Furniture
What Is An HID Lamp
Modified: August 25, 2024
Learn all about HID lamps in our comprehensive guide. Find out how they work, their benefits, and how to choose the right lighting for your furniture.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the wonderful world of HID lamps! In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of HID lamps – what they are, how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, and their common applications. Whether you’re a furniture enthusiast, an interior designer, or simply someone curious about lighting options, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of HID lamps.
So, what exactly is an HID lamp? HID stands for High-Intensity Discharge, and these lamps are renowned for their bright and powerful illumination. They are commonly used in various settings, including residential, commercial, and outdoor environments. With their unique technology and a wide range of applications, HID lamps have become a popular choice for lighting solutions.
To better comprehend HID lamps, it is important to understand their components. The core elements of an HID lamp include the arc tube, the ballast, and the reflector. The arc tube contains a mixture of gases and metal salts, which, when ignited, produce an intense light. The ballast serves as a power source, regulating the electrical current going into the lamp. Finally, the reflector helps to direct and focus the light, maximizing efficiency and ensuring the proper dispersion of light.
Now, let’s delve into how HID lamps work. When the lamp is turned on, the ballast supplies a high voltage electrical pulse to ignite the gases inside the arc tube. This creates an electric arc, causing the metal salts to vaporize and produce a plasma. The plasma emits light across a broad spectrum, including ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The inner surface of the arc tube, coated with phosphor, converts the UV radiation into visible light, allowing for a bright and clear illumination.
HID lamps come in various types, each tailored for specific applications. The most common types include metal halide lamps, high-pressure sodium lamps, and mercury vapor lamps. Metal halide lamps are known for their excellent color rendering properties and are often used in indoor settings like showrooms and retail spaces. High-pressure sodium lamps emit a warm golden light and are commonly used for outdoor lighting, such as streetlights and parking lots. Mercury vapor lamps, while less common nowadays, are still used in specific applications, such as sports stadiums and industrial facilities.
Key Takeaways:
- HID lamps offer powerful and efficient lighting with high brightness, long lifespan, and versatility, making them a reliable choice for various applications from outdoor lighting to retail spaces.
- While HID lamps provide bright and efficient illumination, their warm-up time, UV radiation, heat generation, and size should be considered alongside their benefits when choosing a lighting solution.
Read more: What Is A HID Light Bulb
Definition of HID Lamp
An HID (High-Intensity Discharge) lamp, also known as a gas-discharge lamp, is a type of lighting technology that produces light through the process of exciting gaseous elements or compounds within a sealed arc tube. HID lamps are renowned for their high brightness and energy-efficient illumination, making them a popular choice in various lighting applications.
Unlike traditional incandescent or fluorescent lamps, HID lamps operate by passing an electric current through a gas-filled arc tube. Inside the arc tube, electrical energy is used to create an electric arc between two electrodes. This arc excites the gas or metal-halide mixture contained within the tube, creating an intense light output.
One of the defining features of HID lamps is their ability to generate an extremely high level of brightness. This makes them ideal for applications where visibility and clarity are crucial, such as outdoor lighting, large indoor spaces, and commercial settings.
HID lamps are known for their longevity, allowing them to provide reliable and consistent light output over an extended period. They have a longer lifespan compared to traditional incandescent or fluorescent lamps, which reduces the need for frequent replacements.
Another significant characteristic of HID lamps is their energy efficiency. HID lamps convert a higher proportion of electrical energy into visible light, making them more efficient than many other lighting options. This energy efficiency translates into lower electricity consumption and reduced energy costs.
The color temperature of HID lamps can vary depending on the specific type and application. Metal halide lamps, for example, produce a bright white light that closely resembles daylight, making them suitable for retail displays and other color-critical environments. High-pressure sodium lamps emit a warm golden light, making them a popular choice for streetlights and parking lot lighting.
In summary, HID lamps are a type of gas-discharge lamp that produces bright, energy-efficient light through the excitation of gases or metal-halide mixtures within a sealed arc tube. Their high brightness, longevity, and energy efficiency make them highly versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications.
