

Articles
What Is A High Nitrogen Fertilizer
Modified: January 19, 2024
Learn all about high nitrogen fertilizers and how they can benefit your plants. Read our informative articles on the different types and best practices for using nitrogen-rich fertilizers.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to cultivating healthy and thriving plants, one of the essential elements for their growth is nitrogen. Nitrogen is a vital nutrient that plays a crucial role in various plant processes, including leaf and stem development, photosynthesis, and overall plant vigor. While soil typically contains some amount of nitrogen, it may not always be sufficient to meet the needs of certain plants or to enhance the growth of specific crops.
To address this, gardeners and farmers often turn to high nitrogen fertilizers to supplement the soil with an additional boost of nitrogen. High nitrogen fertilizers are formulated to provide a concentrated dose of this essential nutrient, ensuring that plants have an ample supply of nitrogen available for their optimal growth and development.
In this article, we will delve into the world of high nitrogen fertilizers, exploring their importance in plant growth and the various types available. We will also discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using these fertilizers, as well as provide recommendations on their application and dosage. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of high nitrogen fertilizers and how to make the most effective use of them in your gardening or farming endeavors.
Key Takeaways:
- High nitrogen fertilizers are essential for promoting vigorous plant growth, enhancing chlorophyll production, and increasing crop yield, but their responsible use is crucial to avoid environmental pollution and nutrient imbalances.
- Understanding the specific needs of plants, following recommended application rates, and considering environmental impact are vital for maximizing the benefits of high nitrogen fertilizers while minimizing potential risks.
Read also: 14 Amazing High Nitrogen Fertilizer for 2024
What Is Nitrogen?
Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth and is one of the primary components of amino acids, proteins, and chlorophyll. It is a crucial building block for plant cells and plays a fundamental role in the overall health and development of plants. Nitrogen is obtained by plants from the soil, primarily in the form of nitrate, ammonium, and organic matter.
Plants require a sufficient supply of nitrogen to support various physiological processes. It aids in the formation of new plant tissue, including leaves, stems, and shoots. Nitrogen is also involved in the synthesis of enzymes and proteins, which are vital for carrying out essential functions within plants.
One of the key functions of nitrogen is its role in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color and is essential for photosynthesis, contains nitrogen. Without an adequate supply of nitrogen, plants may exhibit stunted growth, chlorosis (yellowing of leaves), and reduced overall vigor.
Nitrogen is a dynamic nutrient that undergoes various transformations in the soil. It can be easily lost through leaching, volatilization, or denitrification, especially in sandy soils or periods of heavy rainfall. This makes it essential to provide plants with a reliable source of nitrogen through fertilization, especially when natural soil nitrogen levels are insufficient.
High nitrogen fertilizers help fulfill the nitrogen requirements of plants by providing a concentrated source of this essential nutrient. They can be particularly beneficial for crops with high nitrogen demands, such as leafy vegetables, grains, and grasses. However, it is essential to understand the characteristics and considerations associated with high nitrogen fertilizers to use them effectively and avoid any negative impact on plant health or the environment.
The Importance of Nitrogen in Plant Growth
Nitrogen is an integral component for plant growth and development, playing a crucial role in several key processes. Here are some of the primary reasons why nitrogen is essential to plant health:
- Protein Synthesis: Nitrogen is a vital building block for proteins, which are involved in almost all biological processes within plants. Proteins are responsible for cell structure, enzyme production, and metabolic reactions. A sufficient supply of nitrogen ensures that plants can synthesize the proteins needed for their growth and overall function.
- Leaf Development: Nitrogen is instrumental in promoting healthy leaf development. It stimulates the production of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for absorbing sunlight during photosynthesis. Adequate nitrogen levels contribute to lush, green foliage and robust leaf growth.
- Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into energy-rich carbohydrates. Nitrogen is a critical component of chlorophyll, which captures light energy for photosynthesis. Without sufficient nitrogen, plants may struggle to produce energy, leading to reduced growth and productivity.
- Root Growth: Nitrogen is vital for root development and expansion. It promotes the formation of lateral and adventitious roots, which help plants absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Robust root systems aid in nutrient uptake, improve water efficiency, and enhance overall plant stability and resilience.
- Fruit and Seed Formation: Nitrogen is necessary for the formation of reproductive structures in plants. It supports the growth of flowers, fruits, and seeds, influencing their size, quality, and yield. Adequate nitrogen levels contribute to increased flower production, leading to improved fruit set and seed development.
