Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Is Urban Planning?


Planning & Engineering
What Is Urban Planning?
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover the concept of urban planning and its significance in creating sustainable cities. Explore the role of planning engineering in shaping our urban landscapes.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
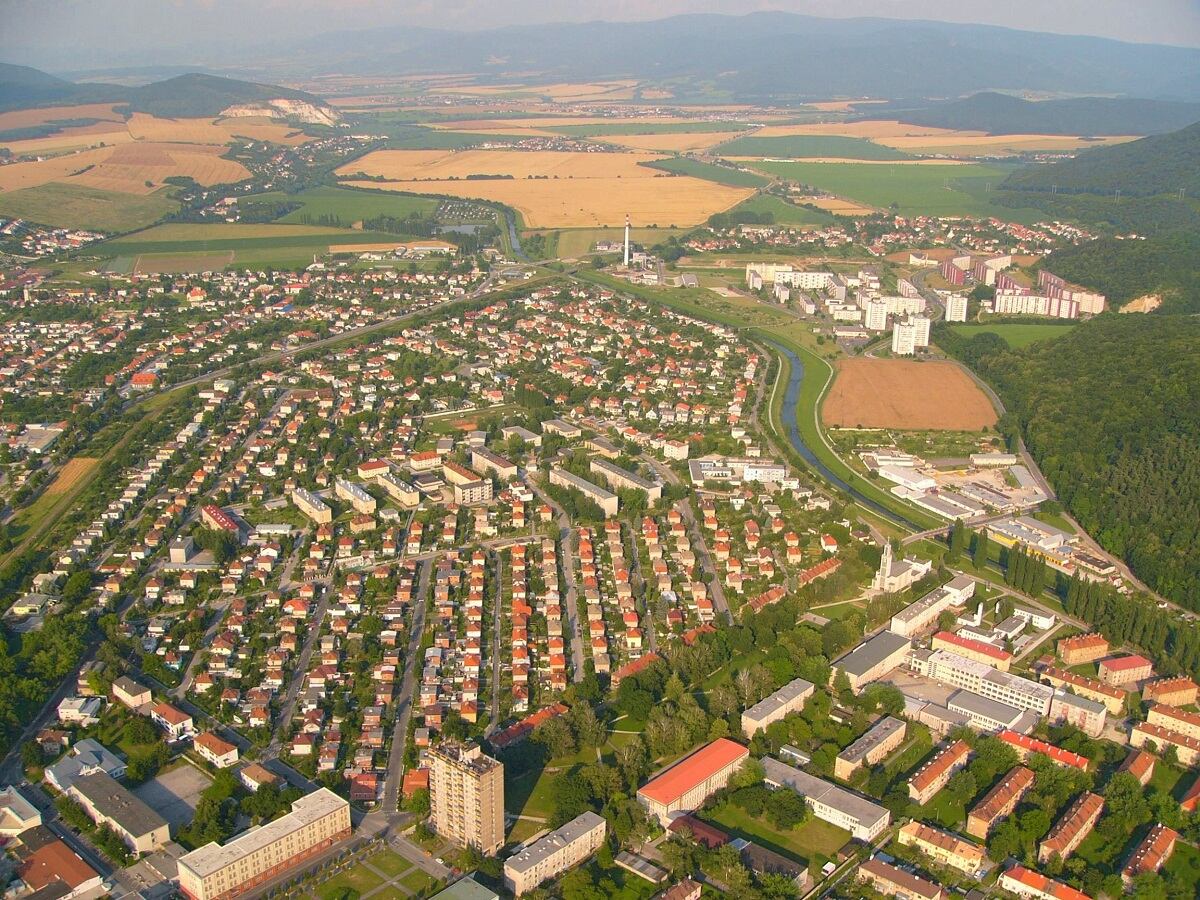
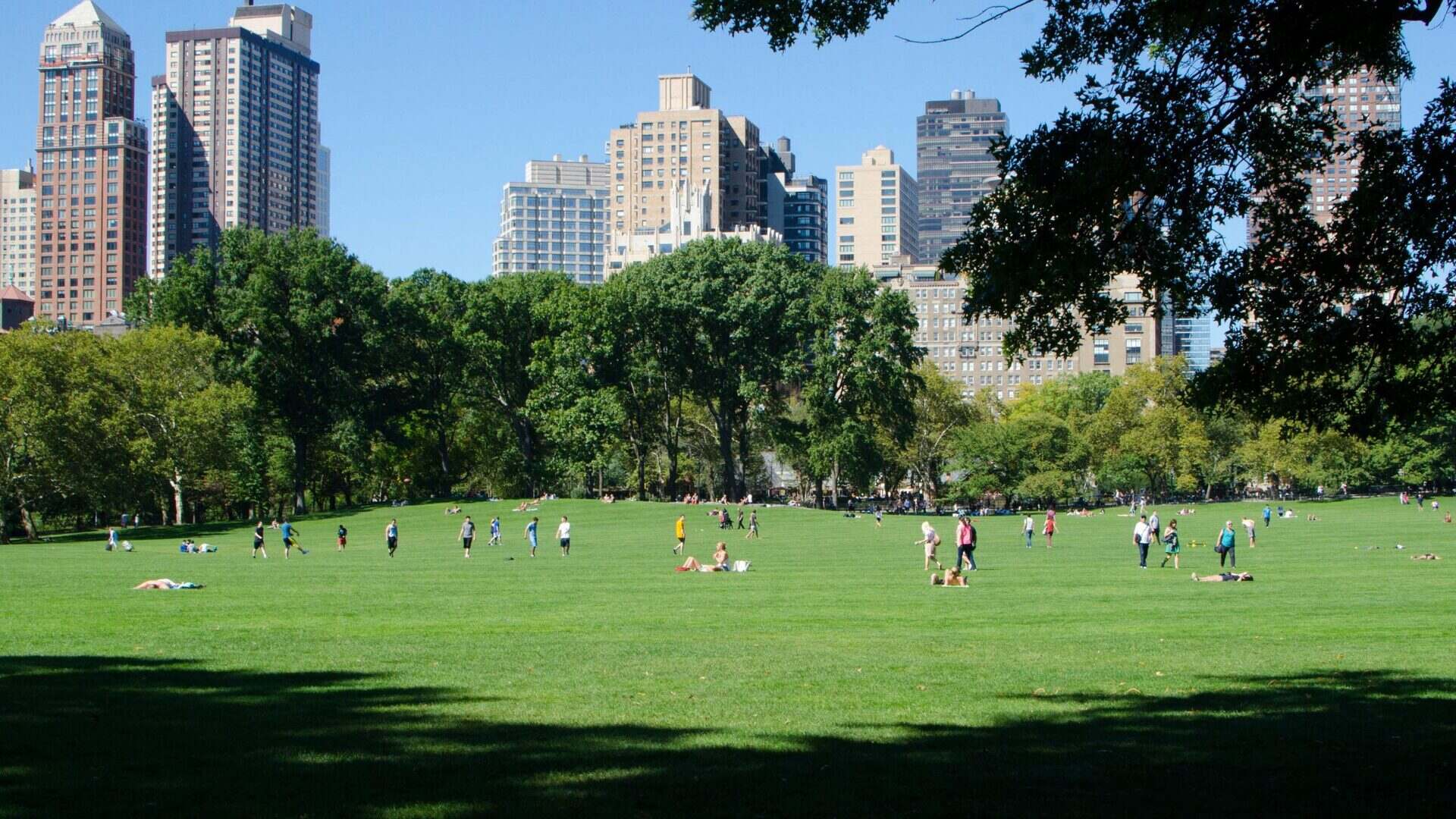
Urban planning is a multidisciplinary field that plays a crucial role in shaping the development and growth of cities and communities. It combines engineering, architecture, economics, and social sciences to create sustainable and livable environments for people.
As the world becomes increasingly urbanized, with more people migrating to cities in search of better opportunities and quality of life, the need for effective urban planning has never been more critical. Urban planners are key players in designing and managing urban spaces, considering factors such as transportation, land use, infrastructure, and environmental sustainability.
In this article, we will explore the definition and role of urban planning, delve into its history, discuss the key concepts and processes involved, examine the tools and techniques used, highlight the challenges faced, and emphasize the importance of sustainable urban planning.
By understanding the fundamentals of urban planning, we can gain insight into how cities are developed and envision a future where urban spaces are well-designed, inclusive, and resilient.
Key Takeaways:
- Urban planning integrates sustainability, inclusivity, and resilience to create vibrant, resilient, and sustainable cities that enhance the quality of life for present and future generations.
- Urban planning is crucial for sustainable development, efficient land use, disaster mitigation, economic growth, and cultural heritage preservation, shaping cities for a better quality of life.
Read more: What Is An Urban Planning Degree
Definition of Urban Planning
Urban planning can be defined as the process of guiding the development, organization, and management of urban spaces to create functional, equitable, and sustainable cities and communities. It involves the analysis, design, and implementation of strategies and policies that ensure efficient land use, transportation systems, infrastructure, public spaces, and environmental protection.
At its core, urban planning aims to improve the quality of life for residents and promote a harmonious balance between economic development, social equity, and environmental stewardship. It takes into account various factors such as population growth, cultural heritage, natural resources, and the needs and aspirations of the community.