Components of an HID Lamp
An HID (High-Intensity Discharge) lamp consists of several essential components that work together to produce bright and efficient light output. Understanding these components is crucial for comprehending the inner workings of an HID lamp. Let’s explore the key components and their roles.
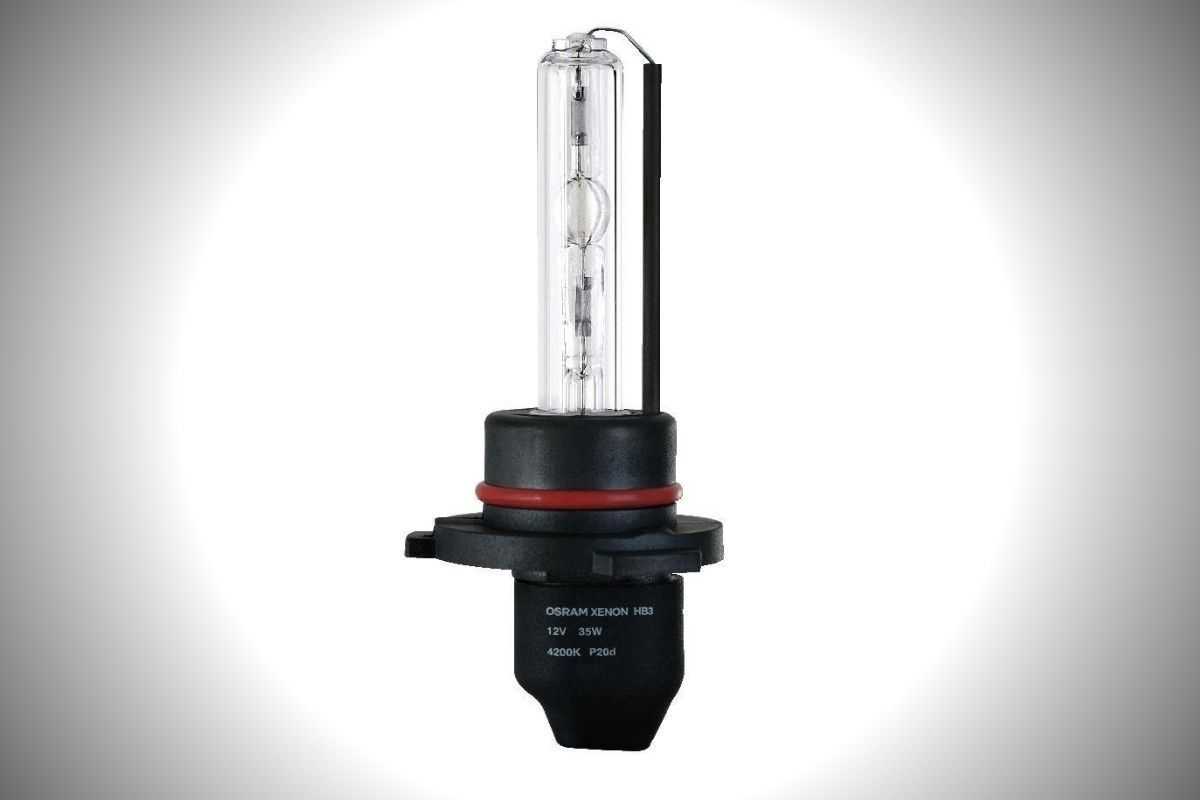
1. Arc Tube: The arc tube is the heart of an HID lamp. It is a sealed, transparent quartz or ceramic tube that contains a mixture of gases or metal halides. When the lamp is turned on, an electric current passes through the arc tube, creating an electric arc. The gas or metal halides within the tube become ionized and produce a high-intensity light output.
2. Electrodes: The electrodes are metal points located at each end of the arc tube. They provide the electrical connection needed to generate the arc. One electrode is the cathode and the other is the anode. When a high voltage is applied, an arc is formed between the electrodes, initiating the light production process.
