Home>Furniture & Design>Interior Design Trends>When Can Glass Thermometers Be Used

Interior Design Trends
When Can Glass Thermometers Be Used
Published: February 4, 2024
Discover the latest interior design trends and learn when glass thermometers can be used to enhance your home decor. Explore innovative ideas and expert tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Glass thermometers have been a staple in temperature measurement for centuries, offering a simple yet effective way to gauge the heat or cold of a substance. These traditional instruments have stood the test of time, providing reliable temperature readings in various settings. Understanding the functionality, advantages, limitations, and ideal applications of glass thermometers is essential for utilizing them effectively. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of glass thermometers, exploring their benefits, drawbacks, and the specific scenarios in which they shine. Whether you're a seasoned professional or an enthusiast seeking to expand your knowledge, this comprehensive guide will shed light on the practical use of glass thermometers in today's diverse environments.
Key Takeaways:
- Glass thermometers are classic, durable, and accurate tools for measuring temperature. They are great for checking body temperature, teaching about temperature, and verifying other temperature sensors.
- While glass thermometers are reliable, they can break easily and have limitations in extreme temperatures. They are best suited for traditional, low-tech, and specific temperature range applications.
Read more: How To Use A Glass Thermometer
Understanding Glass Thermometers
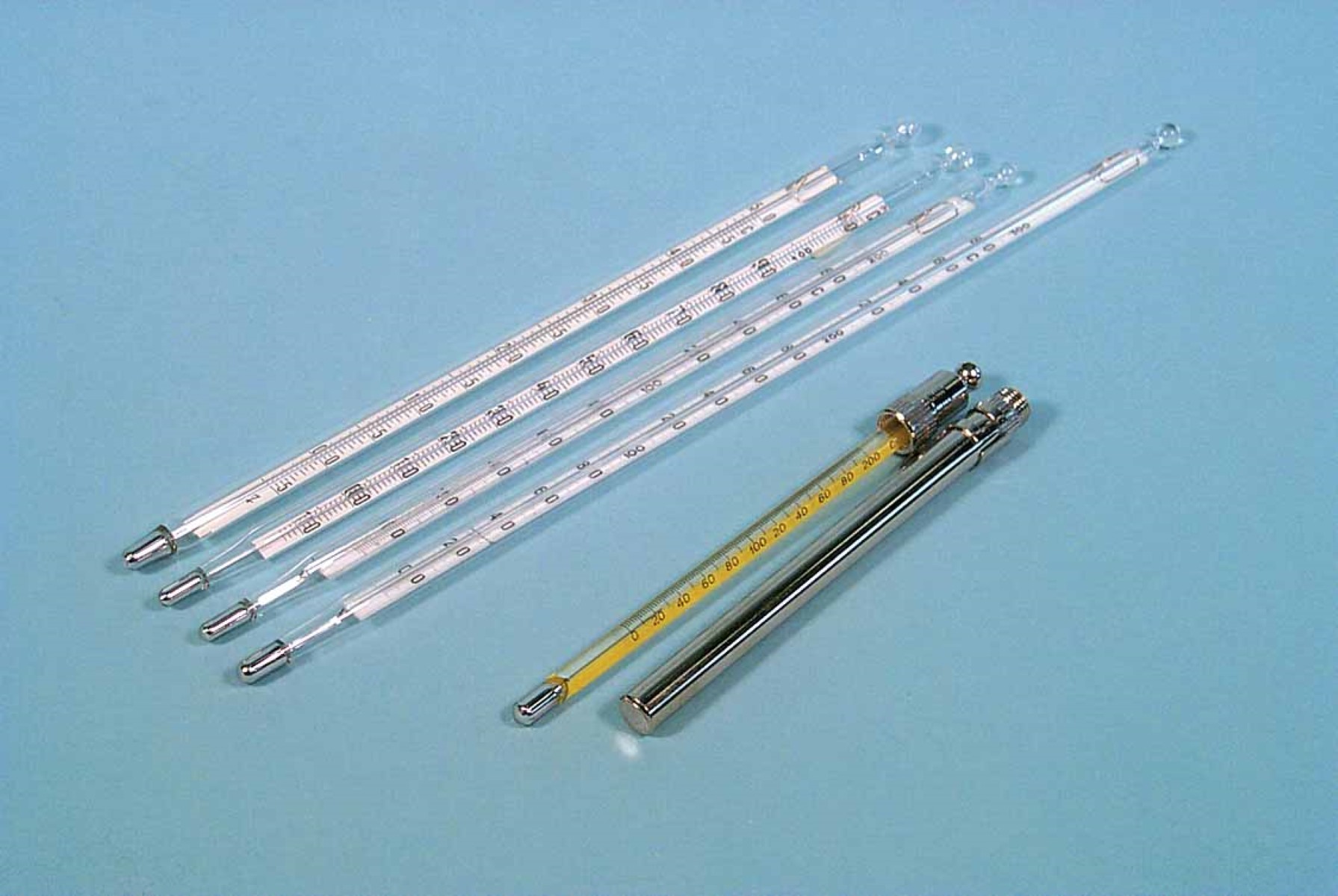
Glass thermometers are classic temperature-measuring devices that consist of a glass tube with a liquid-filled bulb at one end. The most common type is the mercury thermometer, which uses mercury as the temperature-sensitive fluid. When the temperature changes, the volume of the liquid in the bulb expands or contracts, causing it to rise or fall within the narrow capillary tube, indicating the temperature on a scale.
The principle behind glass thermometers is based on the thermal expansion of liquids. As the temperature increases, the liquid inside the bulb expands, causing it to rise in the calibrated tube. Conversely, a decrease in temperature results in the contraction of the liquid, leading to a drop in the column height. This simple yet effective mechanism allows for accurate temperature measurement across a wide range of applications.
