

Articles
What Is A Halogen Bulb
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover the benefits and features of halogen bulbs in our informative articles. Learn about their energy efficiency and long-lasting performance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Lighting is an essential aspect of our daily lives, providing us with illumination and creating a warm and welcoming atmosphere in our homes and workplaces. While there are various types of bulbs available in the market, one popular choice is the halogen bulb. In this article, we will explore what a halogen bulb is, how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, its uses, and how it compares to other types of bulbs.
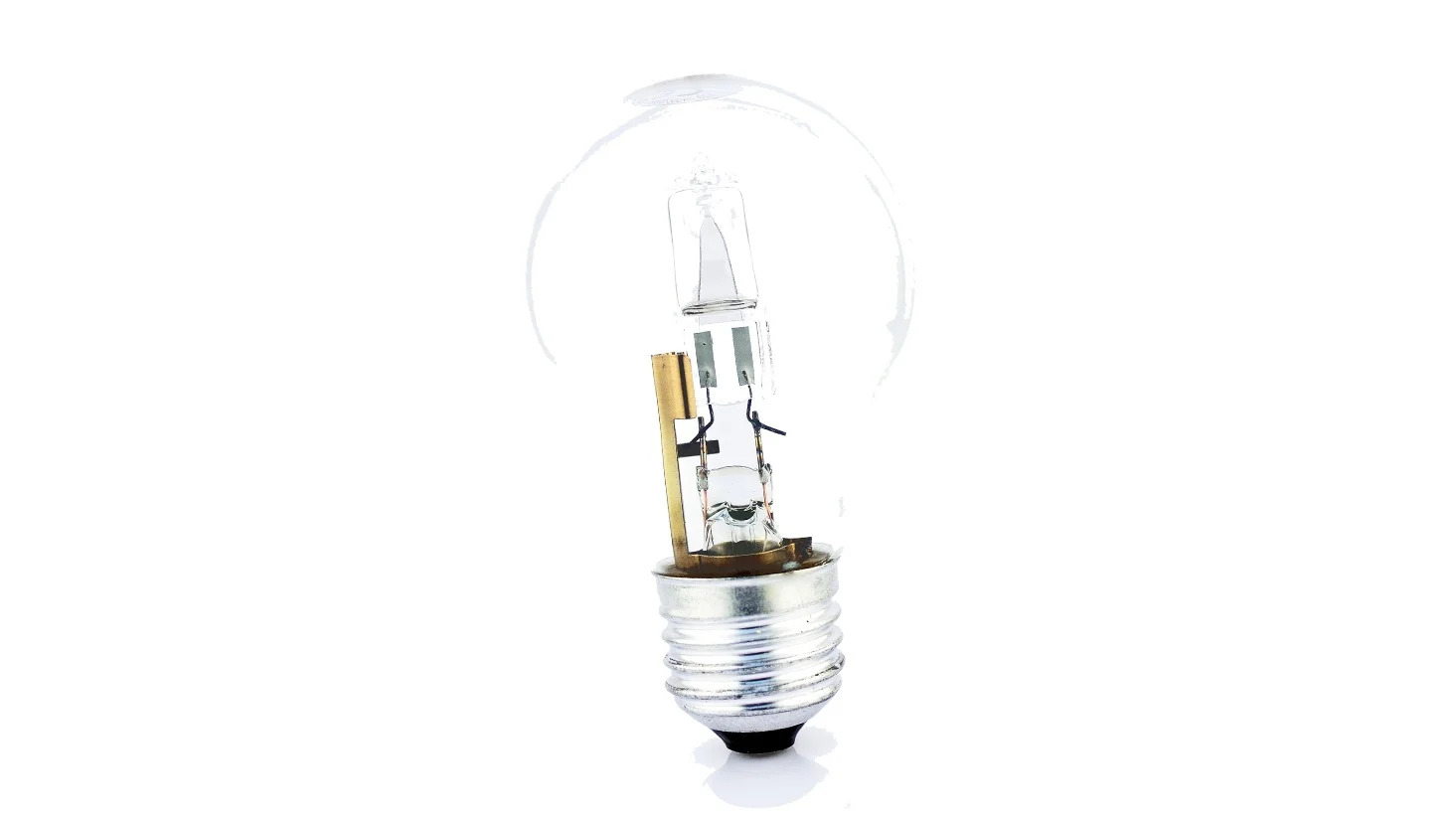
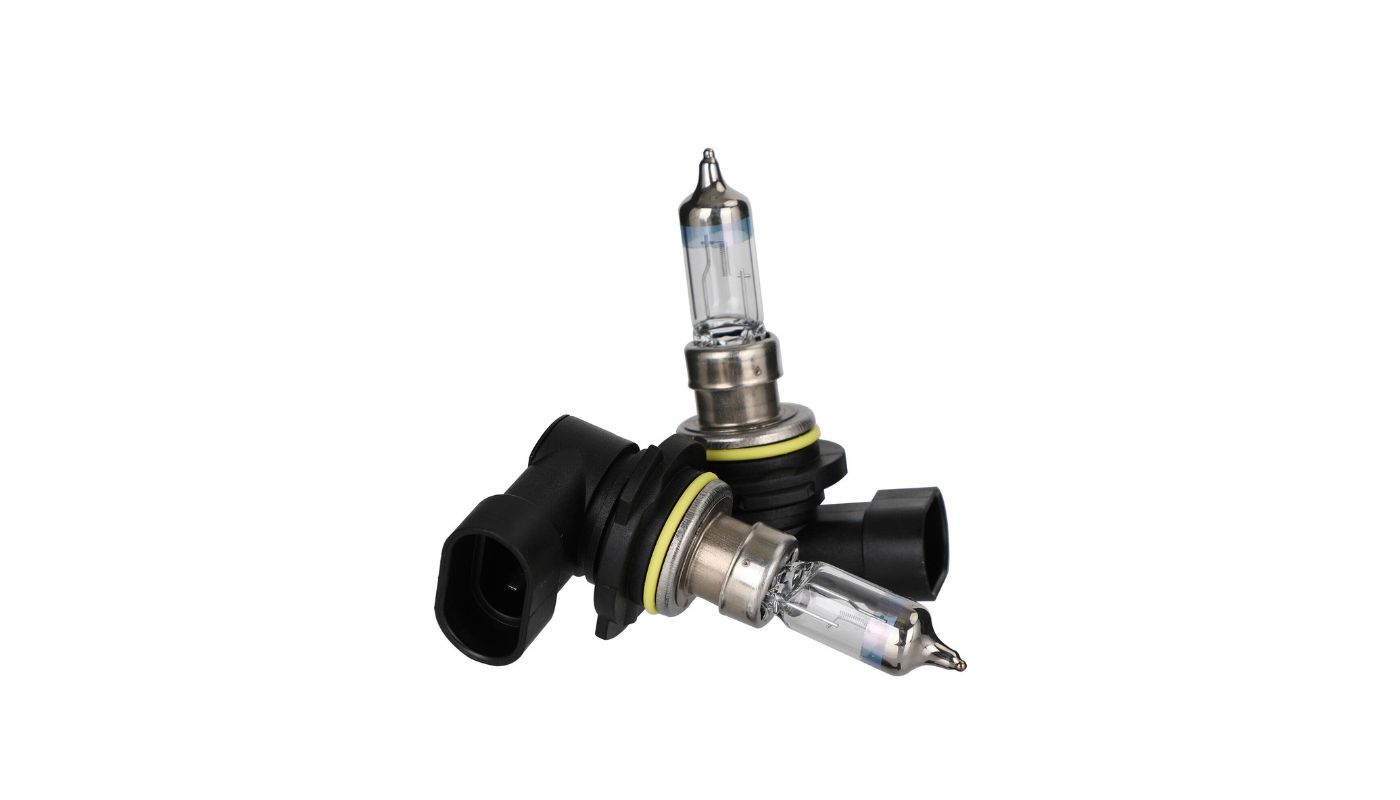
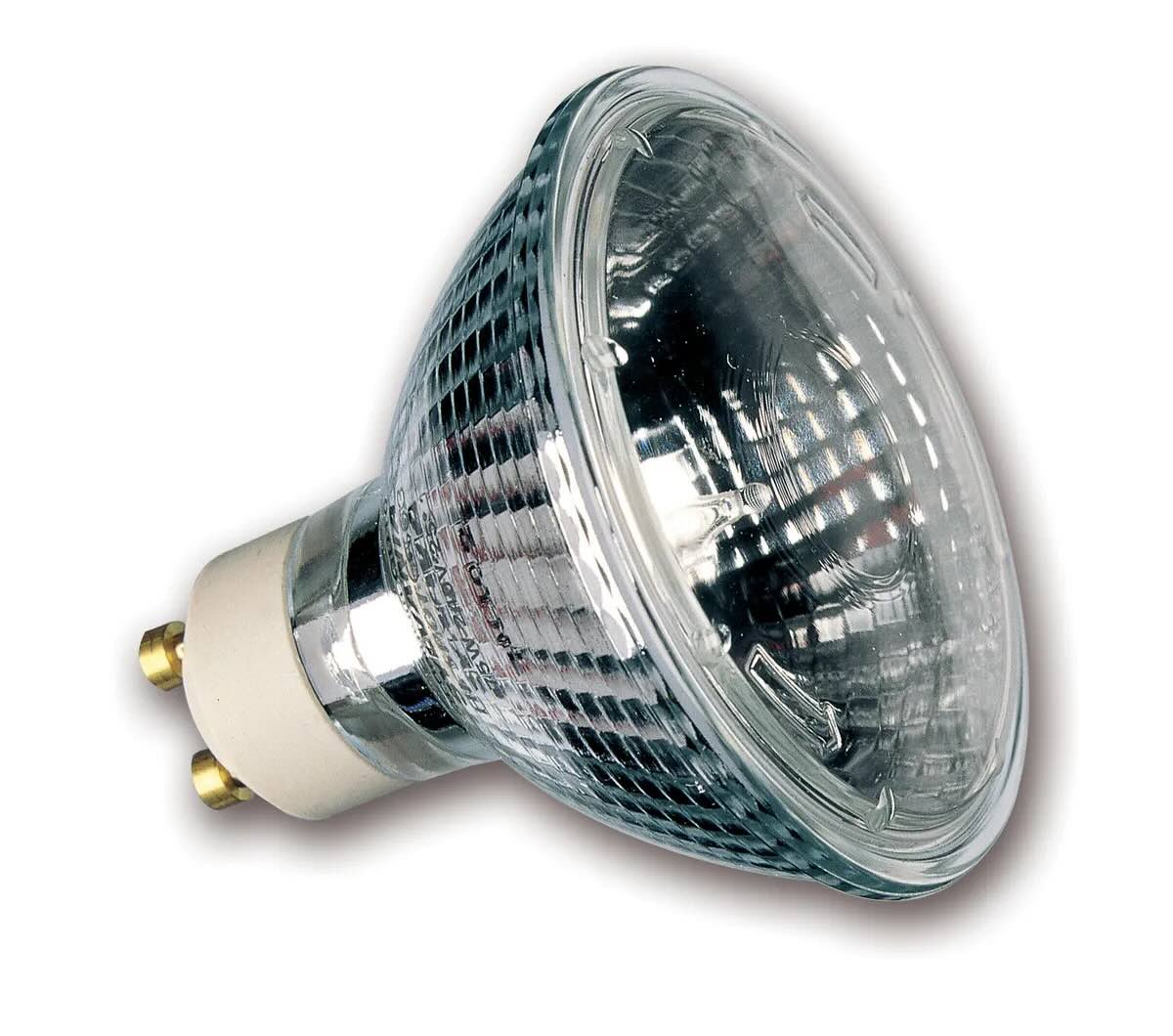
Halogen bulbs are a type of incandescent bulb that use a tungsten filament enclosed in a small, transparent quartz envelope filled with halogen gas. They are known for their bright and crisp light output, making them suitable for various applications ranging from task lighting to accent lighting. Additionally, halogen bulbs offer certain benefits and drawbacks that contribute to their unique appeal.
