Home>Furniture & Design>Interior Design Trends>When Was Glass First Used In Windows


Interior Design Trends
When Was Glass First Used In Windows
Modified: March 23, 2024
Discover the history of using glass in windows and its impact on interior design trends. Learn about the evolution of glass in interior design.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Glass windows have been an integral part of architectural design for centuries, adding elegance and functionality to buildings while allowing natural light to illuminate interior spaces. The evolution of glass in windows reflects the advancement of human civilization and technology, shaping the way we interact with our surroundings. From its humble beginnings to the modern innovations, the journey of glass in windows is a testament to human ingenuity and creativity.
Throughout history, the use of glass in windows has undergone remarkable transformations, influenced by cultural, technological, and artistic developments. The early civilizations' experimentation with translucent materials laid the foundation for the widespread incorporation of glass in architectural designs. As time progressed, the utilization of glass in windows evolved, leading to the creation of stunning stained glass windows in medieval churches and grand palaces, showcasing intricate designs and vibrant colors.
The introduction of clear glass revolutionized the architectural landscape, enabling architects to design buildings with larger windows, thereby maximizing natural light and offering breathtaking views of the surrounding environment. This pivotal advancement not only enhanced the aesthetic appeal of structures but also improved the occupants' quality of life by creating brighter and more inviting living spaces.
As we delve into the history and evolution of glass in windows, it becomes evident that this essential architectural element has transcended mere functionality to become a symbol of artistic expression and technological prowess. The journey of glass in windows is a testament to human creativity and innovation, reflecting our relentless pursuit of beauty, functionality, and sustainability in architectural design. Join us as we embark on a captivating exploration of the early history, use, and advancements of glass in windows, unraveling the fascinating tale of this timeless architectural marvel.
Key Takeaways:
- Glass windows have a rich history dating back to ancient civilizations, showcasing human creativity and innovation in architectural design.
- Advancements in glass windows, from stained glass masterpieces to smart glass technologies, have transformed buildings, offering sustainable, visually striking designs.
Read more: When Were Glass Windows First Used
Early History of Glass
The early history of glass dates back to ancient civilizations, where the origins of this remarkable material can be traced to Mesopotamia around 3500 BCE. Initially, glass was created as a byproduct of ceramic glazes, resulting from the fusion of sand, soda, and lime at high temperatures. This serendipitous discovery marked the inception of glassmaking, laying the groundwork for its future applications in various forms, including windows.
The ancient Egyptians further advanced the art of glassmaking, demonstrating exceptional skill in crafting intricate glass beads and vessels. Their expertise in glass manipulation and decoration paved the way for the widespread use of glass in ornamental and functional objects, setting the stage for its eventual incorporation into architectural elements.
The Romans, renowned for their architectural prowess, played a pivotal role in the evolution of glass, introducing innovative techniques that revolutionized its production. They mastered the art of glassblowing, a groundbreaking method that enabled the creation of glass vessels with unprecedented precision and efficiency. This technological leap not only elevated the status of glass as a coveted commodity but also expanded its potential for architectural applications, including windows.
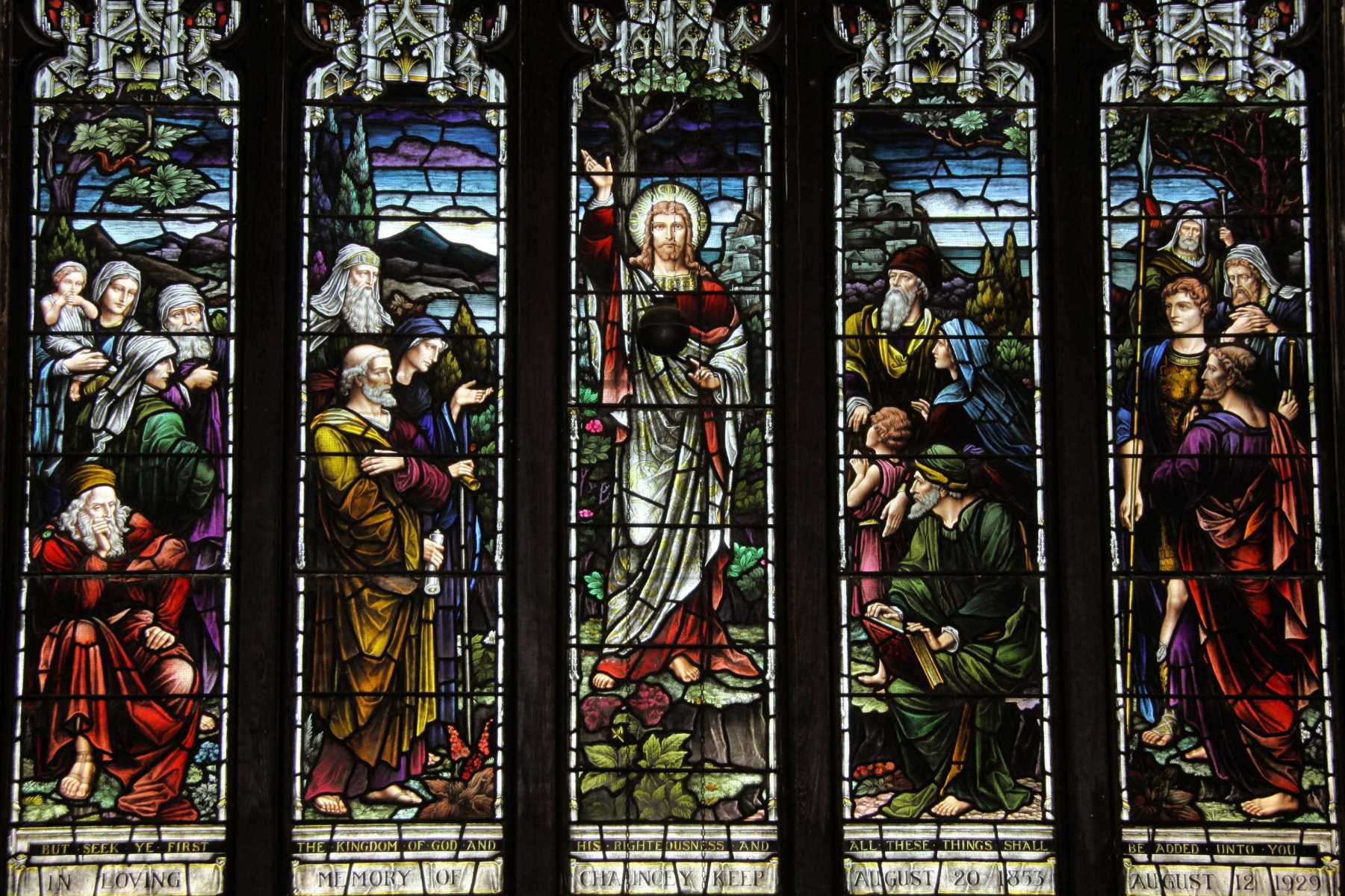
