

Articles
How To Use Calipers To Measure
Modified: January 8, 2024
Learn how to properly use calipers to measure objects in this comprehensive guide. Explore tips, techniques, and best practices for accurate measurements.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
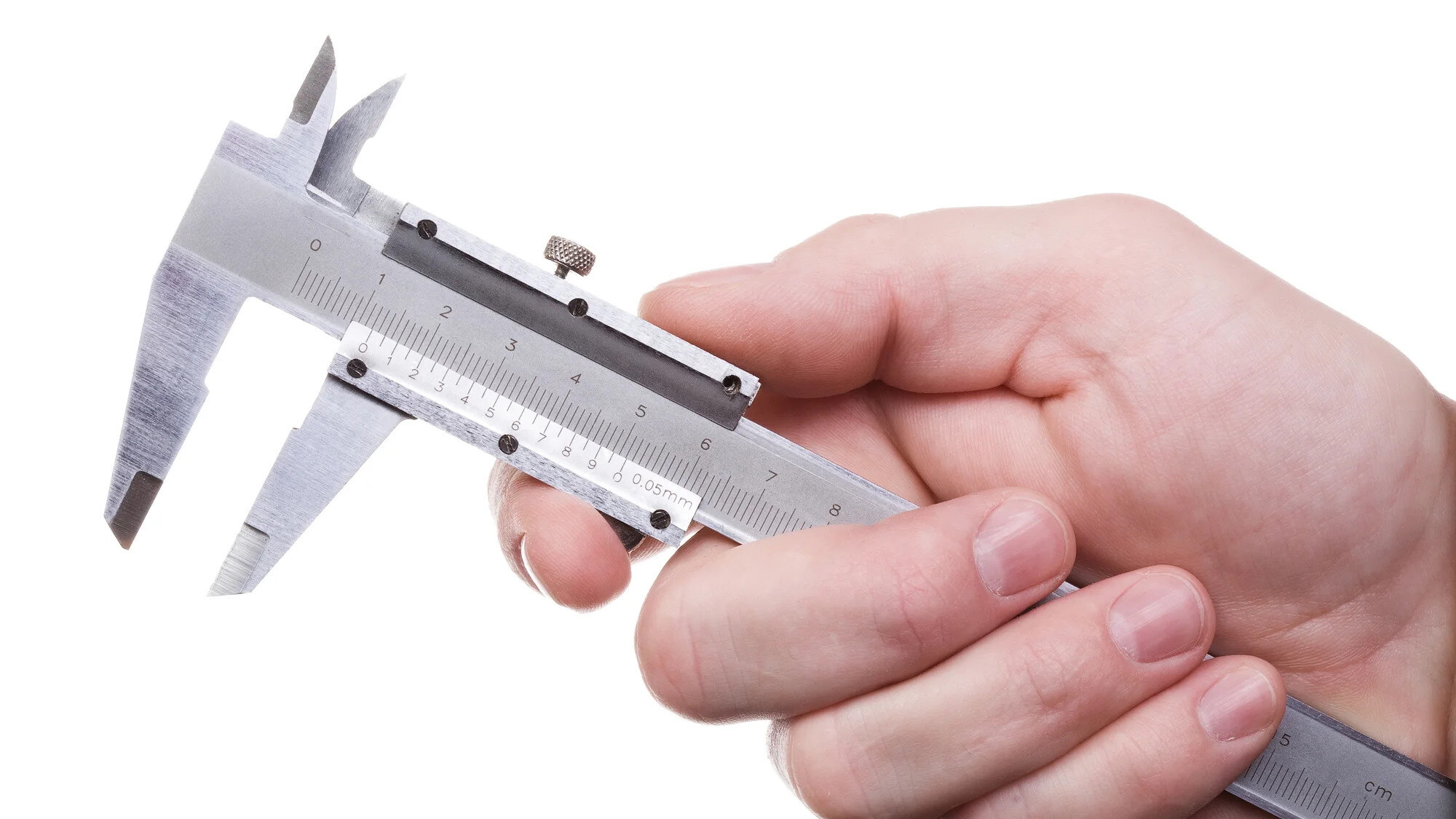
Calipers are versatile and precise measuring tools that are commonly used in various industries, such as manufacturing, engineering, woodworking, and metalworking. Whether you are a professional in one of these fields or an avid DIY enthusiast, understanding how to properly use calipers can greatly improve your accuracy and efficiency in measuring.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide on how to use calipers effectively. We will explore the different types of calipers, the various parts that make up a caliper, and step-by-step instructions on how to take measurements accurately. Additionally, we will cover calibrating calipers and share some useful tips and best practices to help you get the most out of your calipers.