Understanding the inner workings of a halogen bulb is crucial to comprehend its distinct characteristics and advantages. So, let’s dive into the details of how these bulbs operate.
Key Takeaways:
- Halogen bulbs offer bright, crisp light and versatility for various applications, but their higher energy consumption and environmental impact should be considered when choosing lighting options.
- When comparing halogen bulbs to LED and incandescent bulbs, it’s important to weigh factors such as energy efficiency, lifespan, and cost to make informed decisions for specific lighting needs.
Read more: How To Replace A Halogen Bulb
Definition of a Halogen Bulb
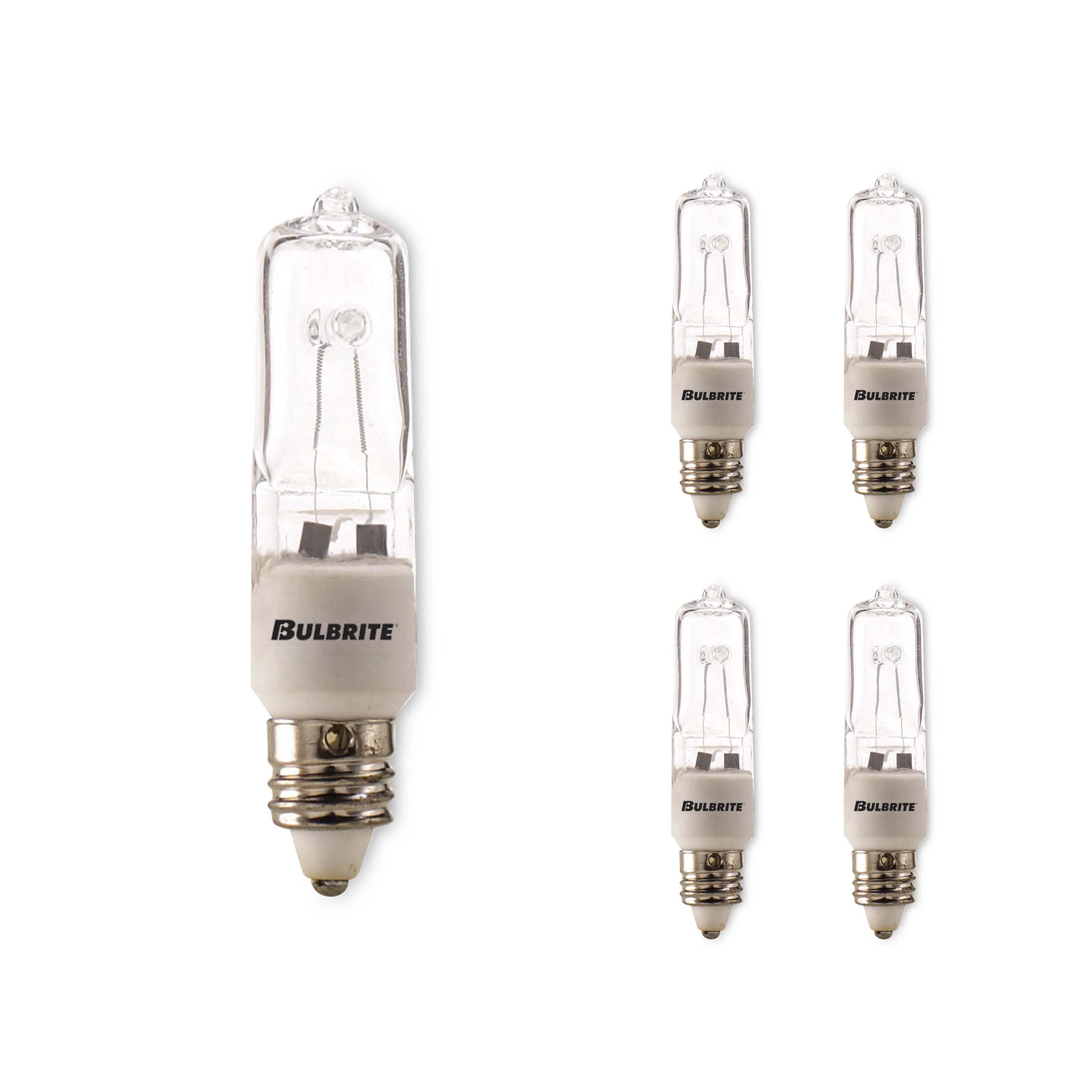
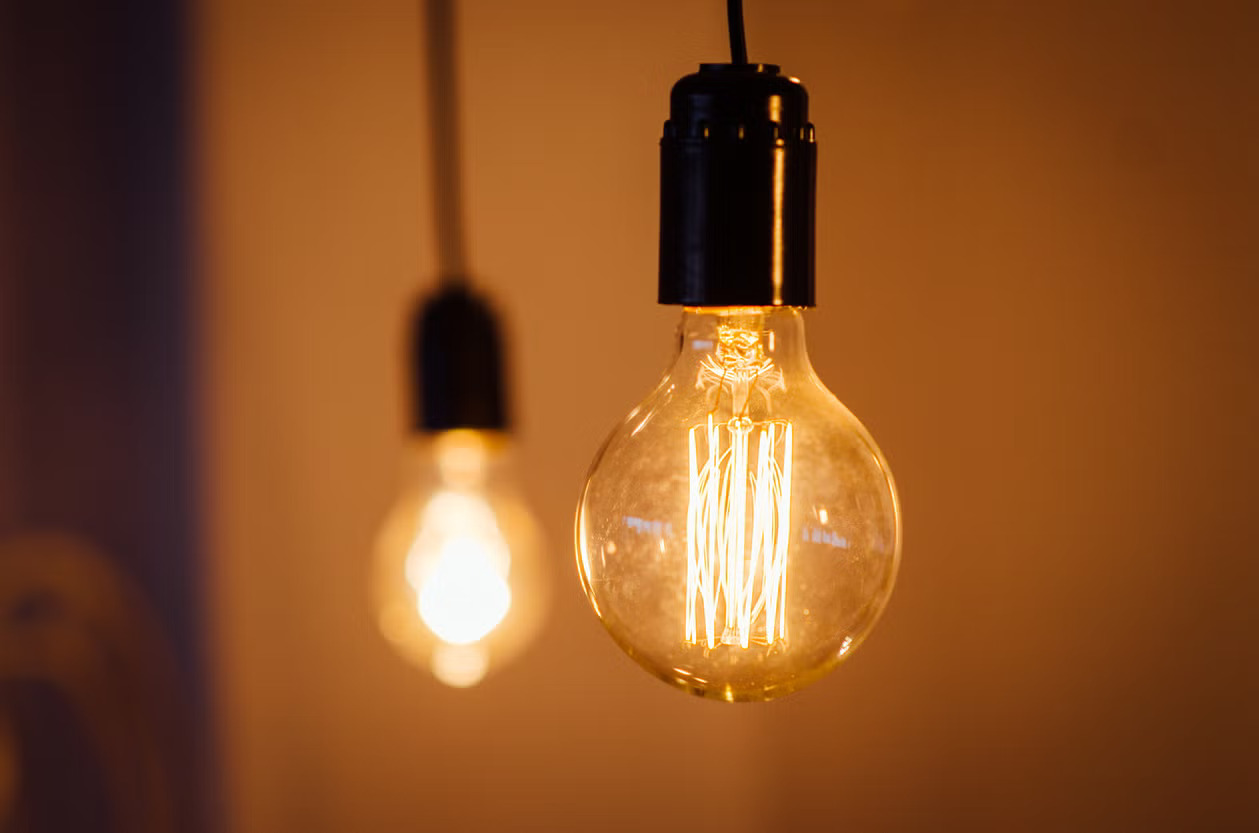
A halogen bulb is a type of incandescent bulb that uses a combination of a tungsten filament and halogen gas to produce light. It is called a “halogen” bulb because the gas inside the bulb is a halogen element, typically iodine or bromine. This unique construction allows halogen bulbs to operate at higher temperatures and produce a brighter, whiter light compared to standard incandescent bulbs.
The tungsten filament in a halogen bulb is similar to that in a traditional incandescent bulb. However, unlike standard incandescent bulbs, the quartz envelope surrounding the filament in a halogen bulb is much smaller and made of a heat-resistant material. This compact design prevents the tungsten filament from evaporating as quickly and extends the lifespan of the bulb.
