Home>Articles>Which Body Composition Measurement Utilizes Calipers

Articles
Which Body Composition Measurement Utilizes Calipers
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover the most effective body composition measurement method utilizing calipers in this informative article. Gain insights on how calipers can accurately assess body fat percentage and track changes over time.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to assessing our overall health and fitness levels, measuring body composition is an important factor to consider. Body composition refers to the proportions of fat, muscle, bone, and water in our bodies. It provides more insight than just measuring weight, as it helps us determine our body fat percentage and muscle mass.
There are several methods available to measure body composition, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), and skinfold calipers. In this article, we will focus on the use of calipers, specifically, to measure body composition.
Calipers are handheld devices that are commonly used to measure skinfold thickness at various anatomical sites. These measurements can be used to estimate body fat percentage, which in turn provides a better understanding of an individual’s overall health and fitness level.
In this article, we will explore the importance of body composition measurements and delve into the specifics of using calipers for this purpose. We will discuss how calipers work, their advantages and limitations, factors to consider before using them, and the steps to take for accurate measurements. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of caliper-based body composition measurements and how they can be utilized in your fitness journey.
Key Takeaways:
- Calipers provide a cost-effective and portable method to estimate body fat percentage, offering insights into subcutaneous fat distribution. However, operator skill and equation selection impact measurement accuracy.
- Consistent technique, multiple measurements, and population-specific equations enhance the reliability of caliper-based body composition measurements. Consider combining methods for a comprehensive understanding of body composition.
Read more: Where To Purchase Body Fat Calipers
What are Calipers?
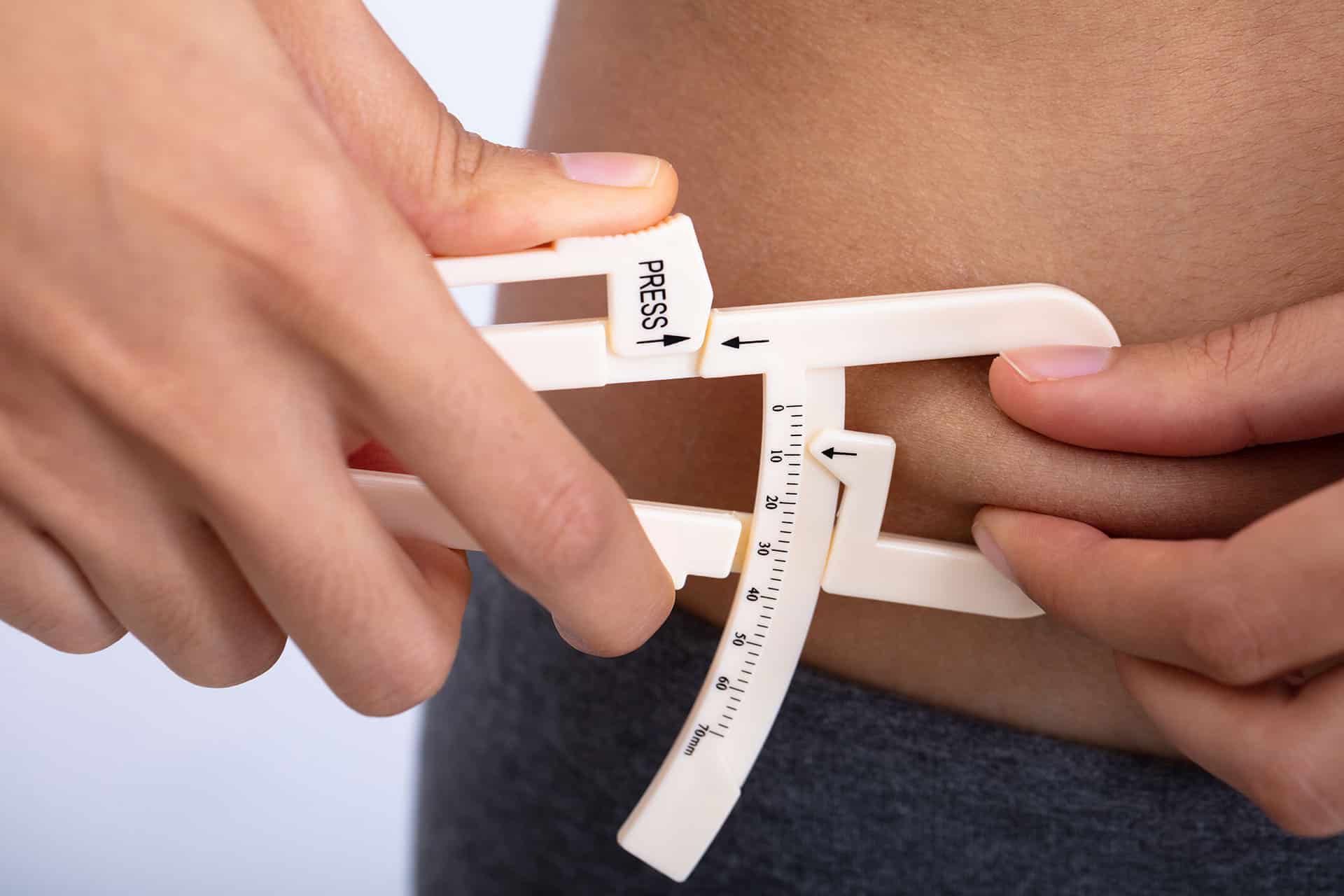
Calipers are handheld devices that are used to measure the thickness of a fold of skin at specific sites on the body. These measurements, known as skinfold measurements, are then used to estimate body fat percentage. Calipers consist of two arms that can be opened and closed, pinchers at the end of each arm, and a dial or digital display to read the measurement.
