

Articles
How To Store Chemicals In The Workplace
Modified: January 6, 2024
Discover the best practices for storing chemicals in the workplace with our informative articles. Ensure safety and compliance with expert tips and guidelines.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how to store chemicals in the workplace. Chemicals are an integral part of many industries, used in various processes such as manufacturing, research, and cleaning. While chemicals are essential for these operations, improper storage and handling can lead to serious safety hazards and environmental risks.
Proper chemical storage is crucial to ensure the safety and well-being of employees, as well as to comply with regulatory standards. This guide will provide you with valuable insights and practical tips on how to store chemicals in the workplace effectively.
Whether you are a business owner, facilities manager, or an employee responsible for chemical storage, understanding the importance of proper storage practices is vital. By following these guidelines, you can mitigate the risks associated with chemical storage and create a safe working environment.
In this guide, we will cover various aspects of chemical storage, including regulatory guidelines, chemical compatibility, storage containers and labels, storage areas and facilities, handling and transportation of chemicals, personal protective equipment, emergency preparedness, spill response, and employee training. Each section aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of best practices for chemical storage, allowing you to implement appropriate measures in your workplace.
It is important to note that while this guide contains valuable information, it should not replace specific regulations or guidelines set by the relevant authorities. Always consult with local regulatory agencies or safety professionals to ensure compliance with specific requirements in your jurisdiction.
Now, let’s delve into the importance of proper chemical storage and explore the regulatory guidelines that govern this practice.
Key Takeaways:
- Prioritize employee safety, environmental protection, and legal compliance by implementing proper chemical storage practices. Understanding regulatory guidelines and providing comprehensive training are essential for creating a safe workplace environment.
- Effective chemical storage involves proper segregation, labeling, and emergency preparedness. By prioritizing employee training and education, businesses can mitigate risks, protect the environment, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Read more: How To Store Borax
Importance of Proper Chemical Storage
Proper chemical storage is of utmost importance in the workplace due to the potential hazards associated with mishandling and improper storage practices. Here are some key reasons why maintaining a safe and organized chemical storage system is crucial:
1. Employee Safety: The primary reason for proper chemical storage is to ensure the safety and well-being of employees. Chemicals can pose significant health risks if not stored and handled correctly. Exposure to hazardous substances can lead to various health issues, including respiratory problems, skin irritations, burns, and even long-term chronic illnesses. By implementing proper storage procedures, you can minimize the risks and create a safer work environment for your employees.
2. Prevent Accidents and Injuries: Inadequate chemical storage can increase the likelihood of accidents and injuries. Mishandled or improperly stored chemicals can lead to spills, leaks, or other incidents that may result in chemical burns, fires, or explosions. By organizing and storing chemicals in a safe and secure manner, you can minimize the risks of accidents and protect both your employees and the surrounding environment.
3. Environmental Protection: Chemical spills and improper disposal can have severe environmental consequences, contaminating soil, water sources, and ecosystems. By storing chemicals properly, you can reduce the risk of spills and leaks, preventing potential harm to the environment. Additionally, adhering to proper disposal guidelines ensures that chemicals are handled and disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner, minimizing the impact on the ecosystem.
4. Legal Compliance: Regulatory agencies have established guidelines and standards for the safe storage and handling of chemicals. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in legal consequences, including fines and penalties. By adopting proper storage practices, you can ensure that your business remains compliant with the relevant laws and regulations, protecting your company from legal repercussions.
5. Efficient Workflow: Storing chemicals in an organized and systematic manner improves workflow efficiency. Properly labeled and categorized chemicals streamline inventory management and make it easier to locate and access specific chemicals when needed. This reduces the time spent searching for materials, ultimately increasing productivity and efficiency in the workplace.
By understanding and acknowledging the importance of proper chemical storage, you can create a safer working environment, protect the environment, and ensure compliance with legal regulations. In the next section, we will explore the regulatory guidelines that govern chemical storage practices.