Glass thermometers are renowned for their precision and reliability. They offer a clear and easy-to-read scale, allowing users to obtain accurate temperature readings with minimal effort. The glass construction ensures durability and resistance to chemical corrosion, making them suitable for various environments, including laboratories, industrial settings, and household use.
In addition to mercury thermometers, alcohol-filled glass thermometers are also widely used. These thermometers utilize colored alcohol, typically red or blue, as the temperature-sensitive fluid. While they offer a safer alternative to mercury thermometers, they are equally effective in measuring temperature variations.
Understanding the construction and functionality of glass thermometers is crucial for their proper utilization. Whether used for monitoring body temperature, assessing environmental conditions, or conducting scientific experiments, glass thermometers remain a fundamental tool for temperature measurement due to their simplicity, accuracy, and versatility.
Advantages of Glass Thermometers
Glass thermometers offer several distinct advantages that contribute to their enduring popularity and widespread use in diverse settings. Understanding these advantages provides valuable insight into the practical benefits of utilizing glass thermometers for temperature measurement.
-
Accuracy and Precision: Glass thermometers are renowned for their accuracy in providing precise temperature readings. The clear and well-calibrated scale allows for easy interpretation of temperature variations, making them reliable instruments for obtaining accurate measurements.
-
Durability: The robust construction of glass thermometers ensures their durability and longevity. The glass material is resistant to chemical corrosion, making these thermometers suitable for use in various environments, including laboratories, industrial facilities, and medical settings.
-
Versatility: Glass thermometers are versatile tools that can be used to measure temperatures in a wide range of applications. From monitoring body temperature to assessing environmental conditions and conducting scientific experiments, glass thermometers offer flexibility in their usage.
-
Ease of Use: Glass thermometers are user-friendly and require minimal training for operation. The straightforward design and clear scale make them accessible to a wide range of users, including professionals, students, and individuals monitoring personal health.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Glass thermometers are cost-effective temperature-measuring devices, offering a practical solution for temperature monitoring without the need for complex technology or frequent calibration.
