Home>Construction & Tools>Building Materials>What Temperature Can Brick Withstand


Building Materials
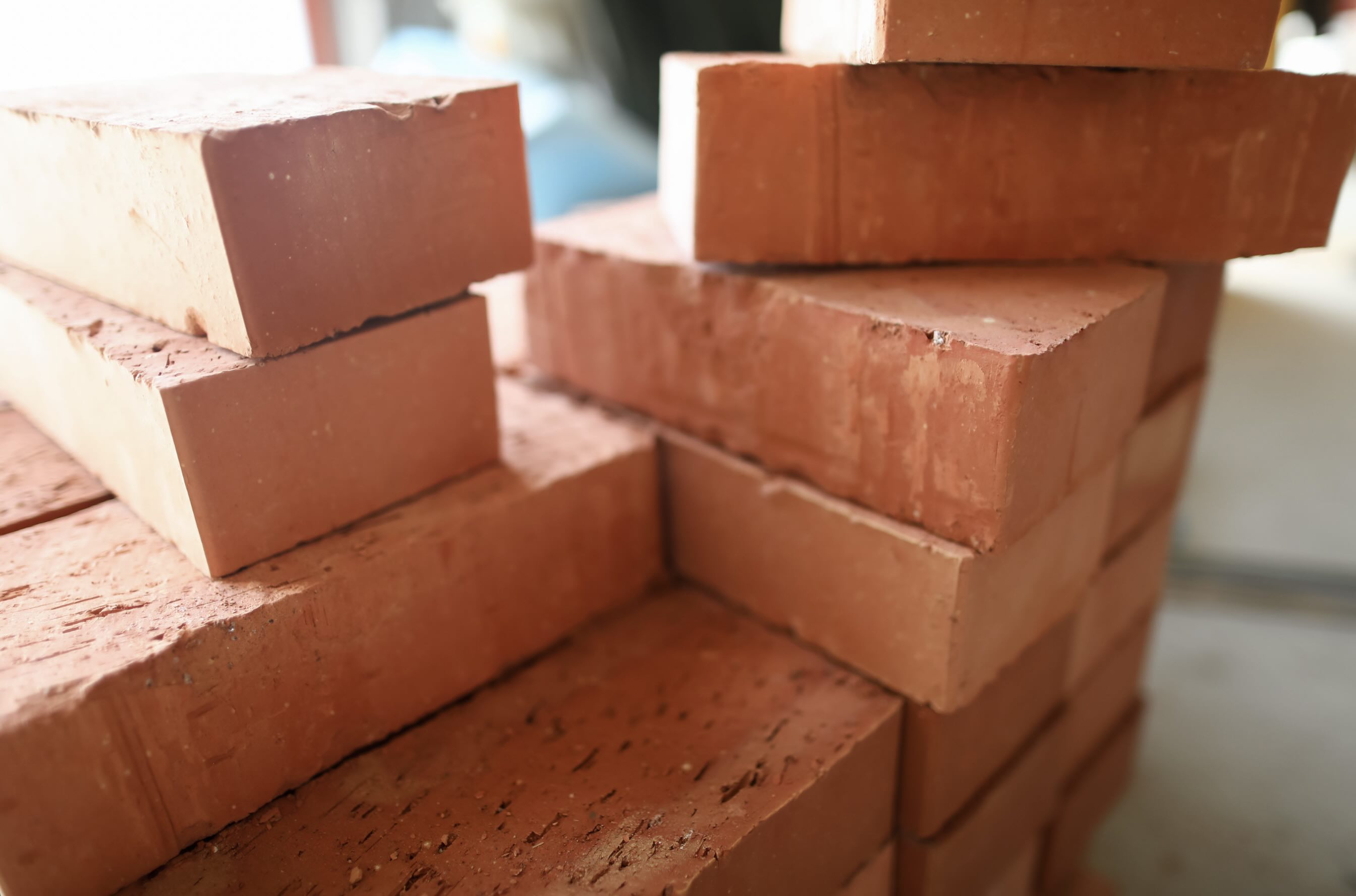
What Temperature Can Brick Withstand
Published: January 23, 2024
Brick, a durable building material, can withstand temperatures up to 1200°C, making it ideal for withstanding high heat in construction projects. Explore its heat-resistant properties and applications.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to building materials, brick has long been a popular choice for its durability, aesthetic appeal, and versatility. Whether used in the construction of homes, commercial buildings, or outdoor structures, brick offers a timeless charm and robustness that withstands the test of time. However, a critical aspect of evaluating the suitability of brick for various applications is understanding its ability to withstand high temperatures. In this article, we will delve into the factors influencing the temperature resistance of brick, explore the maximum temperatures it can endure, and examine the effects of exposure to high temperatures. By gaining insight into these aspects, you will develop a deeper appreciation for the resilience of brick as a building material and its potential limitations in extreme heat scenarios.
Key Takeaways:
- Brick can withstand temperatures up to 2,000°F, making it a reliable choice for construction. However, prolonged exposure to extreme heat can lead to color changes, cracking, and loss of strength.
- Factors like composition, firing technique, and porosity influence brick’s ability to resist high temperatures. Understanding these factors helps builders make informed decisions for various construction applications.
Read more: What Temperature Can Pyrex Glass Withstand
Factors Affecting Temperature Resistance of Brick
Brick, a time-honored building material, exhibits varying degrees of temperature resistance, influenced by several key factors:
- Composition: The composition of the clay used in brick production significantly impacts its ability to withstand high temperatures. High-quality bricks are typically composed of dense, well-fired clay with minimal organic impurities, enhancing their resistance to heat.