- Stress Resistance: Nitrogen plays a role in enhancing plant resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. It strengthens plants’ natural defense mechanisms, making them more resilient to diseases, pests, and environmental challenges such as drought or temperature extremes.
Overall, nitrogen is an indispensable nutrient for plants, impacting their growth, productivity, and overall health. It is important to ensure that plants receive a sufficient and balanced supply of nitrogen to maximize their potential and achieve optimal yields.
Understanding High Nitrogen Fertilizers
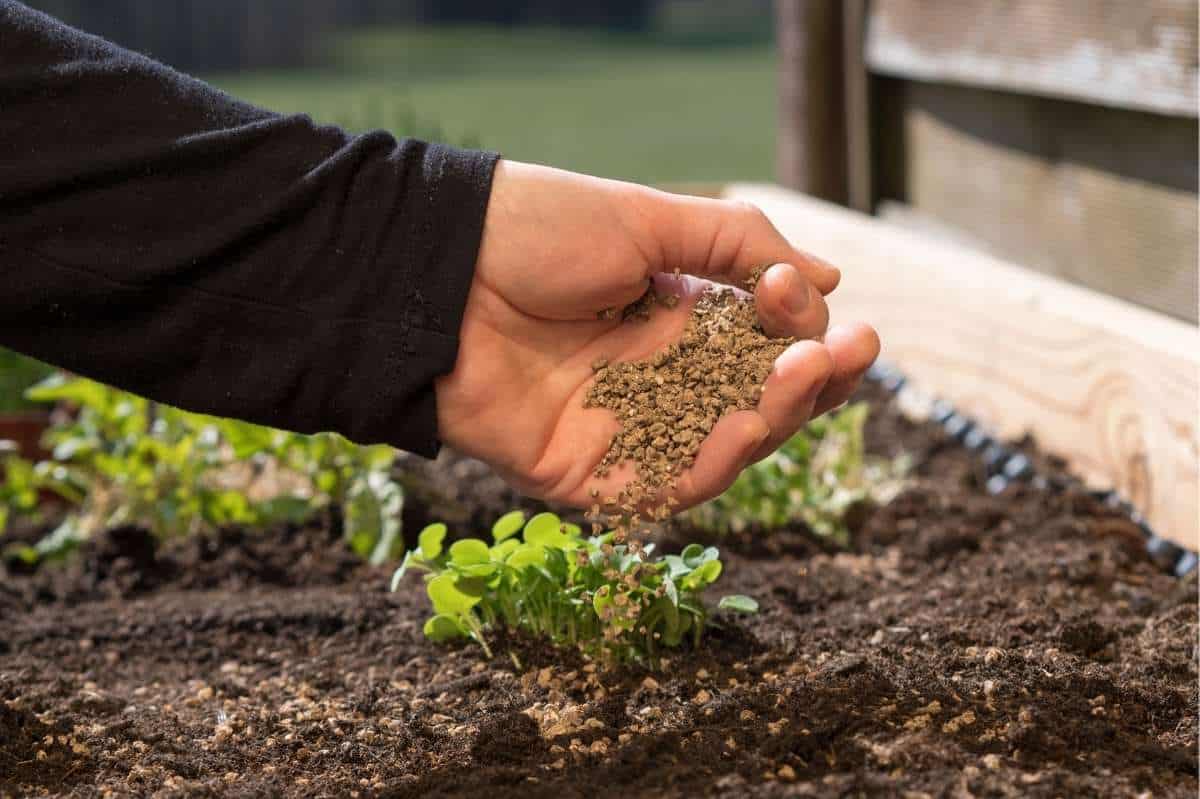
High nitrogen fertilizers are specifically formulated to provide plants with a concentrated source of nitrogen. These fertilizers are designed to replenish nitrogen levels in the soil and ensure plants have an ample supply to support their growth and development. Understanding the characteristics and advantages of high nitrogen fertilizers can help you make informed decisions on their usage in your gardening or farming practices.
