

Articles
How To Store Tinctures
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn the best techniques for storing tinctures in this comprehensive collection of articles. Ensure the longevity and potency of your herbal remedies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
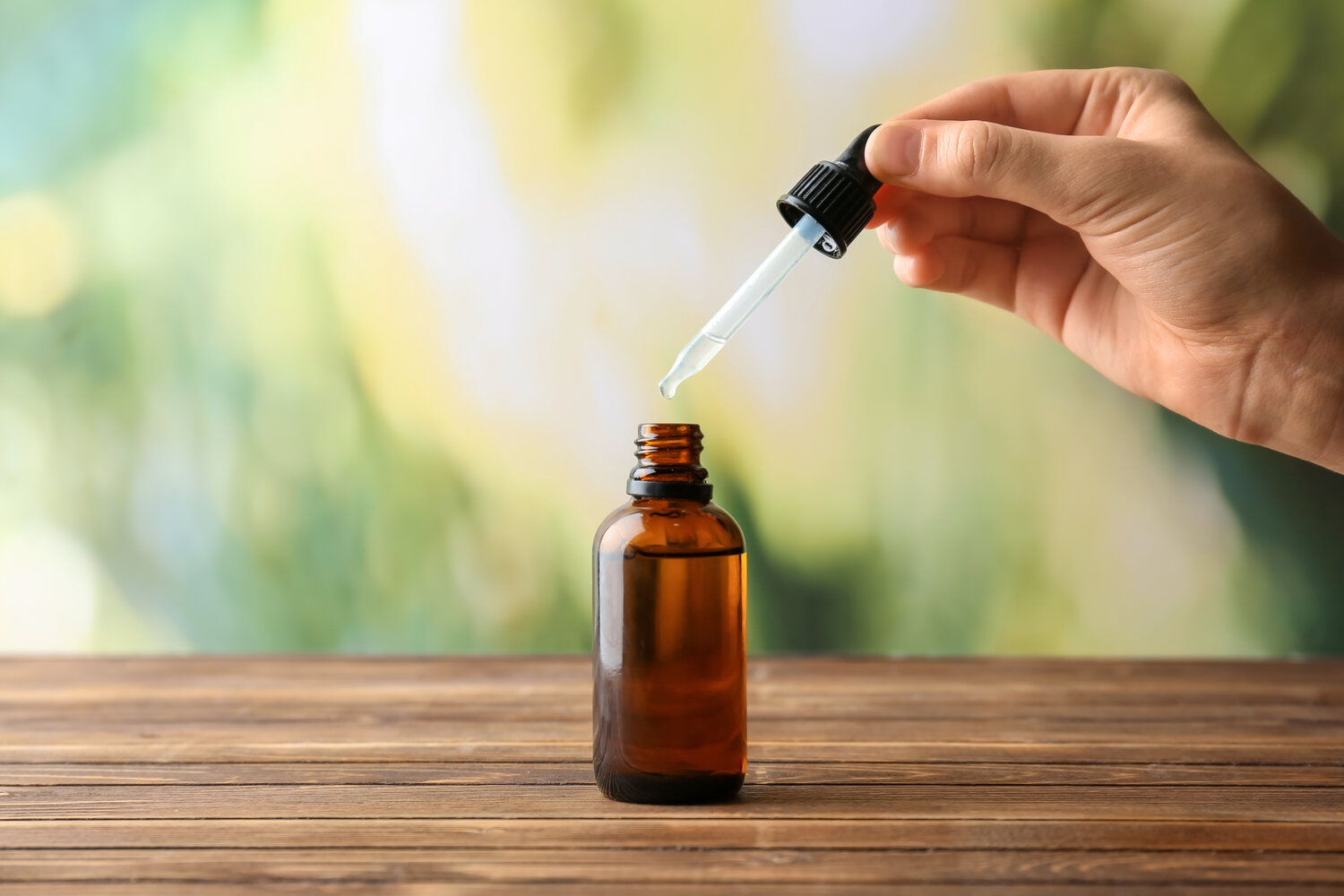
Tinctures are highly concentrated herbal extracts that have been used for centuries for their medicinal properties. They are made by soaking plant materials such as leaves, flowers, or roots in a solvent, typically alcohol or glycerin, to extract their beneficial compounds. Tinctures are a popular form of herbal medicine due to their potency and long shelf-life.
When it comes to storing tinctures, proper care is essential to maintain their potency and quality over time. In this article, we will explore the best practices for storing tinctures to ensure their effectiveness and longevity.