Calipers have been widely used in the field of health and fitness for decades. They provide a simple and cost-effective way to assess body composition without the need for complex equipment or procedures. By measuring skinfold thickness at specific sites, calipers can give an indication of the distribution of subcutaneous fat, which is the fat located just beneath the skin.
While there are different models and variations of calipers available, they all function on the same basic principle. The pinchers of the calipers are placed on the skinfold at the desired site, and then the arms are brought together to apply a gentle pressure. The skinfold measurement is taken by reading the dial or digital display, which indicates the thickness of the skinfold in millimeters. These measurements are then used in equations to estimate body fat percentage.
It is important to note that caliper measurements alone do not provide a direct measurement of body fat percentage. Instead, they estimate body fat based on the assumption that the thickness of the skinfold is proportional to the amount of subcutaneous fat. The accuracy of these estimates depends on various factors, including the skill of the person taking the measurement and the specific equations used.
Calipers are a convenient tool for assessing changes in body composition over time. By taking regular measurements, individuals can track their progress and make necessary adjustments to their fitness and nutrition programs. However, it is crucial to understand that caliper measurements are just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to assessing body composition. It is recommended to combine caliper measurements with other methods, such as DXA or BIA, for a more comprehensive understanding of overall body composition.
Importance of Body Composition Measurements
Body composition measurements play a crucial role in our understanding of health and fitness. They provide valuable insights beyond simply monitoring weight, allowing us to assess the distribution of fat and muscle in our bodies. Here are some key reasons why body composition measurements are important:
- Monitoring Overall Health: Body composition measurements can help us evaluate our overall health and risk for various health conditions. Excessive body fat and low muscle mass have been associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and other chronic diseases. By tracking changes in body composition, we can make informed decisions about our lifestyle to improve our health.
- Evaluating Fitness Progress: Whether our goal is to lose weight, gain muscle, or improve athletic performance, body composition measurements provide a more accurate assessment of our progress than weight alone. Increased muscle mass and reduced body fat percentage are indicators of improved fitness levels, even if the number on the scale stays the same. Tracking body composition allows us to fine-tune our exercise and nutrition plans for optimal results.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Understanding our body composition helps us set realistic and achievable goals. Focusing solely on weight loss can be misleading, as it may not reflect changes in body fat or muscle mass. By using body composition measurements, we can set specific targets for body fat percentage or muscle mass, which are more in line with our desired physique or athletic performance.
- Identifying Imbalances: Body composition measurements can reveal imbalances in muscle development or fat distribution. For example, excessive fat accumulation around the abdomen can indicate a higher risk of metabolic conditions. By identifying these imbalances, we can target specific areas for improvement through targeted exercise and nutrition strategies.
- Monitoring Weight Loss: When aiming for weight loss, body composition measurements allow for a more accurate assessment of progress. It is possible to lose weight but still have a high body fat percentage, meaning that muscle mass is also being lost. By tracking body composition, we can ensure that weight loss is primarily from fat while preserving muscle mass, which is essential for maintaining a healthy metabolism.