The halogen gas inside the bulb plays a crucial role in the operation of a halogen bulb. As the filament heats up, it emits light and heat. The halogen gas combines with the evaporated tungsten atoms, and the heat causes this combination to break apart, redepositing the tungsten back onto the filament. This recycling process increases the efficiency and longevity of the bulb, making halogen bulbs more energy-efficient compared to traditional incandescent bulbs.
It is important to note that halogen bulbs operate at higher temperatures than other types of bulbs, and therefore, caution must be taken when handling them. It is recommended to use protective gloves or a clean cloth when replacing a halogen bulb to avoid touching the glass surface directly, as the oils from our skin can cause the glass to heat unevenly and potentially shatter.
How Halogen Bulbs Work
To understand how halogen bulbs work, we need to delve into their internal mechanisms. The key components of a halogen bulb include the tungsten filament, the halogen gas, and the compact quartz envelope.
When an electric current passes through the tungsten filament, it heats up and emits visible light. The high temperature causes the tungsten atoms to evaporate from the filament surface. Normally, in traditional incandescent bulbs, the tungsten atoms would accumulate on the glass envelope, causing it to darken over time and reducing the efficiency of the bulb.
However, in a halogen bulb, the presence of halogen gas prevents this build-up. As the evaporated tungsten atoms come into contact with the halogen gas, a chemical reaction known as the “halogen cycle” occurs. The halogen gas combines with the tungsten atoms, forming a compound, and carries the tungsten back to the filament surface. This process allows the tungsten atoms to redeposit on the filament, effectively eliminating the darkening of the bulb’s envelope.