Regulatory Guidelines for Chemical Storage
Proper chemical storage is not only essential for the safety of employees and the environment but also a legal requirement. Various regulatory agencies have established guidelines and standards to ensure the safe storage and handling of chemicals in the workplace. Familiarizing yourself with these regulations is crucial for maintaining compliance. Here are some common regulatory guidelines to consider:
1. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): OSHA is a federal agency in the United States that sets and enforces workplace safety regulations. OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HCS), also known as the “Right to Know” law, mandates that employers provide information about chemical hazards and ensure proper storage and handling. The standard includes requirements for labeling containers, maintaining Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for each chemical, and training employees on the hazards and safe work practices.
2. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): The EPA is responsible for protecting human health and the environment. It regulates the storage, transportation, and disposal of hazardous waste, including certain chemicals. EPA regulations, such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), provide guidelines on proper storage methods, reporting requirements, and contingency planning for hazardous materials.
3. National Fire Protection Association (NFPA): The NFPA develops and publishes fire safety codes and standards. The NFPA 30, Flammable and Combustible Liquids Code, provides guidance on the storage of flammable and combustible liquids. It specifies requirements for fire-resistant storage cabinets, maximum allowable quantities per storage area, and proper ventilation.
4. European Union (EU) Regulations: The European Union has its own set of regulations governing chemical storage and handling. The REACH Regulation (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) applies to the registration, evaluation, and authorization of chemicals, including requirements for safe storage and transport. The Classification, Labelling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation establishes criteria for the classification and labeling of hazardous substances.
5. Local and Regional Regulations: Apart from national and international guidelines, there may be additional regulations at the local or regional level. It is important to research and comply with any specific requirements set by local authorities or regulatory bodies in your area.
Staying up-to-date with these regulations is crucial for maintaining a safe and compliant workplace. Regularly review and assess your chemical storage practices to ensure compliance with the relevant guidelines. In the next section, we will discuss chemical compatibility and segregation, which are key considerations for safe chemical storage.
Chemical Compatibility and Segregation
When it comes to chemical storage, one of the vital aspects to consider is chemical compatibility and segregation. Different chemicals can react with each other if stored in close proximity, leading to hazardous reactions, fires, or explosions. Therefore, it is essential to understand the principles of chemical compatibility and segregate incompatible chemicals appropriately. Here are some key considerations:
1. Chemical Compatibility: Chemical compatibility refers to the ability of two or more substances to coexist without causing adverse reactions. Not all chemicals can be safely stored together. It is crucial to consult Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and chemical reference guides to determine the compatibility of different chemicals. Pay attention to factors such as reactivity, flammability, volatility, and sensitivity to moisture or temperature. Segregate incompatible chemicals to minimize the risk of accidental mixing or reactions.
2. Segregation by Chemical Classes: Chemicals can be categorized into different classes based on their properties and hazards. Segregating chemicals by these classes helps to prevent incompatible substances from coming into contact with each other. The most common classes include flammables, corrosives, oxidizers, toxic substances, and reactive chemicals. Keep each class of chemicals stored separately and clearly label storage areas accordingly.
3. Proper Labeling: Clear and accurate labeling is crucial for safe chemical storage. Label each chemical container with the substance’s name, hazard symbols, handling instructions, and any other relevant information. Labeling ensures that employees can identify the contents of each container and understand any necessary precautions or special handling requirements.
4. Physical Separation: In addition to segregating chemicals by classes, physically separate incompatible substances. Use separate storage cabinets or designated areas for different chemical categories to minimize the risk of accidental mixing. Ensure that there are clear boundaries between storage areas to avoid cross-contamination.
5. Secondary Containment: Use secondary containment systems, such as spill trays or secondary containers, to further safeguard against chemical spills or leaks. These measures help contain any potential releases and prevent them from spreading to other storage areas or the environment.
6. Storage Considerations: Follow recommended storage requirements for different chemicals. Some chemicals may require specific storage conditions, such as temperature control, ventilation, or specialized storage cabinets. Adhere to these guidelines to maintain the integrity and stability of the chemicals and reduce the risk of accidents or deterioration.
By understanding chemical compatibility and properly segregating chemicals, you can minimize the risks associated with chemical reactions and ensure the safety of your workplace. In the next section, we will discuss the importance of using appropriate storage containers and labels for chemicals.
