Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>Cities Built Throughout The Roman Empire Modeled Their Urban Planning On Which City?


Planning & Engineering
Cities Built Throughout The Roman Empire Modeled Their Urban Planning On Which City?
Modified: August 16, 2024
Discover which city the cities built throughout the Roman Empire modeled their urban planning and engineering on, and explore the historic significance of this influential city.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
The Roman Empire was renowned for its advanced architecture, engineering marvels, and sophisticated urban planning. Many cities built throughout the empire modeled their urban layouts after the city of Rome, which served as the epitome of Roman urban planning. The influence of Roman urban planning can still be seen today in cities all around the world.
The Romans had a strong vision for organizing cities in a systematic and efficient manner. They believed that a well-planned city would not only enhance the quality of life for its inhabitants, but also promote social order, economic prosperity, and political stability. Consequently, they incorporated various elements and principles into their urban planning that were both practical and aesthetically pleasing.
Rome, as the model city, set the standards for urban planning. Its layout became a template for other cities to follow, and its influence extended throughout the empire. The Romans developed an intricate grid system of streets, established public spaces and forums for civic activities, constructed aqueducts and sanitation systems, and implemented innovative architectural techniques.
This article will delve into the various elements of Roman urban planning and explore the legacy it has left behind. From the grid system of streets to the impressive public spaces, we will uncover the fascinating aspects of how Roman cities were built and designed.
Join us as we take a journey through time to discover the genius of Roman urban planning and the impact it had on the cities that have endured for centuries. Whether you are a history enthusiast or simply curious to learn more about the foundations of modern urban planning, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the role Rome played in shaping the way cities are built. Let’s dive in and explore the impressive influence of Roman urban planning!
Key Takeaways:
- Roman urban planning, with its grid system, public spaces, and infrastructure, continues to influence modern cities worldwide, shaping their functionality, aesthetics, and community engagement.
- The enduring legacy of Roman urban planning showcases the Romans’ ingenuity, foresight, and commitment to creating sustainable, livable cities, leaving an indelible mark on urban landscapes across the globe.
Read more: What Is An Urban Planning Degree
The Influence of Roman Urban Planning
The Roman Empire’s urban planning had a profound and lasting impact on cities throughout history. From their innovative infrastructure to their organized street layouts, the Romans set the stage for modern urban planning principles. Here are some key ways in which the Romans influenced urban planning:
1. Infrastructure: The Romans were renowned for their advanced engineering skills and infrastructure development. They implemented highly sophisticated aqueduct systems that brought fresh water into cities, enabling the population to grow and thrive. This emphasis on infrastructure became a hallmark of Roman urban planning and set the standard for future cities.
2. Grid System: Roman cities were designed with a grid system, characterized by straight, intersecting streets. This layout provided a logical and efficient arrangement of buildings, facilitating easy navigation and effective use of space. The grid system became popular among subsequent civilizations and is still employed in cities worldwide today.
3. Public Spaces: Roman urban planning placed great importance on public spaces such as forums and squares. These areas served as central gathering points, fostering social interaction and hosting various civic activities. Public spaces became vital hubs of community life, and their inclusion in urban planning continued to be embraced in cities throughout history.
4. Zoning: The Romans were early advocates of zoning by creating distinct areas within the city for different purposes. Residential areas, commercial districts, and administrative centers were strategically separated, allowing for better management and organization. This zoning concept continues to shape urban planning practices today.
5. Building Codes: Romans enforced strict building codes and regulations to ensure structural integrity and aesthetic uniformity. These codes specified materials, dimensions, and architectural styles, ensuring a cohesive urban landscape. The implementation of building codes set a precedent for urban planning that prioritized safety, aesthetics, and the overall vision of the city.
6. Road Networks: Roman cities featured an extensive network of well-paved and well-maintained roads. These roads provided efficient transportation, enabling trade, communication, and military movements. The concept of well-connected road networks became a fundamental aspect of urban planning, improving accessibility and connectivity in cities across the globe.