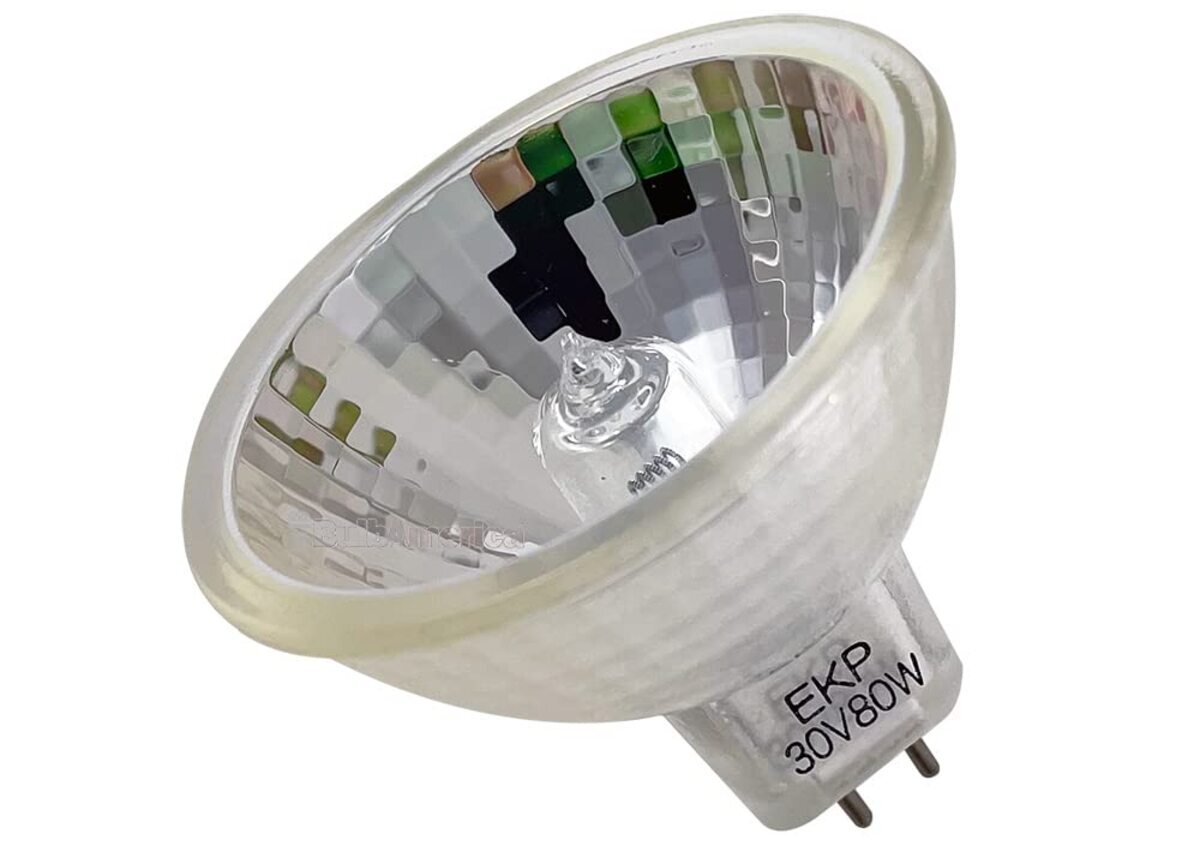
The compact quartz envelope in halogen bulbs serves multiple purposes. Firstly, it is highly heat-resistant, which allows the bulb to operate at higher temperatures. This high temperature contributes to the bright and crisp light output of halogen bulbs. Secondly, the small size of the envelope allows it to be placed closer to the filament, resulting in better control of the light beam’s direction and minimizing light loss.
It is important to note that halogen bulbs require a specific level of heat to maintain the halogen cycle. Therefore, they should not be operated at low temperatures or in enclosed fixtures where heat dissipation is limited. It is recommended to always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding the appropriate usage and handling of halogen bulbs.
Advantages of Halogen Bulbs
Halogen bulbs offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for lighting applications. Here are some of the key benefits of using halogen bulbs:
- Bright and Crisp Lighting: Halogen bulbs produce a bright and crisp light output, resembling natural daylight. This makes them ideal for tasks that require good visibility and color accuracy, such as reading, cooking, and artwork display.
- Wide Range of Colors: Halogen bulbs are available in various color temperatures, allowing users to choose between warm white, cool white, and daylight options. This versatility allows for customized lighting solutions to suit different preferences and settings.
- Instant On and Dimmable: Halogen bulbs provide instant illumination when turned on, eliminating the need to wait for the bulb to reach full brightness. Additionally, they are fully dimmable, offering flexibility in creating the desired lighting ambiance.
- Longer Lifespan: Compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, halogen bulbs have a longer lifespan. The halogen cycle, which prevents the build-up of tungsten on the glass, promotes a longer-lasting filament and overall bulb durability.
- Compact Size: Halogen bulbs are relatively small and compact, making them versatile for various lighting fixtures and applications. They can be easily integrated into recessed lights, track lights, pendant lights, and even smaller decorative fixtures.
It is worth noting that halogen bulbs are also more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs. They provide a higher lumen output per watt consumed, resulting in significant energy savings over time. However, it is important to consider that they are still less energy-efficient compared to newer technologies such as LED bulbs.
When considering the advantages of halogen bulbs, it is essential to weigh them against factors such as energy consumption and environmental impact. Despite their benefits, there may be more sustainable lighting options available for certain applications.
When handling halogen bulbs, avoid touching the glass with your bare hands as the oils from your skin can cause hot spots and reduce the lifespan of the bulb. Use a clean cloth or gloves when installing or replacing halogen bulbs.
Disadvantages of Halogen Bulbs
While halogen bulbs offer several advantages, there are also some drawbacks to consider when choosing this type of lighting. Here are some of the key disadvantages of halogen bulbs:
- Higher Energy Consumption: Halogen bulbs are not as energy-efficient as newer lighting technologies, such as LED bulbs. They consume more energy for the same light output, which can result in higher electricity bills over time.
- Higher Operating Temperatures: Halogen bulbs operate at higher temperatures than other types of bulbs. This can make them hot to the touch and pose a higher risk of burn injuries if not handled with caution. Additionally, the high operating temperature can also contribute to discomfort in enclosed spaces or during warm weather.