3. Ballast: The ballast is an essential component that controls the electrical current flowing through the lamp. It ensures that the lamp operates at the correct voltage and stabilizes the electrical discharge within the arc tube. The ballast also helps initiate the lamp by providing a high-voltage pulse to establish the electrical arc.
4. Reflector: The reflector is a component located behind the arc tube that aids in directing and focusing the light output. It is designed to maximize efficiency by reflecting the light towards the desired area and minimizing light loss due to dispersion. The reflector plays a crucial role in optimizing the overall performance and brightness of the HID lamp.
5. Ignitor: In some HID lamp systems, an ignitor is used to initiate the electrical discharge. The ignitor provides a high voltage spike to jump-start the lamp’s arc. Once the arc is established, the ignitor is no longer required and the ballast takes over the regulation of the electrical current.
6. Outer Bulb: Many HID lamps are enclosed within an outer bulb or envelope. This outer bulb serves as a protective shield, preventing direct contact with the hot arc tube and reducing the risk of breakage. It also helps to maintain the structural integrity of the lamp, ensuring its longevity and durability.
Each component of an HID lamp plays a vital role in the overall functionality and performance of the lamp. The combination of the arc tube, electrodes, ballast, reflector, ignitor (if applicable), and outer bulb work harmoniously to deliver the powerful, efficient, and long-lasting illumination that HID lamps are known for.
How HID Lamps Work
HID (High-Intensity Discharge) lamps operate through a complex electrical process that results in the generation of bright and efficient light. Understanding how HID lamps work can provide insight into the technology behind their impressive performance. Let’s dive into the step-by-step process of how HID lamps produce light.
1. Ignition: When an HID lamp is turned on, the electrical circuit is completed, and power is supplied to the ballast. The ballast delivers a high voltage to the lamp, typically in the range of several thousand volts, to initiate the electrical discharge. This high voltage spike allows the lamp to achieve the necessary conditions for arc formation.
2. Arc Formation: The high voltage causes the electrons to jump across the small gap between the electrodes inside the arc tube. This creates an electric arc, a controlled flow of electricity through the gas or metal-halide mixture within the tube. The arc emits intense light as a result of the ionization of the gases and the excitation of the metal halides.
3. Gas Excitation: The excited gas or metal-halide mixture inside the arc tube begins to release energy in the form of photons. This energy release occurs as the electrons transition from higher energy levels to lower energy levels. The specific gases or metal halides used determine the color temperature and spectral output of the emitted light.
4. Phosphor Coating: To convert the ultraviolet (UV) radiation emitted by the arc into visible light, the inner surface of the arc tube is coated with a layer of phosphor. The phosphor coating absorbs the UV radiation and re-emits it as visible light. This process helps to enhance the efficiency and color rendition of the HID lamp.
5. Light Output: Once the UV radiation is converted into visible light by the phosphor coating, it passes through the transparent arc tube and outer bulb, where it can be directed and dispersed by the reflector. The reflector helps focus the light output and maximize its efficiency by minimizing light loss due to scattering.
Throughout the operation of an HID lamp, the ballast continues to regulate the electrical current flowing through the lamp. It ensures that the lamp receives a stable and consistent power supply, maintaining the stability of the arc and the quality of light output.
HID lamps are characterized by their high brightness, long lifespan, and energy efficiency. They provide a powerful illumination solution for various applications, from outdoor lighting and large indoor spaces to specialized environments where color accuracy is crucial.
In summary, HID lamps work by initiating an electrical discharge through the arc tube, exciting gases or metal-halide mixtures, and converting the resulting UV radiation into visible light with the help of a phosphor coating. This process creates the intense and efficient illumination that HID lamps are known for.
Types of HID Lamps
HID (High-Intensity Discharge) lamps come in various types, each designed for specific applications and lighting needs. These different types of HID lamps offer distinct characteristics in terms of light output, color temperature, and efficiency. Let’s explore some of the most common types of HID lamps:
- Metal Halide Lamps: Metal halide lamps are widely recognized for their excellent color rendering properties and high-quality light output. They produce a bright, white light that closely resembles natural daylight. The color temperature of metal halide lamps typically ranges from 3000K to 6500K, allowing for versatility in various indoor applications, such as showrooms, retail spaces, and stadiums.