Understanding the nature of tinctures is crucial for proper storage. Tinctures are highly concentrated extracts, which means that a small amount can provide a potent dose of medicinal compounds. Therefore, it is vital to protect them from factors that can degrade their quality, such as light, heat, and air.
In the following sections, we will discuss the key considerations for storing tinctures, including choosing the right containers, maintaining proper storage conditions, preventing contamination, and labeling and organizing techniques. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your tinctures remain potent and effective for an extended period.
Key Takeaways:
- Store tinctures in dark glass bottles in a cool, stable location away from light and heat to maintain potency and effectiveness.
- Prevent contamination by using clean utensils, tightly sealing containers, and storing tinctures separately to ensure purity and safety.
Read more: How To Make Thyme Tincture?
Understanding Tinctures
Tinctures are liquid extracts that are made by soaking plant materials in a solvent to extract their beneficial compounds. The solvent used in tincture making is typically alcohol, such as vodka or grain alcohol, but glycerin or vinegar can also be used as alternatives. The process of creating a tincture involves macerating or grinding the plant material and then steeping it in the chosen solvent for a specific period. During this time, the solvent extracts the plant’s active compounds, resulting in a concentrated liquid.
One of the defining characteristics of tinctures is their high concentration. Due to the extraction process, tinctures pack a powerful punch in terms of potency. A small dose can deliver a significant amount of the plant’s medicinal properties. This makes tinctures a popular choice for those seeking an efficient and convenient way to consume herbal remedies.
Tinctures offer several advantages over other forms of herbal medicine. Firstly, they have a longer shelf-life compared to dried herbs or powdered extracts. The concentrated nature of tinctures, coupled with the preservative properties of alcohol, helps to extend their longevity. Proper storage is crucial to maintain the quality and efficacy of tinctures over time.
Another advantage of tinctures is their ease of use. They are highly versatile and can be ingested orally or added to beverages or topical products. By using a dropper, it’s easy to measure and control the dosage, making tinctures a convenient option for those who want precise administration.
Tinctures are available in a wide range of plant varieties, each with its unique medicinal properties. From herbs like echinacea and valerian root to flowers like chamomile and lavender, the possibilities for creating tinctures are endless. Different plants have different solubilities, so it is essential to choose the appropriate solvent and extraction method for optimal potency and effectiveness.
Now that we have a basic understanding of tinctures, let’s explore the best practices for storing them to maximize their shelf-life and maintain their potency.
Choosing the Right Containers
When it comes to storing tinctures, choosing the right containers is of utmost importance. The containers you select should be able to preserve the potency and quality of the tincture while protecting it from environmental factors that can degrade its effectiveness.
Glass containers are the ideal choice for storing tinctures. Amber or cobalt blue glass bottles are particularly recommended as they offer better protection against light. Light exposure can cause the breakdown of important compounds in the tincture, resulting in decreased potency. Additionally, glass containers do not interact with the tincture, ensuring that no unwanted substances leach into the mixture.
Avoid using plastic or metal containers for storing tinctures, as they can react with the solvent or extract and contaminate the tincture. These materials are also more prone to allowing light and air to penetrate, which can degrade the quality and potency of the tincture over time.
Furthermore, the size of the container should be chosen based on the quantity of tincture you anticipate using within a reasonable amount of time. Having a smaller container will prevent excess air inside, reducing oxidation and potential degradation. However, if you plan to store large quantities of tincture, consider using multiple smaller containers to minimize the exposure of the bulk of the tincture to air and light.
In addition to the material and size, consider using containers with a tight-sealing cap or dropper to prevent air and moisture from entering. This will help maintain the tincture’s potency and extend its shelf-life.
To further protect your tinctures, store them in a cool and dark place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Light and heat can accelerate the deterioration of the tincture, leading to a decrease in its medicinal efficacy over time.
By selecting the appropriate glass containers with tight-sealing caps and storing them in a cool, dark location, you can ensure that your tinctures remain potent and effective for an extended period.
Proper Storage Conditions
Proper storage conditions are crucial for maintaining the potency and quality of tinctures. When exposed to unfavorable environments, tinctures can degrade, resulting in a loss of medicinal efficacy. By following the recommended storage conditions, you can ensure that your tinctures remain effective for a longer period of time.
