

Furniture
What Is A Halogen Lamp
Modified: March 24, 2024
Discover the benefits of using halogen lamps for your furniture. Learn how these energy-efficient lighting solutions can enhance the ambiance and showcase the beauty of your home decor.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of halogen lamps! If you’re looking to brighten up your living space or add a touch of elegance to your home decor, then halogen lamps are a fantastic choice. With their bright and focused light, these lamps have become popular options for both practical and aesthetic purposes.
In this article, we will delve into the history, workings, advantages, and disadvantages of halogen lamps. We will also explore their common uses and compare them with other types of lighting options. Lastly, we will discuss some important safety considerations to keep in mind when using halogen lamps.
So, let’s dive in and discover the world of halogen lamps!
Key Takeaways:
- Halogen lamps offer bright, white light ideal for task and accent lighting, with energy efficiency and longer lifespan compared to incandescent bulbs. However, they require careful handling due to high operating temperatures.
- When considering lighting options, compare the advantages and disadvantages of halogen lamps with other types, such as LED, CFL, and fluorescent lights. Prioritize safety and follow guidelines for safe operation and installation.
Read more: What Is A Halogen Bulb
History of Halogen Lamps
The development of halogen lamps dates back to the early 1960s. It was an innovative breakthrough in the field of lighting, introducing a more efficient and long-lasting option compared to traditional incandescent bulbs.
The concept of the halogen lamp originated from the incandescent lamp, which was invented by Thomas Edison in the late 19th century. Incandescent bulbs work by passing an electric current through a filament, heating it to a high temperature and producing light. However, incandescent bulbs have a relatively short lifespan and consume a significant amount of energy.
In the 1950s, researchers began experimenting with adding halogen gases, such as bromine or iodine, to the inert gas filling of incandescent lamps. This addition had a remarkable effect on the performance of the lamp. The halogen gases combine with the evaporated tungsten from the filament, creating a chemical reaction that redeposits the tungsten back onto the filament. This process, known as the “halogen cycle,” significantly prolongs the lifespan of the bulb.
Halogen lamps were first introduced commercially in the early 1960s. They quickly gained popularity due to their enhanced lifespan and improved efficiency. These lamps provided a brighter and whiter light compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, making them ideal for various applications.
Over the years, advancements in technology led to the development of different types of halogen lamps, including quartz halogen lamps and compact halogen lamps. These variations offer even greater efficiency, increased light output, and improved performance.
Today, halogen lamps continue to be widely used in both residential and commercial settings, providing a reliable and cost-effective lighting solution.
How Halogen Lamps Work
To understand how halogen lamps work, let’s take a closer look at their construction and operation.
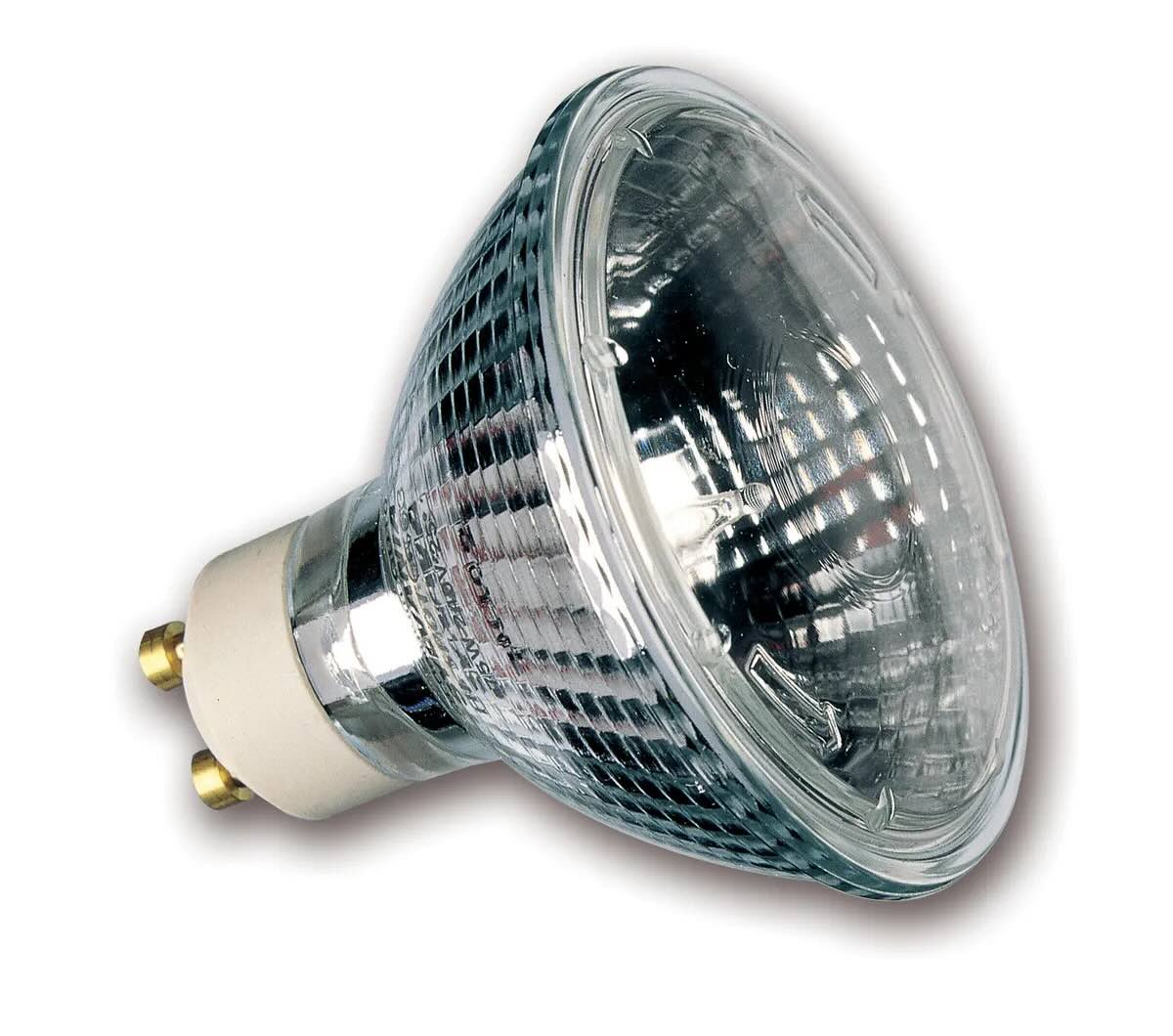