-
Environmental Safety: While mercury-filled glass thermometers have become less common due to environmental concerns, the use of alcohol-filled glass thermometers provides a safer alternative without compromising accuracy. This ensures the safety of both users and the environment.
-
Traditional Reliability: The long-standing reputation of glass thermometers for providing consistent and reliable temperature measurements has solidified their position as a trusted tool in various fields, maintaining their relevance alongside modern digital thermometers.
In summary, the advantages of glass thermometers encompass their accuracy, durability, versatility, ease of use, cost-effectiveness, environmental safety, and traditional reliability. These qualities make glass thermometers a preferred choice for temperature measurement in numerous practical applications, highlighting their enduring significance in the realm of temperature monitoring and assessment.
Glass thermometers can be used to measure temperature in a variety of settings, but they should not be used in situations where breakage could result in injury or contamination, such as in food or medical applications. Always handle with care.
Limitations of Glass Thermometers
While glass thermometers offer several advantages, they are not without limitations. Understanding these constraints is crucial for making informed decisions regarding their usage and considering alternative temperature-measuring methods where necessary.
-
Fragility: Glass thermometers are inherently fragile due to their construction from glass materials. The risk of breakage poses a significant limitation, especially in environments where accidental impacts or mishandling may occur. This fragility can lead to potential safety hazards and the need for careful handling to prevent damage or injury.
-
Mercury Concerns: Traditional mercury-filled glass thermometers raise environmental and health concerns due to the toxic nature of mercury. Accidental breakage can release mercury vapor, posing a risk to human health and the environment. As a result, the use of mercury thermometers has been phased out in many settings, necessitating the adoption of safer alternatives.
-
Limited Temperature Range: Glass thermometers, particularly those filled with mercury, have a limited temperature range. Mercury thermometers are typically suitable for measuring temperatures within a specific range, and exposure to extreme temperatures can affect their accuracy and functionality. This limitation restricts their applicability in environments with fluctuating or extreme temperature conditions.
-
Response Time: Glass thermometers, especially those with a traditional liquid column, may have a slower response time compared to modern digital thermometers. The time required for the liquid column to reach equilibrium with the measured temperature can impact the efficiency of temperature monitoring, particularly in time-sensitive applications.
-
Calibration and Maintenance: Glass thermometers require periodic calibration and maintenance to ensure their accuracy. Over time, factors such as wear, environmental conditions, and handling can affect the calibration of glass thermometers, necessitating regular checks and adjustments to maintain their reliability.
-
Visibility and Readability: In certain lighting conditions or environments with limited visibility, reading the scale of a glass thermometer may pose challenges. The clarity of the scale and the visibility of the liquid column can be affected by external factors, potentially impacting the accuracy of temperature readings.
-
Alternative Technologies: With the advancement of digital and infrared temperature-measuring technologies, glass thermometers face competition from more advanced and versatile instruments. While glass thermometers remain relevant in specific applications, the availability of alternative technologies offers enhanced features and capabilities for temperature monitoring.
Understanding the limitations of glass thermometers is essential for evaluating their suitability in various contexts and considering alternative temperature-measuring solutions where their constraints may pose challenges. By acknowledging these limitations, users can make informed choices and implement appropriate measures to address the inherent constraints of glass thermometers in temperature measurement applications.
When to Use Glass Thermometers
Glass thermometers are well-suited for specific scenarios and environments where their inherent characteristics align with the requirements of temperature measurement. Understanding the optimal conditions for using glass thermometers is essential for leveraging their advantages and ensuring accurate temperature monitoring in diverse applications.
-
Traditional Temperature Measurement: In settings where traditional temperature measurement methods are preferred or mandated, such as in certain laboratory protocols or historical data comparison, glass thermometers remain a relevant choice. Their long-standing reputation for reliability and consistency makes them suitable for adhering to established practices and standards.
