

Articles
When Was Insulation First Used In Homes
Modified: January 23, 2024
Discover the history of insulation in homes. Explore how articles on this topic reveal when insulation was first used and its evolution over time.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Insulation is a crucial component in modern homes, providing thermal resistance and creating a comfortable living environment while reducing energy consumption. It is a material that is installed in the walls, ceilings, and floors of buildings to minimize heat transfer, keeping the interior warm in cold weather and cool in hot weather. The use of insulation dates back centuries, and its evolution has significantly influenced the way we construct and inhabit our homes.
As our understanding of energy efficiency and environmental sustainability has grown, so has the importance of insulation in home design. Today, homeowners and builders alike recognize the value of incorporating insulation materials and techniques that help reduce energy consumption and decrease carbon emissions. This article explores the historical context of insulation in homes, from its earliest recorded use to modern strategies that contribute to energy-efficient living spaces.
Key Takeaways:
- Insulation has evolved from natural materials to modern innovations, impacting energy efficiency, comfort, and environmental sustainability in homes. Future trends focus on eco-friendly materials, smart systems, and multi-functional insulation for enhanced performance.
- Properly installed insulation reduces energy consumption, minimizes air leakage, and improves thermal comfort. Advancements in insulation technology, such as high-performance aerogels and smart systems, are shaping the future of sustainable and efficient building practices.
Read more: When To Use Encapsulated Insulation
What is insulation?
Insulation refers to any material or technique used to prevent or reduce the transfer of heat, sound, or electricity. In the context of homes, insulation primarily focuses on thermal resistance, which helps regulate the temperature inside a building by minimizing heat transfer between the interior and exterior environments.
Insulation works by trapping air, which is a poor conductor of heat, within its structure. This trapped air creates a barrier that inhibits the movement of heat energy, preventing it from escaping or entering a building. By reducing heat transfer, insulation helps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures and reduces the need for excessive heating or cooling, leading to energy savings and lower utility bills.
There are various types of insulation materials available, each with its own unique properties and application methods. Common insulation materials include fiberglass, cellulose, foam boards, and spray foam. The choice of insulation material depends on factors such as budget, climate conditions, and the desired thermal performance of the building.
Insulation is installed in different areas of a home, including walls, roofs, floors, basements, and attics, to create a continuous thermal barrier. It is important to ensure proper installation and coverage to maximize the effectiveness of insulation.
In addition to thermal insulation, sound insulation is also commonly used in homes. Sound insulation materials, such as acoustic panels and mats, help reduce noise transmission between rooms or from outside sources, creating a quieter and more peaceful living environment.
Overall, insulation plays a crucial role in creating comfortable, energy-efficient homes. It helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures, reduces energy consumption, and contributes to a healthier and more sustainable living environment.
Importance of insulation in homes
Insulation is a fundamental aspect of home construction that offers numerous benefits to homeowners. These benefits extend beyond just keeping a home warm in winter or cool in summer. Here are some key reasons why insulation is vital in homes:
- Energy efficiency: Insulation significantly improves the energy efficiency of a home by reducing the amount of heat that escapes or enters through walls, roofs, and floors. This means that homeowners can save money on heating and cooling bills, as their HVAC systems don’t have to work as hard to maintain a comfortable temperature.
- Comfort: Insulation helps create a more comfortable living environment by minimizing temperature fluctuations. It keeps the indoor temperature stable, reducing cold spots, drafts, and uneven heating or cooling. This ensures that residents can enjoy a consistent and comfortable temperature throughout their home.
- Noise reduction: Insulation materials with soundproofing properties can help reduce noise transmission. This is especially important for homes located in noisy areas or near busy roads. Sound insulation creates a quieter living environment by reducing the impact of external noises and preventing sound from traveling between rooms.
- Moisture control: Proper insulation can help prevent moisture problems by creating a barrier that reduces the transfer of moisture-laden air. It helps prevent condensation on walls and ceilings, which can lead to mold and mildew growth. Insulation also protects against dampness and water ingress, ensuring a healthier indoor environment.
- Environmental sustainability: By reducing energy consumption, insulation contributes to a more sustainable living environment. It helps lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with heating and cooling homes, reducing the carbon footprint. Additionally, using eco-friendly insulation materials made from recycled or renewable sources further enhances the environmental benefits.
Understanding the importance of insulation in homes requires examining its historical significance and how it has evolved over time. Let’s explore the historical overview of insulation in home construction.
Historical Overview: Early Home Construction Methods
Before the introduction of modern insulation materials, early homes relied on natural construction methods and design features to provide some level of thermal insulation. These early construction techniques varied across different regions and time periods. Here are some notable examples of early home construction methods:
- Mud and clay: In regions where clay and mud were abundant, homes were often constructed using these materials. Thick walls made from compacted mud or clay provided natural insulation against temperature extremes.