Urban planners work collaboratively with government agencies, private stakeholders, and the public to shape the physical, social, and economic aspects of urban areas. They gather data, conduct research, analyze trends, and utilize their expertise to formulate comprehensive plans and policies.
Key components of urban planning include:
- Land Use Planning: Determining the most appropriate use of land, including residential, commercial, industrial, and recreational areas.
- Transportation Planning: Designing transportation systems that are efficient, accessible, and environmentally friendly, including roads, public transit, and cycling infrastructure.
- Housing Planning: Ensuring the availability of affordable and adequate housing options for all segments of the population.
- Environmental Planning: Protecting and enhancing natural resources, promoting sustainability, and mitigating the impact of urbanization on the environment.
- Community Development: Fostering social cohesion, inclusivity, and community engagement within urban areas.
- Infrastructure Planning: Planning and managing essential facilities and services such as water supply, sewage systems, power grids, and public amenities.
By integrating these components, urban planning seeks to create cities that are vibrant, resilient, and conducive to the well-being of their residents.
Role of Urban Planners
Urban planners play a pivotal role in shaping the physical and social landscapes of cities and communities. They are responsible for studying, analyzing, and making informed decisions regarding the development and management of urban spaces. Their role extends beyond simply designing buildings and infrastructure; they strive to create sustainable and livable environments for people.
Here are some key roles and responsibilities of urban planners:
- Research and Analysis: Urban planners conduct research to gather data on demographics, land use patterns, economic trends, and environmental factors. They analyze this information to identify existing challenges and opportunities and base their planning decisions on empirical evidence.
- Develop Planning Policies: Urban planners formulate planning policies and regulations that guide the future development and land use within a city. These policies consider factors such as zoning regulations, building codes, and environmental guidelines.
- Design and Master Planning: Urban planners are involved in designing and creating master plans for cities and neighborhoods. They consider factors such as transportation networks, public spaces, infrastructure, and land use to ensure a cohesive and well-functioning urban environment.
- Community Engagement: Urban planners work closely with community members, stakeholders, and interest groups to gather input and ensure that the planning process is inclusive and reflects the needs and aspirations of the community. They conduct public hearings, workshops, and surveys to foster engagement and public participation.
- Environmental Protection: Urban planners prioritize environmental sustainability in their plans and designs. They seek to minimize the carbon footprint, promote green spaces, and mitigate the impact of urban development on natural resources.
- Collaboration and Coordination: Urban planners collaborate with various stakeholders, including government agencies, architects, engineers, developers, and community organizations. They coordinate efforts to ensure that the planning objectives are aligned and implemented effectively.
- Policy Implementation and Monitoring: Urban planners are involved in implementing and monitoring planning policies and regulations. They assess the impact of development projects, monitor compliance with zoning laws, and evaluate the effectiveness of planning initiatives.
By fulfilling these roles, urban planners contribute to creating cities that are functional, inclusive, and sustainable. They strive to strike a balance between the social, economic, and environmental aspects of urban development, ultimately improving the quality of life for present and future generations.
History of Urban Planning
Urban planning has a rich and diverse history that spans thousands of years. It originated from the need to establish organized and well-designed cities in ancient civilizations. Throughout history, various cultures and societies have implemented different approaches to urban planning, contributing to the evolution of urban design and development.
Ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley had well-planned cities with advanced infrastructure and architectural features. These cities were characterized by organized street grids, centralized governance, and efficient water management systems.
In ancient Greece, the concept of the polis emerged, emphasizing the importance of public spaces and the integration of cultural, political, and social activities. This influenced urban planning in subsequent eras.