Whether you are measuring the dimensions of a machined part, checking the thickness of a piece of wood, or ensuring precision in your projects, calipers are a valuable tool to have in your arsenal. By mastering the use of calipers, you can achieve precise measurements, resulting in better quality workmanship and improved project outcomes.
So, let’s dive in and discover the fascinating world of calipers, and how they can revolutionize your measurement process.
Key Takeaways:
- Mastering the use of calipers can revolutionize your measurement process, leading to better quality workmanship and improved project outcomes in various industries and applications.
- Understanding the different types of calipers, their parts, and best practices can maximize the accuracy and reliability of your measurements, ensuring successful outcomes in your projects.
Read more: How Accurate Are Digital Calipers
Overview of Calipers
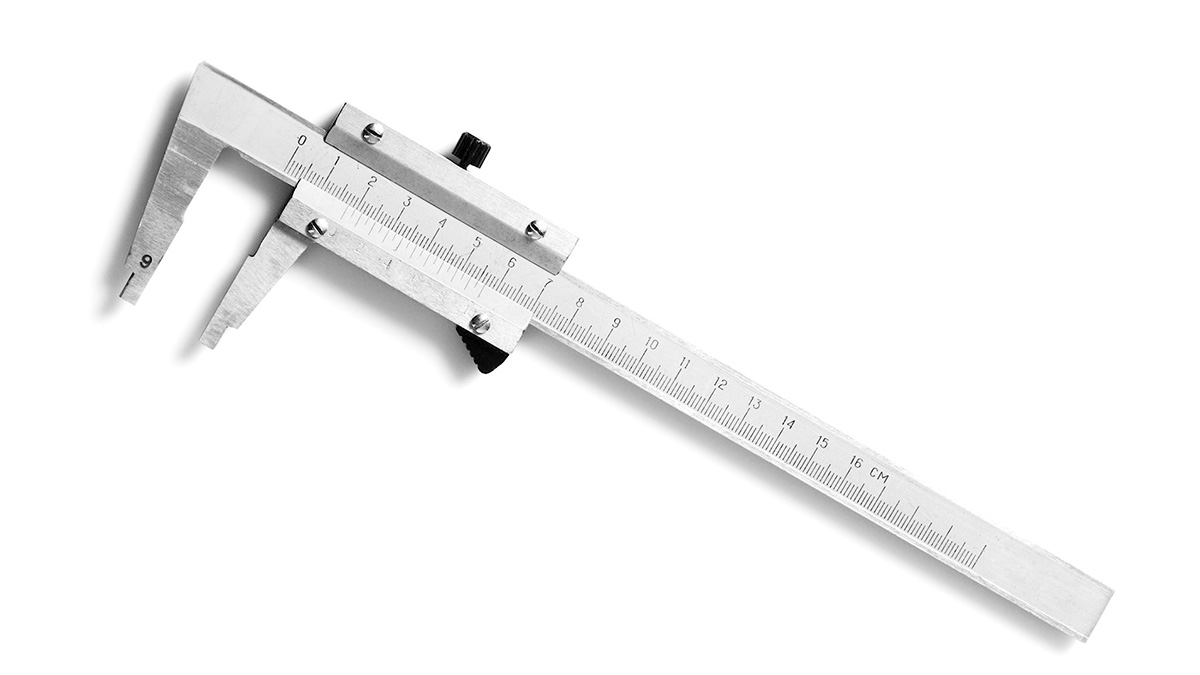
Calipers are measuring instruments designed to accurately determine the dimensions of an object. They are commonly used in various industries and applications where precision measurements are required. Calipers come in different types to suit different measurement needs, but they all share the same basic principle of operation.
The main purpose of calipers is to measure the distance between two opposing sides of an object, such as the length, width, or diameter. They achieve this by utilizing two pairs of jaws or arms that can be adjusted to fit the object being measured. By moving the jaws until they grip the object tightly, the caliper can provide an accurate measurement of the distance between the jaws.
Calipers are typically made of high-quality materials, such as stainless steel or hardened plastic, to ensure durability and accuracy. Some calipers also feature a digital readout, which provides a more precise and convenient measurement reading.
One of the distinct advantages of calipers is their ability to measure both internal and external dimensions. External dimensions refer to measurements taken on the outer surface of an object, such as the length or width of a board. Internal dimensions, on the other hand, are measurements taken inside an object, such as the diameter of a hole or the distance between two walls.