During the medieval period, the use of glass in windows underwent a transformative shift, as evidenced by the emergence of awe-inspiring stained glass windows adorning cathedrals and religious institutions. These magnificent works of art, characterized by vibrant colors and intricate designs, served as visual narratives, depicting religious stories and conveying spiritual symbolism. The intricate craftsmanship and artistic expression showcased in these stained glass windows elevated the status of glass as a medium for storytelling and cultural representation.
The early history of glass reflects a remarkable journey of experimentation, innovation, and artistic expression, culminating in its widespread adoption as a fundamental component of architectural design. The evolution of glass from its humble origins to becoming a symbol of artistic and technological achievement underscores its enduring significance in shaping the built environment. This rich historical tapestry sets the stage for exploring the diverse applications and advancements of glass in windows, offering a glimpse into the enduring legacy of this extraordinary material.
Use of Glass in Windows
The use of glass in windows has played a pivotal role in shaping architectural aesthetics and functionality throughout history. From its early applications in ancient civilizations to the modern era of innovative architectural designs, glass has been a transformative element in defining the character of buildings and interior spaces.
In ancient times, the incorporation of glass in windows was a symbol of luxury and sophistication, reserved for esteemed structures and affluent patrons. The Romans, renowned for their architectural ingenuity, utilized glass panes to enclose openings in their villas, allowing natural light to permeate the interior while providing protection from the elements. This early use of glass in windows marked a significant departure from traditional building materials, ushering in a new era of architectural transparency and luminosity.
The medieval period witnessed a remarkable evolution in the use of glass in windows, particularly in the creation of stunning stained glass masterpieces adorning cathedrals and religious edifices. These intricate works of art, characterized by vibrant hues and intricate designs, served as visual narratives, illuminating sacred spaces with mesmerizing light and conveying spiritual allegories. The symbolic and aesthetic significance of stained glass windows transcended mere functionality, elevating them to the status of revered cultural artifacts and testaments to human creativity.
The Renaissance era saw a resurgence of interest in clear glass windows, as architects and artisans sought to harness natural light to illuminate interior spaces and showcase the surrounding landscapes. The development of larger, more transparent glass panes enabled the creation of expansive windows, blurring the boundaries between indoor and outdoor environments. This architectural innovation not only enhanced the visual appeal of buildings but also transformed the living experience, fostering a deeper connection to nature and the external world.
In the modern era, the use of glass in windows has become synonymous with sleek, minimalist designs and sustainable building practices. Architects and designers leverage advanced glass technologies to create energy-efficient windows that optimize natural light while minimizing heat loss, contributing to environmentally conscious architectural solutions. The seamless integration of glass in contemporary buildings reflects a harmonious blend of form and function, exemplifying the enduring relevance of glass as a versatile and indispensable architectural element.
The use of glass in windows has transcended mere practicality to become a symbol of architectural innovation, artistic expression, and environmental consciousness. Its evolution from ancient luxury to modern necessity underscores the enduring impact of glass on architectural design, shaping the way we perceive and interact with the built environment.