- High-Pressure Sodium Lamps: High-pressure sodium lamps are known for their energy efficiency and long lifespan. They emit a warm, golden light that is commonly used for outdoor lighting, such as streetlights, parking lots, and security lighting. High-pressure sodium lamps have a high efficacy in terms of lumens per watt, making them an excellent choice for applications that require high levels of brightness without compromising energy consumption.
- Mercury Vapor Lamps: While less common in modern lighting applications, mercury vapor lamps still offer unique characteristics. They produce a bluish-white light and have a relatively low color rendering index. These lamps were widely used in the past for outdoor and industrial lighting. However, due to their lower energy efficiency and environmental considerations related to mercury content, they have been largely replaced by more advanced lighting technologies.
- Ceramic Metal Halide Lamps: Ceramic metal halide lamps are an advanced version of standard metal halide lamps. They offer improved color stability, longer lifespan, and higher efficiency. The ceramic arc tube of these lamps allows for better heat dissipation and increased durability. Ceramic metal halide lamps are popular choices for retail lighting, art galleries, and other applications that require precise color rendering and consistent light quality.
- Low-Pressure Sodium Lamps: Low-pressure sodium lamps produce a monochromatic yellow light that is highly efficient. They have excellent luminous efficacy and are often used for street lighting in areas where color rendering is not a priority. The distinctive yellow light emitted by these lamps provides good visibility while minimizing light pollution and skyglow.
Each type of HID lamp has its own advantages and considerations, depending on the specific application requirements. Factors such as color temperature, color rendering properties, efficiency, and lifespan should be taken into consideration when choosing the appropriate HID lamp for a particular lighting project.
It’s worth noting that advancements in lighting technology have led to the development of more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly options, such as LED (Light-Emitting Diode) lamps. However, HID lamps continue to be widely used in many applications due to their proven performance, high brightness, and wide range of options.
Understanding the different types of HID lamps allows designers, architects, and lighting professionals to select the most suitable lighting solution for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and visual appeal.
When handling HID lamps, always ensure that the power is turned off and the lamp has cooled down before attempting to replace or handle it. HID lamps can reach high temperatures and can cause burns if mishandled.
Read more: What Is A Lamp
Advantages of HID Lamps
HID (High-Intensity Discharge) lamps offer numerous advantages over other lighting options, making them a popular choice in various applications. From their high brightness to their energy efficiency, HID lamps provide several benefits that contribute to their widespread use. Let’s explore the advantages of using HID lamps:
- High Brightness: HID lamps are known for their exceptional brightness. They produce a powerful and intense light output, making them ideal for applications where visibility and clarity are crucial. Whether used in outdoor settings like streetlights or indoor spaces like sports stadiums, HID lamps provide a bright and well-illuminated environment.
- Efficiency: HID lamps have high luminous efficacy, meaning they convert a significant portion of electrical energy into visible light. This efficiency is particularly notable in metal halide lamps and high-pressure sodium lamps. By generating more light with less energy consumption, HID lamps contribute to reduced electricity costs and lower environmental impact.
- Long Lifespan: HID lamps have an extended lifespan compared to many traditional lighting options. With proper maintenance and usage, HID lamps can last up to 20,000 hours or more. This longevity results in fewer replacements and reduced maintenance costs, making HID lamps a cost-effective lighting solution in the long run.
- Color Rendering: Metal halide lamps in particular offer excellent color rendering properties. They accurately reproduce colors and allow for enhanced visibility and visual appeal. This feature is highly desirable in applications such as retail spaces, showrooms, and galleries, where accurate color representation is essential for showcasing products or artwork.
- Versatility: HID lamps are available in various types, wattages, and color temperatures, providing versatility for different lighting requirements. Whether you need lighting for indoor spaces, outdoor environments, or specialized applications, there is likely an HID lamp that can meet your specific needs.