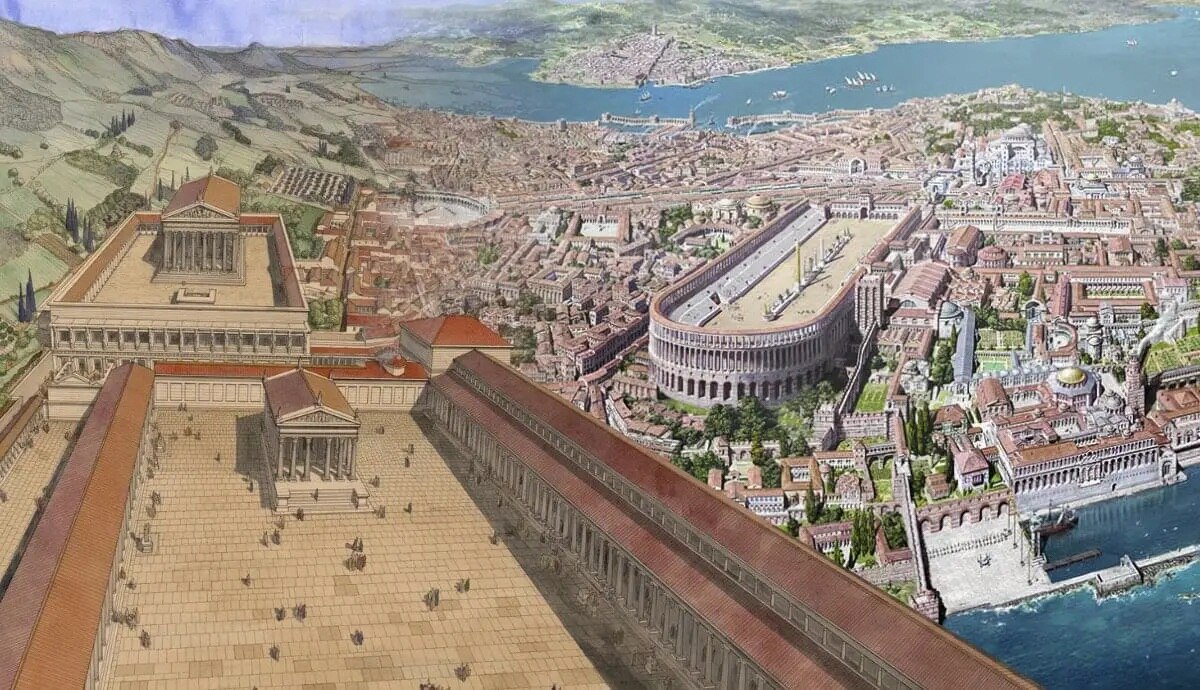
The Roman Empire further advanced urban planning, with the construction of well-designed cities like Rome, which incorporated elements such as a network of roads, public buildings, and sanitation systems.
During the Middle Ages, urban planning took a more decentralized approach, with cities growing organically around castles and religious institutions. The focus shifted to fortification and defense rather than orderly city design.
The Renaissance period witnessed a revival of the classical principles of urban planning. Architectural visionaries like Leon Battista Alberti and Filippo Brunelleschi advocated for harmonious city layouts based on geometrical principles and the integration of public spaces.
The 19th and 20th centuries brought significant changes to urban planning due to rapid industrialization and urbanization. The emergence of the industrial revolution led to overcrowded and unsanitary living conditions in many cities. This prompted the need for urban reforms and the development of new planning practices.
Influential figures such as Ebenezer Howard and Frederick Law Olmsted pioneered new approaches to urban planning. Howard introduced the concept of garden cities, promoting the idea of self-contained communities with a balance of residential, industrial, and agricultural areas. Olmsted is famous for designing urban parks such as Central Park in New York City, recognizing the importance of green spaces in cities.
Throughout the 20th century, urban planning evolved further with the rise of modernism and the development of new planning theories and techniques. The Garden City movement, the City Beautiful movement, and the principles of the modernist movement all influenced urban planning practices.
Today, urban planning continues to evolve in response to contemporary challenges such as climate change, rapid urbanization, and social inequalities. The concept of sustainable urban planning is gaining prominence, with a focus on creating environmentally-friendly, inclusive, and resilient cities.
Overall, the history of urban planning showcases the progression and transformation of cities over time, reflecting the political, social, and cultural contexts of each era.
Key Concepts in Urban Planning
Urban planning encompasses a range of key concepts that guide the development and organization of cities. These concepts help urban planners create sustainable, functional, and livable urban environments. Understanding these concepts is crucial for effective urban planning and design. Here are some key concepts:
- Sustainability: Urban planning emphasizes the importance of sustainability. This involves balancing social, economic, and environmental aspects to ensure the long-term well-being of urban communities. Sustainable practices include energy-efficient buildings, green spaces, public transportation, waste management, and preservation of natural resources.
- Walkability and Transit-Oriented Development: Creating cities that prioritize pedestrians and non-motorized transportation is a key concept in urban planning. Walkability encourages physical activity, reduces car dependency, and improves overall livability. Transit-oriented development focuses on designing neighborhoods around public transportation hubs, enabling easy and convenient access to public transportation for residents.
- Mixed-Use Development: A key concept in urban planning involves creating mixed-use developments that integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within close proximity. This promotes vibrant neighborhoods, reduces commuting distances, and encourages social interaction and economic activity.
- Compact and Efficient Land Use: Urban planning emphasizes efficient land use to accommodate the growing population and limit urban sprawl. Compact development patterns promote the efficient use of land, reduce the need for extensive infrastructure, and foster the use of public transportation.