- Shorter Lifespan: While halogen bulbs have a longer lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, they still have a shorter lifespan compared to alternative options such as LED bulbs. This means that halogen bulbs may require more frequent replacements, which can be inconvenient and add to maintenance costs.
- Higher Cost: Halogen bulbs tend to be more expensive upfront compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Although the price has decreased over the years, they still have a higher price point than some energy-efficient options like LED bulbs.
- Environmental Impact: Halogen bulbs contain halogen gases, which are considered harmful to the environment. If not disposed of properly, these bulbs can contribute to pollution and increase carbon emissions. As a result, many countries have regulations in place for the proper disposal of halogen bulbs.
Despite these limitations, halogen bulbs still have their place in certain lighting applications. However, it is important to consider these disadvantages when deciding whether or not to use halogen bulbs and to explore alternative lighting options that may be more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Read more: How To Clean Halogen Bulb
Uses of Halogen Bulbs
Halogen bulbs are versatile lighting options that find applications in various settings. Here are some common uses of halogen bulbs:
- Task Lighting: With their bright and focused light output, halogen bulbs are commonly used for task lighting. They are ideal for activities that require enhanced visibility and clarity, such as reading, cooking, studying, and working at a desk.
- Accent Lighting: Halogen bulbs are often used for accent lighting purposes. They can be used to highlight specific areas or objects in a room, such as artwork, architectural features, or decorative elements. The crisp and directional light output of halogen bulbs can create a dramatic and visually appealing effect.
- Outdoor Lighting: Halogen bulbs are also suitable for outdoor lighting applications. They can be used in floodlights or spotlights to illuminate outdoor spaces such as gardens, pathways, or driveways. The bright and focused light provided by halogen bulbs can enhance safety and security in outdoor areas.
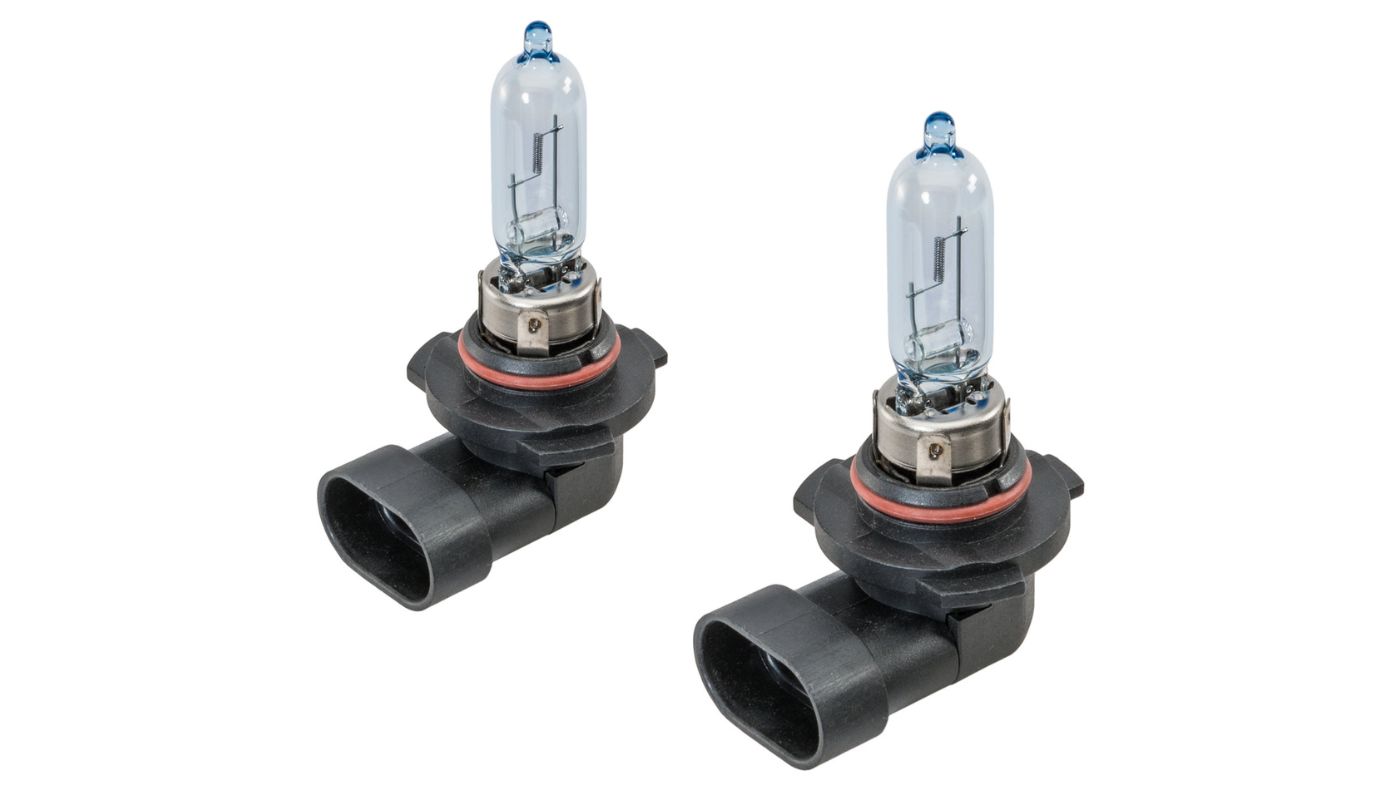
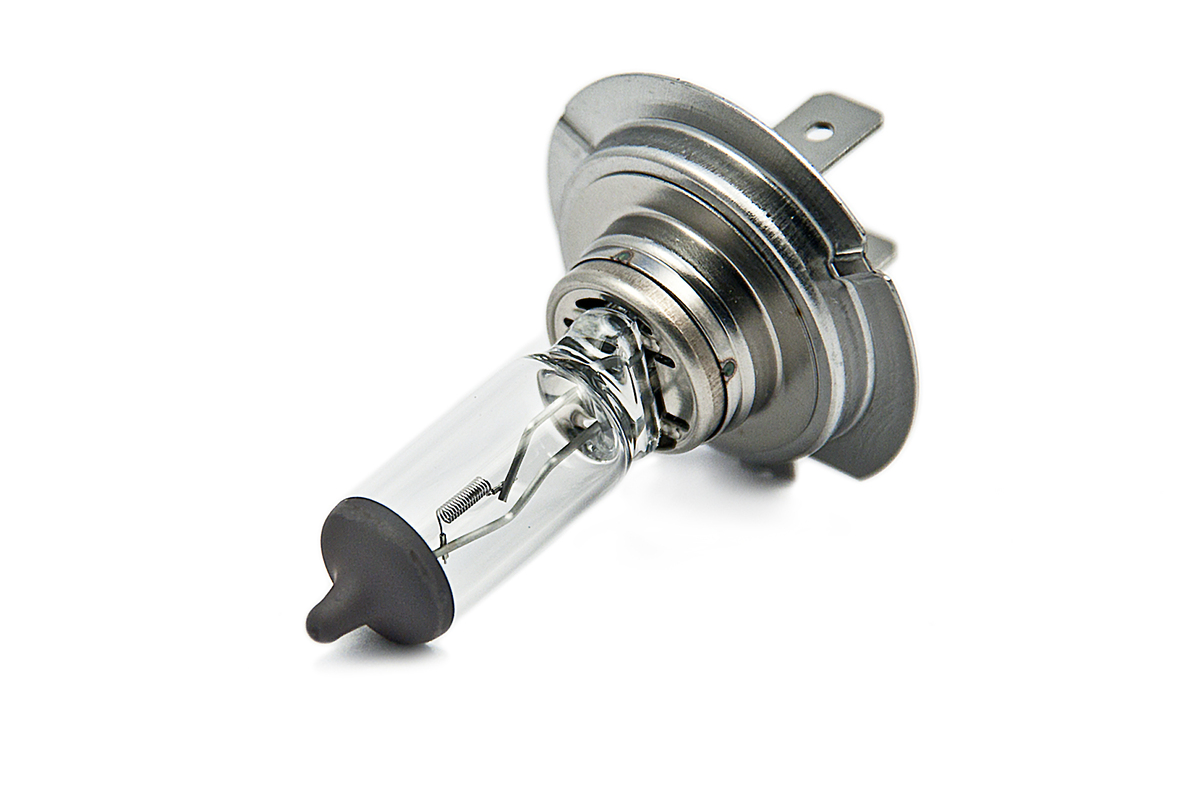
- Automotive Lighting: Halogen bulbs have been widely used in automotive lighting for many years. They are commonly used for headlights, fog lights, and taillights in cars, motorcycles, and other vehicles. Halogen bulbs provide a bright and controlled beam of light, improving visibility for drivers and increasing safety on the road.