- Firing Technique: The firing process plays a crucial role in determining a brick’s thermal resilience. Bricks subjected to high-temperature kiln firing undergo vitrification, a process in which the clay particles fuse together, resulting in a denser and more heat-resistant material.
- Porosity: The porosity of a brick, determined by its internal structure and the presence of microscopic voids, affects its thermal conductivity and resistance to heat. Lower porosity generally indicates higher resistance to temperature fluctuations.
- Chemical Additives: Certain chemical additives, such as alumina and silica, can be incorporated into the brick’s composition to enhance its thermal properties, increasing its ability to withstand extreme temperatures.
- Manufacturing Standards: The adherence to stringent manufacturing standards and quality control measures ensures that bricks are produced with consistent density and structural integrity, contributing to their overall temperature resistance.
Understanding these factors is essential for assessing the suitability of brick in environments where high temperatures are a concern. Whether used in fireplaces, industrial furnaces, or exterior facades exposed to intense sunlight, the composition and characteristics of the brick directly influence its performance in varying temperature conditions.
Maximum Temperature Brick Can Withstand
Brick, renowned for its robustness, demonstrates impressive resilience to high temperatures, making it a favored material in applications where heat exposure is a consideration. The maximum temperature that brick can withstand is influenced by its composition, density, and firing process. Generally, standard clay bricks can endure temperatures ranging from 1,800°F to 2,000°F (982°C to 1,093°C) before exhibiting significant structural changes or failure.
For specific applications requiring even higher temperature resistance, specialized refractory bricks are available. These bricks, engineered for exceptional thermal stability, can withstand temperatures exceeding 2,700°F (1,482°C) and are commonly used in industrial furnaces, kilns, and high-temperature processing environments.
It is important to note that while brick exhibits remarkable resistance to heat, prolonged exposure to temperatures at or near its maximum threshold may lead to gradual deterioration. Factors such as thermal cycling, mechanical stress, and chemical reactions in high-temperature environments can contribute to the degradation of brick over time, necessitating careful consideration of its limitations in extreme heat scenarios.
By understanding the maximum temperatures that standard and refractory bricks can endure, builders, engineers, and architects can make informed decisions regarding their use in diverse applications, ensuring the longevity and safety of structures exposed to elevated temperatures.
Brick can withstand high temperatures, typically up to 1,800°F (980°C). This makes it suitable for use in fireplaces, ovens, and other heat-intensive applications.
Effects of High Temperatures on Brick
When subjected to high temperatures, brick undergoes a series of physical and chemical changes that impact its structural integrity and appearance. Understanding the effects of elevated temperatures on brick is crucial for assessing its performance in environments characterized by heat exposure.
1. Thermal Expansion: High temperatures cause brick to expand, which can lead to stress within the material. While brick is designed to accommodate thermal expansion to a certain extent, prolonged exposure to extreme heat can result in microcracking and gradual deterioration of the material’s mechanical properties.
2. Color Changes: The color of brick may undergo alteration when exposed to high temperatures. This is particularly evident in the case of clay bricks, where the firing process initially determines their color. Prolonged exposure to heat can cause the brick’s surface to darken or develop a metallic sheen, altering its aesthetic appearance.
3. Spalling and Cracking: Intense heat can lead to spalling, a phenomenon in which the surface layers of brick flake off due to thermal stress. Additionally, the expansion and contraction induced by fluctuating temperatures can result in the formation of cracks, compromising the structural integrity of the brick.
4. Loss of Strength: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can diminish the compressive and flexural strength of brick, affecting its load-bearing capacity and overall stability. This reduction in strength may compromise the safety and performance of structures constructed with brick in high-temperature environments.
5. Chemical Changes: High temperatures can induce chemical reactions within the brick material, leading to the breakdown of mineral components and alteration of its physical properties. These chemical changes can contribute to the degradation of the brick over time, particularly in environments with aggressive chemical agents or high-temperature combustion byproducts.
By comprehending the effects of high temperatures on brick, builders and designers can implement appropriate measures to mitigate potential issues and ensure the longevity and performance of brick structures in environments characterized by heat exposure.
Conclusion
Brick, a stalwart in the realm of building materials, exhibits commendable resistance to high temperatures, making it a reliable choice for a wide array of construction applications. The factors influencing its temperature resistance, including composition, firing technique, porosity, chemical additives, and manufacturing standards, play a pivotal role in determining its performance in heat-intensive environments.
Understanding the maximum temperatures that standard and refractory bricks can withstand is essential for making informed decisions regarding their utilization in diverse settings. While standard clay bricks can endure temperatures ranging from 1,800°F to 2,000°F, specialized refractory bricks engineered for exceptional thermal stability can withstand temperatures exceeding 2,700°F, catering to more demanding industrial and high-temperature applications.
However, it is imperative to acknowledge the effects of high temperatures on brick, including thermal expansion, color changes, spalling and cracking, loss of strength, and chemical alterations. These considerations are crucial for evaluating the long-term performance and durability of brick structures exposed to heat, guiding the implementation of preventive measures and maintenance practices to mitigate potential issues.
In conclusion, the enduring appeal and resilience of brick as a building material, coupled with its capacity to withstand high temperatures, underscore its enduring relevance in the construction industry. By comprehensively understanding the factors influencing its temperature resistance, the maximum temperatures it can endure, and the effects of heat exposure, stakeholders can leverage brick’s inherent strengths while proactively addressing its limitations, ensuring the creation of enduring and robust structures capable of withstanding the rigors of heat-intensive environments.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Temperature Can Brick Withstand
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.















0 thoughts on “What Temperature Can Brick Withstand”