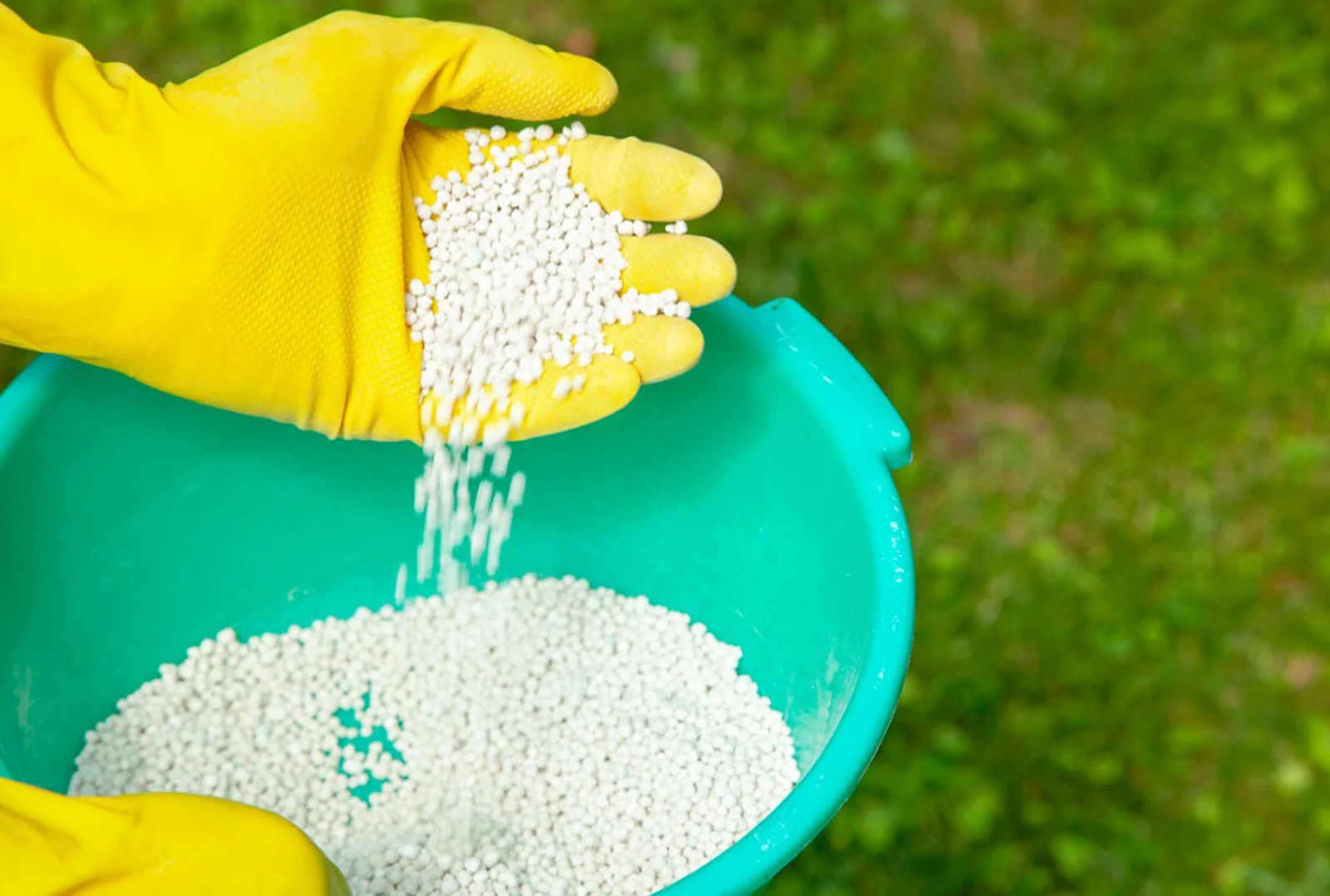
Nitrogen Content: High nitrogen fertilizers are distinguished by their elevated nitrogen content. These fertilizers typically contain nitrogen in the form of ammonium, nitrate, or urea. The nitrogen content is represented as a percentage by weight on fertilizer labels, commonly referred to as the fertilizer’s “N-P-K” ratio. For high nitrogen fertilizers, the nitrogen percentage is significantly higher compared to phosphorus (P) and potassium (K).
Rapid Release: High nitrogen fertilizers are often formulated for rapid release of nitrogen, meaning that the nitrogen becomes quickly available for plant uptake. This is particularly important for crops or plants with high nitrogen demands or in cases where a quick boost of nitrogen is required to address deficiencies.
Water-Soluble: Most high nitrogen fertilizers are water-soluble, allowing the nitrogen to dissolve in water and be readily absorbed by plant roots. This enhances the effectiveness and efficiency of nitrogen uptake by plants, ensuring that they can promptly access this essential nutrient.
