unintended parts of the motor. It plays a vital role in maintaining the electrical integrity and safety of the system. Proper insulation prevents energization of the motor housing, minimizes the risk of electrical faults, and protects personnel and equipment. Here are some important aspects to consider regarding electrical insulation:
- Insulation Materials: Electric motors are typically insulated using materials such as varnishes, resins, tapes, or coatings. These materials are selected for their ability to resist the flow of electrical current and withstand the operating temperature and environmental conditions.
- Protecting Against Electrical Hazards: The primary purpose of insulation is to protect against electrical hazards. By preventing the flow of current to unintended parts of the motor, insulation reduces the risk of short circuits, electrical shocks, and potential fire hazards.
- Deterioration and Aging: Over time, electrical insulation can deteriorate due to factors such as temperature fluctuations, mechanical stress, moisture, and chemical exposure. This can lead to insulation breakdown, reduced effectiveness, and increased risk of electrical faults or energization of the motor housing.
- Insulation Resistance Testing: Insulation resistance testing is a common diagnostic test performed to assess the condition of the insulation. This test measures the electrical resistance between the motor’s windings and its core or grounded components. Low insulation resistance readings indicate potential insulation breakdown and the need for repair or replacement.
- Proper Insulation Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the integrity of the electrical insulation. Inspection of the insulation for signs of damage, such as cracks, charring, or discoloration, should be performed regularly. Any damaged or deteriorated insulation should be repaired or replaced promptly.
- Correct Insulation Application: Ensuring proper application of insulation materials is crucial for its effectiveness. The insulation should be applied evenly and in the recommended thickness, adhering to manufacturer guidelines. Improper insulation application can compromise its performance and increase the risk of electrical issues.
Proper management of electrical insulation is essential in maintaining the optimal performance, safety, and reliability of electric motors. It is crucial to prioritize regular inspections, prompt repairs, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines for insulation maintenance and replacement. By ensuring the integrity of electrical insulation, organizations can reduce the risk of motor housing energization, prevent electrical faults, and maintain a safe working environment.
Grounding Systems
Grounding systems play a crucial role in electrical systems, including electric motors. They provide a safe path for electrical faults and help prevent the energization of the motor housing. Proper grounding is essential for protecting personnel, equipment, and the overall integrity of the electrical system. Here are important aspects to consider regarding grounding systems:
- Purpose of Grounding: The main purpose of grounding is to redirect electrical faults and ensure that excess current flows safely to the earth. Grounding provides a low-resistance path for the fault current, protecting equipment and preventing the buildup of dangerous voltage levels.
- Equipment Grounding: Equipment grounding involves connecting metal parts of electrical equipment, such as the motor housing, to the earth through a grounding conductor. Equipment grounding reduces the risk of electric shock to personnel and helps prevent electrical fires by providing a path for fault current.
- System Grounding: System grounding involves grounding one of the electrical system conductors, typically the neutral conductor, to the earth. This type of grounding helps stabilize system voltage, enhances safety, and facilitates the detection and mitigation of faults.
- Grounding Connections: Proper grounding connections are essential to ensure adequate electrical conductivity. Grounding conductors should be sized correctly and securely connected to the grounding electrode system, which typically consists of grounding rods or a grounding grid.
- Grounding Electrode System: The grounding electrode system provides a connection between the electrical system and the earth. It includes grounding electrodes, such as metal rods or plates, that are installed below the ground level to provide a reliable ground connection.
- Regular Grounding Inspections: Regular inspections of the grounding system should be conducted to ensure its effectiveness. This includes checking for corrosion, damage, or loose connections. A well-maintained grounding system helps ensure reliable grounding and minimizes the risk of electrical hazards.
Compliance with electrical codes and standards is crucial when implementing grounding systems. National and local electrical codes provide guidelines and requirements for proper grounding practices. It is essential to consult these codes and work with qualified professionals to ensure compliance with the applicable regulations.
By implementing proper grounding systems, organizations can mitigate the risk of motor housing energization, protect personnel from electric shock hazards, minimize electrical faults, and ensure the safe and reliable operation of electric motors. Regular inspections and adherence to grounding standards are key elements of maintaining an effective grounding system.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection of electric motors are essential to ensure their optimal performance, longevity, and safety. By implementing a proactive maintenance routine and conducting regular inspections, organizations can identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Here are important aspects to consider regarding regular maintenance and inspection:
- Maintenance Schedule: Establish a regular maintenance schedule for electric motors, considering factors such as manufacturer recommendations, operating conditions, and industry standards. This schedule should include routine tasks such as lubrication, cleaning, and component inspections.
- Component Inspections: Regularly inspect motor components, such as bearings, seals, brushes, and belts, to detect signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Replace any worn-out or faulty components promptly to prevent further damage to the motor and ensure optimal performance.
- Electrical Connections: Regularly check electrical connections, including terminals, connectors, and wiring, to ensure they are secure and free from damage. Loose or corroded connections can lead to increased resistance, heat buildup, and potential hazards. Tighten or replace any faulty connections as necessary.
- Cleaning and Dust Removal: Keep the motor and its surrounding environment clean to prevent the accumulation of dust, dirt, or debris. Regularly clean the motor’s external surfaces, cooling fans, and air vents to ensure proper airflow and prevent overheating.
- Insulation Inspection: Inspect the motor’s insulation for signs of damage, such as cracks, charring, or discoloration. Insulation breakdown can lead to electrical faults, increased heat generation, or short circuits. Promptly repair or replace any damaged insulation to maintain its effectiveness.
- Documentation: Maintain proper documentation of maintenance activities, including dates of inspections, repairs, and replacements. These records are valuable for tracking the motor’s history, identifying patterns, and demonstrating compliance with safety standards and regulations.
Regular maintenance and inspection should be performed by qualified personnel who have the necessary knowledge and skills. These professionals should follow manufacturer guidelines, industry best practices, and safety precautions to ensure the effective maintenance of electric motors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, regular maintenance and inspection of electric motors are essential for optimal performance, safety, and longevity. By implementing a proactive maintenance program and conducting regular inspections, potential issues can be identified and resolved early, minimizing downtime, preventing accidents, and maximizing the lifespan of the motor. Proper maintenance techniques, such as careful component inspections, electrical connection checks, and cleaning, ensure that the motor operates efficiently and reliably.
Additionally, regular inspections help detect issues with insulation, grounding, or other critical components that can lead to motor housing energization and electrical safety hazards. By promptly addressing these issues, organizations can ensure the safety of personnel, prevent equipment damage, and remain in compliance with various regulations and standards.
By prioritizing regular maintenance and inspection of electric motors, organizations can optimize motor performance, enhance personnel safety, extend motor lifespan, and ultimately contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Prevent Your Motor Housing From Becoming Energized
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How To Prevent Your Motor Housing From Becoming Energized”