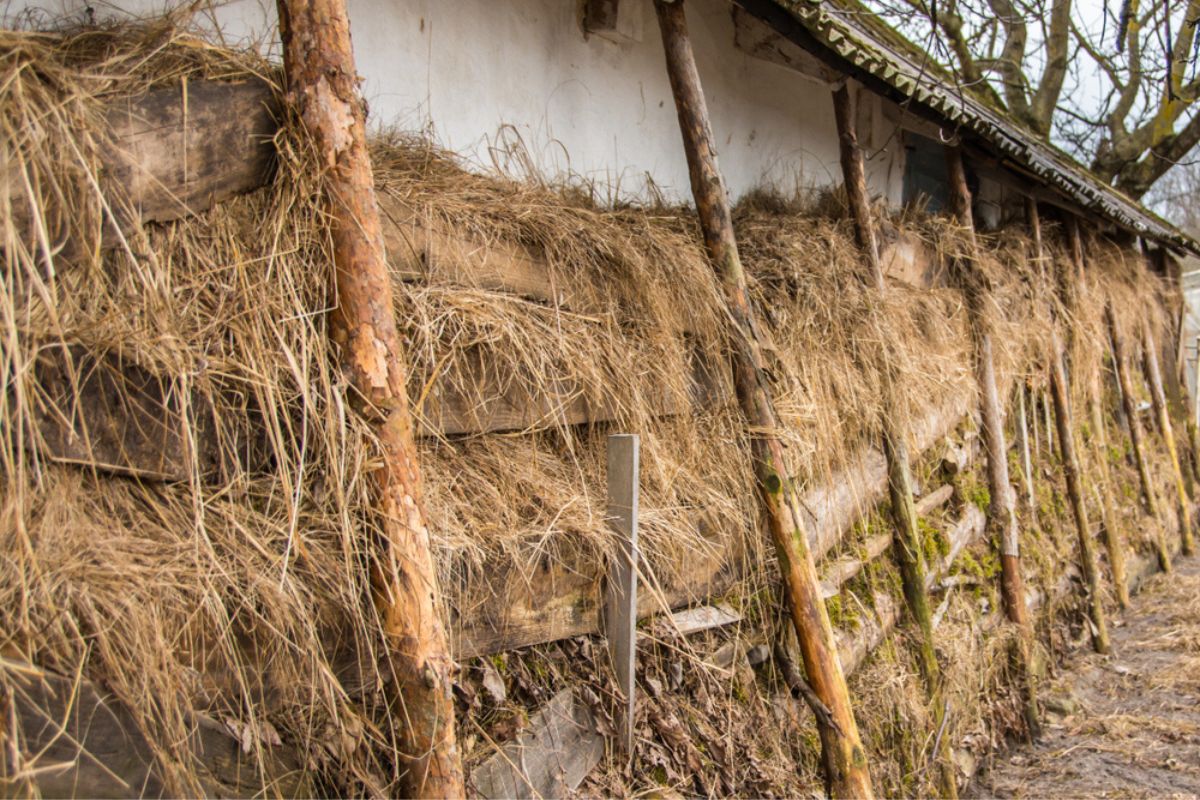
- Thatched roofs: Thatched roofs made from straw or reeds were commonly used in many ancient cultures. The thick layer of thatch acted as insulation, maintaining a more stable indoor temperature.
- Adobe construction: Adobe, a mixture of straw and clay, was widely used in ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and the Incas. Adobe bricks had excellent insulation properties due to the high thermal mass of the material.
- Cobblestone construction: In regions where cobblestones were readily available, homes were constructed using these stones. The use of thick stone walls provided natural thermal insulation and helped regulate indoor temperatures.
- Reinforced earth: Ancient civilizations like the Mesopotamians and the Chinese constructed homes using compacted earth and reinforcing materials like straw or animal hair. This technique provided insulation and structural stability.
These early construction methods demonstrated an understanding of the importance of thermal insulation in maintaining comfortable living conditions. While these methods offered some level of insulation, they were limited in terms of their overall effectiveness and efficiency.
As societies continued to advance technologically, there arose a need for more sophisticated and efficient insulation solutions. This led to the development of the first recorded use of insulation materials specifically designed for home construction.
First Recorded Use of Insulation in Homes
The first recorded instances of insulation materials being used specifically for home construction date back thousands of years. These early insulation materials were typically derived from natural sources and were chosen for their thermal properties. Let’s explore some of the early insulation materials that were utilized:
- Animal fur and feathers: Ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and the Romans used animal fur, feathers, and wool as insulation materials. These natural fibers provided excellent insulation properties due to their ability to trap air and restrict heat flow. Fur and feathers were often used to stuff walls, floors, and roofs.
- Straw and hay: In regions where straw and hay were abundant, these materials were commonly used for insulation. They were often packed into walls and roof spaces to provide thermal insulation. The hollow nature of straw and hay fibers helped to trap air, improving their insulating capabilities.
- Seaweed: Coastal communities in areas such as Ireland and Scotland used seaweed as insulation for their homes. Seaweed was abundant and readily available near the coast, making it an accessible and effective insulating material. It was used to fill gaps in walls and roofs.
- Moss and lichens: In colder regions with a lack of vegetation, moss and lichens were often used as insulation materials. They were harvested and packed tightly into wall cavities to create an insulating layer. The dense structure of moss and lichens helped retain warmth and prevent heat loss.
- Paper and fabric: In more urbanized areas, materials such as paper and fabric were used as insulation. Paper was often crumpled up and used to fill gaps, while fabric was layered and quilted to create insulating barriers within walls and ceilings.
These early insulation materials were effective to some extent in providing thermal insulation for homes. However, they had limitations in terms of durability, fire resistance, and resistance to pests and moisture. As the industrial revolution began to reshape society, new insulation materials were introduced, offering improved performance and durability.
Advancements in insulation technology paved the way for the development of superior and more efficient insulation materials, revolutionizing home insulation practices. Let’s explore how insulation technology progressed over time.
Read more: When Was Vermiculite Insulation Used
Natural Materials
Throughout history, humans have utilized a variety of natural materials for insulation purposes in homes. These materials, derived from renewable sources, offered effective insulation properties and contributed to sustainable building practices. Here are some noteworthy natural insulation materials:
- Wool: Wool is one of the oldest and most widely used natural insulation materials. It is derived from the fleece of sheep and has excellent insulating properties. Wool fibers possess natural air pockets, which help trap air and inhibit heat transfer. Wool insulation is known for its moisture-wicking capabilities, fire resistance, and sound-absorbing qualities.