Chemical Storage Containers and Labels
Choosing the right storage containers and using proper labels are crucial aspects of safe chemical storage. The right containers not only help protect the integrity of chemicals but also prevent leaks and spills that could lead to accidents or environmental contamination. Here are some key considerations for selecting chemical storage containers and labels:
1. Container Materials: Chemical storage containers should be made of materials that are compatible with the specific chemicals being stored. Avoid containers that may react with or be degraded by the chemicals. Commonly used materials for chemical storage containers include high-density polyethylene (HDPE), glass, stainless steel, or specific plastics designed for chemical compatibility.
2. Sealability: Ensure that the storage containers have tight-fitting lids or closures to prevent leaks or spills. A proper seal helps to maintain chemical integrity and reduce the risk of exposure or accidental mixing with incompatible substances.
3. Size and Capacity: Choose storage containers that are appropriately sized for the quantity of chemicals being stored. Overfilling containers can lead to spills and increase the risk of accidents. Consider factors such as chemical reactivity, volatility, and usage frequency when determining the container size and capacity.
4. Labeling: Every chemical container should be clearly labeled with the name of the chemical, hazard symbols, and any relevant safety information. Labels should be legible, durable, and resistant to fading or smudging. Use chemical-resistant labels or affix labels in areas where they won’t be easily damaged or removed.
5. Information on Labels: In addition to the chemical name, labels should include any necessary handling precautions, such as personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements, first aid instructions, and emergency contact information. Labels should also indicate the date of receipt or manufacture of the chemical and provide a unique identifier for easy inventory tracking.
6. Color Coding: Consider implementing a color-coding system to further enhance safety and facilitate identification. Assign specific colors to different hazard categories or chemical classes. For example, flammable substances could be designated with red labels, while corrosive materials use yellow labels. This visual cue helps quickly identify the hazard associated with each chemical.
7. Regular Inspection and Replacement: Regularly inspect storage containers and labels to ensure they are in good condition. If a container is damaged or a label becomes illegible or faded, replace it promptly to maintain clear identification and reduce the risk of accidents or confusion.
By carefully selecting appropriate storage containers and utilizing clear and accurate labels, you contribute to a safer working environment and minimize the potential risks associated with chemical storage. In the next section, we will discuss the importance of designated storage areas and facilities for chemicals.
Read more: How To Store Pool Chemicals
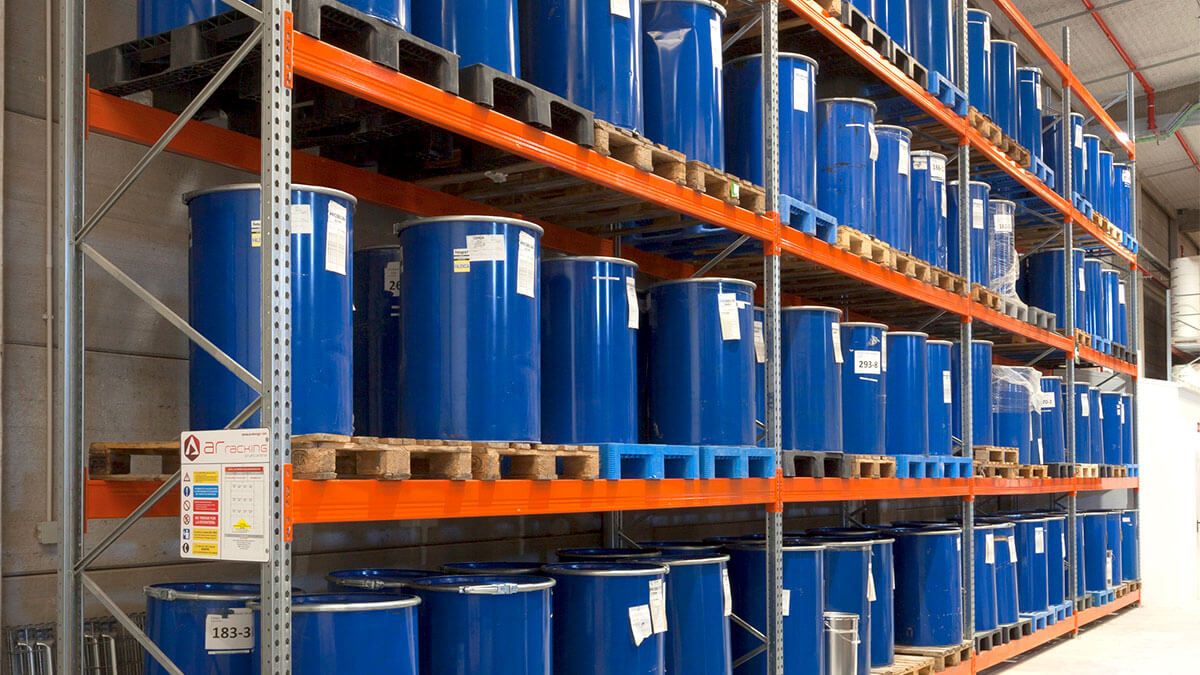
Storage Areas and Facilities
Designating proper storage areas and facilities for chemicals is essential for maintaining a safe and organized workplace. Establishing dedicated storage spaces helps prevent accidents, control chemical inventories, and facilitate efficient use and retrieval of chemicals. Here are some key considerations when setting up storage areas and facilities for chemicals:
1. Controlled Access: Limit access to the designated chemical storage areas to authorized personnel only. Restricting access reduces the risk of unauthorized handling or accidental exposure to hazardous substances. Implement measures such as keycard entry systems or locked cabinets to ensure only trained and authorized individuals have access.
2. Adequate Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial in chemical storage areas to prevent the buildup of toxic vapors or fumes. Ventilation systems help maintain air quality and reduce the risk of exposure to harmful substances. Ensure that storage areas have adequate ventilation or install local exhaust systems where necessary.