- Instant On/Off: HID lamps have the advantage of instant on/off capabilities. Unlike some other lighting technologies that require warm-up or cool-down periods, HID lamps can be immediately turned on and provide full brightness. This feature is particularly valuable in situations where instant illumination is critical, such as in security lighting or emergency situations.
These advantages, combined with the reliability and quality of HID lamps, make them a popular choice for a wide range of applications. Whether it’s for outdoor lighting, large indoor spaces, or specialized environments, HID lamps provide powerful, efficient, and long-lasting illumination.
It’s important to note that while HID lamps offer many benefits, advancements in LED (Light-Emitting Diode) technology have led to increased energy efficiency, longer lifespans, and improved color rendering. Nevertheless, HID lamps continue to be a viable and widely used lighting solution, especially when specific requirements and budget constraints are taken into consideration.
Disadvantages of HID Lamps
While HID (High-Intensity Discharge) lamps offer numerous advantages, they also come with a few drawbacks that should be considered when choosing a lighting solution. It is important to weigh the disadvantages alongside the benefits to make an informed decision. Let’s explore the potential disadvantages of using HID lamps:
- Warm-Up and Restrike Time: HID lamps require a warm-up period to reach their full brightness after being turned on. This warm-up time can range from several minutes to 10 minutes or more, depending on the lamp type and wattage. Additionally, if the lamp is turned off and needs to be restarted shortly after, a restrike time is required, during which the lamp cannot be immediately turned back on. This warm-up and restrike time may not be suitable for applications that require instant and frequent on/off cycling of the lights.
- UV Radiation: HID lamps emit a significant amount of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. While the outer bulb of the lamp helps to filter and reduce UV emissions, some UV radiation can still pass through. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can be harmful to human skin and cause fading or damage to certain materials. It is important to take proper precautions by using UV-filtering or UV-blocking coatings on lamps or ensuring sufficient distance and shielding between the lamp and sensitive objects or people.
- Heat Generation: HID lamps produce a considerable amount of heat during operation. This heat can create discomfort in indoor environments and may require additional cooling measures to maintain a comfortable temperature. In enclosed fixtures, proper ventilation is necessary to dissipate the heat and prevent premature degradation of the lamp or other associated components. It’s important to consider the heat output of HID lamps and ensure proper heat management to prevent any potential issues.
- Size and Bulky Design: HID lamps, especially those with higher wattages, can be quite large and bulky. This can pose challenges when designing lighting fixtures or spaces with limited room for installation. It’s important to consider the size and weight of HID lamps when planning the layout and arrangement of the lighting system.
- Environmental Considerations: Some types of HID lamps, such as mercury vapor lamps, contain small amounts of mercury, a hazardous material. Improper disposal of these lamps can lead to potential environmental contamination if not handled in accordance with regulations and guidelines. It is crucial to follow proper disposal protocols for end-of-life HID lamps to minimize their environmental impact and ensure safe handling.
While the disadvantages of HID lamps should be taken into account, they should not overshadow the overall benefits they offer. Understanding these limitations allows for intentional and informed decision-making when choosing the right lighting solution for specific applications.
It’s worth noting that advancements in LED (Light-Emitting Diode) technology have mitigated some of these disadvantages, with LED lamps offering instant on/off capabilities, reduced UV radiation, lower heat generation, and more compact designs. However, HID lamps continue to be a reliable and widely used lighting solution in applications that can accommodate their characteristics and requirements.