Multiple Nitrogen Sources: High nitrogen fertilizers may contain a combination of different nitrogen sources to provide a balanced and sustained supply of nitrogen. This can include ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, urea, or other nitrogen-rich compounds. The use of multiple nitrogen sources helps ensure a steady and prolonged release of nitrogen, providing continuous nutrition to plants.
Application Methods: High nitrogen fertilizers can be applied to plants and soil through various methods. These include broadcasting the fertilizer uniformly over the soil surface, banding it alongside the planting rows, or incorporating it into the soil before planting. The appropriate application method will depend on the specific crop, soil conditions, and desired nutrient distribution.
High nitrogen fertilizers can be highly effective in boosting plant growth, especially when used judiciously and in conjunction with proper soil testing and analysis. However, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of your plants and the existing soil conditions to determine the appropriate dosage and application frequency of high nitrogen fertilizers.
Types of High Nitrogen Fertilizers
High nitrogen fertilizers come in various forms, each offering different nitrogen compounds and release rates. Understanding the different types can help you choose the most suitable high nitrogen fertilizer for your specific needs.
1. Ammonium Nitrate: Ammonium nitrate is a commonly used high nitrogen fertilizer that contains both ammonium and nitrate nitrogen. It is highly soluble and quickly releases nitrogen into the soil, making it readily available for plant uptake. However, due to its potential for misuse in certain industries, it may be restricted or unavailable for home gardeners in some regions.
2. Ammonium Sulfate: Ammonium sulfate is another popular high nitrogen fertilizer. It contains ammonium nitrogen and sulfur, providing a source of both essential nutrients. This fertilizer is relatively quick-release and works well in acidic soils, helping to lower pH levels.
3. Urea: Urea is a high nitrogen fertilizer that contains nitrogen in the form of urea. It is a solid, granular fertilizer that is easily diluted in water, making it suitable for irrigation systems or foliar applications. Urea has a slower release rate compared to other nitrogen fertilizers, providing a sustained supply of nitrogen over time.
4. Blood Meal: Blood meal is an organic high nitrogen fertilizer derived from dried and powdered animal blood. It is a slow-release fertilizer that provides a steady supply of nitrogen to plants. Blood meal is particularly beneficial for organic gardening and is commonly used to enhance nitrogen levels in soil. It also promotes healthy microbial activity in the soil.
5. Feather Meal: Feather meal is another organic high nitrogen fertilizer made from processed poultry feathers. It has a slow-release nature and gradually releases nitrogen into the soil as it breaks down. Feather meal is rich in protein and contains other essential nutrients, making it a valuable choice for organic gardeners.
6. Fish Emulsion: Fish emulsion is an organic liquid fertilizer made from fermented fish. It is a fast-acting fertilizer that provides an immediate dose of nitrogen to plants. Fish emulsion is often used as a foliar spray or in drip irrigation systems to supply plants with nutrients quickly.
Each type of high nitrogen fertilizer has its own characteristics and advantages. Consider factors such as the desired release rate, application method, and the specific needs of your plants when choosing the most suitable fertilizer for your gardening or farming practices.
Read more: What Fertilizer Is High In Phosphorus
Advantages of Using High Nitrogen Fertilizers
Using high nitrogen fertilizers can offer several advantages when it comes to promoting plant growth and maximizing agricultural productivity. Here are some of the key benefits of incorporating high nitrogen fertilizers into your gardening or farming practices:
- Promotes Vigorous Growth: High nitrogen fertilizers provide plants with a concentrated source of nitrogen, which is essential for promoting lush, green foliage and overall plant vigor. Nitrogen stimulates leaf and stem development, resulting in more robust and healthy plants.
- Enhances Chlorophyll Production: Nitrogen is a crucial component of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for capturing sunlight and driving photosynthesis. Adequate nitrogen levels ensure that plants can produce sufficient chlorophyll, maximizing their ability to convert sunlight into energy.
- Increases Crop Yield: When plants have access to an ample supply of nitrogen, they can allocate more resources towards reproductive growth, such as flower and fruit production. This, in turn, increases crop yield and improves the quality of harvested produce.
- Improves Nutrient Uptake: Nitrogen is involved in enhancing the uptake of other essential nutrients by plants. It plays a role in root development and the formation of root hairs, which increase the surface area for nutrient absorption. By using high nitrogen fertilizers, you can boost nutrient uptake efficiency and ensure that plants have access to a balanced nutrient supply.