3. Separation from Ignition Sources: Store flammable or combustible chemicals in areas away from heat sources, open flames, or electrical equipment that could potentially ignite the chemicals. Maintaining proper distance reduces the risk of fires or explosions. Follow the guidelines provided by regulatory authorities, such as the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), for required separation distances.
4. Temperature and Humidity Control: Some chemicals require specific temperature or humidity conditions to maintain their stability and integrity. Ensure that storage areas are appropriately climate-controlled to meet the requirements of the chemicals being stored. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or guidelines for temperature and humidity ranges for optimal chemical storage.
5. Spill Containment: Implement spill containment measures in chemical storage areas to mitigate the risks associated with spills or leaks. Use spill trays or containment pallets to capture any potential releases and prevent them from spreading. Have appropriate spill response kits readily available for quick and effective cleanup in case of an accident.
6. Shelving and Organization: Utilize shelves, racks, or storage cabinets to keep chemicals organized and prevent accidental falls or spills. Consider the weight and stability of the storage units to accommodate the load of the chemicals being stored. Implement a logical arrangement and use clear labeling to facilitate easy identification and retrieval of chemicals.
7. Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect the storage areas and facilities to ensure compliance with the established guidelines and regulations. Check for any signs of damage, leaks, or improper storage practices. Conduct routine inspections to identify and resolve any potential safety hazards promptly.
8. Emergency Equipment: Have emergency equipment readily available in the storage areas, such as fire extinguishers, eye wash stations, and safety showers. These resources are crucial in case of chemical spills, releases, or other emergencies. Ensure that employees are trained on how to properly use the emergency equipment and know the location of each item.
By establishing designated storage areas and facilities and following these guidelines, you create a safe and efficient environment for storing chemicals. In the next section, we will discuss the proper handling and transportation of chemicals.
Always store chemicals in their original containers with proper labels. Keep them in a well-ventilated, cool, and dry area away from direct sunlight and incompatible materials.
Handling and Transportation of Chemicals
The proper handling and transportation of chemicals are critical to maintaining a safe workplace and preventing accidents or incidents. Whether you are moving chemicals within the facility or transporting them externally, following safe practices is essential. Here are some key considerations for the handling and transportation of chemicals:
1. Training and Education: Ensure that employees who handle and transport chemicals are properly trained on the specific hazards and safe handling procedures. Training should cover topics such as proper lifting techniques, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and awareness of chemical properties and hazards. Regular refresher training and updates are also essential to keep employees informed about any changes or new best practices.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Utilize appropriate personal protective equipment depending on the hazards associated with the chemicals being handled or transported. This may include gloves, safety goggles, face shields, lab coats, and respiratory protection. Ensure that employees are trained on the correct use, maintenance, and disposal of PPE. Regularly inspect and replace damaged or worn-out equipment.