Common Applications of HID Lamps
HID (High-Intensity Discharge) lamps are widely used in various applications that require powerful and efficient lighting solutions. Their high brightness, long lifespan, and versatile options make them suitable for a range of environments and requirements. Let’s explore some of the common applications where HID lamps are frequently used:
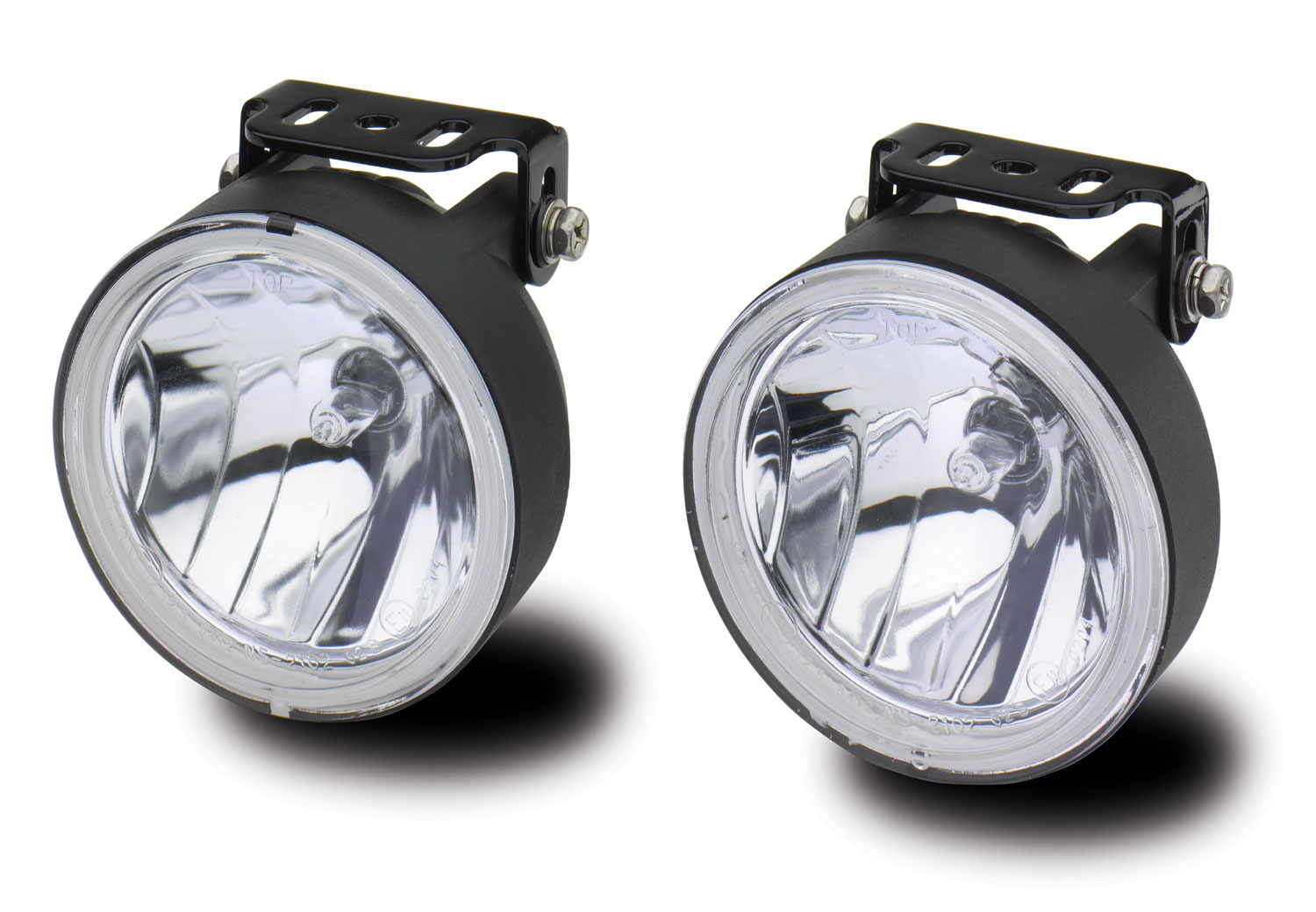
- Outdoor Lighting: HID lamps are commonly employed for outdoor lighting purposes due to their high brightness and wide area coverage. They are commonly used for street lighting, illuminating highways, roads, and parking lots. HID lamps provide excellent visibility during nighttime hours, ensuring safer navigation and enhanced security in outdoor spaces.