7. Monumental Architecture: Roman cities were adorned with impressive architectural wonders, such as amphitheatres, bath complexes, and triumphal arches. This emphasis on grand and monumental structures not only enhanced the aesthetic appeal of the cities but also showcased the power and grandeur of the empire. The incorporation of monumental architecture became an integral part of urban planning, aiming to create iconic landmarks and landmarks that defined the city’s identity.
The influence of Roman urban planning extended far beyond the Roman Empire’s territorial boundaries. As subsequent civilizations sought to establish functional and aesthetically appealing cities, they looked to Roman principles for guidance. The impact of Roman urban planning can still be seen in cities worldwide today, where the concepts of infrastructure development, grid layouts, public spaces, and zoning all owe their origins to the Romans.
By understanding the influence of Roman urban planning, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the enduring legacy of this ancient civilization. The principles and concepts they established continue to shape urban environments and contribute to the functionality and beauty of cities around the world. Roman urban planning serves as a testament to the ingenuity and foresight of the Romans, leaving an indelible mark on the urban landscape for generations to come.
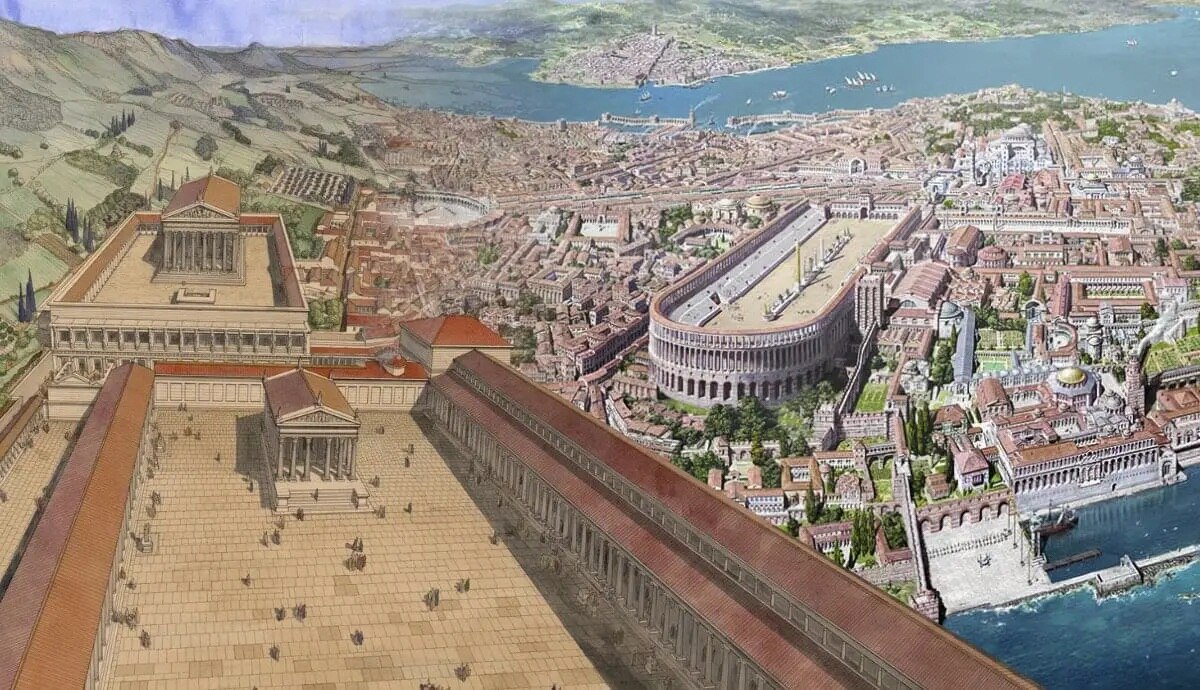
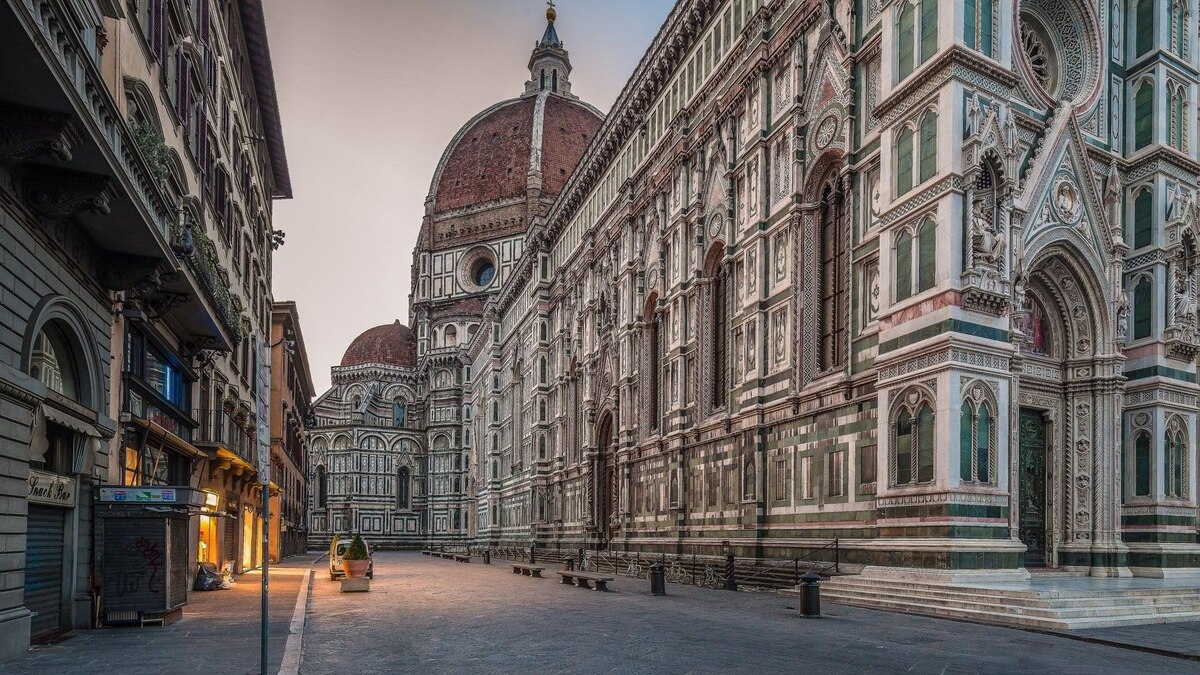
The Model City: Rome
Rome, the capital of the Roman Empire, served as the ultimate model for urban planning during ancient times. It was a city of immense importance, not only politically and economically but also as a center for architectural and engineering innovation. Rome’s urban planning influenced cities across the empire and beyond, leaving an indelible mark on the development of urban landscapes.
Rome’s urban design was characterized by a sense of grandeur, order, and functionality. Its layout incorporated various elements that were aimed at enhancing the quality of life for its inhabitants and showcasing the power and prestige of the empire. Let’s explore some of the key features that made Rome the model city for urban planning.
1. Centrality: Rome was built along the Tiber River in central Italy, strategically positioned to serve as a hub for trade, communication, and governance. Its central location made it accessible from all parts of the empire, facilitating the flow of people, goods, and information. This centrality became a defining characteristic of Rome’s urban planning and influenced subsequent cities to prioritize strategic positioning.
2. Seven Hills: Rome was famously built on seven hills, which added a unique topographical element to its urban layout. The hills not only provided natural defenses but also created distinct neighborhoods and vistas across the city. Each hill had its own distinct character and function, contributing to the diversity and charm of Rome’s urban landscape.