Halogen lamps consist of a tungsten filament enclosed in a glass envelope filled with a halogen gas, such as bromine or iodine. The glass envelope is made from quartz or a high-temperature resistant glass to withstand the high temperatures generated by the filament.
When the lamp is turned on and an electric current passes through the tungsten filament, it heats up and emits light. The halogen gas plays a crucial role in the operation of the lamp. As the filament heats up, tungsten atoms evaporate and combine with the halogen gas. This forms a tungsten halide compound, which vaporizes and moves away from the filament.
However, the halogen cycle comes into play to prevent the tungsten from being lost forever. The higher temperature regions of the lamp, such as the glass envelope, are cooler than the filament. As the tungsten halide vapor reaches these cooler areas, it condenses back onto the filament, rejuvenating and redepositing the tungsten back onto the filament surface.
This constant cycling of tungsten prevents the filament from deteriorating and prolongs the lifespan of the lamp. It also allows halogen lamps to operate at higher temperatures and produce a brighter, whiter light compared to traditional incandescent bulbs.
Halogen lamps also possess another distinctive feature – their small size. The compact design of halogen lamps allows for versatility in installation and makes them suitable for various lighting applications. They can be used in desk lamps, track lighting fixtures, pendant lights, and even automotive headlights.
It’s important to note that halogen lamps should always be handled with care. The oils from our skin can damage the quartz or glass envelope, leading to premature failure of the lamp. Therefore, it’s recommended to wear gloves or use a clean cloth when installing or replacing halogen lamps.
Now that we have a better understanding of how halogen lamps work, let’s explore their advantages in the next section.
Advantages of Halogen Lamps
Halogen lamps offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for lighting solutions. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of using halogen lamps:
- Bright and White Light: Halogen lamps produce a bright and crisp white light that closely resembles natural daylight. This makes them ideal for tasks that require focused and accurate lighting, such as reading, studying, or working on intricate projects. The color temperature of halogen lamps ranges from 2800K to 3200K, creating a warm and inviting atmosphere in any space.
- High Efficiency: Compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, halogen lamps are more energy-efficient. They convert a larger proportion of the electrical energy into light, rather than heat. This results in lower energy consumption and reduced electricity bills.
- Longer Lifespan: The halogen cycle in these lamps helps to prolong their lifespan. On average, halogen lamps can last two to three times longer than traditional incandescent bulbs. This reduces the frequency of bulb changes and saves money in the long run.
- Instant and Flicker-free Lighting: Halogen lamps provide instant illumination when turned on. Unlike some other types of lighting, they do not require any warm-up time. Additionally, halogen lamps do not produce any noticeable flickering, ensuring a stable and comfortable lighting experience.