- Sports Stadiums and Arenas: HID lamps are often used to illuminate sports stadiums, arenas, and other large outdoor venues. Their bright and intense light output allows for optimal visibility during sporting events, concerts, and other performances. HID lamps can effectively light up the entire playing field, ensuring an enjoyable experience for both the athletes and spectators.
- Industrial Facilities: HID lamps are frequently utilized in industrial settings such as warehouses, manufacturing plants, and construction sites. The bright and efficient lighting provided by HID lamps enhances visibility and safety in these work environments. HID lamps are often preferred due to their durability and ability to withstand harsh conditions and vibrations.
- Retail Spaces: HID lamps, particularly metal halide lamps, are commonly used in retail spaces to showcase products in an appealing and vibrant manner. The bright and accurate color rendering of HID lamps enhances the visual appeal of merchandise, making them excellent choices for showrooms, displays, and retail store lighting.
- Indoor Sports Facilities: HID lamps are widely employed in indoor sports facilities such as gyms, arenas, and indoor courts. They provide bright and uniform lighting that enhances visibility and performance during sporting events and training sessions. HID lamps offer excellent light quality for indoor sports, ensuring that athletes can perform at their best.
- Airports and Seaports: HID lamps play a crucial role in illuminating airport runways, taxiways, and aprons, as well as seaport terminals. Their powerful light output ensures clear visibility, allowing pilots, ground crew, and dockworkers to carry out their tasks safely and efficiently, especially during low-light conditions or inclement weather.
- Parking Lots: HID lamps are commonly used for parking lot lighting due to their high brightness and broad coverage. They provide well-lit and safe parking areas for vehicles and pedestrians, deterring potential security risks. HID lamps are an energy-efficient option, reducing operating costs for large parking areas.
- Greenhouses: HID lamps, especially metal halide lamps, are often utilized in greenhouses for plant growth and optimal development. The intense light output of HID lamps promotes photosynthesis and provides the required light spectrum for healthy plant growth. HID lamps can supplement natural sunlight or serve as the primary light source in indoor gardening environments.
These are just a few examples of the many applications where HID lamps have proven to be valuable lighting solutions. Their versatility, long lifespan, and powerful illumination make them well-suited for a wide range of environments, from outdoor spaces to indoor facilities. Understanding the unique benefits of HID lamps allows for making informed decisions when choosing lighting solutions for specific applications.
Conclusion
HID (High-Intensity Discharge) lamps offer a powerful and efficient lighting solution for a variety of applications. From their high brightness and long lifespan to their versatility and color rendering capabilities, HID lamps have established themselves as a reliable choice for many lighting needs.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of HID lamps and their key components. We have learned about how HID lamps work, with their process of electrical discharge and the conversion of UV radiation into visible light. The types of HID lamps were discussed, highlighting their unique characteristics and applications.
Despite their advantages, HID lamps are not without their drawbacks. The warm-up time, UV radiation, heat generation, and bulky size should be taken into consideration when deciding on the most suitable lighting solution. It’s important to weigh these disadvantages against the overall benefits offered by HID lamps.
Common applications of HID lamps were also examined, ranging from outdoor lighting and sports stadiums to retail spaces and industrial facilities. HID lamps excel in providing bright and efficient illumination needed for these environments, enhancing visibility, safety, and visual appeal.
In conclusion, HID lamps continue to be a popular choice for many lighting projects due to their high brightness, energy efficiency, and longevity. However, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of each application and evaluate the advantages and disadvantages to determine the most suitable lighting solution.
As technology continues to advance, other lighting options such as LED lamps are gaining popularity for their improved efficiency and versatility. Nonetheless, HID lamps continue to hold their position as a reliable and effective lighting solution for those seeking powerful illumination and performance.
Whether you are lighting up a street, a retail store, or an indoor sports facility, HID lamps can provide the brightness and efficiency you need. By understanding their capabilities and limitations, you can make informed decisions and create a well-lit environment that meets your specific lighting requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is An HID Lamp
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.