- Addresses Nitrogen Deficiencies: High nitrogen fertilizers are particularly valuable in cases where soil nitrogen levels are insufficient to meet the demands of plants. These fertilizers effectively replenish nitrogen levels, alleviating nutrient deficiencies that can hinder plant growth and development.
- Flexible Application Methods: High nitrogen fertilizers can be applied using various methods, including soil incorporation, foliar sprays, and irrigation systems. This flexibility allows for convenient application and precise nutrient delivery, depending on the specific needs of your plants.
- Promotes Healthy Soil Microbial Activity: Nitrogen is essential for the growth and activity of soil microorganisms, which play a crucial role in the breakdown of organic matter and nutrient cycling. By supplying plants with high nitrogen fertilizers, you promote a healthy microbial community, leading to improved soil structure and nutrient availability.
It is important to note that while high nitrogen fertilizers offer many advantages, it is crucial to use them judiciously and follow recommended application rates. Excessive use of high nitrogen fertilizers can lead to nutrient imbalances, environmental pollution, and the potential for plant stress or damage. Therefore, it is essential to understand the specific needs of your plants, monitor soil nutrient levels, and adjust fertilizer applications accordingly.
When choosing a high nitrogen fertilizer, look for a product with a higher first number in the N-P-K ratio, such as 10-5-5. This will provide the necessary nutrients for promoting healthy leafy growth in plants.
Disadvantages of Using High Nitrogen Fertilizers
While high nitrogen fertilizers can provide numerous benefits, it is important to be aware of their potential drawbacks and disadvantages. Here are some of the key considerations when using high nitrogen fertilizers:
- Environmental Impact: Excessive use or improper application of high nitrogen fertilizers can contribute to environmental pollution. Nitrogen runoff from fertilized fields can contaminate water bodies, leading to water pollution and the formation of algal blooms. These blooms can deplete oxygen levels, harming aquatic life.
- Nutrient Imbalance: High nitrogen fertilizers, when used without considering other nutrient requirements, can lead to nutrient imbalances in the soil. Excessive nitrogen can inhibit the uptake of other essential nutrients, such as phosphorus and potassium, affecting overall plant health and reducing nutrient use efficiency.
- Plant Stress: In some cases, an excessive supply of nitrogen can lead to imbalances that cause stress in plants. This can manifest as delayed flowering, reduced fruit set, or weakened plant resistance to diseases and pests.
- Dependency on Fertilizers: Over-reliance on high nitrogen fertilizers can create a dependency on external inputs. This can lead to reduced soil fertility over time, as plants become reliant on fertilizers instead of utilizing natural nutrient sources present in the soil or through organic matter decomposition.
- Financial Costs: High nitrogen fertilizers, particularly those with rapid-release formulations, can be more expensive compared to other types of fertilizers. The higher price may pose challenges for those with budget constraints, especially for larger-scale agriculture operations.
- Leaching and Volatilization: High nitrogen fertilizers, if not properly managed, can be prone to leaching and volatilization. Nitrogen can easily dissolve in water and be lost through runoff, especially in sandy soils or during heavy rainfall. Additionally, some forms of nitrogen can volatilize into the atmosphere if not incorporated into the soil quickly after application.
- Impact on Soil pH: Certain high nitrogen fertilizers, such as ammonium-based fertilizers, can contribute to soil acidification over time. Prolonged use of these fertilizers without balancing the pH can lead to adverse effects on soil health and nutrient availability.
It is essential to carefully consider these potential disadvantages and take appropriate measures to mitigate them. This includes adopting proper nutrient management practices, such as soil testing, using nitrogen fertilizers responsibly, and incorporating organic matter to enhance soil health and fertility in the long term.
Application and Dosage Recommendations of High Nitrogen Fertilizers
Proper application and dosage of high nitrogen fertilizers are crucial to ensure effective and efficient nutrient utilization by plants while minimizing the risk of adverse effects. Here are some recommendations to consider:
- Soil Testing: Before applying high nitrogen fertilizers, it is advisable to conduct a soil test to determine the current nutrient levels in the soil. This helps in identifying any nutrient deficiencies or imbalances and allows for targeted fertilization.
- Follow Fertilizer Labels: Read and follow the instructions provided on the fertilizer labels. This includes recommended application rates, timing, and application methods specific to the fertilizer product you are using.