The first step in ensuring proper storage is to find a cool and dark location. Tinctures are sensitive to light, heat, and humidity, which can accelerate their degradation. Direct sunlight can cause the breakdown of the active compounds in the tincture, leading to a decrease in its potency. Heat can also have a negative impact by speeding up the oxidation process. Consequently, it is important to store tinctures away from windows or other areas prone to direct sunlight, as well as heat sources like radiators or stoves. Keeping tinctures in a cool and dark place, such as a pantry or cupboard, will help maintain their integrity.
In addition to temperature and light, humidity can also affect the quality of the tincture. Excessive moisture in the air can lead to mold or bacterial growth, which can contaminate the tincture and render it unsafe for use. Therefore, it is important to choose a storage location that has low humidity levels and ensure that the tincture is tightly sealed to prevent moisture from entering.
If you live in a particularly humid climate, consider using desiccant packets or silica gel packs inside the storage container to absorb excess moisture and maintain the integrity of the tincture.
Another factor to consider is the stability of the storage environment. Fluctuating temperature and humidity levels can accelerate the degradation of tinctures. Aim for a stable storage environment with consistent temperature and humidity to prolong the shelf-life of the tincture.
Lastly, it is important to keep tinctures out of reach of children and pets. Tinctures contain concentrated medicinal compounds and should be stored in a secure location, preferably in a locked cabinet or high shelf.
By adhering to these proper storage conditions, you can ensure your tinctures remain potent and effective for an extended period, preserving their medicinal properties and providing you with the desired health benefits.
Avoiding Exposure to Light
Exposure to light is one of the primary factors that can degrade the quality and potency of tinctures. Light, particularly sunlight and fluorescent lighting, can break down the active compounds present in tinctures, resulting in a decrease in their medicinal effectiveness over time. Therefore, it is crucial to store tinctures in a way that minimizes their exposure to light.
The best way to protect tinctures from light is to store them in dark-colored glass bottles. Amber or cobalt blue glass bottles are highly recommended for their ability to filter out harmful UV rays and minimize light penetration. These darker glass bottles provide an extra layer of protection, shielding the tincture from direct light and reducing the risk of degradation.
When storing tinctures, keep them in a cool, dark place away from direct sunlight. Avoid placing them near windows or in areas where they can be exposed to excessive light. Even small amounts of light over time can contribute to the degradation of the tincture’s active compounds.
If you prefer to display your tinctures for easy access, consider using opaque or dark-colored storage containers to preserve their integrity. This way, you can still have them readily available while minimizing their exposure to light.
It is also important to note that some tinctures may be more sensitive to light than others. Certain herbal extracts, such as those derived from plants with light-sensitive pigments or volatile compounds, may require even greater protection from light exposure. In these cases, consider storing them in an additional layer of dark wrapping or in a box to provide extra shielding.
Additionally, you should handle tincture bottles with care to avoid unnecessary exposure to light. Avoid opening the bottles for extended periods and be mindful when dispensing the tincture to minimize exposure to light and air. Reseal the bottle tightly immediately after each use to maintain its potency.
By taking the necessary precautions to avoid exposure to light, you can ensure that your tinctures retain their potency and effectiveness for a longer duration. By preserving the integrity of the active compounds, you can continue to benefit from the therapeutic properties of your tinctures.
Store tinctures in a cool, dark place away from direct sunlight and heat to maintain their potency. A cabinet or drawer works well for this purpose.
Read more: Where Can I Buy Thyme Tincture
Maintaining Consistent Temperature
Maintaining a consistent temperature is essential for preserving the potency and quality of tinctures. Fluctuations in temperature can accelerate the degradation process, leading to a decrease in the effectiveness of the tincture over time. Therefore, it is important to store tinctures in an environment with a stable temperature.
Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can adversely affect the integrity of tinctures. High temperatures can promote chemical reactions that degrade the active compounds in the tincture, while low temperatures can cause the formation of crystals or other solid precipitates that alter the composition of the liquid.
It is recommended to store tinctures at a cool and constant temperature. Aim for a range between 59°F (15°C) and 77°F (25°C). Avoid storing tinctures in areas that experience significant temperature fluctuations, such as near radiators, ovens, or windows. It is best to select a location that maintains a relatively stable temperature throughout the year.
If you live in a region with extreme temperatures, consider storing your tinctures in a temperature-controlled environment, such as a cupboard or pantry. These areas tend to have a more consistent temperature compared to other parts of the house.
In addition to the ambient temperature, it is important to also consider the temperature during transportation or travel. If you need to transport your tinctures, try to keep them in insulated containers or bags to mitigate temperature fluctuations. This is especially important when traveling in hot or cold weather conditions, as the tinctures can be exposed to extreme temperatures that can compromise their quality.
