

Articles
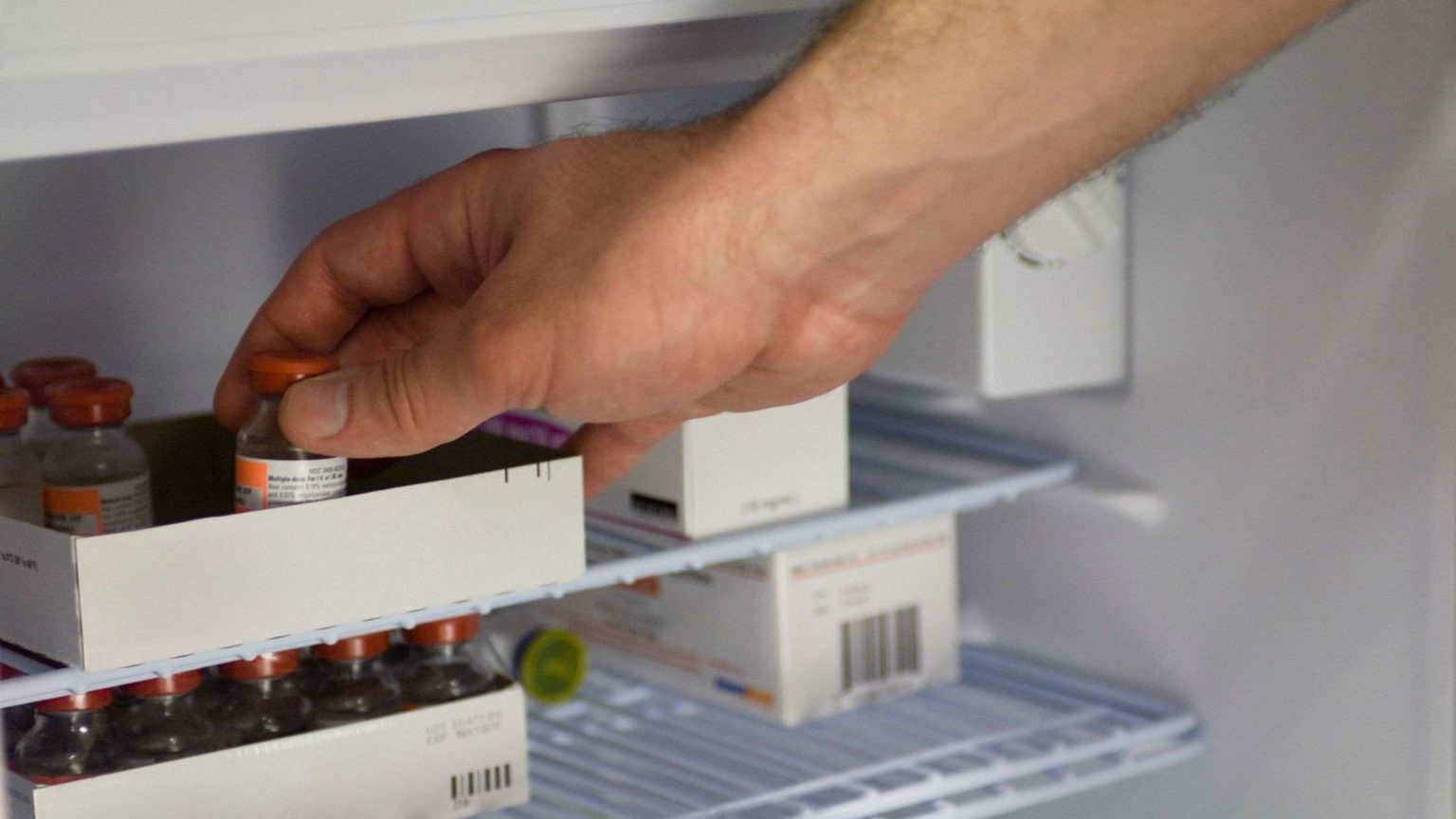
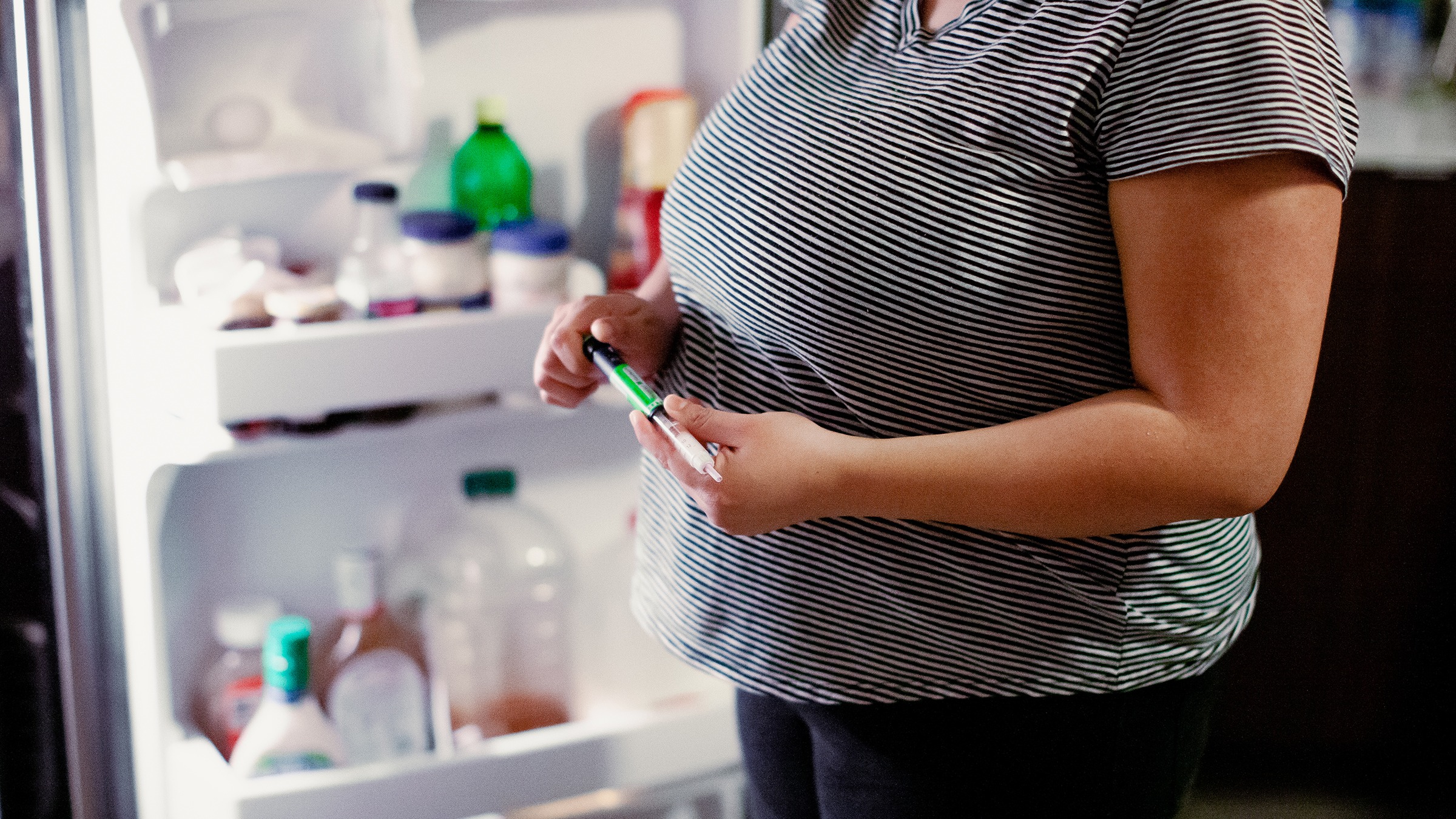
How To Store Insulin Without Refrigeration
Modified: January 6, 2024
Learn how to store insulin without refrigeration in our informative articles. Find helpful tips and guidelines to keep your insulin safe and effective.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Insulin is a life-saving medication for individuals with diabetes. It is essential to store insulin properly to maintain its effectiveness. While refrigeration is the recommended storage method, there may be situations where access to refrigeration is limited or not available. This article will explore alternative storage methods for insulin when refrigeration is not possible.