- Cotton: Cotton, a plant-based fiber, has been used as an insulation material for many years. Cotton insulation is typically made from recycled denim or cotton scraps. It offers good thermal insulation, sound absorption, and resistance to pests and mold. Cotton insulation is also considered environmentally friendly due to its recycled content.
- Cork: Cork insulation is produced from the bark of cork oak trees, making it a sustainable and renewable material. Cork has excellent thermal and acoustic insulation properties while being lightweight and flexible. It is often used in wall and floor insulation and contributes to noise reduction and energy efficiency.
- Hemp: Hemp insulation is derived from the fibers of the hemp plant. It is a sustainable and eco-friendly choice due to its fast-growing nature and low environmental impact. Hemp insulation provides good thermal and sound insulation while also offering moisture resistance and breathability.
- Straw bales: Straw bales have been used as insulation material for centuries, particularly in agricultural regions. Straw bales provide excellent thermal insulation due to the insulating properties of the trapped air within the straw stems. They can be stacked and used as load-bearing walls or incorporated as infill insulation within a timber or masonry framework.
These natural insulation materials offer a range of benefits, including thermal insulation, sound absorption, fire resistance, and sustainability. They provide environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic insulation materials and contribute to healthier indoor air quality.
While natural insulation materials have their advantages, they are not without limitations. Depending on the material and its application, they may require additional protection against moisture, pests, and fire. Additionally, natural insulation materials may have higher costs compared to some synthetic alternatives.
With the advancement of technology, synthetic insulation materials have emerged as popular alternatives to natural options. Let’s explore the early developments in synthetic insulation materials.
Early Synthetic Materials: Advancements in Insulation Technology
The development of synthetic insulation materials in the early 20th century marked a significant milestone in insulation technology. These materials offered enhanced insulation performance, durability, and resistance to common issues such as pests and moisture. Here are some of the early synthetic insulation materials that revolutionized the industry:
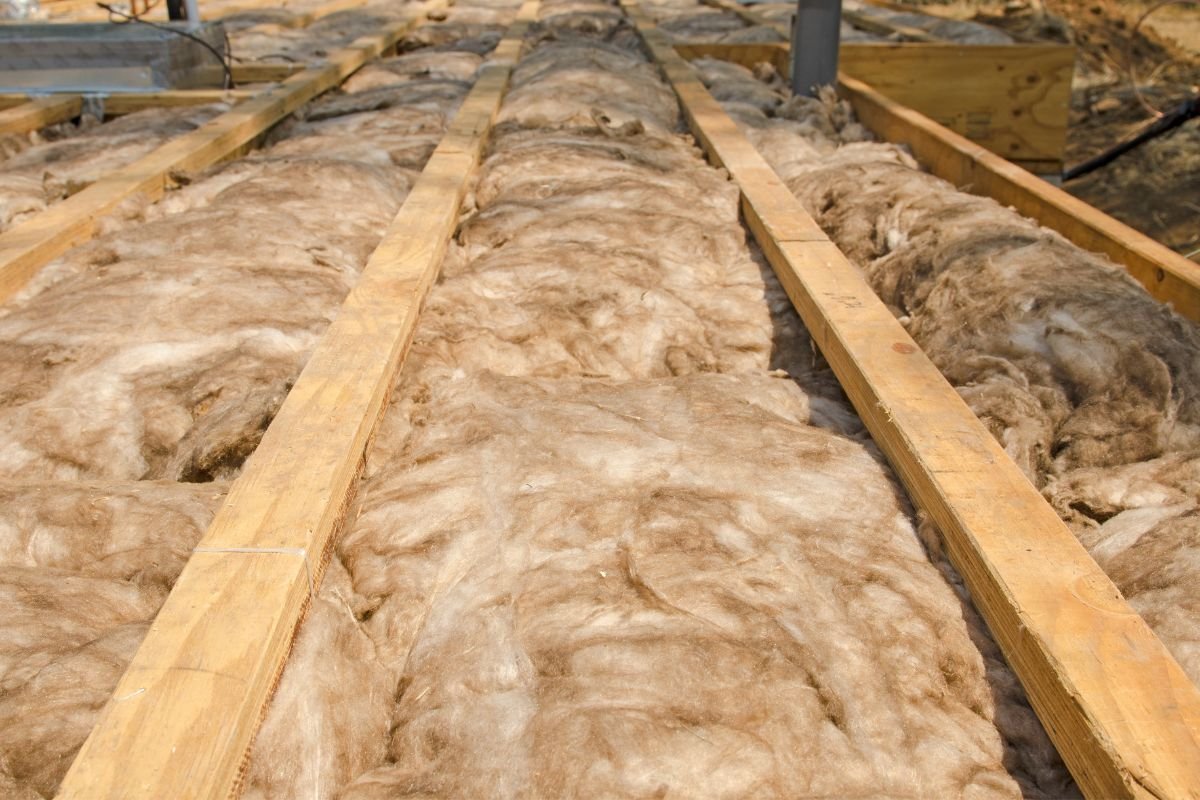
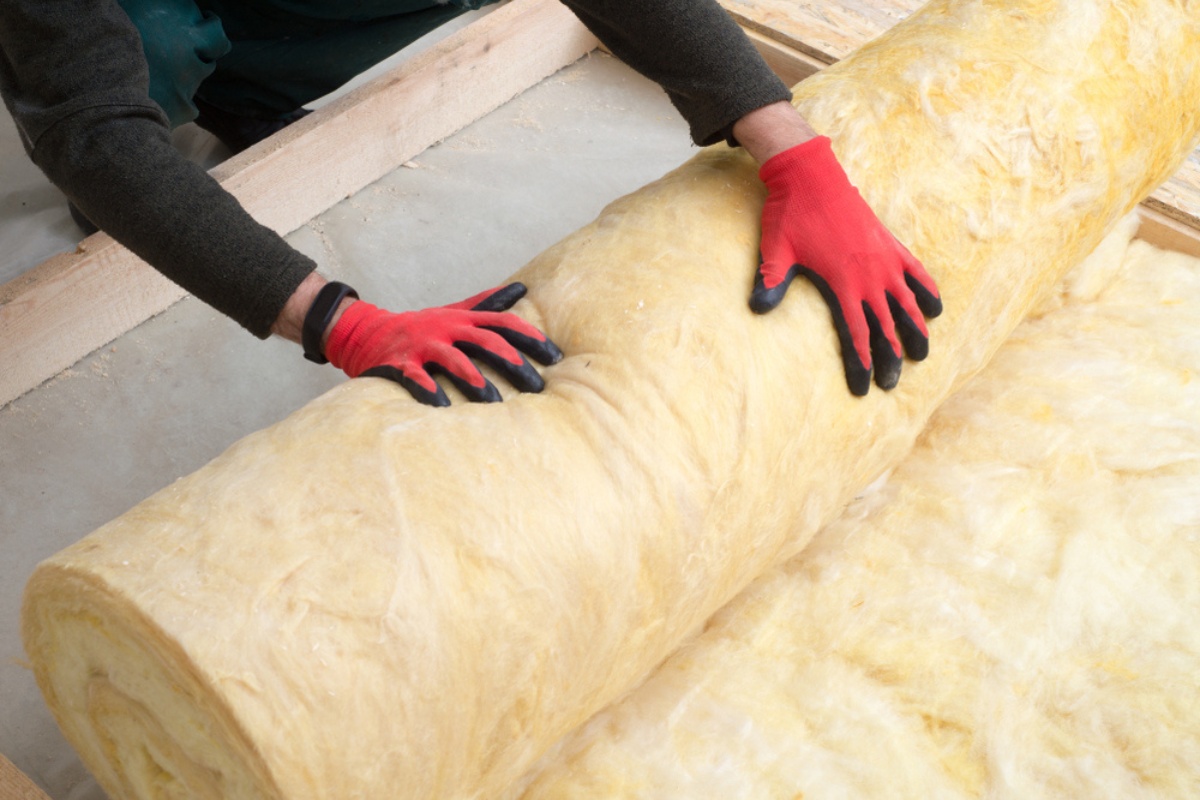
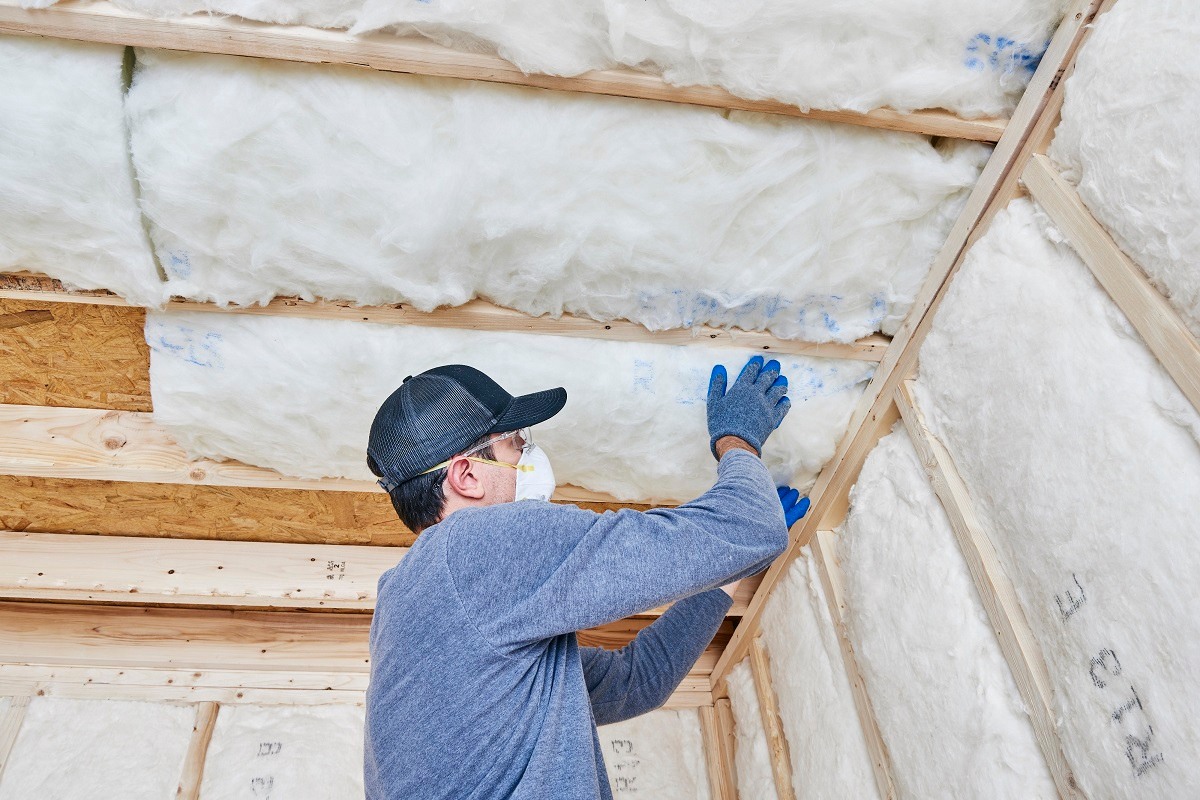
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass insulation was first introduced in the 1930s and quickly gained popularity. It is made from fine glass fibers that are woven together to create a fluffy material. Fiberglass insulation offers excellent thermal resistance and is resistant to fire, pests, and moisture. It is commonly used in attics, walls, and crawl spaces.