- Flexibility and Versatility: Halogen lamps come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and wattages, offering flexibility in installation and usage. They are compatible with a wide range of fixtures, including recessed lights, track lights, sconces, and desk lamps. This versatility makes halogen lamps suitable for both residential and commercial applications.
With their combination of brightness, efficiency, longevity, and flexibility, halogen lamps are an excellent choice for various lighting needs. However, it’s important to consider the disadvantages of halogen lamps before making a final decision, which we will explore in the next section.
Disadvantages of Halogen Lamps
While halogen lamps offer numerous advantages, they also come with a few drawbacks. Let’s take a look at some of the disadvantages of using halogen lamps:
- Higher Operating Temperatures: Halogen lamps operate at higher temperatures compared to other types of lighting, such as LED or fluorescent. This elevated temperature can pose a safety risk, especially if the lamp is installed in close proximity to flammable materials or if it is accidentally touched while hot. It is crucial to exercise caution and follow safety guidelines when using halogen lamps.
- Higher Energy Consumption: Although halogen lamps are more efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs, they still consume more energy than newer lighting technologies, such as LEDs. This means that over time, the energy savings may not be as significant compared to more energy-efficient options.
- Shorter Lifespan Compared to LEDs: While halogen lamps have a longer life expectancy than traditional incandescent bulbs, they still have a shorter lifespan compared to LED lights. LED lights can last up to 25 times longer than halogen lamps, reducing the frequency of bulb replacements and maintenance.
- Heat Emission: Halogen lamps emit a considerable amount of heat during operation. This heat emission can be uncomfortable in small spaces or during hot weather. It is important to allow adequate ventilation and not touch the lamp when it is in use or immediately after turning it off to avoid burns.
- Higher Cost: Halogen lamps tend to have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Although the initial investment may be higher, the longer lifespan and energy efficiency can offset the initial expense in the long run.
It’s essential to consider these disadvantages when deciding whether halogen lamps are the right lighting choice for your needs. Assessing your specific requirements, budget, and safety concerns can help you make an informed decision.
Now that we have explored the advantages and disadvantages of halogen lamps, let’s move on to discussing their common uses in the next section.
When handling a halogen lamp, avoid touching the glass with bare hands as the oils from your skin can cause the lamp to heat unevenly and potentially lead to premature failure. Use a clean cloth or gloves when installing or replacing the lamp.
Read more: What Is A Halogen Cooktop
Common Uses of Halogen Lamps
Halogen lamps are versatile lighting options that find a wide range of applications in both residential and commercial settings. Let’s explore some of the common uses of halogen lamps:
- Task Lighting: Halogen lamps are frequently used for task lighting purposes. The bright and focused light they emit makes them ideal for illuminating specific areas where detailed work is performed. Whether it’s reading, studying, cooking, or working on crafts, halogen lamps provide the necessary brightness and clarity.
- Accent Lighting: Halogen lamps are fantastic for accent lighting. Their directional light can highlight art pieces, decorative objects, or architectural features, creating a visually appealing focal point in a room. They offer flexibility in adjusting the angle and intensity of the light, allowing for precise control over the illuminated areas.
- Spotlighting: In commercial settings, halogen lamps are commonly used for spotlighting. Their focused beam allows for highlighting specific products or areas of interest, such as in retail stores, galleries, or museums. The crisp and vibrant light of halogen lamps can enhance the visual appeal and draw attention to the desired focal points.
- Landscape Lighting: Halogen lamps are also popular for outdoor lighting, particularly for landscape illumination. They can be used to highlight trees, shrubs, pathways, and architectural details in gardens or outdoor spaces. The bright and white light of halogen lamps can create a welcoming and visually striking ambiance in outdoor areas.