Understanding how to store insulin without refrigeration is crucial for individuals who are traveling, camping, or facing power outages. It is important to note that insulin should not be exposed to extreme temperatures, as both heat and freezing can degrade its potency.
In this article, we will discuss the factors that can affect insulin storage and explore alternative storage methods to ensure the integrity and efficacy of this life-sustaining medication.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper insulin storage is crucial for maintaining its effectiveness and ensuring optimal blood sugar control. Alternative storage methods, such as cooling cases and deep storage, provide solutions when refrigeration is not available.
- Factors like temperature, humidity, and light exposure can impact insulin storage. Following recommended storage tips and consulting healthcare professionals are essential for preserving insulin potency and effectiveness.
Read more: How To Store Insulin
Understanding Insulin Storage
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels in the body. It is commonly used by individuals with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2 diabetes who require insulin therapy. Insulin is typically supplied in vials, cartridges, or pre-filled pens. These containers can be sensitive to temperature fluctuations, which can affect insulin’s potency and effectiveness.
The ideal temperature range for storing insulin is between 36°F (2°C) and 46°F (8°C). However, most types of insulin can be stored at room temperature (between 59°F and 86°F or 15°C and 30°C) for up to 28 days, as long as they are kept away from direct heat and sunlight. Insulin that is stored at room temperature should be discarded after the recommended number of days, as indicated on the packaging or by the manufacturer.
It is important to note that insulin should never be frozen, as freezing can damage the molecular structure of the medication and render it ineffective. Additionally, excessively high temperatures, such as those above 86°F (30°C), can also degrade insulin and decrease its potency.
Some insulin preparations, such as insulin suspensions, may require gentle agitation or mixing before use. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper handling and use of the specific type of insulin.
Proper insulin storage is vital to maintain its therapeutic effects and ensure accurate dosing. Failure to store insulin correctly can lead to inadequate blood sugar control, which can have serious health consequences for individuals with diabetes.
Factors Affecting Insulin Storage
Several factors can affect the storage of insulin and compromise its effectiveness. It is important to be aware of these factors and take necessary precautions to maintain the integrity of the medication:
- Temperature: Insulin is highly sensitive to temperature. Extreme heat or cold can impact its quality and potency. It is crucial to store insulin within the recommended temperature range of 36°F (2°C) to 46°F (8°C). Avoid exposing insulin to direct sunlight or placing it near heat sources such as radiators or heating vents.
- Humidity: High humidity can cause moisture to enter insulin vials or cartridges, affecting their stability and potency. It is best to store insulin in a dry environment and avoid exposing it to excessive moisture.
- Light exposure: Insulin should be kept away from direct sunlight or bright artificial light sources. Light exposure can degrade insulin and reduce its effectiveness. It is advisable to store insulin in a dark place or use an opaque storage case.
- Vibration: Vigorous shaking or excessive vibration can affect the structure of insulin molecules, leading to reduced efficacy. Avoid storing insulin near vibrating appliances or in areas prone to regular movement or agitation.
- Expiration dates: Always check the expiration date on insulin packaging. Expired insulin may not be effective in managing blood sugar levels and can lead to inadequate control. Discard any insulin that has expired.
- Contamination: Proper hygiene practices are essential when handling insulin. Contamination can occur from touching the rubber stopper of a vial or cartridge with bare hands or reusing needles. Clean hands and the use of new sterile needles for each injection are vital to prevent contamination and maintain insulin storage integrity.