3. Civic Architecture: Rome was adorned with magnificent civic buildings and landmarks, such as the Colosseum, the Forum, and the Pantheon. These structures showcased the power and influence of Rome and served as gathering places for various social, political, and religious events. The inclusion of grand civic architecture in Rome’s urban planning set the precedent for subsequent cities to incorporate monumental landmarks that define their identities.
4. Transportation Infrastructure: Rome had an extensive network of roads and bridges that connected different parts of the city and facilitated trade and travel throughout the empire. The Romans placed great emphasis on the construction and maintenance of well-paved roads, ensuring efficient transportation within the city and beyond. This focus on transportation infrastructure became a hallmark of Roman urban planning and shaped subsequent cities’ approach to connectivity.
5. Axial Planning: Rome’s urban layout prioritized axial planning, with major streets and thoroughfares radiating outward from central points. The most famous example is the Via Appia, which led directly from Rome to the port city of Brindisi. Axial planning facilitated efficient movement throughout the city and ensured easy access to important destinations.
6. Aesthetic Unity: Roman urban planning emphasized aesthetic unity and architectural consistency. Buildings were constructed using similar materials and styles, creating a cohesive visual aesthetic. This attention to detail and uniformity in architectural design contributed to the overall harmony and beauty of the city.
Rome’s urban planning influenced cities not only within the Roman Empire but also in subsequent civilizations. Cities such as Paris, Washington D.C., and Brasilia drew inspiration from Rome’s grandeur, order, and functionality. Even today, the principles established in Rome continue to influence urban planning, reminding us of the enduring legacy of this remarkable city.
As we explore cities built throughout the Roman Empire and beyond, we will encounter the influence of Rome’s urban planning at every turn. The model city of Rome set the stage for the organization and design of cities for centuries to come, leaving an invaluable blueprint for urban planners and architects alike.
Elements of Roman Urban Planning
Roman urban planning was a meticulous and systematic process, encompassing various elements that contributed to the functionality, aesthetics, and overall organization of cities. From the layout of streets to the construction of public spaces, each element played a crucial role in shaping the urban landscape. Let’s explore some key elements of Roman urban planning:
1. Grid System of Streets: Roman cities were known for their well-organized grid system of streets. Streets intersected at right angles, creating a logical and efficient network that facilitated navigation and connectivity. This grid layout allowed for easy expansion of cities and provided a clear structure for urban development.
2. Cardo and Decumanus: The two main thoroughfares in Roman cities were the cardo and decumanus. The cardo ran north to south while the decumanus ran east to west, dividing the city into quadrants. These major streets served as vital arteries, c
Grid System of Streets
One of the defining features of Roman urban planning was the implementation of a grid system of streets. This layout consisted of intersecting streets that created a logical and efficient network of roads throughout the city. The grid system facilitated navigation, allowed for easy expansion, and provided a clear structure for urban development.
The grid system was based on a simple concept: streets running parallel to each other in one direction, intersected by streets running perpendicular to them. The resulting blocks formed by these intersecting streets were usually square or rectangular in shape, creating a uniform and organized layout.
One of the primary advantages of the grid system was its ease of navigation. The streets were numbered or named, providing a clear reference point for residents and visitors. With a regular pattern of streets, it was relatively simple to find one’s way around the city, even for those unfamiliar with the area.
In addition to enhancing navigation, the grid system allowed for efficient land use and easy expansion. The uniform size and shape of the blocks made it easier to divide land for residential, commercial, and public purposes. This division of land into smaller plots facilitated systematic development and ensured that no space went unused.
The grid system also facilitated infrastructure development. Streets were constructed in a straight line, with well-defined intersections and crossings. This made it easier to plan and construct water supply systems, drainage networks, and other utilities essential for the functioning of the city.
Furthermore, the grid system enabled effective transportation and trade. Straight, intersecting streets provided direct routes for the transportation of goods and facilitated the movement of people. Roman cities were often well-connected to each other, with roads leading to important trade routes and neighboring settlements.