- Mineral wool: Mineral wool, also known as rock wool or stone wool, was developed in the 1930s as an alternative to asbestos insulation. It is made from molten rock or slag spun into fibers. Mineral wool insulation provides good thermal and sound insulation, as well as fire resistance. It is commonly used in industrial and commercial buildings.
- Polystyrene foam: Polystyrene foam insulation, commonly known as Styrofoam, was introduced in the 1940s. It is a rigid foam board insulation material that offers excellent thermal resistance and moisture resistance. Polystyrene foam insulation is commonly used in foundations, walls, and roofs.
- Polyurethane foam: Polyurethane foam insulation became popular in the 1950s. It is a spray-applied insulation material that expands and solidifies to form a dense insulating layer. Polyurethane foam insulation provides high thermal resistance and creates an airtight seal. It is commonly used in walls, roofs, and crawl spaces.
- Polyisocyanurate foam: Polyisocyanurate foam insulation, also known as polyiso, emerged in the 1970s. It is an improved version of polyurethane foam with higher thermal resistance. Polyisocyanurate foam insulation offers excellent insulation performance and is commonly used in roofs, walls, and ceilings.
These early synthetic insulation materials provided superior thermal insulation properties, better durability, and resistance to common issues such as moisture and pests. They offered increased efficiency and allowed for more precise and effective insulation installation.
Advancements in insulation technology continued as researchers and manufacturers sought to further improve insulation performance and address evolving needs. The next section will explore modern insulation solutions, including energy-efficient materials and smart insulation technologies.
Insulation was first used in homes in ancient Egypt, where reeds and mud were used to insulate walls. The concept of using insulation to regulate temperature has been around for thousands of years.
Introduction of Fiberglass Insulation
One of the most significant advancements in insulation technology was the introduction of fiberglass insulation. Fiberglass insulation revolutionized the industry and quickly became a popular choice for residential and commercial applications. Here’s a closer look at the introduction and benefits of fiberglass insulation:
Fiberglass insulation was first developed in the 1930s by Owens Corning, a leading manufacturer of insulation materials. It is made from thin glass fibers that are carefully woven together to form a fluffy and flexible material. The process involves melting glass and then spinning it into fibers, which are then bonded together using a binding agent.
The introduction of fiberglass insulation brought several notable benefits to the insulation industry. Here are some key advantages:
- Thermal insulation: Fiberglass insulation offers excellent thermal resistance. The air trapped within the glass fibers slows down heat transfer, keeping the interior of a building warmer in winter and cooler in summer. This helps to reduce the reliance on heating and cooling systems, leading to energy savings and lower utility bills.
- Fire resistance: Fiberglass insulation is naturally fire-resistant. The glass fibers do not burn or contribute to the spread of flames, providing an extra layer of safety in homes and commercial buildings.
- Sound absorption: In addition to thermal insulation, fiberglass insulation has excellent sound absorption properties. It helps reduce noise transmitted between rooms, creating a quieter and more comfortable living or working environment.
- Moisture resistance: Fiberglass insulation is resistant to moisture, making it suitable for areas prone to high humidity or condensation. The non-absorbent nature of fiberglass prevents the growth of mold, mildew, and rot, ensuring a healthier indoor environment.
- Easy installation: Fiberglass insulation is available in various forms, including batts, rolls, and loose-fill. It can be easily installed in walls, attics, and floors, fitting snugly into cavities and maintaining its shape over time.
- Cost-effective: Fiberglass insulation is relatively affordable compared to other insulation options. Its cost-effectiveness, combined with its long lifespan and energy-saving benefits, makes it a popular choice for homeowners and builders.
Fiberglass insulation has become a staple in the construction industry and is widely used in both residential and commercial buildings. It has played a significant role in improving energy efficiency, comfort, and safety in homes and commercial spaces.
In recent years, there have been advancements in fiberglass insulation technology, including the development of high-density insulation with even greater thermal resistance. These advancements continue to enhance the effectiveness and performance of fiberglass insulation.
The introduction of fiberglass insulation paved the way for further innovations in insulation technology. One such innovation is the development of spray foam insulation, which offers unique advantages in terms of installation and performance.