It is important to be mindful of these factors and take appropriate measures to ensure that insulin remains safe and effective for use. Lack of proper storage can lead to suboptimal blood sugar control and potentially harmful health consequences.
Alternative Storage Methods
When refrigeration is not accessible or feasible, there are alternative storage methods available to keep insulin safe and effective. Here are some options to consider:
- Insulin Cooling Cases: Insulin cooling cases are portable devices designed to keep insulin at the recommended temperature range even when refrigeration is unavailable. These cases typically use a gel pack or cooling element to maintain a cool temperature. They are convenient for travel or situations where access to a refrigerator is limited. Insulin cooling cases come in various sizes and can be easily carried in bags or pockets.
- Thermos or Vacuum Flask: A thermos or vacuum flask can also be used to store insulin without refrigeration. These containers provide insulation and can help maintain a consistent temperature for an extended period. It is important to pre-cool the thermos or vacuum flask before placing the insulin inside to ensure optimal storage conditions.
- Deep Storage: Deep storage refers to storing insulin in a cool, dry place such as a basement or cellar. These areas tend to maintain a more stable temperature compared to other parts of the house. It is essential to monitor the temperature regularly and ensure that it stays within the recommended range.
- Cooler Bags: Cooler bags, often used for food storage, can also be utilized to keep insulin cool. By placing ice packs or frozen gel packs in the cooler bag along with the insulin, a cool environment can be maintained. It is important to ensure that the insulin does not come into direct contact with the ice packs, as extreme cold can damage the medication.
- Absorption Material: Some individuals use insulation material, such as towels or bubble wrap, to create a protective barrier around insulin vials or cartridges. This helps in reducing temperature fluctuations and preventing exposure to excessive heat or cold. However, it is important to monitor the temperature regularly to ensure that the insulation material is effective.
When using alternative storage methods, it is crucial to monitor the temperature regularly and ensure that it stays within the recommended range. Insulin should be visually inspected for any changes in appearance or consistency before each use. If there are any doubts about the quality or effectiveness of the insulin, it is best to err on the side of caution and consult a healthcare professional.
It is important to note that alternative storage methods are intended for short-term use. If refrigeration is not available for an extended period, it is advisable to seek an alternative solution or consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Store insulin at room temperature (59-86°F) for up to 28 days. Keep it away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Once in use, keep it at room temp for up to 28 days.
Using Insulin Cooling Cases
Insulin cooling cases are a popular and convenient solution for storing insulin without refrigeration. These portable devices are designed to maintain the optimal temperature range for insulin storage, ensuring its effectiveness. Here are some tips on effectively using insulin cooling cases:
- Choose the right size: Insulin cooling cases come in various sizes to accommodate different quantities of insulin. Select a case that can comfortably fit your insulin vials, cartridges, or pens.
- Pre-cool the case: Before placing the insulin inside the cooling case, make sure to pre-cool it. This can be done by leaving the case in a refrigerator or freezer for a couple of hours. Pre-cooling helps to maintain the desired temperature once the insulin is inside.
- Place the cooling element: Most insulin cooling cases come with a cooling element, such as a gel pack or ice pack. Insert the cooling element into the designated compartment of the case. Some cases require activation by immersing the cooling element in cold water before placing it in the case.
- Organize the insulin: Arrange the insulin vials, cartridges, or pens securely within the cooling case, making sure they are not in direct contact with the cooling element. Some cases have elastic straps or pouches to hold the insulin in place and prevent movement.
- Monitor the temperature: Insulin cooling cases typically have a temperature display or indicator to help you monitor the internal temperature. Regularly check the temperature to ensure it remains within the recommended range.
- Replace cooling element as needed: Depending on the type of cooling element used, it may need to be replaced periodically. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper maintenance and replacement of the cooling element.