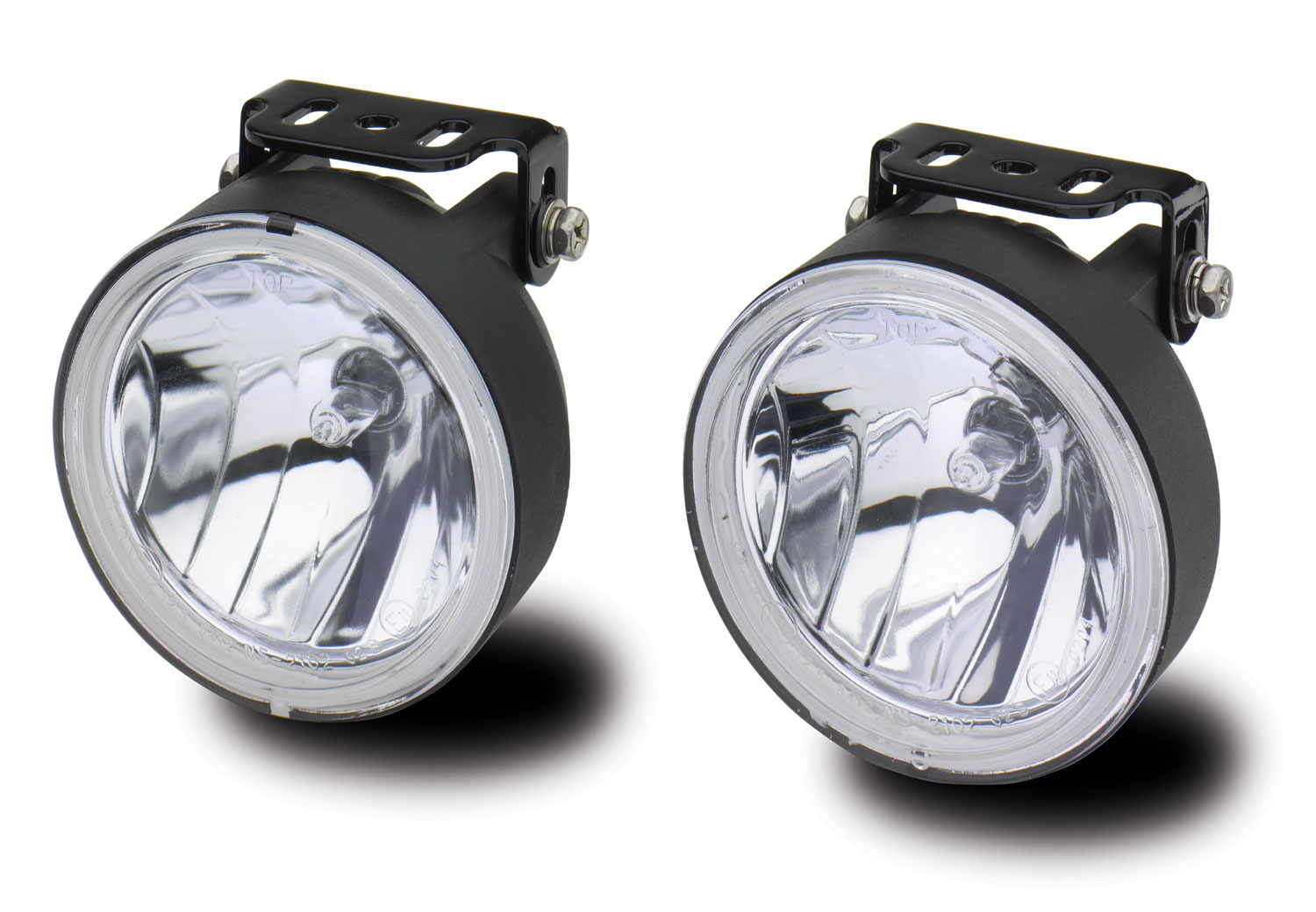
- Automotive Lighting: Halogen lamps are widely used in automotive lighting, including headlights and fog lights. Their bright and focused beam helps to improve visibility on the road, ensuring safety during nighttime driving. Halogen headlights emit a warm, white light that closely resembles natural daylight, providing a clear view of the surroundings.
These are just a few examples of the common uses of halogen lamps. Their versatility, brightness, and ease of installation make them a popular choice for various lighting applications.
Now, let’s move on to comparing halogen lamps with other types of lighting to help you make an informed decision about which option suits your needs best.
Comparison with Other Types of Lighting
When choosing the right lighting option, it’s essential to consider the different types available and compare their features. Let’s compare halogen lamps with other popular types of lighting:
- Incandescent Bulbs: Halogen lamps are an improved version of traditional incandescent bulbs. While both types use a filament to produce light, halogen lamps have a longer lifespan, higher efficiency, and emit a brighter light. Incandescent bulbs are less energy-efficient and have a shorter lifespan compared to halogen lamps.
- LED Lights: LED lights have gained popularity in recent years due to their exceptional energy efficiency and longevity. When compared to halogen lamps, LED lights consume significantly less energy, have a much longer lifespan, and produce less heat. LED lights also come in various colors and can be dimmable. However, LED lights can be more expensive upfront, although the long-term energy savings make them cost-effective.
- CFL Lights: Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFL) are another energy-efficient alternative to halogen lamps. CFL lights have a longer lifespan and consume less energy compared to halogen lamps. However, they may take a few seconds to reach full brightness and contain a small amount of mercury, requiring proper disposal procedures.