- Smart Growth: Smart growth is a concept that focuses on developing urban areas in a sustainable and intelligent manner. It involves designing compact, walkable neighborhoods with a range of housing options, accessible services, and job opportunities. Smart growth principles also prioritize the preservation of open spaces and natural resources.
- Placemaking: Placemaking involves creating vibrant, attractive, and people-centered public spaces. It focuses on transforming underutilized spaces into community gathering places, where people can socialize, engage in activities, and strengthen the sense of community.
- Resilience: Urban planning considers the resilience of cities in the face of natural disasters, climate change, and other challenges. Resilient cities are designed to withstand and recover from these events by implementing measures such as flood-resistant infrastructure, green infrastructure, and disaster management strategies.
- Inclusive Planning: Inclusive planning promotes the involvement of a diverse range of stakeholders, including marginalized communities, in the decision-making process. It ensures that there is equitable access to resources, services, and opportunities within the city.
- Historic Preservation: Urban planning recognizes the importance of preserving and celebrating a city’s historic and cultural heritage. It involves protecting historic buildings and neighborhoods, promoting adaptive reuse, and integrating historical assets into urban development.
- Participatory Planning: Participatory planning involves engaging the public and stakeholders in the planning process. It encourages collaboration, community input, and the consideration of diverse perspectives, ultimately leading to more inclusive and transparent decision-making.
These key concepts shape the vision and implementation of urban planning initiatives, guiding the creation of sustainable, inclusive, and resilient cities that enhance the quality of life for their residents.
Read more: What Does An Urban Planning Engineer Do
Urban Planning Process
The urban planning process is a systematic approach that guides the development and implementation of plans to shape and manage urban areas effectively. It involves a series of interconnected steps and stages, each playing a crucial role in the creation of sustainable and livable cities. Here are the key steps in the urban planning process:
- Understanding and Assessment: The first step in the urban planning process is to gain a deep understanding of the existing urban context. This involves studying the demographics, land use patterns, transportation systems, infrastructure, and environmental conditions of the area. Assessing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats helps in identifying areas that require improvement and formulating appropriate planning strategies.
- Goal Setting and Vision: Urban planners work with stakeholders, government officials, and the public to establish goals and a shared vision for the city’s future. This involves identifying key objectives such as sustainability, resilience, social equity, economic growth, and cultural preservation.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Urban planners collect and analyze various data sets to inform the planning process. This includes demographic data, land use data, transportation data, and environmental data. The analysis helps in understanding existing patterns, trends, and challenges and supports evidence-based decision-making.
- Plan Formulation: Based on the goals, vision, and data analysis, urban planners formulate comprehensive plans and strategies. This includes land use plans, transportation plans, environmental plans, and implementation frameworks. The plans consider factors such as zoning regulations, infrastructure requirements, public spaces, and community needs.
- Public Participation: Public participation is a critical aspect of the urban planning process. Urban planners engage with the community through public meetings, workshops, surveys, and online platforms to gather feedback, suggestions, and concerns. This helps ensure that the plans reflect the aspirations and needs of the community.
- Plan Review and Approval: After formulating the plans, they undergo a thorough review and evaluation process. This involves assessing the compliance with existing regulations, reviewing the environmental impact, and considering feedback from various stakeholders. The plans are then revised based on this feedback and approved by relevant authorities.
- Implementation: Once the plans are approved, the implementation phase begins. This involves working closely with government agencies, developers, architects, and community organizations to execute the strategies outlined in the plans. It includes managing land development, coordinating infrastructure projects, promoting affordable housing initiatives, preserving cultural heritage, and monitoring the progress.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: The urban planning process does not end with implementation. Continuous monitoring and evaluation are necessary to assess the effectiveness of the plans and make necessary adjustments. This includes tracking progress against the goals and objectives, analyzing the impact on the community, and addressing any emerging challenges or opportunities.
The urban planning process is iterative and dynamic, adapting to the changing needs and contexts of cities. Effective implementation requires collaboration, coordination, and ongoing community engagement to ensure that the plans are responsive to the evolving urban environment.
Tip: Urban planning is the process of designing and organizing the development of cities and towns to create functional, attractive, and sustainable communities. It involves land use, transportation, infrastructure, and environmental considerations.
Tools and Techniques in Urban Planning
Urban planning utilizes a wide range of tools and techniques to support the planning process and aid in the development of sustainable and well-designed cities. These tools and techniques involve data analysis, visualization, simulation, and stakeholder engagement. Here are some commonly used tools and techniques in urban planning:
- Geographical Information Systems (GIS): GIS is a powerful tool in urban planning that combines mapping and data analysis capabilities. It allows planners to overlay and analyze various data sets, including land use, transportation networks, demographics, and infrastructure, to inform decision-making and visualize spatial relationships.