Calipers are an essential tool for tasks that require precise measurements, such as fitting components together, ensuring tolerance specifications are met, or determining the thickness of materials. They provide a level of accuracy that is difficult to achieve with other manual measuring tools.
Overall, calipers are versatile and reliable tools that play a crucial role in various industries. Their ability to provide precise measurements makes them indispensable for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Types of Calipers
Calipers come in various types, each designed for specific measurement purposes. Understanding the different types of calipers can help you choose the right tool for the job and ensure accurate measurements. Here are some of the most commonly used types of calipers:
- Vernier Calipers: Vernier calipers are one of the most popular types of calipers. They consist of a main scale and a sliding vernier scale, allowing for precise measurement readings. This type of caliper is versatile and suited for a wide range of measurement tasks.
- Dial Calipers: Dial calipers, also known as dial gauges, feature a dial indicator that displays the measurement reading. This type of caliper provides a digital-like readout but without the need for batteries. Dial calipers are ideal for tasks where accurate measurements need to be easily read and recorded.
- Digital Calipers: Digital calipers are equipped with an electronic digital display that provides a precise measurement reading. They offer quick and easy measurements without the need for manual reading or interpretation. Digital calipers are especially useful when dealing with complex measurements or when multiple readings need to be taken.
- Inside Calipers: Inside calipers, also known as internal calipers, are specifically designed to measure the inside diameter or width of an object. They feature curved legs that can be adjusted to fit inside a hole or opening, allowing for accurate internal measurements.
- Outside Calipers: Outside calipers, also known as external calipers, are used to measure the outer dimensions of an object. They have straight legs that can be adjusted to fit around the outside of an object, providing accurate external measurements.
- Dividers: Dividers, although not technically calipers, serve a similar purpose in measuring distances and transferring measurements. They have two pointed legs that can be adjusted to mark or divide distances accurately.
Each type of caliper offers its own advantages and is suited for specific measurement tasks. It is important to choose the right type of caliper based on the nature of your measurement needs to ensure accurate and reliable results.
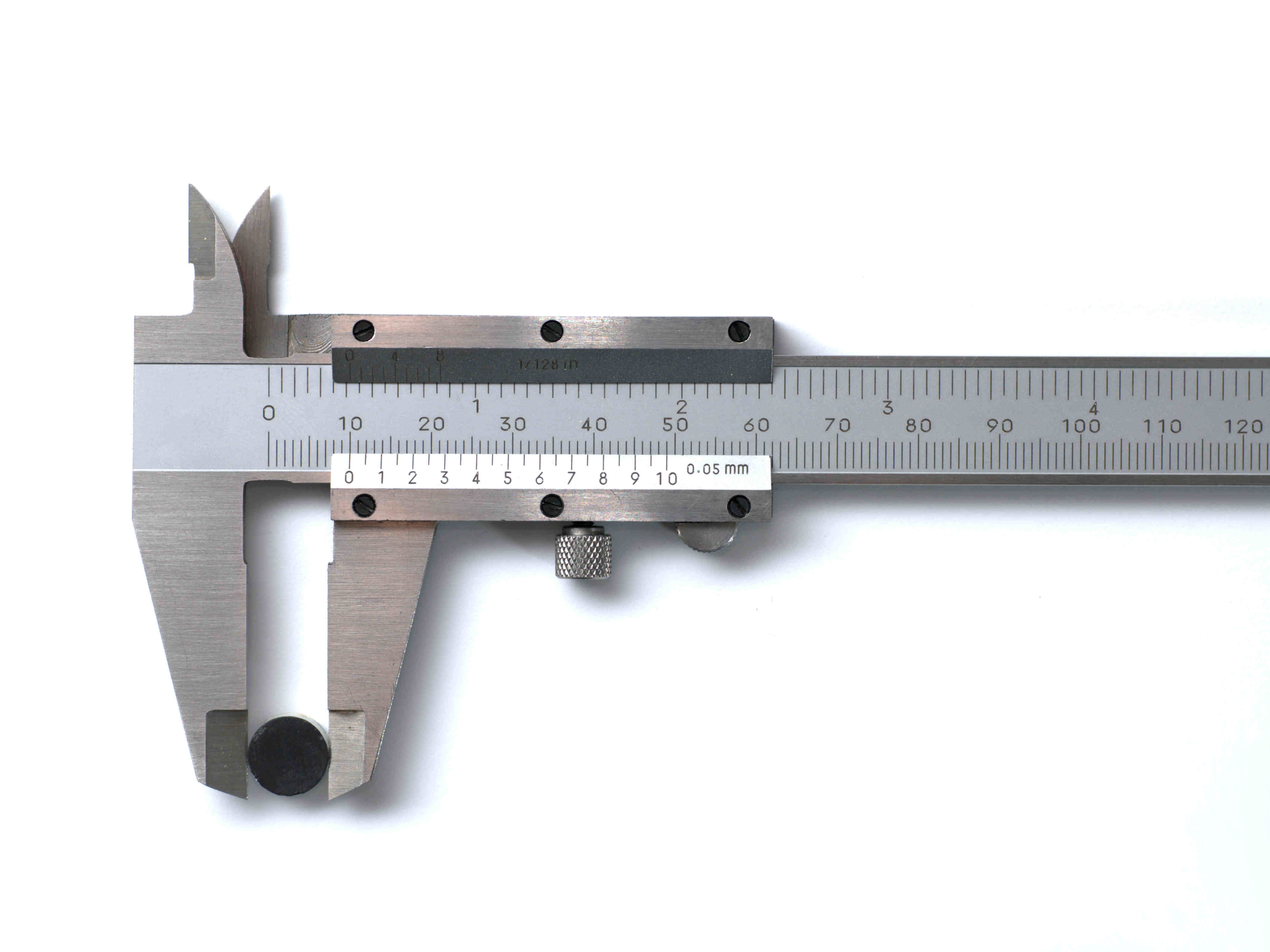
Parts of Calipers
To effectively use calipers for accurate measurements, it is essential to understand the different parts that make up this measuring instrument. Here are the key components of most calipers:
- Jaws: The jaws of a caliper are the primary components used to grip and measure the object being measured. There are typically two sets of jaws – the fixed jaws and the movable jaws. The fixed jaws remain in a fixed position, while the movable jaws can be adjusted to fit the object.