Furthermore, avoid storing tinctures in the refrigerator unless specific instructions indicate that refrigeration is necessary. While refrigeration can help prolong the shelf-life of certain medications, it is generally not recommended for most herbal tinctures. The low temperatures and condensation in refrigerators can negatively impact the quality and stability of the tincture by introducing moisture and potential contamination.
By maintaining a consistent temperature within the recommended range, you can help preserve the potency and quality of your tinctures. Ensuring a stable environment for storage will contribute to their effectiveness and longevity, allowing you to benefit from the full therapeutic properties of the tinctures.
Preventing Contamination
Preventing contamination is crucial for maintaining the quality and safety of tinctures. Contamination can occur from various sources, such as airborne particles, microorganisms, or improper handling techniques. By following proper storage and handling practices, you can minimize the risk of contamination and ensure the longevity of your tinctures.
One of the most important steps in preventing contamination is to ensure that all the equipment and containers used for making and storing tinctures are thoroughly cleaned and sterilized. Before starting the tincture-making process, sanitize bottles, jars, and equipment by washing them with hot, soapy water and rinsing them thoroughly. Allow them to air dry or use a clean cloth to dry them completely.
When handling tinctures, remember to use clean utensils and tools to prevent cross-contamination. Avoid using your bare hands when dispensing tinctures, as it can introduce bacteria or other impurities. Instead, use droppers or pipettes to transfer the tincture from the storage container to the desired application or measurement.
It is also essential to avoid touching the dropper or pipette directly to any surface or body part to prevent the transfer of contaminants. Instead, hold the dropper or pipette a few inches above the intended target and allow the liquid to dispense without contact.
Proper hygiene practices, such as washing hands before handling tinctures, can also help minimize contamination risks. Regularly clean the storage area and any surfaces that come into contact with the tinctures to ensure a clean and sanitary environment.
When using tinctures, be sure to properly close the containers after each use to prevent the entry of contaminants. Make sure the lids or caps are tightly sealed to maintain the integrity of the tincture and avoid exposure to air, moisture, or foreign particles.
Additionally, it is essential to store different tinctures separately to avoid cross-contamination. Mixing different tinctures in the same container can not only affect their individual properties but also increase the risk of contamination. Store each tincture in its own properly labeled container to maintain its distinct characteristics and prevent potential interactions.
Lastly, be mindful of the expiration dates of your tinctures. Over time, tinctures may lose their potency or become susceptible to contamination. Take note of the recommended shelf-life and storage duration provided by the manufacturer or herbalist and discard any tinctures that have expired or show signs of spoilage.
By following these preventive measures, you can safeguard the quality and purity of your tinctures, allowing you to continue benefiting from their therapeutic properties without any concerns of contamination or degradation.
Labeling and Organizing
Labeling and organizing your tinctures is essential for easy identification, proper usage, and maintaining an efficient storage system. By implementing effective labeling and organizing techniques, you can ensure that your tinctures are well-managed and easily accessible when needed.
The first step in this process is to label each tincture container accurately and clearly. Include the name of the plant or herbs used to make the tincture, the date of preparation, and any specific instructions or dosage recommendations. Additionally, it is helpful to note any additional information, such as the intended purpose or the extraction method used.
When labeling, use high-quality markers or labels that will not easily fade or rub off. Ensure that the labels are securely affixed to the containers and won’t easily detach or become illegible over time. If possible, opt for water-resistant or smudge-proof labels to prevent damage from spills or handling.
Organizing your tinctures in a systematic manner is equally important. Consider arranging them alphabetically, by the plant name or primary ingredient, to make it easy to find the desired tincture quickly. Alternatively, you can categorize them based on their purpose, such as immune support, digestive health, or sleep aid, to suit your preferences and needs.
Choose a dedicated storage space for your tinctures, such as a designated cupboard, shelf, or drawer. This will help keep them organized and prevent potential mix-ups or accidental misuse. Keep in mind the storage conditions discussed earlier, such as avoiding exposure to light and maintaining a consistent temperature, as you select the ideal location for your collection.
Avoid overcrowding the storage area to ensure proper air circulation and prevent accidental spills or breakage. Allow enough space between containers to facilitate easy retrieval without knocking over neighboring tinctures.
Consider using additional storage accessories to enhance organization and accessibility. For example, small baskets, dividers, or labeled boxes can help separate tinctures based on specific categories, making it easier to locate them when needed. Applying a color-coding system using stickers or markers can offer a visual cue for quick identification.