3. Secure Packaging: Package chemicals securely to prevent leaks, spills, or breakages during handling or transportation. Use appropriate containers designed for chemical compatibility and ensure they are tightly closed and properly sealed. Consider using secondary containment measures, such as spill-proof bags or trays, for added protection.
4. Proper Lifting and Carrying: When manually handling chemical containers, employ proper lifting techniques to avoid strain or injury. Lift with your legs, not your back, and use mechanical aids such as trolleys or dollies whenever possible to reduce the risk of accidents or physical strain.
5. Segregation during Transport: During transportation, segregate incompatible chemicals to prevent accidental mixing or reactions. Use separate compartments or secure dividers in vehicles or containers to keep different chemicals properly separated. Ensure that drivers or handlers are aware of the segregation requirements and follow safe practices during transportation.
6. Compliance with Transportation Regulations: When transporting chemicals externally, ensure compliance with applicable transportation regulations, such as those provided by the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States or the International Air Transport Association (IATA) for air transportation. Adhere to labeling requirements, packaging standards, and any special permits or documentation needed for hazardous materials transportation.
7. Vehicle Safety and Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain vehicles used for chemical transportation to ensure their safe operation. Check for any leaks, damages, or faulty equipment that could jeopardize the integrity of the chemicals or pose a risk to drivers and the public. Implement protocols for routine inspections, maintenance, and cleaning of the vehicles.
8. Emergency Preparedness: Have a comprehensive emergency response plan in place for handling potential accidents or spills during transportation. Train drivers and handlers on the proper response procedures and provide them with the necessary emergency contact information. Equip vehicles with spill kits, fire extinguishers, and other emergency equipment, and ensure that drivers are trained in their use.
By following proper handling and transportation practices, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with the movement of chemicals and ensure the safety of employees, the public, and the environment. In the next section, we will discuss the importance of personal protective equipment (PPE) for chemical storage.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Chemical Storage
When working with or handling chemicals, it is crucial to prioritize the safety of employees by providing the necessary personal protective equipment (PPE). PPE acts as a barrier between the hazardous chemicals and the individual, reducing the risk of exposure and potential harm. Here are some key points to consider when selecting and using PPE for chemical storage:
1. Assess Hazards: Before selecting the appropriate PPE, perform a thorough hazard assessment to identify potential risks associated with the chemicals being stored. Consider factors such as toxicity, flammability, corrosiveness, and reactivity. Hazard information can be found on Safety Data Sheets (SDS) or chemical labels.
2. PPE Selection: Based on the identified hazards, select the appropriate PPE to provide adequate protection. This may include gloves, goggles, face shields, safety glasses, respirators, lab coats, aprons, and safety footwear. Choose PPE that is specifically designed for protecting against the types of chemicals being handled and ensure it meets appropriate safety standards.
3. Gloves: Gloves are a fundamental PPE item for hand protection when working with chemicals. Different types of gloves are available, including nitrile, neoprene, latex, and butyl rubber gloves. Select gloves that have appropriate chemical resistance for the specific chemicals being handled.
4. Eye and Face Protection: Chemical splashes or airborne particles can cause severe eye and face injuries. Provide employees with appropriate eye protection, such as safety glasses, goggles, or face shields. Ensure the chosen eyewear offers proper coverage, a snug fit, and is compatible with other PPE being worn.
5. Respiratory Protection: When working with chemicals that generate vapors, dusts, or mists, respiratory protection may be necessary. Use respirators that are specifically designed to filter out hazardous airborne substances. Ensure employees are trained in proper respirator use, including fitting, maintenance, and storage.
6. Protective Clothing: Provide employees with suitable protective clothing, such as lab coats or full-body coveralls, to minimize skin contact with hazardous chemicals. The clothing should be made from chemical-resistant materials and cover the entire body, including arms and legs. Regularly inspect clothing for damage and replace as needed.
7. Training and Education: Proper training on the use, limitations, and care of PPE is essential. Educate employees about why PPE is necessary, how to properly use and maintain it, and the signs of wear or damage to look out for. Reinforce the importance of wearing PPE consistently in designated chemical storage areas.
8. Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections of all PPE to ensure its integrity and effectiveness. Inspect for any signs of damage, deterioration, or degradation that may compromise its protective capabilities. Replace worn-out or damaged PPE promptly to maintain employee safety.
Implementing and enforcing the use of appropriate PPE plays a crucial role in preventing injuries and illnesses associated with chemical storage. By providing the necessary protective gear and ensuring employees are trained on its proper use, you create a safer environment for working with chemicals. In the next section, we will discuss emergency preparedness and spill response for chemical storage facilities.
Emergency Preparedness and Spill Response
Emergency preparedness and an effective spill response plan are essential components of safe chemical storage. Being prepared for emergencies helps mitigate the potential risks associated with chemical spills, releases, or accidents and allows for a prompt and effective response. Here are some key considerations for emergency preparedness and spill response:
1. Emergency Response Plan: Develop an emergency response plan tailored to your specific chemical storage facility. The plan should outline the actions to be taken in the event of a chemical spill or release, including evacuation procedures, communication protocols, and emergency contact information. Ensure that all employees are familiar with the plan and participate in regular drills or simulations to practice emergency response procedures.
2. Spill Response Team: Establish a spill response team or designate trained individuals responsible for responding to chemical spills or releases. These individuals should receive specialized training in spill response techniques, including containment, cleanup, and proper disposal. Provide them with the necessary equipment and resources to efficiently and safely handle spills.
3. Spill Response Equipment: Maintain spill response kits in easily accessible locations throughout your facility. These kits should include appropriate absorbent materials, spill containment booms, neutralizing agents, personal protective equipment (PPE), and cleanup tools. Regularly inspect and replenish the kits to ensure they are fully stocked and ready for use in case of spills.
4. Emergency Equipment: Install emergency equipment, such as eyewash stations, safety showers, and fire extinguishers, in close proximity to chemical storage areas. Regularly inspect and test this equipment to ensure it is functioning properly. Clearly mark the location of emergency equipment and provide training to employees on its proper use.
5. Evacuation Procedures: Establish clear evacuation procedures in the event of a chemical spill or other emergencies. Designate assembly points away from the affected area and ensure that all employees are familiar with evacuation routes and procedures. Regularly conduct drills to practice evacuation scenarios and identify any gaps or areas for improvement.
6. Communication and Notification: Establish a reliable communication system to quickly inform employees, emergency responders, and appropriate authorities in the event of a spill or emergency. Ensure that contact information for emergency services, hazardous materials response teams, and any regulatory agencies is readily available. Regularly test communication systems to ensure they are operational.
7. Reporting and Documentation: Develop a system for reporting and documenting all incidents, including spills and near misses. Promptly report any spills or releases to the appropriate authorities and keep records of the incident, response actions, and any follow-up measures taken. This documentation helps identify trends, evaluate response effectiveness, and ensure compliance with reporting requirements.
8. Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and evaluate your emergency preparedness and spill response procedures. Identify areas for improvement and implement necessary changes based on lessons learned from drills, incidents, and updates in industry best practices. Encourage employee feedback and involvement to foster a culture of safety and continuous improvement.
By having a well-developed emergency preparedness plan and an effective spill response system in place, you can minimize the impact of chemical spills and protect the safety of employees, the environment, and surrounding communities. In the final section, we will discuss the importance of employee training and education in chemical storage.
Read more: How To Store Mineral Spirits
Employee Training and Education
Employee training and education play a vital role in ensuring safe practices for chemical storage in the workplace. Properly trained and knowledgeable employees are essential for preventing accidents, handling chemicals correctly, and responding appropriately to emergencies. Here are some key points to consider when it comes to employee training and education:
1. Hazard Communication: Train employees on the hazards associated with the chemicals they work with or are exposed to in the workplace. Provide thorough information on the potential health effects, physical properties, and safe handling practices of each chemical. This training should include understanding Safety Data Sheets (SDS), chemical labels, and hazard symbols.
2. Safe Handling Procedures: Educate employees on proper procedures for safely handling, storing, and disposing of chemicals. This includes information on personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements, safe storage practices, and the use of appropriate tools and equipment. Encourage adherence to established protocols to minimize risks and ensure consistency in safe practices.