- Main Scale: The main scale is a ruler-like feature on the body of the caliper. It displays the primary measurement increments, such as centimeters, inches, or millimeters. The main scale provides a reference point for the measurement.
- Vernier Scale: Some calipers, such as vernier and dial calipers, have a secondary scale called the vernier scale. It is used to provide more precise measurement readings by matching the markings on the vernier scale with the main scale.
- Depth Rod: The depth rod is a protruding rod or extension on some calipers, allowing for depth measurements. It helps measure the depth of holes, grooves, or recesses accurately.
- Locking Screw: The locking screw is a small screw or knob located near the movable jaws. It is used to lock the position of the movable jaws once the object is correctly fitted. Locking the screw ensures that the measurement does not change while reading or recording the measurement.
- Display: Digital calipers have an electronic display that shows the measurement reading. The display provides a clear and easy-to-read measurement, eliminating the need to manually interpret the scale markings.
- Thumbwheel: The thumbwheel is a small wheel or dial located on the caliper’s body. It is used to finely adjust the position of the movable jaws for precise measurement. The thumbwheel allows for easy and controlled movement of the movable jaws.
- Frame: The frame of the caliper is the main body that holds all the components together. It provides stability and support to ensure accurate measurements.
Understanding the different parts of a caliper is crucial for using the tool effectively and obtaining precise measurements. Familiarize yourself with these parts to maximize the functionality of your caliper and achieve accurate results in your measurement tasks.
Preparing for Measurement
Before beginning any measurement with calipers, it is important to properly prepare both the calipers and the object being measured. Here are the steps to follow to ensure accurate and reliable measurements:
- Clean the Calipers: Ensure that the calipers are clean and free from any debris or dirt that could affect the accuracy of the measurement. Wipe the jaws and the scales with a soft, lint-free cloth to remove any residue.
- Zero the Calipers: If you are using digital calipers, it is essential to zero or reset the reading before each measurement. This sets the starting point for the measurement and eliminates any previous measurement values.
- Inspect the Object: Examine the object you are measuring to ensure it is clean and free from any debris or imperfections that could affect the measurement. If necessary, clean the object or remove any surface contaminants to ensure accurate results.
- Position the Object: Place the object in a stable position, ensuring it is secure and will not move during the measurement process. If necessary, use clamps, vices, or other holding mechanisms to keep the object steady.
- Fit the Jaws: Adjust the movable jaws of the calipers to fit the object being measured. Ensure that the jaws are firmly but not overly tight against the object. The object should be securely gripped without causing any deformation or distortion.