- Urban Design Software: Urban design software, such as AutoCAD and SketchUp, enables planners to create digital representations of proposed developments. It facilitates the design and layout of buildings, streetscapes, and public spaces, allowing for visualizations and simulations of future scenarios.
- Transportation Modeling: Transportation modeling software, such as VISSIM and TRANSIMS, simulates traffic flow and transportation patterns. It helps planners optimize road networks, evaluate the impact of new developments on traffic, and design efficient public transportation systems.
- Social and Economic Impact Analysis: Tools for social and economic impact analysis enable planners to assess the potential effects of proposed developments on communities. These tools use demographic, economic, and social data to evaluate factors such as housing affordability, job creation, neighborhood change, and social equity.
- Visualization Tools: Visualization tools, including 3D modeling, virtual reality, and augmented reality, help planners and stakeholders visualize and understand the impact of proposed developments. These tools create immersive experiences that can be used to showcase design concepts, identify potential conflicts, and engage communities in decision-making processes.
- Community Engagement Platforms: Online platforms, such as interactive websites and mobile apps, provide platforms for community engagement in the planning process. These platforms enable residents to provide feedback, participate in surveys, and access information about ongoing projects, promoting transparency and inclusivity.
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): EIA is a tool that assesses the potential environmental impacts of proposed developments. It considers factors such as air quality, water resources, biodiversity, and climate change to ensure that development projects adhere to environmental regulations and promote sustainability.
- Land Use and Zoning Regulations: Land use and zoning regulations serve as important tools in urban planning. These regulations govern how land can be used and guide the spatial distribution of different land uses such as residential, commercial, and industrial. They help maintain order, address compatibility issues, and promote efficient land use.
- Public Surveys and Workshops: Surveys and workshops are traditional tools for engaging the public in the planning process. They provide opportunities for residents to voice their opinions, express concerns, and contribute to decision-making. Surveys can be conducted online or in-person, while workshops allow for more interactive discussions and collaboration.
- Policy Planning Tools: Various software tools assist in policy planning, such as scenario modeling and policy simulation tools. These tools help planners evaluate the impacts of different policy options, such as affordable housing initiatives or transportation strategies, and determine the most effective and sustainable solutions.
These tools and techniques are invaluable in urban planning, providing planners with the means to collect, analyze, and visualize data, engage stakeholders, and make informed decisions about the development and management of cities.
Challenges in Urban Planning
Urban planning is a complex and dynamic process that faces numerous challenges in the pursuit of creating sustainable and livable cities. These challenges arise from various social, economic, and environmental factors. Addressing these challenges is crucial for effective urban planning. Here are some of the key challenges:
- Rapid Urbanization: Rapid population growth and urbanization exert immense pressure on cities. Urban planners need to accommodate the increasing population while ensuring adequate infrastructure, housing, and services. Balancing the demand for development with the preservation of natural and cultural assets is a significant challenge.
- Urban Sprawl: Uncontrolled urban sprawl leads to the expansion of cities into surrounding rural areas, resulting in fragmented and inefficient land use patterns. Managing urban sprawl, promoting compact development, and preserving open spaces are ongoing challenges in urban planning.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Many cities struggle with aging infrastructure, insufficient transportation networks, and inadequate public services. Upgrading and expanding infrastructure to meet the demands of growing cities while considering environmental sustainability and affordability poses significant challenges.
- Inequality and Social Exclusion: Inequitable access to resources, services, and opportunities is a persistent challenge in urban planning. Ensuring inclusive development that addresses social disparities, provides affordable housing, and promotes social cohesion requires innovative and targeted strategies.
- Climate Change and Resilience: Urban areas are vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as rising sea levels, heatwaves, and extreme weather events. Urban planning must address climate change adaptation and mitigation, integrating sustainable design, green infrastructure, and resilient strategies to protect cities and their populations.
- Public Engagement and Participation: Engaging and involving the public in the planning process can be challenging. Ensuring meaningful public participation from diverse communities, overcoming language and accessibility barriers, and incorporating community input into decision-making processes are ongoing challenges in urban planning.
- Financial Constraints: Urban planning requires significant financial resources to implement infrastructure projects, public services, and housing initiatives. Securing adequate funding and managing budgetary constraints is a challenge for many cities, particularly in developing regions.
- Governance and Policy Alignment: Coordinating and aligning policies and governance structures across different levels of government can be complex and challenging. Urban planning involves multiple stakeholders and requires effective collaboration and coordination to ensure coherent and integrated planning outcomes.