This section provides a glimpse into the historical and cultural significance of glass in windows, highlighting its transformative influence on architectural aesthetics and spatial dynamics. As we continue to explore the advancements in glass windows, we gain a deeper appreciation for the enduring legacy of this remarkable architectural element.
Glass was first used in windows during the Roman Empire, around the 1st century AD. It was initially used in small pieces and later developed into larger panes.
Advancements in Glass Windows
The evolution of glass windows has been marked by groundbreaking advancements that have redefined architectural possibilities and transformed the way we experience interior spaces. From the development of clear, flat glass to the integration of cutting-edge technologies, the progression of glass windows reflects a continuous quest for innovation, sustainability, and aesthetic enhancement.
One of the most significant advancements in glass windows came with the invention of the float glass process in the mid-20th century. This revolutionary technique enabled the mass production of high-quality, uniform glass sheets with exceptional flatness and clarity. The float glass method involves pouring molten glass onto a bed of molten tin, allowing it to spread and form a perfectly smooth surface. This breakthrough not only facilitated the widespread availability of clear, distortion-free glass but also set the stage for architectural designs that prioritized transparency and unobstructed views.
The advent of insulated glass units (IGUs) represented another milestone in the evolution of glass windows. IGUs consist of two or more glass panes separated by a hermetically sealed airspace, creating a thermal barrier that enhances energy efficiency and sound insulation. This innovation has revolutionized building envelopes, enabling architects to design structures with expansive windows while mitigating heat loss and external noise. The versatility of IGUs has made them indispensable in contemporary architectural practices, contributing to sustainable building designs and occupant comfort.
In recent years, the integration of smart glass technologies has ushered in a new era of dynamic and responsive windows. Smart glass, also known as switchable glass, can alter its transparency or opacity in response to external stimuli such as light, heat, or electrical signals. This transformative capability offers unprecedented control over privacy, daylighting, and solar heat gain, making smart glass an attractive option for sustainable building designs. By dynamically adjusting its properties, smart glass enhances occupant comfort, reduces energy consumption, and elevates the overall building performance.
Furthermore, the exploration of innovative glass coatings and treatments has expanded the functional and aesthetic potential of glass windows. Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings, for instance, minimize heat transfer through windows, contributing to energy-efficient building designs. Additionally, self-cleaning and anti-reflective coatings have enhanced the durability and visual appeal of glass windows, offering practical solutions for maintenance and optical clarity.
The advancements in glass windows have not only transformed architectural aesthetics but have also redefined the relationship between interior and exterior environments. The seamless integration of advanced glass technologies has empowered architects to create sustainable, visually striking buildings that prioritize occupant well-being and environmental stewardship. As the pursuit of innovation continues, the future of glass windows holds promise for further enhancements in performance, functionality, and design versatility, shaping the architectural landscape for generations to come.
Conclusion
The journey of glass in windows is a captivating narrative that spans millennia, encompassing ancient discoveries, artistic expressions, and technological breakthroughs. From its humble origins in ancient Mesopotamia to the modern era of smart glass innovations, the evolution of glass windows reflects the enduring human quest for beauty, functionality, and sustainability in architectural design.
Throughout history, the use of glass in windows has transcended mere practicality to become a symbol of artistic expression and cultural significance. The mesmerizing stained glass windows of medieval cathedrals, with their intricate designs and vibrant hues, stand as timeless testaments to human creativity and spiritual storytelling. The Renaissance era witnessed a renewed appreciation for clear glass windows, fostering a deeper connection to nature and the external world while illuminating interior spaces with natural light.
The advancements in glass windows, from the float glass process to insulated glass units and smart glass technologies, have revolutionized architectural possibilities and transformed the built environment. The mass production of high-quality, uniform glass sheets has enabled architects to design structures with expansive, unobstructed views, blurring the boundaries between indoor and outdoor spaces. The integration of insulated glass units has enhanced energy efficiency and occupant comfort, contributing to sustainable building practices and environmental stewardship. Smart glass technologies have ushered in a new era of dynamic and responsive windows, offering unprecedented control over privacy, daylighting, and solar heat gain.
As we look to the future, the evolution of glass windows holds promise for further enhancements in performance, functionality, and design versatility. The exploration of innovative glass coatings and treatments continues to expand the functional and aesthetic potential of glass windows, offering practical solutions for energy efficiency, maintenance, and visual clarity. The seamless integration of advanced glass technologies in architectural designs underscores the enduring relevance of glass as a versatile and indispensable architectural element.
In conclusion, the history and advancements of glass in windows serve as a testament to human ingenuity, creativity, and the enduring pursuit of architectural excellence. The timeless allure of glass windows, from the ancient marvels to the cutting-edge innovations, continues to shape the way we perceive and interact with the built environment, leaving an indelible mark on architectural history and inspiring future generations of designers and visionaries.
Frequently Asked Questions about When Was Glass First Used In Windows
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “When Was Glass First Used In Windows”