- Lock the Jaws: Once the jaws are properly fitted to the object, lock them in place using the locking screw or mechanism on your calipers. This prevents the jaws from moving and ensures that the measurement remains consistent throughout the process.
By following these steps, you can ensure that both the calipers and the object are prepared for an accurate measurement. Proper preparation is crucial for obtaining precise results and maintaining consistency in your measurement process.
When using calipers to measure, make sure to zero the calipers before taking any measurements. This ensures accurate and precise readings.
Read more: How To Use Micrometers And Calipers
Taking Measurements
Once you have properly prepared the calipers and the object for measurement, it’s time to take the actual measurement. Here are the steps to follow for accurate and precise measurements with calipers:
- Read the Main Scale: Start by reading the main scale on the caliper. Identify the measurement increment being used, whether it is inches, centimeters, or millimeters. This will be the primary reference point for your measurement.
- Read the Vernier Scale (if applicable): If you are using vernier or dial calipers with a vernier scale, align the markings on the vernier scale with the closest matching marking on the main scale. Note the value on the vernier scale that aligns with the main scale. This will provide the additional measurement increment for a more accurate reading.
- Read the Digital Display (if applicable): If you are using digital calipers, simply read and record the measurement displayed on the electronic display. The digital display provides an accurate measurement reading without the need for manual interpretation.
- Take the Measurement: Gently close the movable jaws of the calipers until they firmly grip the object being measured. Ensure that both jaws make contact with the object simultaneously. Take care not to apply excessive force that could distort the object or the measurement.
- Record the Measurement: Once the jaws are securely in place, carefully read and record the measurement value from the main scale, vernier scale (if applicable), or digital display. Note down the precise measurement for future reference or use in your project.
It is important to note that when taking measurements with calipers, it is advisable to take multiple readings to ensure accuracy and consistency. Repeat the measurement process several times and compare the readings to verify that they are consistent. If there are any discrepancies, recalibrate the calipers or reassess the measurement technique.
By following these steps, you can confidently take accurate measurements with calipers and obtain reliable data for your projects or applications.
Reading the Measurement
Reading the measurement obtained from calipers requires understanding the markings on the main scale, vernier scale (if applicable), or digital display. Here are the steps to help you accurately interpret and read the measurement:
- Main Scale: The main scale on the caliper provides the primary measurement increment, such as inches, centimeters, or millimeters. Locate the zero point on the main scale, which aligns with the fixed jaws, and note the value corresponding to the position of the movable jaws. This value represents the whole units of measurement.
- Vernier Scale (if applicable): If you are using vernier or dial calipers with a vernier scale, align the markings on the vernier scale with the main scale. Determine which marking on the vernier scale aligns exactly with a marking on the main scale. Note the value on the vernier scale that matches with the main scale marking. This value represents the additional measurement increment.
- Digital Display (if applicable): If you are using digital calipers, simply read the measurement value displayed on the electronic digital display. The digital display provides an accurate reading, typically displayed in decimal form.
- Combine the Readings: If you have both a main scale and a vernier scale, combine the readings to get the final measurement. Add the value obtained from the main scale to the value obtained from the aligned vernier scale marking. The sum of these two values represents the precise measurement.
- Include Decimal Places (if necessary): If your measurement requires decimal places, round the measurement to the desired decimal point based on the precision needed for your specific application. Use the appropriate rounding rules to ensure accuracy.
It is essential to take your time and read the measurement carefully to avoid any errors. Double-check your readings, especially if you are using a vernier scale or a digital display, to ensure precise and reliable results.
By following these steps and thoroughly understanding the measurement readings, you can confidently interpret and record the measurements obtained from your calipers.
Calibrating Calipers
Calibrating calipers is a crucial step to ensure their accuracy and reliability in measurements. Over time, calipers may become misaligned or lose their calibration due to wear and tear. Here are the steps to calibrate your calipers:
- Verify Zero Reading: Start by ensuring that your calipers are properly zeroed. If you have digital calipers, make sure the display reads zero when the jaws are closed and not measuring anything. If you have vernier or dial calipers, ensure that the zero point lines up accurately with the fixed jaws.
- Check for Parallel Alignment: Close the jaws of your calipers and observe if the jaws remain parallel to each other. They should not be misaligned or tilted. If you notice any misalignment, adjust the calipers until the jaws are parallel through the entire range. Use a calibration block or a known reference object to verify parallel alignment.