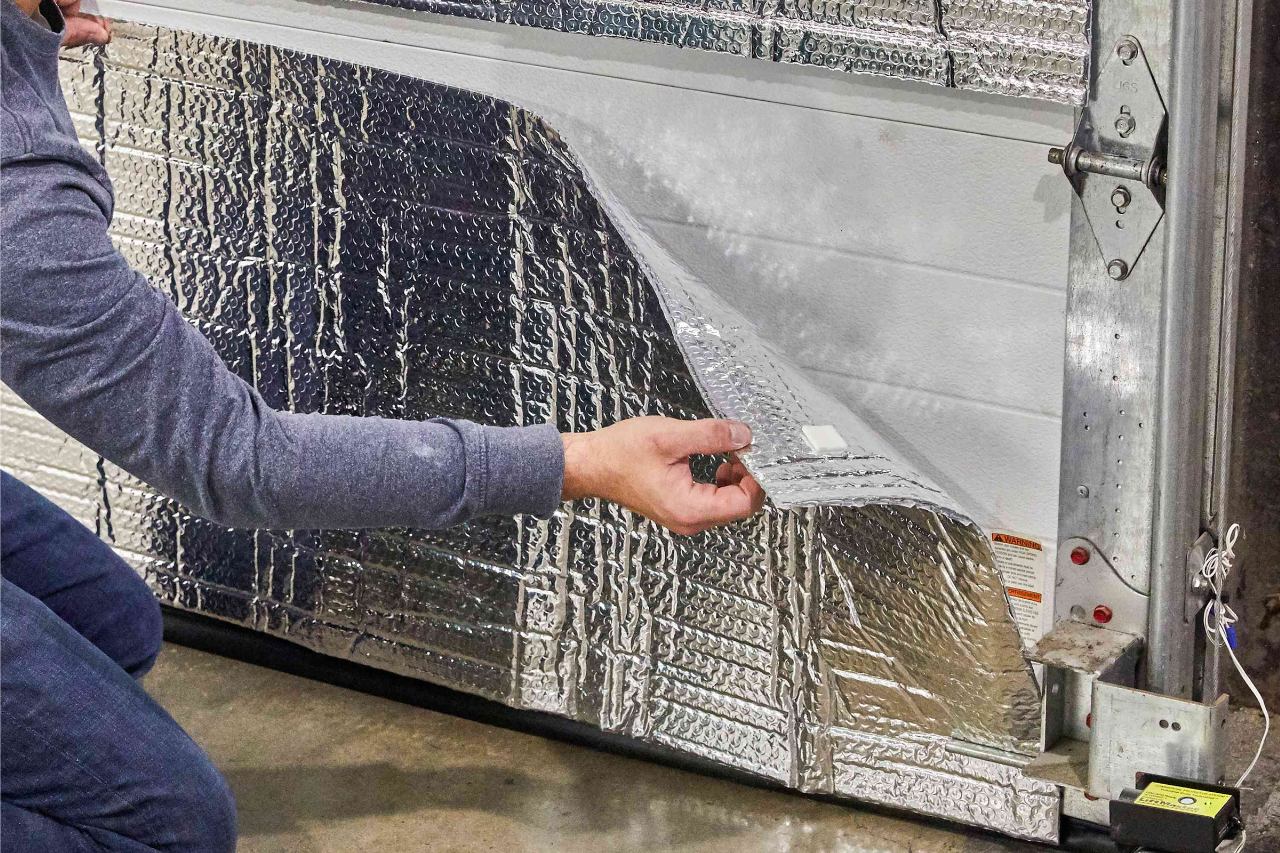
Development of Spray Foam Insulation: Modern Insulation Solutions
Spray foam insulation is a modern and highly effective insulation solution that has gained popularity in recent years. It offers unique advantages over traditional insulation materials, providing superior thermal insulation and air sealing capabilities. Here’s an overview of the development of spray foam insulation and its role as a modern insulation solution:
Spray foam insulation was first developed in the 1940s, but it gained wider use and recognition in the 1980s and 1990s. It is a polymeric material that is applied as a liquid mixture and expands into a foam when sprayed onto surfaces. The expanding foam fills voids, crevices, and irregular spaces, creating a seamless insulating barrier.
Spray foam insulation comes in two main types: open-cell and closed-cell foam. Open-cell foam has a lower density and is more flexible, while closed-cell foam has a higher density and is more rigid. Both types offer excellent insulation properties, but they differ in their air permeability and moisture resistance.
The development of spray foam insulation introduced several significant advantages over traditional insulation materials:
- Superior thermal insulation: Spray foam insulation provides excellent thermal resistance, offering higher insulation values compared to conventional insulation materials. The ability of the foam to expand and fill gaps ensures a tightly sealed and continuous thermal barrier, minimizing heat transfer and maximizing energy efficiency.
- Air sealing properties: One of the key benefits of spray foam insulation is its ability to provide air sealing for buildings. The expanding foam fills cracks, gaps, and tiny openings, creating an airtight seal. This prevents air leakage, reducing drafts and creating a more comfortable and energy-efficient environment.
- Moisture control: Spray foam insulation acts as a moisture barrier, helping to prevent the ingress of moisture into the building’s envelope. Closed-cell spray foam in particular has a higher resistance to water vapor, reducing the risk of condensation and moisture-related issues such as mold and rot.
- Noise reduction: Spray foam insulation has sound-dampening properties, helping to reduce noise transmission between rooms and from exterior sources. It improves the acoustic quality of a space, providing a quieter and more peaceful living or working environment.
- Improved indoor air quality: Spray foam insulation helps to create a healthier indoor environment by reducing the infiltration of outdoor pollutants, allergens, and dust. The air sealing properties of spray foam insulation help maintain better indoor air quality by minimizing the entry of outdoor contaminants.
- Longevity and durability: Spray foam insulation forms a durable and long-lasting insulation barrier when properly installed. It does not settle, sag, or deteriorate over time, ensuring its effectiveness and insulation performance for the life of the building.
Due to its numerous benefits, spray foam insulation has become increasingly popular in modern construction and renovations. It is commonly used in various applications, including walls, roofs, attics, and crawl spaces, to provide superior insulation and air sealing.
While spray foam insulation offers incredible advantages, it requires professional installation due to the specialized equipment and expertise needed. This ensures proper application and maximizes its effectiveness.