- Historical Preservation: Balancing the preservation of historical and cultural heritage with the need for urban development presents a challenge. Protecting historic buildings and neighborhoods while accommodating growth and modernization requires careful planning and adaptive reuse strategies.
- Data Management and Analysis: Urban planning relies heavily on data analysis and information management. Collecting, analyzing, and interpreting vast amounts of data can be challenging. Ensuring the availability of accurate, up-to-date, and reliable data to inform decision-making is essential but can be resource-intensive.
Overcoming these challenges requires innovative approaches, integrated planning strategies, and collaboration between governments, communities, and stakeholders. Urban planners must adapt to the evolving urban landscape and employ creative solutions to create sustainable, inclusive, and resilient cities for future generations.
Sustainable Urban Planning
Sustainable urban planning is a critical approach to urban development that aims to create cities that are environmentally, socially, and economically sustainable. It involves integrating principles of sustainability into all stages of the planning process, from design and implementation to monitoring and evaluation. Sustainable urban planning seeks to balance the needs of communities, the economy, and the environment to ensure the long-term well-being of present and future generations. Here are key aspects of sustainable urban planning:
- Compact and Mixed-Use Development: Sustainable urban planning encourages compact and mixed-use development to minimize urban sprawl and reduce commuting distances. By creating a mix of residential, commercial, recreational, and public spaces within close proximity, it promotes walkability, reduces reliance on cars, and facilitates vibrant and socially inclusive communities.
- Efficient Land Use: Utilizing land efficiently is crucial for sustainable urban planning. It involves optimizing land use through density planning, infill development, and brownfield redevelopment. Efficient land use reduces pressure on greenfield areas, preserves natural habitats, and promotes the efficient use of infrastructure and resources.
- Public Transportation and Active Transportation: Sustainable urban planning prioritizes the development and improvement of public transportation systems, including buses, trains, and light rail. It also promotes active transportation options such as walking and cycling, ensuring that cities are accessible and connected, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions and traffic congestion.
- Green Infrastructure and Open Spaces: Integrating green infrastructure and open spaces into urban planning is essential for sustainable cities. This includes parks, green roofs, urban agriculture, and green corridors. These elements enhance the quality of life, improve air quality, mitigate the urban heat island effect, and support biodiversity.
- Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: Sustainable urban planning emphasizes energy efficiency and the use of renewable energy sources. It involves designing buildings with high energy performance standards, incorporating renewable energy generation, promoting energy conservation measures, and implementing sustainable building practices.
- Water Management: Sustainable urban planning addresses water management through strategies such as rainwater harvesting, stormwater management, and water conservation. It aims to minimize water consumption, reduce runoff and flooding, and protect water quality through the implementation of sustainable drainage systems and water-sensitive design.
- Social Equity and Inclusivity: Sustainable urban planning recognizes the importance of social equity and inclusivity. It ensures affordable housing options, promotes mixed-income communities, and provides access to essential services and amenities for all residents. It also considers the needs of marginalized groups, promotes social cohesion, and addresses issues of social inequality.
- Climate Change Adaptation and Resilience: Sustainable urban planning incorporates climate change adaptation and resilience measures. This includes designing buildings and infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events, integrating green and blue infrastructure for climate regulation, and implementing strategies to reduce vulnerability to climate change impacts.
- Participatory Planning: In sustainable urban planning, the participation of the community and stakeholders is crucial. It encourages active involvement in decision-making processes, fosters collaboration, and ensures that diverse perspectives, needs, and aspirations are considered. Participatory planning enhances transparency, accountability, and the overall quality of urban development projects.
- Long-Term Monitoring and Evaluation: Sustainable urban planning goes beyond the initial design and implementation stages. It requires ongoing monitoring and evaluation to assess the effectiveness of planning initiatives, measure progress towards sustainability goals, and make necessary adjustments to ensure continuous improvement and adaptation to changing circumstances.
Sustainable urban planning recognizes the interconnectedness of social, economic, and environmental factors. By integrating sustainability principles into all aspects of urban development, it creates cities that are resilient, livable, and environmentally responsible. Through sustainable urban planning, we can shape a future where cities are equitable, prosperous, and in harmony with the natural environment.
Read more: Why Urban Planning Is Important
Importance of Urban Planning
Urban planning plays a crucial role in shaping the development and growth of cities, making it a vital discipline for creating sustainable and livable urban environments. Here are several key reasons why urban planning is important:
- Sustainable Development: Urban planning promotes sustainable development by integrating environmental, social, and economic considerations. It helps cities achieve a balance between economic growth, social equity, and environmental protection. By guiding land use, transportation systems, and infrastructure development, urban planning ensures cities can grow and thrive in a sustainable manner.