-
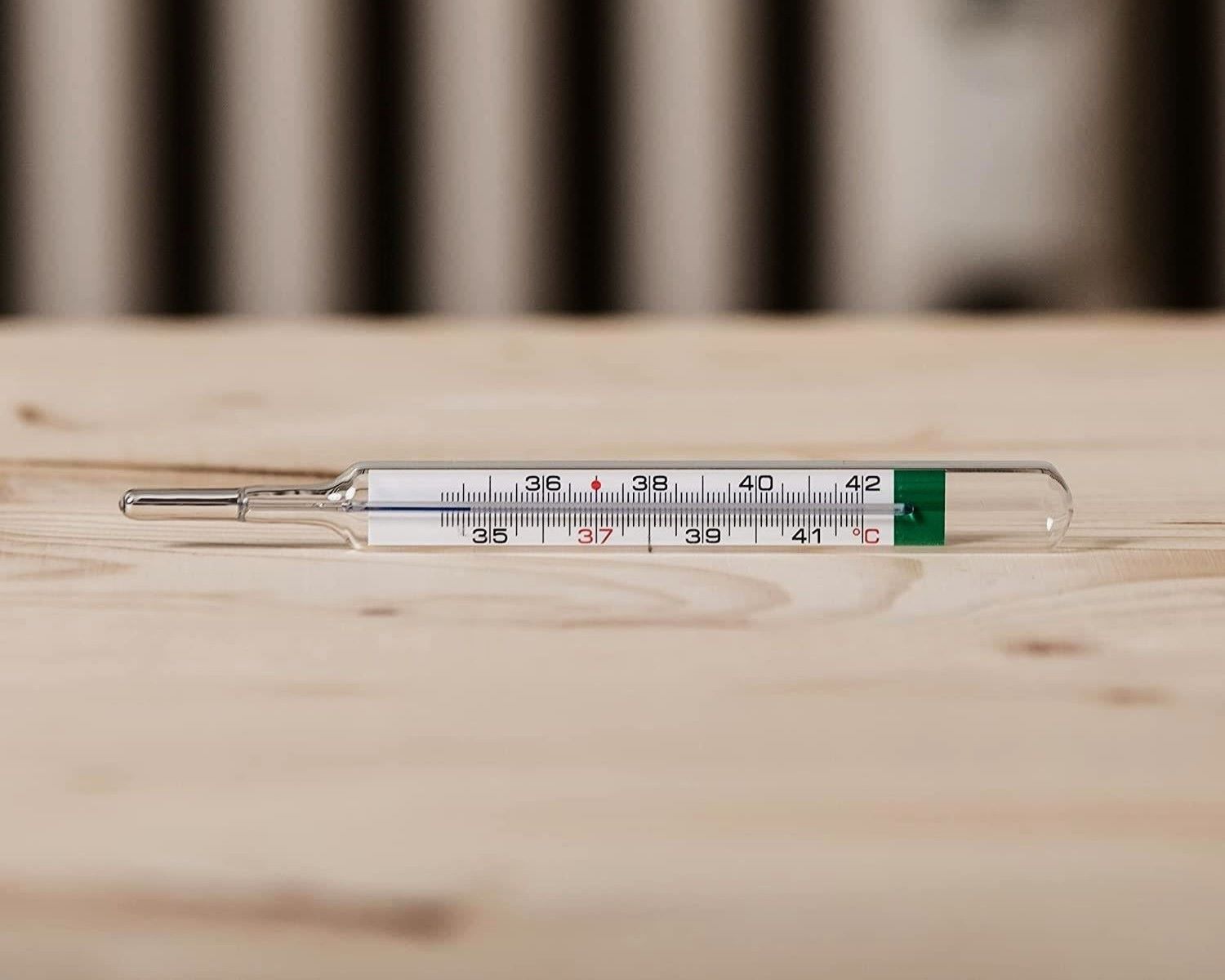
Routine Body Temperature Monitoring: Glass thermometers, particularly alcohol-filled variants, are commonly used for routine body temperature monitoring in healthcare facilities, clinics, and home settings. Their ease of use, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness make them practical tools for assessing individual health and detecting fevers or fluctuations in body temperature.