Overall, body composition measurements provide a comprehensive snapshot of our health and fitness. They offer valuable information beyond weight alone and help guide us in making informed decisions to achieve our desired body composition goals. Whether it is for improving health, enhancing athletic performance, or simply feeling confident in our bodies, understanding and monitoring body composition is an essential aspect of our overall well-being.
Different Methods to Measure Body Composition
There are several methods available to measure body composition, each with its own advantages and limitations. Here are some commonly used methods:
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA): DXA is considered one of the most accurate methods to measure body composition. It uses low-dose X-rays to differentiate between fat, muscle, and bone mass. DXA provides precise measurements of regional fat distribution and is often used in research settings and clinical practice. However, it can be costly, requires specialized equipment, and exposes individuals to radiation.
- Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA): BIA works by measuring the body’s resistance to a small electrical current. This method estimates body fat percentage based on the principle that fat tissue conducts less electrical current than lean tissue. BIA is quick, non-invasive, and relatively inexpensive. However, its accuracy may be affected by factors such as hydration status, body temperature, and the presence of certain medical conditions.
- Hydrostatic Weighing: Hydrostatic weighing, also known as underwater weighing, measures body density by weighing an individual in and out of water. It uses the principle that lean tissue is denser than water while fat tissue is less dense. From body density, body composition can be estimated. Hydrostatic weighing is highly accurate but requires specialized equipment and expertise. It may also be inconvenient for individuals who are uncomfortable with underwater submersion.
- Dual-Energy Absorptiometry (DEXA): DEXA is similar to DXA but uses a different technique to estimate body composition. It utilizes a single X-ray beam instead of dual beams, providing measurements of bone mineral density as well as fat and lean mass. DEXA is less commonly used than DXA but offers similar advantages and limitations.
- Body Mass Index (BMI): BMI is a simple calculation based on an individual’s weight and height. It provides a general indication of body composition and is commonly used as a screening tool for obesity. However, BMI does not differentiate between fat and muscle mass, making it less accurate for assessing body composition.
- Calipers: Calipers, as mentioned earlier, are handheld devices used to measure skinfold thickness at specific sites on the body. These measurements are used in equations to estimate body fat percentage. Calipers are cost-effective, portable, and widely accessible. However, their accuracy depends on the skill of the person taking the measurements and the specific equations used.
Each method has its own advantages and limitations, as well as varying levels of accuracy. The choice of method depends on factors such as cost, availability, accuracy requirements, and individual preferences. It is important to consider these factors when selecting the most appropriate method for assessing body composition.
Overview of Caliper-Based Body Composition Measurement
Caliper-based body composition measurement is a widely used method to estimate body fat percentage. It involves using specialized calipers to measure the thickness of skinfold at specific sites on the body. These skinfold measurements are then used in equations to calculate body fat percentage.
The concept behind caliper-based measurements is that the thickness of the skinfold is proportional to the amount of subcutaneous fat, which is the fat located just beneath the skin. By measuring skinfold thickness at different sites, we can estimate the total amount of body fat.
The most common sites for taking skinfold measurements include the triceps, biceps, subscapular, and suprailiac regions. These sites are chosen based on their ability to represent different fat deposition patterns in the body. The measurements are typically taken on the right side of the body, and multiple measurements are taken at each site to ensure accuracy.
Once the skinfold measurements are obtained, they are input into equations to estimate body fat percentage. Different equations have been developed based on population-specific data, and they take into account factors such as age, gender, and ethnicity.
It is important to note that caliper-based body composition measurement provides an estimate rather than an exact measurement of body fat percentage. The accuracy of these estimates can vary depending on several factors:
- Operator Skill: The skill of the person taking the measurements is crucial for accurate results. Proper technique, consistent measurement placement, and appropriate calibration of the calipers are essential for reliable outcomes.
- Equation Selection: Different equations may yield different results, so it is important to choose an equation that is appropriate for the population being measured.
- Intra- and Inter-Observer Variability: Even with skilled operators, there can be variability in measurement techniques and interpretation. This means that measurements taken by different people or even the same person on different occasions may differ slightly.
- Individual Variation: Body composition can vary greatly among individuals, meaning that caliper-based measurements may not accurately represent everyone’s actual body fat percentage. Factors such as genetics, hydration levels, and muscle mass can influence the results.
- Subcutaneous Fat Distribution: Caliper-based measurements primarily estimate subcutaneous fat, which may not reflect visceral fat (fat around organs). Visceral fat is associated with higher health risks but cannot be measured using calipers.