In addition to spray foam insulation, there are other innovative insulation solutions available that contribute to energy-efficient and sustainable homes. Let’s explore some of these modern insulation technologies.
Read more: When Was Silverware First Used
Energy-Efficient Insulation Materials
In the pursuit of creating more energy-efficient homes, innovative insulation materials have been developed to enhance thermal performance and reduce energy consumption. These materials offer superior insulating properties and contribute to sustainable building practices. Here are some of the energy-efficient insulation materials that have gained prominence:
- Spray Polyurethane Foam (SPF): Spray polyurethane foam insulation provides exceptional thermal insulation and air sealing properties. It forms a continuous and seamless layer, adhering to surfaces and expanding to fill gaps and voids. SPF insulation offers high R-values (a measure of thermal resistance) and excellent air leakage control, resulting in reduced energy usage and enhanced indoor comfort.
- Vacuum Insulation Panels (VIPs): Vacuum insulation panels consist of a core material enclosed in a vacuum-sealed panel. The vacuum insulation eliminates air, minimizing heat transfer by conduction and convection. VIPs offer outstanding insulation performance with a thin profile, making them ideal for situations where space is limited, such as in retrofit applications or high-performance building envelopes.
- Aerogel: Aerogel insulation is a lightweight and highly insulating material composed of a gel structure with air-filled pores. It has an extremely low thermal conductivity, providing exceptional insulation performance. Aerogel is used in various forms, including rigid panels, flexible blankets, and powder additives, for different applications such as walls, windows, and roofs.
- Cellulose: Cellulose insulation is composed of recycled paper fibers treated with fire retardants. It offers excellent thermal performance and sound absorption capabilities. Cellulose insulation can be blown into wall cavities or attic spaces, creating a dense barrier that reduces heat transfer. It is a sustainable option that helps recycle paper waste and promote energy conservation.
- Rigid Polyisocyanurate: Rigid polyisocyanurate (polyiso) insulation is a type of foam board insulation. It has high R-values and provides excellent thermal resistance. Polyiso insulation has low moisture absorption, making it suitable for roofs, walls, and foundations. It is often used in commercial and industrial buildings but can also be used in residential applications.
- Reflective Insulation: Reflective insulation is composed of one or more reflective surfaces to reduce radiant heat gain or loss. It consists of a layer of reflective material, typically aluminum foil, applied to a substrate such as foam or bubble wrap. Reflective insulation reflects radiant heat, helping to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature and reducing the need for excessive cooling or heating.
These energy-efficient insulation materials provide superior thermal resistance, reduce energy loss, and contribute to sustainable building practices. They play a vital role in creating comfortable and energy-efficient homes, helping homeowners reduce their carbon footprint and lower their energy bills.
It is important to note that the choice of insulation material depends on various factors, including climate conditions, building design, and budget. Consulting with insulation professionals or conducting energy audits can help determine the most suitable insulation material for specific applications.
While energy-efficient insulation materials are essential, advancements in technology have also led to the development of smart insulation solutions that further enhance energy efficiency and comfort. Let’s explore some of these cutting-edge technologies.
Smart Insulation Technologies
In the era of digital advancements, smart insulation technologies have emerged as innovative solutions to further improve energy efficiency and comfort in buildings. These technologies integrate sensors, controls, and automation to optimize insulation performance and enhance the overall energy management system. Here are some examples of smart insulation technologies:
- Thermal Imaging: Thermal imaging technology uses infrared cameras to detect heat patterns and temperature differences. By identifying areas of heat loss or inadequate insulation, it helps locate potential insulation deficiencies and allows for targeted improvements.
- Smart Insulation Systems: Smart insulation systems incorporate sensors and controls to monitor and regulate insulation performance. These systems can analyze and adjust insulation properties based on real-time data, ensuring optimal thermal efficiency and energy savings.
- Dynamic Insulation: Dynamic insulation involves the use of phase change materials (PCMs) that can store and release heat energy. These materials change phase between solid and liquid states, absorbing or releasing heat as needed to maintain a stable indoor temperature. This technology effectively reduces heating and cooling demands.
- Energy Monitoring and Management: Smart insulation technologies can be integrated into building energy management systems, allowing for continuous monitoring, analysis, and optimization of insulation performance. These systems provide real-time data on energy usage, insulation efficiency, and potential areas for improvement.
- IoT-enabled Insulation: The Internet of Things (IoT) technology enables the connection and communication between devices and systems. IoT-enabled smart insulation systems can control and adjust insulation properties based on various environmental factors, occupancy patterns, and weather conditions, ensuring optimal energy efficiency and comfort.
Smart insulation technologies not only contribute to energy savings but also enhance occupant comfort and overall building performance. They provide valuable insights into insulation efficiency, enable proactive maintenance, and optimize energy usage, leading to reduced carbon emissions and lower operating costs.
Conclusion
Insulation is a vital component of home construction, providing thermal comfort, energy efficiency, and soundproofing capabilities. From natural materials used thousands of years ago to the modern-day advancements in synthetic and smart insulation technologies, the development of insulation has come a long way.
Early insulation materials, such as animal fur, straw, and mud, laid the groundwork for insulation practices. The introduction of fiberglass insulation in the 20th century revolutionized the industry, offering superior thermal insulation and durability. Spray foam insulation further advanced insulation technology, providing exceptional air sealing properties and improved energy efficiency.
