Furniture
What Is A Gas Lamp
Modified: February 22, 2024
Discover the charm of gas lamps with our exquisite furniture collection. Enhance your outdoor space with timeless elegance and warm, ambient lighting.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
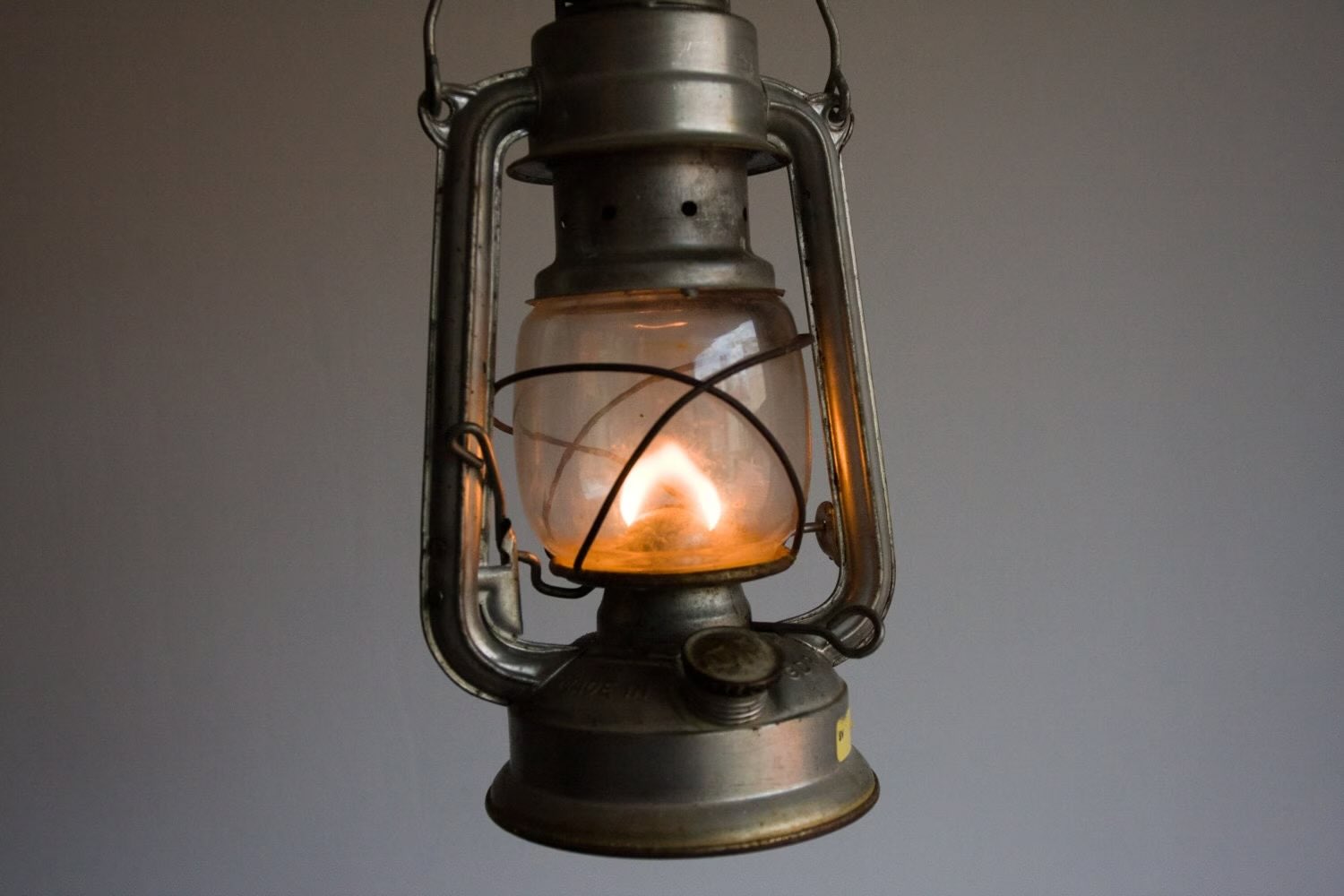
Gas lamps have a rich history and continue to be a fascinating aspect of lighting design. These timeless fixtures have endured the test of time and have evolved to become focal points in modern urban settings and outdoor spaces. Known for their warm and nostalgic glow, gas lamps provide a unique ambiance that cannot be replicated by electric lighting. In this article, we will delve into the history, mechanics, advantages, disadvantages, and modern applications of gas lamps.
Key Takeaways:
- Gas lamps have a rich history dating back to ancient civilizations and continue to offer a timeless elegance, making them a preferred choice for creating a unique and nostalgic ambiance in modern outdoor spaces.
- While gas lamps offer a warm and inviting glow, their installation and maintenance costs, limited light control, and environmental impact should be carefully considered. However, they remain a popular choice for enhancing the visual appeal of outdoor settings.
Read more: Where Was The Gas Lamp Invented
History of Gas Lamps
The history of gas lamps dates back to ancient civilizations. The earliest documented evidence of gas lighting can be traced back to ancient Mesopotamia, where hollowed-out pottery vessels were filled with flammable materials, such as oil or animal fat, and lit to provide light. However, it was not until the 18th century that gas lamps as we know them today began to take shape.