- Dosage Adjustment: Adjust the dosage of high nitrogen fertilizers based on the specific requirements of your plants and the nutrient levels indicated by the soil test. Avoid over-application, as excessive nitrogen can lead to nutrient imbalances and environmental pollution.
- Splitting Applications: Consider splitting the application of high nitrogen fertilizers into multiple smaller doses throughout the growing season. This helps to provide a steady supply of nitrogen to plants, reducing the risk of nutrient leaching and ensuring that plants have a continuous nutrient source.
- Timing of Application: Time the application of high nitrogen fertilizers to coincide with the growth stages of your plants. For example, in annual crops, it is beneficial to apply fertilizers before or during periods of rapid vegetative growth.
- Incorporation: For granular high nitrogen fertilizers, incorporate them into the soil gently to prevent nitrogen losses through volatilization. Watering after application can help facilitate nutrient distribution and reduce nutrient loss.
- Foliar Sprays: In some cases, high nitrogen fertilizers can be applied as foliar sprays, especially when immediate nitrogen uptake is required. This method allows for efficient nutrient absorption through the leaves, but it should be used judiciously and following manufacturer recommendations.
- Consider Nutrient Interactions: High nitrogen fertilizers can interact with other nutrients in the soil, affecting their availability to plants. Consider the specific nutrient requirements of your plants and avoid imbalances by incorporating balanced fertilizers or supplementing with other essential nutrients when needed.
It is important to note that the specific application and dosage recommendations may vary depending on factors such as crop type, soil conditions, climate, and local regulations. Consulting agricultural extension services or seeking guidance from professionals can provide valuable insights tailored to your specific circumstances.
By carefully following recommended application rates and adopting appropriate nutrient management practices, you can maximize the benefits of high nitrogen fertilizers while minimizing potential adverse effects on the environment and plant health.
When to Use High Nitrogen Fertilizers
The timing of high nitrogen fertilizer application plays a crucial role in maximizing its benefits and ensuring optimal plant growth. Here are some common scenarios when it is appropriate to use high nitrogen fertilizers:
- Early Growth Stage: During the early stages of plant growth, when establishing seedlings or transplants, high nitrogen fertilizers can provide a nutrient boost to support vigorous root and shoot development. This helps plants establish a strong foundation for future growth.
- Leafy Vegetables and Grasses: Leafy vegetables such as lettuce, spinach, and kale, as well as grasses like lawn turf or pasture grass, have high nitrogen requirements. Using high nitrogen fertilizers at key growth stages, such as during active leaf production, can promote lush foliage and encourage healthy plant growth.
- Periods of Nutrient Deficiency: If a plant exhibits symptoms of nitrogen deficiency, such as pale or yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or overall weakened appearance, applying a high nitrogen fertilizer can help correct the deficiency and restore optimal nutrient levels.
- Prior to Intense Growth Phases: Some plant species experience periods of rapid growth or flowering, where their nitrogen demands increase significantly. Applying high nitrogen fertilizers before these growth phases can ensure that plants have an ample nutrient supply to support their increased metabolic activities and achieve their growth potential.
- After Harvesting or Pruning: High nitrogen fertilizers can be beneficial after harvesting or pruning, as plants may have depleted nitrogen reserves. Applying a high nitrogen fertilizer at this stage can help replenish the nutrient levels, encourage new growth, and prepare the plants for their next growth cycle.
- For Nitrogen-Loving Crops: Certain crops, such as corn, tomatoes, and potatoes, are known for their high nitrogen demands. Using high nitrogen fertilizers throughout their growth cycle, particularly during active vegetative growth stages, can support optimal plant development and enhance their yield potential.
- When Recommended by Soil Testing: Soil tests can provide valuable insights into nutrient deficiencies or imbalances. If a soil test indicates a need for additional nitrogen, high nitrogen fertilizers can be applied to correct the deficiency and ensure that plants have access to sufficient nitrogen for their growth.
It is important to note that the specific timing of high nitrogen fertilizer application may vary depending on regional climate, crop type, and specific growth characteristics of plants. Monitoring plant health, understanding the specific nutrient requirements of your crops, and consulting local gardening resources or agricultural experts can help guide you in determining the appropriate timing for using high nitrogen fertilizers.
Remember to use high nitrogen fertilizers judiciously and in accordance with recommended application rates to avoid nutrient imbalances, environmental pollution, or plant stress. Always consider the specific needs of your plants and adapt your fertilization practices accordingly.