The grid system was not limited to Roman cities within Italy but also extended to the far reaches of the empire. As the Romans expanded their dominance, they adapted their urban planning principles to suit the various regions they conquered. This led to the establishment of grid-based cities throughout Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
Today, the legacy of the Roman grid system can still be observed in many cities around the world. From the layout of streets in New York City’s Manhattan to the planned communities of Brasilia in Brazil, the influence of Roman urban planning is evident. The grid system continues to provide a practical and organized approach to city planning, ensuring efficient land use and easy navigation.
Overall, the grid system of streets was a pivotal element of Roman urban planning. It allowed for efficient navigation, facilitated land development, promoted infrastructure development, and contributed to the growth and expansion of Roman cities. The lasting impact of the grid system is a testament to the foresight and ingenuity of Roman urban planners, forever shaping the way cities are designed and organized.
Look into the city of Rome as the primary model for urban planning in cities built throughout the Roman Empire. Its grid layout, public spaces, and infrastructure were often replicated in other cities.
Read more: Why Urban Planning Is Important
Public Spaces and Forums
Public spaces and forums were integral elements of Roman urban planning, serving as central gathering places for civic, social, and commercial activities. These spaces played a crucial role in fostering community interaction, political engagement, and economic exchange. Let’s explore the significance of public spaces and forums in Roman cities.
1. Forum: The forum was the heart of Roman city life. It was a large open space, often located at the center of the city, where important civic and commercial activities took place. The forum served as a marketplace for trade, a venue for public speeches and debates, and a central hub where citizens could meet, interact, and engage in social and political affairs. It was adorned with grand architectural structures, such as basilicas, temples, and administrative buildings, which added to its importance and grandeur.
2. Baths: Baths were essential public facilities in Roman cities, providing hygiene, relaxation, and socialization opportunities for the citizens. These bathing complexes were often extensive and luxurious, featuring hot and cold baths, steam rooms, exercise areas, and gardens. Bathhouses were not just places to cleanse the body but also served as meeting places, where people from different walks of life could come together and socialize.
3. Theaters and Amphitheaters: Roman cities had prominent theaters and amphitheaters, which hosted various forms of entertainment, including theatrical performances, musical recitals, and gladiatorial contests. These venues were designed to accommodate large audiences and provided a space for leisure and cultural activities. Theaters and amphitheaters were not just sources of entertainment but also points of pride for Roman cities, showcasing their wealth, artistic prowess, and commitment to public enjoyment.
4. Triumphal Arches and Monuments: Roman cities were adorned with triumphal arches and monuments that commemorated military victories, celebrated emperors, and marked important events in history. These monumental structures added to the visual grandeur and prestige of the city, serving as landmarks and symbols of Roman power and influence. They often stood at key intersections or gateways, creating a sense of awe and civic pride.
5. Landscape Design: Roman urban planning incorporated green spaces, gardens, and promenades within the city. Landscaped areas provided relief from the hustle and bustle of urban life and offered opportunities for relaxation and recreation. Gardens, fountains, and statues adorned public squares, creating a pleasant and aesthetically pleasing environment for residents and visitors alike.
The incorporation of public spaces and forums in Roman urban planning demonstrated a keen understanding of the importance of social interaction, civic engagement, and leisure activities for a thriving community. These spaces were carefully designed to facilitate gatherings, foster a sense of community, and promote the overall well-being of the population.
The influence of Roman public spaces and forums can still be seen in modern city planning. The concept of creating central gathering places for social, cultural, and political activities continues to shape the development of public parks, plazas, and community centers in cities around the world.
Roman cities understood the significance of providing spaces where citizens could come together, exchange ideas, express their opinions, and participate in public life. The legacy of these public spaces and forums serves as a reminder of the importance of creating inclusive and accessible environments that promote community engagement and a sense of belonging.