It is important to consider the specific lighting needs of each application when choosing halogen bulbs. Factors such as the desired light intensity, color temperature, and beam angle should be taken into account. The versatility of halogen bulbs allows them to be used in various fixtures, including recessed lights, track lights, pendant lights, and desk lamps.
However, it is worth noting that as technology advances, alternatives such as LED bulbs are becoming increasingly popular due to their energy efficiency and longer lifespan. When considering the uses of halogen bulbs, it is important to weigh the pros and cons in relation to the specific lighting requirements and consider if other options may be more suitable.
Comparison with Other Types of Bulbs
When it comes to choosing the right type of bulb for your lighting needs, it’s helpful to understand how halogen bulbs compare with other commonly used types of bulbs. Here is a comparison between halogen bulbs, incandescent bulbs, and LED bulbs:
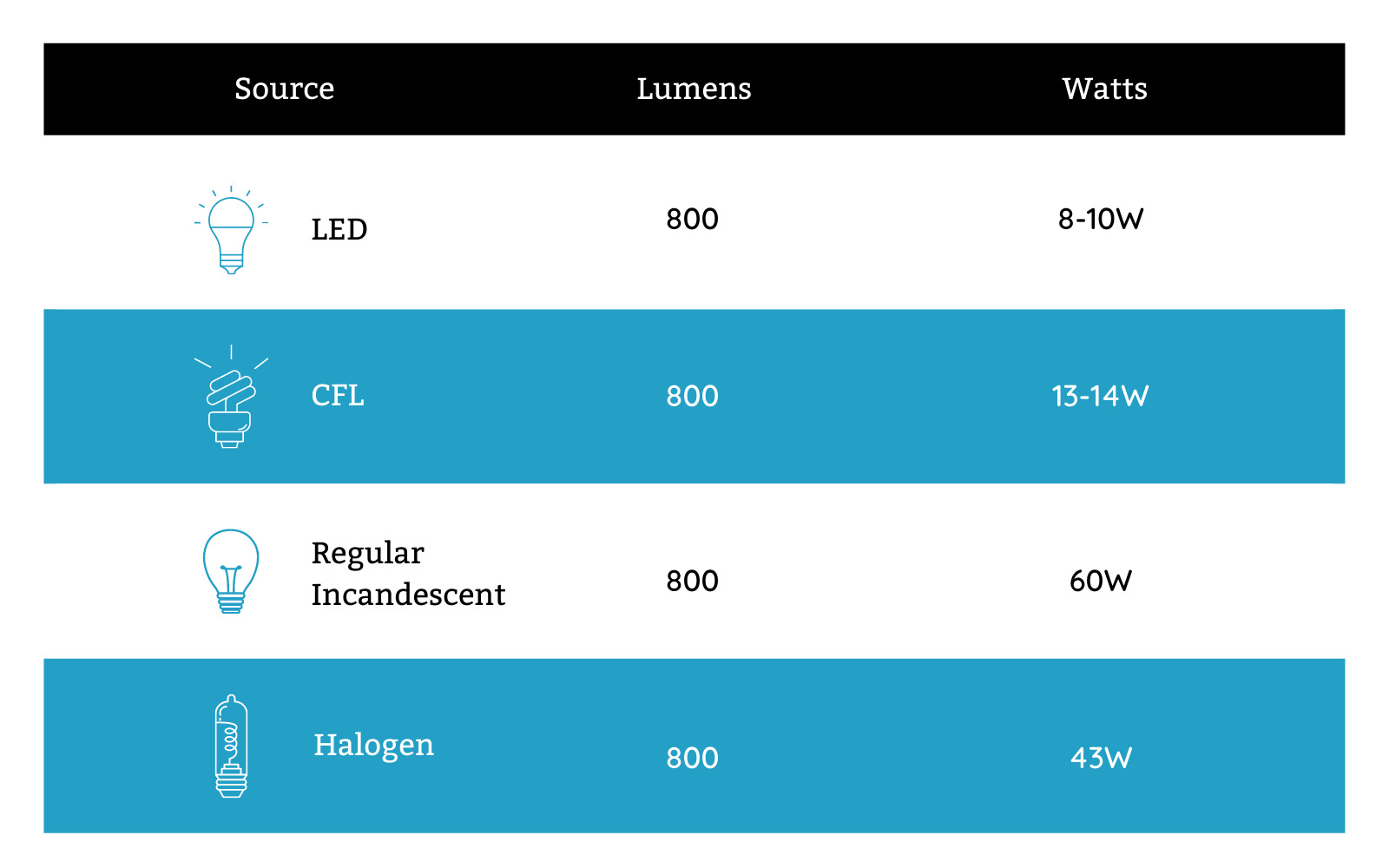
- Energy Efficiency: Halogen bulbs are more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs but less efficient than LED bulbs. LED bulbs are known for their exceptional energy efficiency, consuming significantly less electricity to produce the same amount of light. Switching from halogen or incandescent bulbs to LED bulbs can result in significant energy savings in the long run.
- Lifespan: Halogen bulbs have a longer lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, typically lasting around 2,000 to 4,000 hours. However, LED bulbs far surpass both halogen and incandescent bulbs in terms of lifespan, with an average of 25,000 to 50,000 hours or even more. The longer lifespan of LED bulbs reduces the frequency of replacing bulbs, resulting in cost savings.
- Warm-Up Time: Halogen bulbs provide instant illumination when turned on, similar to incandescent bulbs. On the other hand, LED bulbs often have a slight delay in reaching full brightness. However, advancements in LED technology have reduced the warm-up time, and most LED bulbs now reach their full brightness quickly.
- Heat Emission: Halogen bulbs produce a significant amount of heat during operation due to their high operating temperatures. This can be a consideration in enclosed spaces or for long periods of use. Incandescent bulbs also emit a substantial amount of heat. In contrast, LED bulbs generate very little heat, making them more suitable for applications where heat emission is a concern.
- Cost: Halogen bulbs are generally more cost-effective compared to LED bulbs upfront but are more expensive than traditional incandescent bulbs. However, the overall cost of ownership should be considered, taking into account factors such as energy consumption and lifespan. LED bulbs may have a higher initial cost but can result in significant energy savings and reduced maintenance costs over time.