- Efficient Land Use: Urban planning is instrumental in optimizing land use within cities. Through strategies such as compact development, mixed-use zoning, and infill development, urban planners help reduce urban sprawl, preserve natural habitats, and promote efficient use of land and resources.
- Quality of Life: Good urban planning enhances the quality of life for residents. By creating well-designed neighborhoods, accessible public spaces, and reliable infrastructure, urban planners contribute to vibrant and inclusive communities. They prioritize factors such as walkability, access to green spaces, and connectivity, ensuring that cities are enjoyable and meet the needs of their residents.
- Disaster Mitigation and Resilience: Urban planning plays a crucial role in mitigating and managing the impact of natural disasters and climate change. Through measures such as floodplain management, the incorporation of green infrastructure, and the design of resilient buildings, urban planners help cities become more resilient and better equipped to withstand and recover from disasters.
- Transportation and Mobility: Urban planning influences transportation systems, ensuring their efficiency and sustainability. By promoting public transportation networks, pedestrian-friendly infrastructure, and safe cycling options, urban planners reduce congestion, improve air quality, and enhance mobility within cities.
- Economic Development: Effective urban planning drives economic development and prosperity. By strategically locating commercial areas, industrial zones, and recreational spaces, urban planners create an environment conducive to business growth, job creation, and economic opportunity. They also consider factors such as affordable housing, mixed-use development, and access to amenities that contribute to a thriving urban economy.
- Cultural Heritage Preservation: Urban planning takes into account the preservation and integration of cultural heritage within cities. It helps protect historically significant sites and buildings, fosters cultural diversity, and creates opportunities for cultural expression. By preserving cultural heritage, urban planners contribute to the unique identity and character of cities.
- Community Engagement: Urban planning involves engaging the community and stakeholders in decision-making processes. By facilitating participatory planning and incorporating diverse perspectives, urban planners empower residents to shape the future of their cities. This fosters a sense of ownership and strengthens social cohesion within communities.
- Environmental Stewardship: Urban planning prioritizes environmental sustainability and promotes responsible resource management. It encourages the use of renewable energy sources, green building practices, waste reduction, and the protection of natural habitats. By integrating green infrastructure and sustainable practices, urban planners help reduce the ecological footprint of cities and preserve the natural environment.
- Long-Term Vision and Adaptation: Urban planning takes a long-term perspective, considering future needs and challenges. It anticipates population growth, technological advancements, and environmental changes, and plans accordingly. By fostering adaptability and flexibility, urban planning ensures that cities can accommodate evolving circumstances and continue to meet the needs of their residents.
Urban planning is a dynamic and essential discipline that shapes the physical, social, and economic aspects of cities. By guiding development with foresight and creativity, urban planners create cities that are sustainable, inclusive, and resilient, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for present and future generations.
Conclusion
Urban planning is a multidisciplinary field that plays a crucial role in shaping the development and growth of cities and communities. It integrates various factors such as land use, transportation, infrastructure, and environmental sustainability to create functional, equitable, and sustainable urban environments. The importance of urban planning cannot be overstated, as it addresses the complex challenges and opportunities posed by rapid urbanization, social inequality, climate change, and resource management.
Throughout history, urban planning has evolved, incorporating lessons learned from past civilizations to guide the development of modern cities. Key concepts such as sustainability, inclusivity, and resilience drive the planning process, ensuring that cities are designed to meet the present needs without compromising the future generations’ well-being.
The urban planning process includes stages like understanding and assessment, goal setting, data collection and analysis, plan formulation, public participation, plan review and approval, implementation, and monitoring and evaluation. Urban planners utilize a range of tools and techniques such as GIS, urban design software, transportation modeling, and community engagement platforms to support their planning efforts.
However, urban planning is not without its challenges. Rapid urbanization, urban sprawl, infrastructure deficiencies, social inequality, and climate change are some of the complex issues that urban planners face. Overcoming these challenges requires innovative approaches, collaboration, and long-term vision to create sustainable and equitable urban environments.
In conclusion, urban planning is of utmost importance for creating cities that are livable, inclusive, and environmentally responsible. It promotes sustainable development, efficient land use, and quality of life. It addresses the needs of diverse communities, protects natural and cultural heritage, and fosters economic growth. By integrating sustainability principles and engaging the community, urban planners can shape the future of cities in a way that ensures a better quality of life for all residents.
With the continued efforts and creative solutions of urban planners worldwide, we can envision a future where cities are vibrant, resilient, and sustainable, meeting the needs and aspirations of present and future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Urban Planning?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is Urban Planning?”