- Test Accuracy: Use a known reference object of a predefined dimension to test the accuracy of your calipers. Measure the object multiple times from different angles and positions to ensure consistent and accurate readings. Compare the measurement obtained with the known dimension to identify any discrepancies.
- Make Adjustments: If your calipers are not providing accurate measurements, it may be necessary to make adjustments. Some calipers have adjustment screws or knobs that can be used to fine-tune the calibration. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to make the necessary adjustments to bring the calipers back into accuracy.
- Periodic Calibration: Regular calibration is recommended to maintain the accuracy of your calipers. How often you calibrate depends on the frequency of use and the level of precision required in your measurements. It is generally advisable to calibrate your calipers at least once a year or more frequently if they are used extensively.
Calibrating your calipers ensures that they provide accurate and reliable measurements. It is an essential step to maintain the integrity of your measurements and ensure the quality of your work. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and instructions for specific calibration procedures for your calipers.
By following these steps and regularly calibrating your calipers, you can have confidence in the accuracy of your measurements and produce reliable results in your projects or applications.
Tips and Best Practices
Using calipers effectively requires not only understanding their features and functions but also adopting certain tips and best practices. Here are some valuable tips to consider when using calipers:
- Clean and Maintain: Keep your calipers clean and free from debris to ensure accurate measurements. Regularly wipe the jaws and scales with a soft, lint-free cloth.
- Practice Consistency: Minimize variations in your measurements by maintaining a consistent approach. Apply the same amount of pressure and grip the object in the same manner each time you measure.
- Take Multiple Measurements: To improve accuracy, take multiple measurements of the same object and compare the results. This helps identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies and ensures a more reliable measurement.
- Verify with Other Tools: If precision is critical, use alternative measuring tools, such as micrometers or gauge blocks, to verify the accuracy of your caliper measurements.
- Consider Calibration Blocks: Investing in calibration blocks or known reference objects can assist in verifying the calibration and accuracy of your calipers.
- Avoid Excessive Force: Apply just enough pressure to grip the object being measured. Excessive force can distort the object and lead to inaccurate measurements.
- Protect and Store Properly: Keep your calipers in a protective case or pouch when not in use to prevent damage. Store them in a dry and controlled environment to avoid humidity or temperature fluctuations.
- Use the Right Type of Calipers: Choose the appropriate type of caliper for the specific measurement task at hand. Different calipers offer different measurement capabilities, so select the one that suits your needs.
- Stay Updated with Technology: Embrace the advancements in digital technology by considering digital calipers. They provide instant and accurate measurements, making your task easier and more efficient.
- Continual Learning: Stay curious and continually seek knowledge about caliper usage, maintenance, and best practices. This will improve your skills and proficiency in using calipers effectively.
By following these tips and implementing best practices, you can maximize the accuracy and reliability of your caliper measurements. Remember to adapt these suggestions to your specific measurement needs and always prioritize safety and precision in your work.
Read also: 11 Best Calipers for 2024
Conclusion
Calipers are essential tools for precise and accurate measurements in various industries and applications. Understanding how to use calipers effectively can greatly enhance your measurement capabilities, improving the quality and efficiency of your work.
In this article, we explored the different types of calipers available, including vernier calipers, digital calipers, and dial calipers. We discussed the various parts that make up a caliper, such as the jaws, main scale, vernier scale (if applicable), locking screw, and digital display. Properly preparing for measurement by cleaning the calipers and the object, fitting the jaws correctly, and locking them in place is crucial for obtaining accurate results.
We also delved into the steps involved in taking measurements with calipers, including reading the main scale, vernier scale (if applicable), or digital display. We emphasized the importance of multiple readings and the recording of precise measurements. Additionally, we highlighted the significance of calibrating calipers regularly to maintain their accuracy and reliability.
To ensure successful measurement outcomes, we provided tips and best practices, such as cleaning and maintaining calipers, practicing consistency, and considering the use of calibration blocks. We also stressed the significance of using the right type of calipers for specific measurement tasks and staying updated with digital technology.
By following these guidelines and incorporating these best practices into your measurement processes, you can confidently use calipers to achieve precise and reliable measurements. Calipers are powerful tools that can significantly enhance your workmanship and contribute to the success of your projects.
So, equip yourself with a quality set of calipers, familiarize yourself with their features and functions, and embrace the art of accurate measurement. With practice and attention to detail, you will become proficient in using calipers and unlock a world of precision in your work.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Use Calipers To Measure
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How To Use Calipers To Measure”