- Consider the duration of use: Insulin cooling cases are designed for temporary storage when refrigeration is not available. If you anticipate longer periods without refrigeration, it is advisable to seek alternative storage options or consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Insulin cooling cases provide a convenient and reliable solution for storing insulin without refrigeration, especially during travel or other situations where access to a refrigerator is limited. However, it is important to remember that these cases are not a substitute for proper refrigeration and should be used as a temporary measure.
Always inspect the insulin before use to ensure it remains clear and free of particles. If there are any doubts about the quality or effectiveness of the insulin, discard it and consult a healthcare professional for further guidance.
Read more: How To Store Insulin Pen
Insulin Storage Tips and Recommendations
Proper insulin storage is crucial to maintaining its potency and effectiveness. Here are some important tips and recommendations to ensure the optimal storage of insulin:
- Keep insulin refrigerated when possible: Refrigeration is the preferred method of insulin storage. It helps maintain a consistent and appropriate temperature for insulin. Store insulin in the refrigerator between 36°F (2°C) and 46°F (8°C), away from food items.
- Avoid freezing insulin: Freezing temperatures can damage insulin and render it ineffective. Keep insulin away from the freezer compartment of the refrigerator and prevent exposure to extreme cold.
- Store insulin away from direct heat and sunlight: Insulin should be protected from exposure to direct heat sources, such as stoves, heaters, and direct sunlight. Heat can degrade the medication and reduce its efficacy. Store insulin in a cool, dark place away from these sources.
- Do not store insulin in the car: Temperature extremes in a parked car can greatly affect insulin. Avoid leaving insulin inside a car, especially during hot or cold weather.
- Check expiration dates: Insulin has an expiration date indicated on the packaging. Always check the expiration date before using insulin, and discard any expired medication. Using expired insulin may lead to inadequate blood sugar control.
- Inspect insulin before use: Before each use, visually inspect the insulin for any changes in appearance, such as clumps, discoloration, or particles. If the insulin appears abnormal or different, it is best to discard it and use a new vial or cartridge.
- Keep insulin in its original packaging: Insulin should be stored in its original packaging until ready for use. This helps protect it from light exposure and maintains its integrity.
- Keep insulin out of reach of children and pets: Insulin is a medication that should be kept out of reach and sight of children and pets. Accidental ingestion can be dangerous and require immediate medical attention. Always store insulin in a secure and safe location.
- Consult with healthcare professionals: If you have any concerns or questions regarding insulin storage, it is always best to consult with your healthcare team. They can provide specific recommendations and guidance based on your individual needs.
Following these storage tips and recommendations will help ensure the potency and effectiveness of your insulin. It is important to remember that proper storage is essential for maintaining blood sugar control and overall diabetes management.
Conclusion
Proper insulin storage is essential for maintaining its effectiveness and ensuring optimal blood sugar control for individuals with diabetes. While refrigeration is the recommended method, there are alternative storage options available when access to a refrigerator is not possible. Understanding the factors that can affect insulin storage and implementing the appropriate measures can help preserve its potency.
Factors such as temperature, humidity, light exposure, vibration, expiration dates, and contamination can impact insulin storage. Being aware of these factors and taking necessary precautions can help maintain the integrity of the medication.
Alternative storage methods, such as insulin cooling cases, thermos/vacuum flasks, cooler bags, deep storage, and insulation materials, can be effective in keeping insulin at the recommended temperature range. It is important to monitor the temperature regularly and replace cooling elements or insulation materials as needed.
In addition to alternative storage methods, following recommended insulin storage tips is crucial. Keeping insulin refrigerated, avoiding freezing, protecting it from heat and light, checking expiration dates, and inspecting insulin before use are key practices to ensure its effectiveness.
Consulting with healthcare professionals is always advisable when it comes to insulin storage and diabetes management. They can provide personalized recommendations based on individual needs and specific situations.
Remember that proper insulin storage is a vital part of diabetes care. By following these guidelines, individuals can maintain the potency and effectiveness of insulin, enabling them to effectively manage their blood sugar levels and lead a healthy and active life.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Insulin Without Refrigeration
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Store Insulin Without Refrigeration”