Read also: 13 Best Nitrogen Fertilizer for 2024
Considerations and Precautions with High Nitrogen Fertilizers
While high nitrogen fertilizers can be beneficial for promoting plant growth, it is important to take certain considerations and precautions to ensure their effective and responsible use. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Soil Testing: Conduct regular soil tests to assess the nutrient levels in your soil. This helps determine the specific nutrient requirements of your plants and ensures that you only apply high nitrogen fertilizers when necessary.
- Proper Nutrient Balance: Consider the overall nutrient balance in your soil. High nitrogen fertilizers should be used in conjunction with other essential nutrients, such as phosphorus and potassium, to maintain a well-rounded nutrition for plants. Avoid overemphasizing one nutrient at the expense of others.
- Environmental Impact: Be mindful of potential environmental consequences associated with high nitrogen fertilizers. Excessive or improper use can lead to nutrient runoff, water pollution, and ecological imbalances. Follow local regulations and best practices to minimize environmental impact.
- Appropriate Application Rates: Follow recommended application rates and avoid excessive use of high nitrogen fertilizers. Over-application can lead to nitrogen imbalances, nutrient leaching, and negative impacts on plant health and the environment.
- Timing of Application: Apply high nitrogen fertilizers at the right time to ensure maximum effectiveness. Consider the specific growth stages of your plants and apply fertilizers when they have the highest demand for nitrogen, such as during the active vegetative growth phase.
- Sensitive Plants: Some plants may be more sensitive to high nitrogen levels than others. Be aware of the nitrogen tolerance of your plants and adjust fertilizer applications accordingly. Monitor plants for any signs of nutrient burn or stress and adjust nutrient levels as needed.
- Storage and Handling: Store high nitrogen fertilizers in a cool, dry place and follow proper handling procedures. Keep them away from children and pets, and avoid direct contact with skin or eyes. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for safe storage and use.
- Proper Equipment and Calibration: Use appropriate equipment for fertilizer application and ensure proper calibration to prevent over- or under-application. This helps ensure uniform nutrient distribution and avoids wastage or uneven nutrient availability in the soil.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: Regularly monitor the growth and health of your plants, as well as soil nutrient levels. Adjust fertilizer applications as necessary based on plant responses and ongoing soil testing to prevent nutrient deficiencies or imbalances.
By taking these considerations and precautions into account, you can effectively utilize high nitrogen fertilizers while minimizing any potential risks or negative impacts. Responsible fertilization practices not only support plant growth but also contribute to environmental sustainability and long-term soil health.
Conclusion
High nitrogen fertilizers provide an effective means of supplementing soil with the essential nutrient nitrogen, supporting healthy plant growth and maximizing agricultural productivity. Understanding the importance of nitrogen in plant growth and the characteristics of high nitrogen fertilizers is key to making informed decisions regarding their usage.
High nitrogen fertilizers offer several advantages, including promoting vigorous growth, enhancing chlorophyll production, increasing crop yield, improving nutrient uptake, and addressing nitrogen deficiencies. They can be particularly beneficial for leafy vegetables, grasses, and crops with high nitrogen demands.
However, it is important to be aware of the potential disadvantages and take precautions when using high nitrogen fertilizers. Nutrient imbalances, environmental pollution, plant stress, and dependency on fertilizers are some of the challenges that can arise if these fertilizers are not used responsibly.
Appropriate application and dosage of high nitrogen fertilizers, following soil testing and fertilizer label instructions, are crucial. Splitting applications, considering nutrient interactions, and timing the fertilization to target specific growth stages of plants can greatly enhance the efficacy and efficiency of high nitrogen fertilizers.
It is also important to consider the potential environmental impact, handle and store fertilizers safely, and maintain a balanced nutrient approach in soil management. Regular monitoring of plants and soil nutrient levels, as well as adjusting fertilizer applications accordingly, contribute to sustainable and responsible use of high nitrogen fertilizers.
In conclusion, while high nitrogen fertilizers can play a vital role in promoting healthy plant growth, it is essential to use them judiciously and with environmental consciousness. By following recommended guidelines, considering specific plant requirements, and adopting responsible fertilization practices, you can harness the benefits of high nitrogen fertilizers while safeguarding the health of your plants and the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A High Nitrogen Fertilizer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is A High Nitrogen Fertilizer”