-
Educational and Training Environments: In educational institutions, training facilities, and scientific workshops, glass thermometers serve as valuable teaching aids for demonstrating temperature measurement principles. Their simplicity and clear visual representation of temperature variations make them effective tools for educating students and trainees on the fundamentals of temperature monitoring.
-
Low-Tech or Remote Environments: In situations where access to advanced temperature-measuring technologies is limited, such as in remote locations, field research, or resource-constrained settings, glass thermometers offer a reliable and accessible means of temperature assessment. Their minimal requirements for operation and maintenance make them suitable for low-tech environments.
-
Specific Temperature Ranges: Glass thermometers are well-suited for applications that fall within their calibrated temperature ranges. For instance, in environments where temperatures remain within the optimal range of a particular glass thermometer, such as refrigeration units, climate-controlled storage facilities, or certain industrial processes, these thermometers provide accurate and consistent temperature readings.
-
Verification and Cross-Checking: Glass thermometers are often used for verification and cross-checking purposes in conjunction with digital or electronic temperature-measuring devices. Their role in validating the accuracy of other temperature sensors or systems adds an additional layer of assurance in critical temperature-sensitive processes and equipment.
-
Historical Preservation and Restoration: In the context of historical preservation and restoration efforts, glass thermometers may be utilized for assessing environmental conditions in museums, archives, and heritage sites. Their compatibility with preservation guidelines and the preservation of historical measurement practices make them valuable tools in such specialized applications.
Understanding the specific contexts in which glass thermometers excel enables users to make informed decisions regarding their utilization. By recognizing the scenarios where the characteristics of glass thermometers align with the requirements of temperature measurement, individuals and organizations can leverage the strengths of these traditional instruments for effective temperature monitoring and assessment.
Read more: Why Are Glass Thermometers Rarely Used Today
Conclusion
In conclusion, glass thermometers, with their timeless functionality and enduring relevance, continue to hold a significant place in the realm of temperature measurement. Despite the availability of modern digital and infrared temperature-measuring technologies, glass thermometers offer distinct advantages and find their niche in specific applications and environments.
The enduring appeal of glass thermometers lies in their accuracy, durability, versatility, ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and traditional reliability. These qualities make them well-suited for traditional temperature measurement, routine body temperature monitoring, educational and training environments, low-tech or remote settings, specific temperature ranges, verification and cross-checking, as well as historical preservation and restoration efforts.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of glass thermometers, including fragility, mercury concerns, limited temperature range, response time, calibration and maintenance requirements, visibility and readability challenges, and competition from alternative technologies. Understanding these constraints is crucial for making informed decisions regarding their usage and considering alternative temperature-measuring methods where necessary.
As technology continues to advance, the role of glass thermometers may evolve, with a shift towards specialized applications where their unique characteristics are valued. The ongoing emphasis on environmental safety and the development of safer alternatives to traditional mercury-filled glass thermometers reflect the adaptability and responsiveness of temperature-measuring practices to contemporary concerns and requirements.
Ultimately, the practical use of glass thermometers hinges on a nuanced understanding of their advantages, limitations, and optimal applications. By recognizing the specific scenarios where glass thermometers shine, users can harness their enduring benefits for accurate temperature monitoring while addressing their inherent constraints with informed considerations and appropriate measures.
In today's diverse landscape of temperature-measuring instruments, glass thermometers stand as a testament to the enduring legacy of traditional measurement practices, offering a timeless and reliable approach to temperature assessment in a rapidly evolving technological era.
Frequently Asked Questions about When Can Glass Thermometers Be Used
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “When Can Glass Thermometers Be Used”