Despite these limitations, caliper-based body composition measurements are still widely used due to their accessibility, affordability, and portability. They provide a practical and relatively accurate estimation of body fat percentage, making them valuable tools for monitoring changes in body composition over time.
Read more: How To Use Calipers To Measure
How Do Calipers Work?
Calipers work based on the principle that the thickness of a skinfold is a reflection of subcutaneous fat beneath the skin. The process involves using handheld calipers to measure the thickness of the skinfold at specific sites on the body. Here’s a closer look at how calipers work:
- Site Selection: Before taking measurements, specific sites on the body are selected for skinfold measurement. Common sites include the triceps, biceps, subscapular, and suprailiac regions. These sites are chosen because they are easily accessible and representative of different fat deposition patterns.
- Measurement Procedure: Once the sites are determined, the calipers are used to pinch the skinfold at the selected site. The pinch should include both the skin and underlying subcutaneous fat, but not the muscle or bone. The operator must ensure a firm but gentle grip to accurately measure the skinfold thickness.
- Reading the Calipers: Calipers are equipped with a dial or digital display to read the measurement. The operator brings the arms of the caliper together until the pinchers make contact with the skinfold. The measurement is then read from the dial or digital display, and the result is recorded in millimeters (mm).
- Repeat Measurements: To enhance accuracy, it is common practice to take multiple measurements at each site. Typically, three measurements are taken, and the average of these measurements is calculated to reduce variability.
- Recording Measurements: The measurements are recorded for each site, and the data is used in specific equations to estimate body fat percentage. These equations take into account factors such as age, gender, and ethnicity to provide a more accurate estimation.
- Estimating Body Fat Percentage: Once all the measurements are obtained, they are input into equations that estimate body fat percentage. These equations have been developed based on research and population-specific data. The result gives an estimation of the proportion of body fat.
It is important to note that the accuracy of caliper-based measurements relies on several factors, including the skill of the operator, equation selection, and individual variability. Skilled operators follow standardized procedures and understand the correct placement of the calipers to maximize accuracy.
While calipers can provide a convenient and cost-effective method for estimating body fat percentage, it is important to understand that they provide an estimate rather than an exact measurement. Factors such as hydration levels, muscle mass, and other individual variations can influence the accuracy of the results. Nevertheless, with proper technique and understanding, caliper measurements can be a valuable tool for tracking changes in body composition over time.
When using calipers to measure body composition, it’s important to consistently apply the same amount of pressure and measure at the same anatomical sites for accurate results.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Calipers
Using calipers for body composition measurement offers several advantages and limitations. Understanding these can help us assess the suitability of calipers for our specific needs. Here’s a closer look at the advantages and limitations of using calipers:
- Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Calipers are a relatively inexpensive tool compared to other body composition measurement methods, making them accessible to a wide range of individuals.
- Portability: Calipers are small and easily portable, allowing for measurements to be taken in various settings without the need for specialized equipment.
- Non-Invasive: Caliper measurements involve a simple pinch of the skinfold, making them non-invasive and comfortable for most individuals.
- Suitable for Tracking Changes: Caliper measurements allow for the monitoring of changes in body composition over time, making them valuable for tracking progress in fitness and weight loss goals.
- Limitations:
- Operator Skill: The accuracy of caliper measurements heavily relies on the skill of the operator. Proper training and consistent technique are essential for obtaining reliable and consistent results.
- Equation Variability: Different equations are used to estimate body fat percentage based on caliper measurements, and the choice of equation can affect the accuracy of the results. It is crucial to use appropriate equations based on the population being measured.
- Individual Variability: Body composition varies among individuals, and caliper measurements may not accurately represent everyone’s actual body fat percentage. Factors such as genetics, hydration levels, and muscle mass can influence the results.
- Subcutaneous Fat Bias: Caliper-based measurements primarily estimate subcutaneous fat, and may not provide an accurate reflection of visceral fat (fat around organs), which is associated with higher health risks.
- Location-Specific: Caliper measurements focus on specific sites of the body, and may not provide a comprehensive picture of overall body composition.
Despite these limitations, caliper-based body composition measurements can still be a valuable tool for assessing changes in body fat percentage over time. They provide a relatively inexpensive and portable method to estimate body fat, which can be useful for monitoring progress and making informed decisions regarding fitness and nutrition goals. However, it is important to consider the limitations and potential sources of error associated with caliper measurements, and to use them in combination with other methods for a more comprehensive understanding of body composition.