Considering these factors, it is clear that LED bulbs offer the highest energy efficiency, longest lifespan, and lowest heat emission among these three types of bulbs. However, halogen bulbs still have their place in certain applications where instant brightness and color rendering are important, and LED bulbs may not be as suitable or practical.
Ultimately, the choice between halogen bulbs, incandescent bulbs, and LED bulbs will depend on individual preferences, lighting needs, and budget considerations. It is important to evaluate the specific requirements of each lighting application and weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each bulb type before making a decision.
Conclusion
Halogen bulbs have long been a popular choice for lighting due to their bright and crisp light output. They offer advantages such as instant illumination, dimmability, and a wide range of color temperatures. Additionally, halogen bulbs are versatile and find applications in task lighting, accent lighting, outdoor lighting, and automotive lighting.
However, it is important to consider the disadvantages of halogen bulbs, including their higher energy consumption, shorter lifespan compared to LED bulbs, higher operating temperatures, and environmental impact. These drawbacks have led to the rise of more energy-efficient lighting options, particularly LED bulbs, which offer superior energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and lower heat emission.
When deciding whether to use halogen bulbs or explore alternative lighting options, it is crucial to consider the specific lighting requirements, energy efficiency goals, and budget constraints. LED bulbs provide superior energy efficiency and longer-lasting performance, making them a popular choice for many lighting applications. However, for applications that require instant and bright light output or specific color temperatures, halogen bulbs can still be a suitable option.
As lighting technology continues to advance, it is important to stay informed about the latest developments and make environmentally conscious choices. Whether it’s halogen bulbs, LED bulbs, or other lighting technologies, understanding their advantages and disadvantages will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your lighting needs and sustainability goals.
Remember to always consider factors such as energy efficiency, lifespan, heat emission, and cost when selecting the right type of bulb for your specific lighting requirements. By doing so, you can create well-lit spaces that are both aesthetically pleasing and environmentally responsible.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Halogen Bulb
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is A Halogen Bulb”