- Fluorescent Lights: Fluorescent lights are known for their energy efficiency and are widely used in commercial settings. They provide a diffuse light and can cover larger areas. However, fluorescent lights tend to have a cooler color temperature and contain mercury, requiring careful handling and disposal.
Each type of lighting has its own set of advantages and drawbacks. The choice between halogen lamps and other types of lighting depends on your specific requirements, including brightness, energy efficiency, longevity, and budget.
It’s worth noting that advancements in technology have led to the development of energy-efficient halogen lamps, such as energy-saving halogen bulbs. These bulbs are designed to reduce energy consumption while still maintaining the brightness and color quality of traditional halogen lamps.
Considering your lighting needs, preferences, and energy-saving goals will help you select the most suitable lighting option for your space.
Now, let’s move on to discussing safety considerations when using halogen lamps.
Safety Considerations with Halogen Lamps
While halogen lamps offer numerous benefits, it’s important to keep safety in mind when using them. Here are some key safety considerations to ensure safe operation and minimize any potential risks:
- Heat: Halogen lamps operate at high temperatures, and their surfaces can become extremely hot during use. To prevent burns or fire hazards, it’s crucial to avoid touching the lamp or its fixtures when in operation or immediately after turning it off. Allow the lamp to cool down before handling or replacing it.
- Flammable Materials: Due to the high heat output, halogen lamps should be kept away from flammable materials such as curtains, papers, or any objects that could easily catch fire. Ensure that there is sufficient distance between the lamp and any combustible materials to prevent accidents.
- Proper Installation: When installing halogen lamps, ensure that they are correctly fitted into their fixtures and secured. Loose connections can cause electrical issues, including short circuits or electrical shocks. If you are unsure about installation, it’s best to consult a professional electrician.
- Voltage and Wattage: Always use halogen lamps that are compatible with the voltage and wattage specified for the fixture. Using lamps with incorrect specifications can lead to overheating and potential hazards.
- Handling: When replacing or handling halogen lamps, it’s important to wear gloves or use a clean cloth. The oils from our skin can damage the glass envelope and reduce the lifespan of the lamp. Additionally, avoid touching the glass envelope with bare hands as the oils can cause the lamp to overheat and break.
- Child Safety: If you have young children at home, make sure to keep halogen lamps out of their reach. The hot surface of the lamp can cause burns, and the lamp could be easily knocked over, leading to accidents. Use childproof measures, such as placing the lamp in secure fixtures or using protective covers if necessary.
By following these safety considerations, you can enjoy the benefits of halogen lamps while minimizing any potential risks. It’s crucial to prioritize safety and take the necessary precautions to ensure a safe and enjoyable lighting experience.
Now, let’s conclude our exploration of halogen lamps.
Conclusion
Halogen lamps have cemented their place in the world of lighting, providing bright, focused, and energy-efficient illumination for various applications. With their long lifespan, versatility, and ease of installation, halogen lamps have become popular choices for both residential and commercial lighting needs.
The history of halogen lamps traces back to the 1960s, when the introduction of halogen gases revolutionized traditional incandescent bulbs, offering improved efficiency and longevity. Through the halogen cycle, these lamps rejuvenate the tungsten filament, resulting in extended lifespan and superior performance.
The advantages of using halogen lamps include their bright and white light, high efficiency, longer lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, instant illumination, and flexibility in installation. They are commonly used for task lighting, accent lighting, spotlighting, landscape lighting, and even automotive lighting.
However, it’s important to consider a few disadvantages of halogen lamps as well. Their higher operating temperatures, relatively higher energy consumption compared to LED lights, shorter lifespan compared to LEDs, heat emission, and higher upfront cost are factors that should be taken into account when deciding on the best lighting option for specific needs.
When using halogen lamps, it’s essential to follow safety considerations to ensure safe operation. Precautions include avoiding touching the lamp when hot, keeping them away from flammable materials, ensuring proper installation, using gloves or a clean cloth during handling, and considering child safety.
Ultimately, the choice of lighting depends on individual preferences, energy-saving goals, and specific requirements. Comparing halogen lamps with other types of lighting, such as incandescent bulbs, LED lights, CFL lights, and fluorescent lights, can help make an informed decision.
Halogen lamps continue to be a popular lighting solution, combining efficiency, brightness, and versatility. By considering the advantages and disadvantages, adhering to safety guidelines, and evaluating individual preferences, one can make the right choice and enjoy the benefits of halogen lamps in their living spaces or work environments.
So, whether you need focused lighting for your study area, accent lighting to highlight artwork, or bright illumination for outdoor spaces, halogen lamps can meet your needs and add a touch of elegance and brilliance to your surroundings.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Halogen Lamp
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is A Halogen Lamp”