Today, energy-efficient insulation materials, such as spray polyurethane foam, cellulose, and aerogel, contribute to sustainable building practices and improved thermal performance. The integration of smart insulation technologies enhances energy management by incorporating sensors, controls, and automation to optimize insulation efficiency and overall building performance.
As we continue to prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability, advancements in insulation technology will continue to emerge. Future trends may include the development of new eco-friendly materials, enhanced smart insulation systems, and increased integration of renewable energy sources.
With the ongoing innovations in insulation technology, homeowners and builders have a wide array of options to create comfortable, energy-efficient, and sustainable living spaces. By making informed choices and investing in quality insulation solutions, we can reduce energy consumption, lower carbon emissions, and positively impact our environment.
Impact of Insulation on Home Energy Efficiency
Insulation plays a crucial role in improving the energy efficiency of homes. By reducing heat transfer and minimizing air leakage, insulation helps to create a thermal barrier that prevents the escape of heated or cooled air, thereby reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. Here are some key impacts of insulation on home energy efficiency:
- Reduced heating and cooling needs: Insulation significantly reduces heat loss during winter and heat gain during summer. By providing an effective thermal barrier, insulation helps to maintain a more stable indoor temperature, reducing the need for continuous heating or cooling. This results in lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills.
- Minimized air leakage: Insulation, particularly materials with air sealing properties like spray foam, helps to minimize air leakage in homes. Air leaks are common sources of energy waste, as they allow heated or cooled air to escape and outdoor air to enter. By sealing gaps and cracks, insulation prevents uncontrolled air exchange, reducing the need for additional heating or cooling.
- Enhanced HVAC system efficiency: With adequate insulation, the workload of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems is reduced. HVAC systems can operate more efficiently when they don’t have to compensate for heat loss or gain caused by inadequate insulation. This leads to energy savings and extends the lifespan of the HVAC equipment.
- Improved thermal comfort: Insulation helps to maintain a consistent indoor temperature, minimizing temperature fluctuations and cold spots. This creates a more comfortable living environment throughout the year. Insulation also reduces drafts and uneven heating or cooling, ensuring a more pleasant and consistent comfort level in the home.
- Reduced environmental impact: Improving the energy efficiency of homes through insulation has a positive environmental impact. Reduced energy consumption means lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to combatting climate change. Additionally, some insulation materials are made from recycled or renewable resources, promoting sustainable building practices.
- Noise reduction: Insulation materials with soundproofing properties help reduce noise transmission, creating a quieter indoor environment. This is especially beneficial for homes located in noisy areas or near busy roads, enhancing overall comfort and quality of life.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of insulation depends on proper installation and coverage. Insulation should be correctly installed without gaps or compression, ensuring a continuous thermal barrier throughout the building envelope.
Homeowners can consult insulation professionals or conduct energy audits to determine the most suitable insulation materials and installation techniques for their homes. By investing in quality insulation and ensuring proper installation, homeowners can experience the maximum energy efficiency benefits, reduce energy consumption, and contribute to a sustainable future.
Read more: When Was Stucco First Used
Future Trends in Insulation Technology
As the demand for energy-efficient and sustainable building practices continues to rise, the insulation industry is constantly evolving to meet these needs. Innovations in insulation technology are driving advancements towards more efficient, environmentally-friendly, and cost-effective solutions. Here are some future trends in insulation technology:
- Eco-friendly materials: The development of insulation materials that are more sustainable and environmentally friendly is a prevailing trend. Manufacturers are exploring alternatives to traditional insulation materials, such as utilizing renewable resources, recycled materials, and bio-based materials. These eco-friendly options aim to reduce carbon footprint without compromising insulation performance.
- High-performance aerogels: Aerogel insulation, already known for its exceptional thermal properties, is undergoing further advancements. Ongoing research aims to improve the cost-effectiveness, production methods, and durability of aerogel materials. This may lead to increased availability and wider adoption of aerogel insulation for various applications.
- Smart insulation systems: The integration of smart technologies into insulation systems is expected to become more prevalent. Smart insulation systems can monitor, analyze, and adjust insulation performance in real-time, optimizing energy efficiency. These systems may utilize IoT connectivity, artificial intelligence, and advanced sensors to enhance insulation control and contribute to smart building energy management.
- Multi-functional insulation: Insulation materials with additional functionalities are becoming more prominent. For example, new products may incorporate properties such as fire resistance, moisture management, air purification, or even self-cleaning capabilities. The development of multi-functional insulation materials offers increased value and performance in building envelope systems.
- Thermal batteries: Thermal battery technology involves the use of phase change materials (PCMs) that can store and release thermal energy. These materials can absorb heat during warmer periods and release it during cooler periods, assisting in temperature regulation. The integration of thermal batteries into insulation systems can help optimize energy usage and reduce reliance on heating and cooling systems.
- Nanotechnology-based insulation: Advances in nanotechnology have the potential to revolutionize insulation materials. Nanoparticles can be incorporated into insulation materials to improve their thermal efficiency and properties such as fire resistance and durability. Nanotechnology-based insulation materials may offer enhanced performance and energy savings compared to traditional insulation options.
These future trends indicate an exciting direction for insulation technology, focusing on sustainability, efficiency, and versatility. The ongoing efforts to develop and improve insulation materials and systems demonstrate a commitment to creating high-performance solutions that meet the evolving needs of the construction industry.
As these trends continue to unfold, it is crucial for homeowners, builders, and industry professionals to stay informed about the latest developments in insulation technology. By embracing these advancements, we can strive towards more energy-efficient, sustainable, and comfortable living environments while reducing our environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions about When Was Insulation First Used In Homes
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “When Was Insulation First Used In Homes”