The breakthrough in gas lighting came in the late 18th century with the discovery of coal gas. In 1792, William Murdock, a Scottish engineer, used coal gas to illuminate his house in Cornwall, England. This marked the beginning of the gas lighting revolution. Murdock’s successful experiment prompted further exploration and development of gas lighting technology.
By the early 19th century, gas lamps became more widely adopted, particularly in urban areas. The streets of cities such as London, Paris, and Berlin were illuminated by gas lamps, replacing older forms of lighting like oil lamps and candles. Gas companies were established to produce and distribute coal gas, and gasworks became a common sight in industrialized cities.
The design of gas lamps also underwent significant advancements during this period. The development of the mantle in the late 19th century greatly improved the efficiency and brightness of gas lighting. Mantles, made from materials such as thorium or incandescent gas mantles, enhanced the luminosity and longevity of the gas flame, leading to a brighter and more consistent light output.
However, gas lighting started to decline in the early 20th century with the widespread adoption of electric lighting. The invention and rapid advancement of incandescent bulbs and later, fluorescent and LED lighting, made gas lamps gradually obsolete in most residential and commercial settings. Today, gas lamps are primarily used for decorative purposes or to evoke a nostalgic atmosphere in parks, historic districts, and upscale neighborhoods.
How Gas Lamps Work
Gas lamps operate on the principle of combustion, utilizing a fuel source to produce light. The most common type of gas used in lamps is natural gas or propane, although older lamps may use coal gas. Understanding the mechanics behind gas lamps helps us appreciate the beautiful and mesmerizing glow they emit.
At the core of a gas lamp is the burner assembly, which consists of a control valve, a mixing chamber, and a flame spreader. The control valve allows for the regulation of the gas flow, while the mixing chamber combines the gas with air to create a combustible mixture. The flame spreader helps distribute the flame evenly across the burner.
Upon lighting the gas lamp, the control valve is adjusted to control the flow of gas. As the gas passes through the mixing chamber, it combines with air to create a proper fuel-to-air ratio. This mixture is then ignited using a spark or a pilot light, initiating the combustion process.
Once ignited, the gas flame heats the mantle or burner element of the lamp. The mantle, typically made of a special heat-resistant fabric, absorbs the heat and begins to emit a bright and steady light. The mantle glows due to incandescence, the emission of light as a result of being heated to a high temperature.
The flame spreader plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the gas flame. It helps shape and distribute the flame evenly around the burner, ensuring a consistent and balanced illumination. Without a proper flame spreader, the gas flame may flicker or become unstable, leading to an uneven and less efficient light output.
To ensure the longevity and safety of the gas lamp, regular maintenance is essential. This includes cleaning and replacing the mantle, checking and adjusting the burner assembly, and inspecting the gas lines and connections. Proper ventilation is also crucial to prevent the buildup of carbon monoxide, a byproduct of combustion.
Overall, gas lamps offer a unique and captivating lighting experience. The combination of the flickering flame and the soft glow of the mantle creates a warm and inviting ambiance that is difficult to replicate with other lighting sources.
Advantages of Gas Lamps
Gas lamps offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for outdoor lighting and decorative purposes. Here are some of the key benefits of using gas lamps:
- Aesthetics: Gas lamps exude a classic and elegant charm, adding a touch of sophistication to any outdoor space. Their warm and flickering glow creates a cozy and inviting atmosphere, perfect for evening gatherings or romantic settings.
- Nostalgia: Gas lamps evoke a sense of nostalgia and remind us of a bygone era. They are often associated with historic neighborhoods or heritage sites, contributing to the preservation of architectural and cultural heritage.
- Energy Efficiency: Gas lamps are highly energy-efficient compared to electric lighting. The combustion of natural gas or propane produces a bright and long-lasting light, requiring less fuel consumption and reducing energy costs.
- Reliability: Gas lamps are not dependent on electricity and are unaffected by power outages. This makes them a reliable lighting option in areas prone to blackouts or where access to electricity may be limited.
- Low Maintenance: Gas lamps require minimal maintenance compared to electric or solar-powered lights. Regular cleaning and occasional replacement of the mantle are typically the only maintenance tasks needed to keep gas lamps in optimal condition.
- Increased Safety: Gas lamps are designed with safety features, such as flame spreaders and gas control valves, to ensure a controlled and steady flame. They also pose less risk of electrical hazards or fire accidents commonly associated with faulty electrical wiring.
- Flexibility: Gas lamps come in various styles, sizes, and designs, allowing for customization to suit different architectural and aesthetic preferences. Whether for residential walkways, public parkways, or historic landmarks, there is a gas lamp that can enhance the visual appeal of any space.
With their timeless beauty and functional advantages, gas lamps continue to be a preferred choice for those seeking to create an enchanting and distinctive outdoor lighting experience.
When using a gas lamp, always make sure to check for any leaks in the gas lines and to keep the lamp well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of carbon monoxide. Regular maintenance and inspection are crucial for safe and efficient operation.