Regularly perform inventory checks to ensure you have a clear understanding of the tinctures you have on hand. Discard any expired or degraded tinctures and make note of those that may require replenishment. This will help maintain an up-to-date and effective herbal medicine collection, ensuring that you always have access to high-quality tinctures when needed.
By implementing effective labeling and organizing strategies, you can easily identify and locate your tinctures, promote proper usage, and maintain a well-managed storage system. This not only saves time and minimizes potential confusion but also helps to preserve the quality and potency of your tinctures for maximum benefit.
Shelf-Life and Storage Duration
Understanding the shelf-life and storage duration of tinctures is vital to ensure their effectiveness and safety. While tinctures have a longer lifespan compared to other forms of herbal preparations, they can still degrade over time if not stored properly.
The shelf-life of a tincture can vary depending on several factors, including the type of plant material used, the extraction method, and the storage conditions. Generally, alcohol-based tinctures have a longer shelf-life compared to glycerin-based ones.
On average, properly stored tinctures can maintain their potency for about 3 to 5 years. However, it is important to note that this is a general guideline, and some tinctures may last shorter or longer depending on their specific characteristics.
During the storage duration, it is recommended to periodically check the tinctures for any signs of spoilage or degradation. Examine the color, aroma, and taste of the tincture. Any significant changes, such as a foul smell or a noticeable difference in color, may indicate that the tincture has degraded and should be discarded.
To ensure the longevity of your tinctures, it is crucial to store them in ideal conditions. As discussed earlier, store the tinctures in dark-colored glass bottles to protect them from light. Keep them in a cool and stable environment, avoiding exposure to direct sunlight, heat sources, and excessive humidity.
Properly sealed and labeled containers also help maintain the quality of the tinctures. Make sure the lids or caps are tightly sealed after each use to prevent air, moisture, or contaminants from entering the tincture. Properly labeled bottles help track their preparation date and usage, allowing you to monitor their freshness and potency accurately.
It is important to note that some tinctures may require specific storage conditions or have a shorter shelf-life. For example, tinctures made from delicate herbs or volatile compounds may be more prone to degradation and may require additional precautions or a shorter storage duration. Always consult the specific guidelines provided by the herbalist, manufacturer, or reference sources for optimal storage practices.
Additionally, consider the frequency of use when preparing tinctures. It is advisable to make smaller batches that can be used within a reasonable time frame, rather than making large quantities that may not be consumed before their potency diminishes.
If you have tinctures that have exceeded their storage duration or show signs of spoilage, it is best to discard them. Using degraded tinctures may result in reduced effectiveness and potential safety risks.
By understanding the shelf-life of tinctures and implementing proper storage practices, you can maximize their potency and safety, ensuring that your herbal remedies remain effective and beneficial for an extended period.
Read more: How To Store Basil From Store
Conclusion
Properly storing tinctures is essential for maintaining their potency, quality, and effectiveness. By understanding the nuances of tincture storage and following best practices, you can ensure that your herbal extracts remain fresh and therapeutic for an extended period.
Choosing the right containers, such as dark-colored glass bottles, helps shield tinctures from light and air exposure. Avoid using containers made of plastic or metal, as they can react with the tincture or allow light and contaminants to penetrate.
Maintaining consistent temperature and humidity levels is critical for preserving the integrity of tinctures. Fluctuations in temperature and exposure to excessive heat or cold can accelerate degradation, compromising their effectiveness. Find a cool and stable storage location, away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
Preventing contamination requires proper hygiene practices, including sanitizing the containers and tools used for tincture preparation, as well as using clean utensils. Keep tinctures tightly sealed to avoid air, moisture, and contaminants. Store different tinctures separately to avoid cross-contamination and label them accurately for clear identification.
Labeling and organizing your tincture collection enhances easy retrieval and proper usage. Clearly label each container with key information, such as the plant or herb used, the date of preparation, and any specific instructions. Organize your tinctures in a logical manner, whether alphabetically or by purpose, in a dedicated storage space.
Understanding the shelf-life and storage duration of tinctures ensures their potency and safety. While most tinctures can last 3 to 5 years when stored properly, it is essential to periodically check for signs of spoilage or degradation. Discard any tinctures that have surpassed their shelf-life or show noticeable changes in color, aroma, or taste.
By following these guidelines, you can confidently store and maintain your tinctures, optimizing their longevity and therapeutic benefits. Proper storage practices allow you to harness the full potential of these concentrated herbal extracts whenever you need them, promoting your overall well-being naturally.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Tinctures
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How To Store Tinctures”