Aqueducts and Sanitation Systems
Aqueducts and sanitation systems were fundamental components of Roman urban planning, showcasing the empire’s advanced engineering techniques and commitment to public health. These infrastructure marvels played a crucial role in providing clean water, managing wastewater, and promoting hygiene in Roman cities. Let’s explore the significance of aqueducts and sanitation systems in Roman urban planning.
1. Aqueducts: The Romans developed an extensive network of aqueducts to bring fresh water from distant sources to their cities. These aqueducts consisted of channels, pipes, and underground tunnels that transported water from springs, rivers, and lakes and delivered it to public fountains, baths, and private residences. Aqueducts were meticulously engineered, taking advantage of gravity to ensure a constant flow of water. This innovation not only satisfied the daily water needs of the population but also allowed for the development of larger-scale public infrastructure, such as baths and fountains.
2. Public Fountains: Roman cities were adorned with ornate public fountains, which served as sources of clean water for residents. These fountains were typically centrally located and provided a convenient place for citizens to gather and access fresh water. The presence of public fountains not only promoted hygiene but also symbolized the city’s prosperity and civic pride.
3. Sewer Systems: In addition to providing clean water, the Romans developed sophisticated sewer systems to efficiently manage wastewater and maintain sanitation. These systems consisted of underground channels that carried sewage away from the city to rivers or designated drainage points. By separating wastewater from the water supply, Roman cities significantly reduced the risk of waterborne diseases and ensured a healthier living environment for their inhabitants.
4. Public Toilets: Roman cities featured public toilets, known as latrines, which were connected to the sewer systems. These communal facilities provided a hygienic and convenient option for citizens to relieve themselves. Public toilets were designed with stone or marble seats, running water, and a constant flow of fresh air to maintain cleanliness and minimize odors.
5. Public Baths: The Roman emphasis on cleanliness extended to public baths, where citizens could bathe and socialize. These bathing complexes were equipped with hot and cold water pools, steam rooms, and exercise areas. The design of these baths incorporated water supply systems, heating systems, and efficient wastewater drainage. Public baths were not only places for personal hygiene but also cultural and social centers that fostered community interactions.
The development of aqueducts and sanitation systems in Roman cities demonstrated the empire’s commitment to public health and well-being. These advancements in engineering and infrastructure not only improved the quality of life for Roman citizens but also set a precedent for future civilizations in managing water supply and waste disposal.
The influence of Roman aqueducts and sanitation systems can still be seen in modern urban planning. The concept of centralized water supply, wastewater management, and public sanitation continues to inform the design and development of cities worldwide. Efforts to ensure clean water, efficient drainage, and proper sanitation are integral for maintaining public health and creating sustainable urban environments.
The legacy of Roman aqueducts and sanitation systems serves as a testament to the advanced engineering skills and innovative thinking of the Romans. By incorporating these systems into their urban planning, they not only created healthier cities but also set a standard that has shaped urban development for centuries to come.
Architecture and Building Techniques
Roman architecture and building techniques were key elements of urban planning, contributing to the grandeur, durability, and functionality of Roman cities. The Romans were renowned for their innovative architectural designs, the use of various construction materials, and their engineering prowess. Let’s explore the significance of architecture and building techniques in Roman urban planning.
1. Masonry and Concrete: The Romans pioneered the use of masonry and concrete in construction, revolutionizing the building industry. They employed a technique known as opus caementicium, where a mixture of lime, sand, and volcanic ash (called pozzolana) was combined with stone rubble to create a durable and versatile form of concrete. This invention allowed the Romans to construct monumental buildings, arches, and bridges with both strength and elegance.
2. Arches and Vaults: Roman architecture prominently featured arches and vaults, which allowed for the construction of larger, more stable structures. The Romans developed the technique of using the weight-bearing properties of arches to distribute weight and create spacious interior spaces. This enabled the construction of grand structures such as amphitheaters, basilicas, and monumental gateways.