Disadvantages of Gas Lamps
While gas lamps have many advantages, there are also some disadvantages to consider before choosing them as a lighting option. Here are a few factors to keep in mind:
- Higher Cost: Gas lamps can be more expensive to install and maintain compared to other lighting options. The initial setup requires professional installation and the cost of gas fuel can be relatively higher than electricity, especially in some regions.
- Limited Light Control: Gas lamps provide a consistent and warm glow, but they lack the ability to adjust the brightness or direction of light like electric lights. This makes it challenging to achieve specific lighting effects or to illuminate specific areas with precision.
- Fuel Availability and Accessibility: Gas lamps require a steady supply of natural gas or propane. In rural or remote areas, accessing a reliable gas supply might be more challenging compared to the accessibility of electricity.
- Maintenance: While gas lamps generally have low maintenance requirements, they still need periodic cleaning and replacement of the mantle. This upkeep can be time-consuming and may require special tools or expertise.
- Environmental Impact: The combustion of natural gas or propane emits carbon dioxide, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. While gas lamps are more energy-efficient than some other forms of lighting, they are still not as environmentally friendly as solar-powered or energy-efficient electric lights.
- Fire Hazard: Although gas lamps are designed with safety features to minimize the risk of fire accidents, there is still a potential hazard associated with open flames. Extra caution must be taken to prevent flammable objects from coming into contact with the lamp, especially during windy conditions.
Despite these disadvantages, gas lamps continue to be a popular choice for their timeless beauty and unique ambiance. It is important to weigh the pros and cons based on your specific needs and circumstances before deciding whether gas lamps are the right choice for your lighting requirements.
Read more: How To Light A Gas Lamp Post
Modern Applications of Gas Lamps
While gas lamps have become less common in everyday lighting, they still find their place in modern applications where their unique charm and ambiance are highly valued. Here are some of the modern uses for gas lamps:
- Outdoor Decor: Gas lamps are often used as decorative elements in outdoor spaces. They add a touch of elegance and create a warm and inviting atmosphere in gardens, patios, and outdoor dining areas. The flickering flame and gentle glow of the gas lamp enhance the beauty of the surroundings, making it a popular choice for upscale residences and commercial establishments.
- Historic Preservation: Gas lamps play a crucial role in preserving the heritage and character of historic districts or landmark areas. They help recreate the ambiance of the past and maintain the authenticity of the architectural style. Gas lamps are often used in historic city centers, museums, and cultural sites to provide an immersive and authentic experience for visitors.
- Urban Landscapes: Gas lamps are frequently employed in urban landscape design to add a touch of sophistication and enhance the overall aesthetics of city streets, parks, and public spaces. The gentle and warm illumination of gas lamps creates an inviting and safe environment for pedestrians, making them ideal for street lighting in upscale neighborhoods and commercial districts.
- Event Lighting: Gas lamps are also popular choices for outdoor events such as weddings, parties, and festivals. Their romantic and nostalgic appeal adds a special ambiance to the occasion, creating a captivating and memorable atmosphere for guests.
- Resorts and Hotels: Gas lamps are frequently used in luxury resorts and hotels to create a welcoming and intimate atmosphere. The soft glow of the gas lamp adds a touch of elegance to outdoor walkways, entrances, and patios, providing guests with a unique and memorable experience.
- Smart Gas Lighting: Advancements in technology have led to the development of smart gas lighting systems. These systems allow for remote control and automation of gas lamps using apps or central control panels, offering convenient control over brightness, scheduling, and even monitoring gas levels or maintenance needs.
Gas lamps have found a niche in modern applications where their aesthetic value and captivating charm are highly sought after. As technology continues to advance, gas lamps are likely to evolve further, adapting to the demands of contemporary design and sustainability.
Conclusion
Gas lamps have a rich history and continue to have a place in modern lighting design. From their humble beginnings in ancient civilizations to their widespread use during the gas lighting revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries, gas lamps have left an indelible mark on the world of lighting. While they have predominantly been replaced by electric lighting in most residential and commercial settings, gas lamps still hold a special allure that cannot be replicated.
The warm and nostalgic glow of gas lamps brings a timeless elegance to outdoor spaces, creating a unique ambiance that is highly sought after in today’s world. Whether used for decorative purposes, historical preservation, urban landscapes, or special events, gas lamps continue to evoke a sense of nostalgia and charm that captivates all who encounter them.
While gas lamps have their advantages, such as energy efficiency, reliability, and low maintenance requirements, they also come with some drawbacks, including higher installation and fuel costs, limited light control, and environmental considerations.
Despite these limitations, gas lamps have found their place in modern applications where their aesthetics and ambiance enhance the overall visual appeal of the surroundings. Whether illuminating historic neighborhoods, adorning luxurious resorts, or creating a romantic atmosphere, gas lamps continue to be a testament to the power and enduring beauty of traditional lighting.
As technology advances, gas lamps may continue to evolve and adapt to meet the demands of contemporary design and sustainability. By embracing both the history and the potential future of gas lamps, we can continue to appreciate and enjoy their distinctive charm in the modern world.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Gas Lamp
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.