3. Training on Emergency Response: Provide employees with specific training on emergency response procedures in the event of chemical spills, leaks, or accidents. This should include information on evacuation procedures, how to use emergency equipment such as eyewash stations and safety showers, and the importance of promptly reporting incidents to the appropriate authorities.
4. Equipment and Machinery Training: If employees are required to operate equipment or machinery involved in chemical storage, provide proper training on their safe operation. Ensure employees understand how to use equipment safely, perform routine inspections, and recognize signs of malfunction or damage that may pose risks to themselves or others.
5. Regular Refresher Training: Conduct regular refresher training sessions to reinforce safe practices, refresh employees’ knowledge, and provide updates on any changes in regulations or best practices. This helps to ensure that employees consistently follow safe procedures, remain aware of potential hazards, and stay up-to-date with any new developments in chemical storage practices.
6. Communication and Reporting: Foster a culture of open communication and encourage employees to report any safety concerns, near misses, or incidents related to chemical storage. Create channels for effective communication between employees and management to address safety-related issues promptly.
7. Documentation: Keep detailed records of employee training sessions, including dates, topics covered, and attendees. This documentation provides evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements and serves as a reference for audits or inspections. It also helps track employee training progress and identify areas that may require additional focus or reinforcement.
8. Continuous Learning: Encourage employees to engage in continuous learning related to chemical storage and safety. Provide access to resources, such as webinars, workshops, and industry publications, to enhance their knowledge. Promote involvement in safety committees or forums where employees can share experiences, learn from one another, and contribute to ongoing improvement initiatives.
By prioritizing employee training and education, you empower your workforce to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and actively contribute to creating a safe environment for chemical storage. Remember to regularly assess training needs and adapt programs accordingly to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
With the information provided in this guide, combined with diligent implementation and adherence to best practices, you can successfully store chemicals in the workplace while safeguarding the well-being of your employees and minimizing environmental risks.
Conclusion
Proper chemical storage is of utmost importance in the workplace to ensure the safety of employees, protect the environment, and comply with regulatory standards. By following best practices and implementing effective strategies, businesses can mitigate the risks associated with chemical storage and create a safe working environment.
In this comprehensive guide, we have discussed various aspects of chemical storage. We explored the importance of proper chemical storage, emphasizing the significance of employee safety, accident prevention, environmental protection, legal compliance, and efficient workflow. Understanding the regulatory guidelines governing chemical storage is essential to maintain compliance and ensure the well-being of all employees.
We then delved into the importance of chemical compatibility and segregation. By categorizing chemicals into appropriate classes and properly labeling storage areas, businesses can minimize the risk of hazardous reactions and protect both employees and the environment.
The selection of suitable chemical storage containers and the use of proper labeling are essential to maintain the integrity of chemicals and prevent leaks and spills. By choosing the right materials, ensuring proper sealability, and using clear and accurate labels, businesses can enhance safety and organization within their chemical storage facilities.
Designating specific storage areas and facilities for chemicals helps minimize risks and streamline inventory management. Adequate ventilation, temperature control, and segregation from ignition sources are crucial considerations when setting up storage areas. Additionally, implementing spill containment measures and providing emergency equipment ensures preparedness for potential incidents.
Employees’ safety is further enhanced through proper training and education. By providing comprehensive training on hazard communication, safe handling procedures, emergency response, and the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), businesses empower their employees to make informed decisions, effectively respond to emergencies, and contribute to a culture of safety.
Finally, maintaining a robust emergency preparedness plan and having effective spill response procedures in place are essential components of safe chemical storage. By being well-prepared for emergencies and having a trained spill response team, businesses can minimize the impact of spills and protect the well-being of employees, the environment, and surrounding communities.
By implementing the strategies and practices outlined in this guide, you can create a safe and compliant environment for storing chemicals in your workplace. Remember to regularly review and update your procedures, staying informed about regulatory changes and industry best practices. Prioritizing the safety of employees and the environment is not only responsible business practice but also a commitment to creating a healthy and sustainable working environment for all.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Chemicals In The Workplace
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Store Chemicals In The Workplace”