Factors to Consider Before Using Calipers
Before using calipers for body composition measurement, there are several factors to consider to ensure accurate and reliable results. Taking these factors into account will help you make the most of caliper-based measurements and improve the overall accuracy of your body composition assessment. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Operator Training and Skill: The accuracy of caliper measurements is highly dependent on the skill and training of the operator. Proper training ensures consistent measurement techniques, correct placement of the calipers, and accurate interpretation of the results. Consider seeking guidance from a qualified professional or undergoing training to ensure proficiency in using calipers.
- Equipment Quality: The quality and condition of the calipers themselves can impact the accuracy of measurements. Ensure that the calipers are properly calibrated and well-maintained to obtain reliable results.
- Measurement Site Selection: Choosing the appropriate measurement sites on the body is crucial for accurate results. Familiarize yourself with the recommended anatomical sites for skinfold measurement, such as the triceps, biceps, subscapular, and suprailiac regions. Understanding the importance of site selection helps ensure consistency in your measurements.
- Measurement Consistency: Consistency in measurement technique is vital for reliable results. Pay attention to the angle, pressure, and duration of the pinch, as variations in these aspects can impact the skinfold measurement. Practice consistency to minimize potential errors and improve the reliability of your caliper-based measurements.
- Measurement Timing: Timing of measurements can influence the results. It is recommended to take measurements under the same conditions each time, such as at the same time of day and under similar circumstances regarding factors like hydration and activity level. Consistent timing helps to eliminate potential variables that may affect the accuracy of your measurements.
- Individual Factors: Individual factors, such as age, gender, and ethnicity, can influence the accuracy of caliper-based measurements. Different equations have been developed based on these factors, so ensure that you select the appropriate equation for your specific population to obtain more accurate estimations of body fat percentage.
- Interpretation: Caliper measurements provide an estimate of body fat percentage, and it is essential to understand the limitations of these estimations. Factors like individual variation, subcutaneous fat bias, and the specific equation used can impact the accuracy. Consider using caliper measurements as part of a comprehensive assessment that incorporates other body composition measurement methods for a more accurate understanding of your overall body composition.
By considering these factors and taking steps to ensure consistency, accuracy, and proper technique, you can maximize the effectiveness of caliper-based body composition measurements. Remember that caliper measurements provide estimations rather than precise measurements, but with attention to these factors, you can obtain valuable insights into your body composition and track changes over time.
Steps to Take While Using Calipers for Body Composition Measurement
Using calipers for body composition measurement requires careful technique and attention to detail. By following these steps, you can ensure accurate and consistent results when using calipers to estimate body fat percentage:
- Educate Yourself: Familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the body and the specific skinfold measurement sites recommended for caliper-based assessment. Understanding the correct locations for measurements is essential for consistent and accurate results.
- Pick Reliable Calipers: Invest in a high-quality caliper that is well-calibrated and specifically designed for measuring skinfold thickness. Quality calipers ensure more precise measurement and reduce variability.
- Prepare the Site: Prepare the skinfold measurement site by cleaning the area and removing any excess moisture or oils. This helps ensure a secure grip of the calipers and accurate measurement.
- Standardize Measurement Technique: Adopt a standardized technique for taking skinfold measurements. This includes ensuring the same amount of pressure is applied during each pinch, and the pinch is held for a consistent duration to obtain accurate and consistent results.
- Take Multiple Measurements: Take multiple measurements at each chosen site to minimize variability. Generally, three measurements are taken, allowing for calculation of an average. This helps reduce the impact of measurement errors and increases the reliability of the results.
- Record and Document: Record the measurements for each site to ensure proper monitoring of changes over time. Keep a record of the measurements, dates, and any other relevant details to assist with tracking progress and comparing future measurements.
- Use Appropriate Equations: Utilize validated equations to estimate body fat percentage based on the skinfold measurements. Ensure that the equations used are suitable for the specific population being measured to obtain more accurate estimations.
- Consider Professional Assistance: If you are uncertain about taking accurate caliper measurements on your own, consider seeking assistance from a trained professional. They can provide guidance, ensure correct technique, and offer more precise measurements.
- Combine with Other Assessment Methods: Keep in mind that caliper-based measurements should not be the sole method used to assess body composition. For a more comprehensive understanding, consider combining caliper measurements with other methods such as DXA, BIA, or hydrostatic weighing. This will offer a more complete picture of your body composition.
By following these steps, you can enhance the accuracy and consistency of your caliper-based body composition measurements. Remember, the skill and technique of the operator greatly influence the results, so practice and attention to detail are key. Additionally, it is crucial to interpret the results within the context of their limitations and consider them as part of a broader assessment of body composition.