3. Columns and Capitals: The use of columns and capitals was a defining characteristic of Roman architecture. Roman columns were typically made of stone and featured ornate capitals, with various designs such as Corinthian, Ionic, and Doric. These columns were not only structural elements but also decorative features that added sophistication, elegance, and a sense of grandeur to buildings.
4. Vaulted Ceilings and Domes: Roman architecture employed vaulted ceilings and domes to create expansive interior spaces. The use of techniques such as the groin vault and the dome allowed for the construction of large halls, temples, and bath complexes. These architectural elements provided structural strength while also adding beauty and drama to the buildings.
5. Marble and Decorative Elements: The Romans prized marble as a luxurious building material and extensively used it in their architecture. The use of marble not only enhanced the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also demonstrated the wealth and power of the Roman Empire. Elaborate decorative elements, such as intricate carvings, statues, and mosaics, adorned buildings and added artistic value to the urban landscape.
6. Urban Planning Principles: Roman urban planning incorporated architectural elements into the overall design of cities. Buildings were strategically placed within the urban fabric to create visually pleasing vistas, axial alignments, and focal points. The integration of architecture into urban planning ensured a cohesive and aesthetically pleasing environment.
The architectural achievements of the Romans had a profound impact on subsequent civilizations. Their building techniques, use of concrete, and architectural design principles were copied and adapted by later cultures. Many architectural styles and features inspired by Roman architecture can still be found in cities around the world today.
The Romans’ commitment to innovative construction techniques and architectural excellence contributed to the longevity of their buildings. Many Roman structures have survived for centuries, serving as a testament to the durability and craftsmanship of their construction.
The influence of Roman architectural techniques and designs can be seen in prominent buildings and landmarks, including neoclassical structures, governmental buildings, and cultural institutions. The enduring legacy of Roman architecture serves as a testament to the timeless appeal and ingenuity of their building techniques.
Roman architecture and building techniques played a significant role in the development of Roman cities, contributing to their visual splendor, structural integrity, and cultural significance. The incorporation of architectural elements into urban planning ensured that Roman cities were not only functional but also breathtaking works of art.
The Legacy of Roman Urban Planning
Roman urban planning left a lasting legacy that continues to impact cities across the globe. The innovation, efficiency, and grandeur embedded in Roman urban planning principles have influenced urban landscapes since ancient times. Let’s explore the enduring legacy of Roman urban planning.
1. Grid System and Street Layout: The Roman grid system of streets, with its organized and intersecting roads, has become a standard in urban planning. This layout provides a logical framework for city expansion, efficient navigation, and easy identification of addresses. Today, cities like New York, Barcelona, and Melbourne embrace the grid system, demonstrating the Roman legacy in urban planning.
2. Centrality: Rome’s concept of centralization influenced the significance of central nodes in urban planning. Central squares, plazas, and commercial hubs continue to be focal points in modern cities, fostering social interactions, economic activities, and civic engagement.
3. Infrastructure Development: Roman expertise in infrastructure development set a benchmark for subsequent civilizations. The use of aqueducts, sewage systems, and well-paved roads not only enhanced the functionality of Roman cities but also inspired the integration of such features in urban planning around the world.
4. Public Spaces and Civic Buildings: Roman cities were built with public spaces and civic buildings, such as forums, theaters, baths, and amphitheaters, at their core. These elements enriched public life, facilitated social interactions, and served as cultural and administrative centers. Modern urban planning acknowledges the importance of public spaces and includes parks, squares, and cultural institutions for community gatherings.
5. Building Codes and Aesthetic Unity: Roman urban planning introduced building codes and regulations to ensure structural integrity and aesthetic consistency. This emphasis on architectural standards shaped subsequent urban planning practices, leading to the implementation of zoning regulations, building permits, and design guidelines that maintain aesthetic unity within cities.