Read more: Which Is The Best Composite Decking
Recommendations for Accurate Caliper-Based Body Composition Measurements
Accurate caliper-based body composition measurements require attention to detail and adherence to standardized techniques. By following these recommendations, you can improve the accuracy and reliability of your caliper measurements:
- Exercise Proper Technique: Master the correct technique for taking skinfold measurements using calipers. Ensure that the pinchers of the calipers grasp only the skinfold and not underlying muscle or bone.
- Consistency is Key: Maintain consistency in your measurement techniques, including the pressure applied during the pinch, the duration of the pinch, and the placement of the calipers. Consistency helps minimize variability and improve the reliability of the results.
- Take Multiple Measurements: Perform multiple measurements at each site to account for any outliers or variations. Taking three measurements and calculating the average helps reduce the impact of measurement errors and enhances accuracy.
- Choose Skilled Operators: If possible, have measurements taken by a trained and skilled professional to ensure accurate and consistent results. Professionals are knowledgeable in proper technique and can minimize sources of error.
- Keep the Skin Dry: Moisture on the skin can affect the grip of the calipers and impact the accuracy of the measurement. Ensure the skin is clean and dry before conducting the measurements.
- Consider Measurement Timing: Try to take measurements at the same time of day to minimize factors that may cause variation, such as changes in hydration levels or temporary fluid retention.
- Use Population-Specific Equations: Choose equations that are specific to the population being measured. Different equations have been developed based on age, gender, and ethnicity, and using population-specific equations improves the accuracy of the estimations.
- Combine Methods: While caliper measurements are a valuable tool, they should not be used in isolation. To obtain a more comprehensive assessment of body composition, consider combining caliper measurements with other methods, such as DXA or BIA.
- Regularly Calibrate the Calipers: Ensure that your calipers are calibrated regularly to maintain accuracy. Calibration helps confirm that the calipers are functioning properly and providing reliable measurements.
- Record and Track Measurements: Keep a record of your caliper measurements, including the measurement sites, dates, and any significant details. Tracking the measurements over time provides a comprehensive picture of your body composition changes.
- Interpret with Context: Understand the limitations associated with caliper-based measurements and interpret the results in the context of these limitations. Consider them as estimation tools rather than precise measurements, and factor in other indicators of body composition and overall health.
By following these recommendations, you can enhance the accuracy and reliability of your caliper-based body composition measurements. Consistent technique, multiple measurements, skilled operators, and the inclusion of other assessment methods all contribute to a more accurate understanding of your body composition. Remember to use the results as part of a comprehensive approach to assessing your overall health and fitness.
Conclusion
Body composition measurements are a valuable tool for assessing overall health and fitness. Among the various methods available, caliper-based measurements provide a cost-effective, portable, and accessible way to estimate body fat percentage. By measuring skinfold thickness at specific sites on the body, calipers offer insights into the distribution of subcutaneous fat and provide an estimation of body fat percentage.
While caliper measurements have certain advantages, such as their affordability and portability, it is important to be aware of their limitations. Factors such as operator skill, equation selection, individual variation, and subcutaneous fat bias can impact the accuracy of the results. To improve the reliability of caliper-based measurements, it is crucial to follow standardized techniques, take multiple measurements, use appropriate equations, and consider combining caliper measurements with other assessment methods for a more comprehensive understanding of body composition.
Accurate caliper-based body composition measurements require attention to detail and consistency. Educating oneself, using reliable calipers, following proper technique, and recording measurements are all keys to obtaining accurate and meaningful results. It is recommended to seek assistance from trained professionals if needed and to keep in mind that caliper measurements are estimations rather than exact measurements, offering insights into body composition changes over time.
By considering the factors discussed in this article and implementing the recommendations for accurate caliper-based measurements, individuals can effectively track and monitor changes in body fat percentage. Understanding body composition provides valuable information for setting realistic goals, monitoring progress, and making informed decisions regarding overall health and fitness.
In conclusion, caliper-based body composition measurements serve as a valuable tool in assessing and understanding our bodies. They allow us to go beyond just weight and gain insights into the distribution of fat and muscle. When used properly and in conjunction with other methods, caliper measurements can help individuals achieve their health and fitness goals and ultimately lead to improved overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about Which Body Composition Measurement Utilizes Calipers
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Which Body Composition Measurement Utilizes Calipers”