6. Legacy in European Architecture: Roman architectural styles and elements significantly influenced European architecture during the Renaissance and Neoclassical periods. The revival of Roman-inspired architecture, characterized by the use of columns, arches, and domes, can be seen in iconic landmarks, such as the U.S. Capitol, the Louvre, and St. Peter’s Basilica.
7. Waste Management and Sanitation: Roman advancements in waste management and sanitation systems set a precedent for the importance of hygiene and public health in urban planning. The separation of wastewater from water supply and the development of sewage systems continue to be cornerstones of modern urban sanitation practices.
8. Global Influence: The Roman Empire’s reach and influence spread across continents, leaving a footprint on urban planning worldwide. Cities in Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East demonstrate the impact of Roman urban planning with their architectural design, street layouts, and incorporation of public spaces.
The legacy of Roman urban planning serves as a testament to the Empire’s forward-thinking vision and technical expertise. The principles and concepts developed by the Romans continue to shape urban environments, emphasizing functionality, efficiency, and aesthetics.
By studying the legacy of Roman urban planning, modern urban planners gain valuable insights into the timeless principles that contribute to creating sustainable, livable cities. The enduring influence of Roman urban planning ensures that the genius of ancient Rome lives on through the cities we inhabit today.
Read more: What Does An Urban Planning Engineer Do
Conclusion
Roman urban planning was a remarkable feat of innovation, engineering, and foresight that left an indelible mark on cities throughout history. The influence of Roman urban planning can be seen in the grid systems of streets, the integration of public spaces, the development of infrastructure, and the incorporation of architectural principles. The legacy of Roman urban planning continues to shape the way cities are designed, organized, and experienced.
The Romans understood the importance of well-planned cities in promoting social order, economic prosperity, and political stability. They incorporated elements such as the grid system of streets, public forums, aqueducts, and sanitation systems into their urban planning, creating cities that were not only functional but also aesthetically impressive.
The Romans’ commitment to infrastructure development, including aqueducts and well-paved roads, revolutionized urban living. It ensured the provision of clean water, efficient transportation, and effective waste management. These advancements in engineering and urban planning continue to inspire modern cities in their pursuit of sustainable and livable environments.
Furthermore, the Romans recognized the significance of public spaces and civic buildings. Their forums, theaters, baths, and monuments served as centers for community interactions, cultural events, and political discourse. The inclusion of public spaces in urban planning continues to foster a sense of belonging and civic engagement in cities around the world.
In addition, Roman architectural techniques and design principles have stood the test of time. The use of arches, columns, vaulted ceilings, and decorative elements showcased the Romans’ mastery of construction and aesthetics. These architectural innovations continue to inspire and influence architects and urban planners globally.
The legacy of Roman urban planning extends far beyond the boundaries of the Roman Empire. Cities built throughout the empire and beyond still bear the influence of Rome’s organizational expertise, architectural beauty, and engineering marvels. The principles and concepts established by the Romans serve as a reminder of the enduring relevance of their urban planning legacy.
As we walk the streets of ancient Rome in our modern cities, we can see the footsteps of the Romans in the grid-like patterns, the grand public squares, and the awe-inspiring architecture. Roman urban planning continues to shape our cities, facilitating efficient movement, fostering community engagement, and enhancing the quality of life for urban dwellers.
In conclusion, Roman urban planning stands as a testament to the Romans’ ingenuity, efficiency, and commitment to creating thriving cities. Their principles and innovations continue to shape modern urban planning practices, leaving an enduring legacy that highlights the importance of functionality, sustainability, and beauty in our urban environments. As we gaze upon the cities built throughout the Roman Empire, we are reminded of the timeless wisdom of the Roman urban planners and their profound influence on urban landscapes across the world.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cities Built Throughout The Roman Empire Modeled Their Urban Planning On Which City?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “Cities Built Throughout The Roman Empire Modeled Their Urban Planning On Which City?”